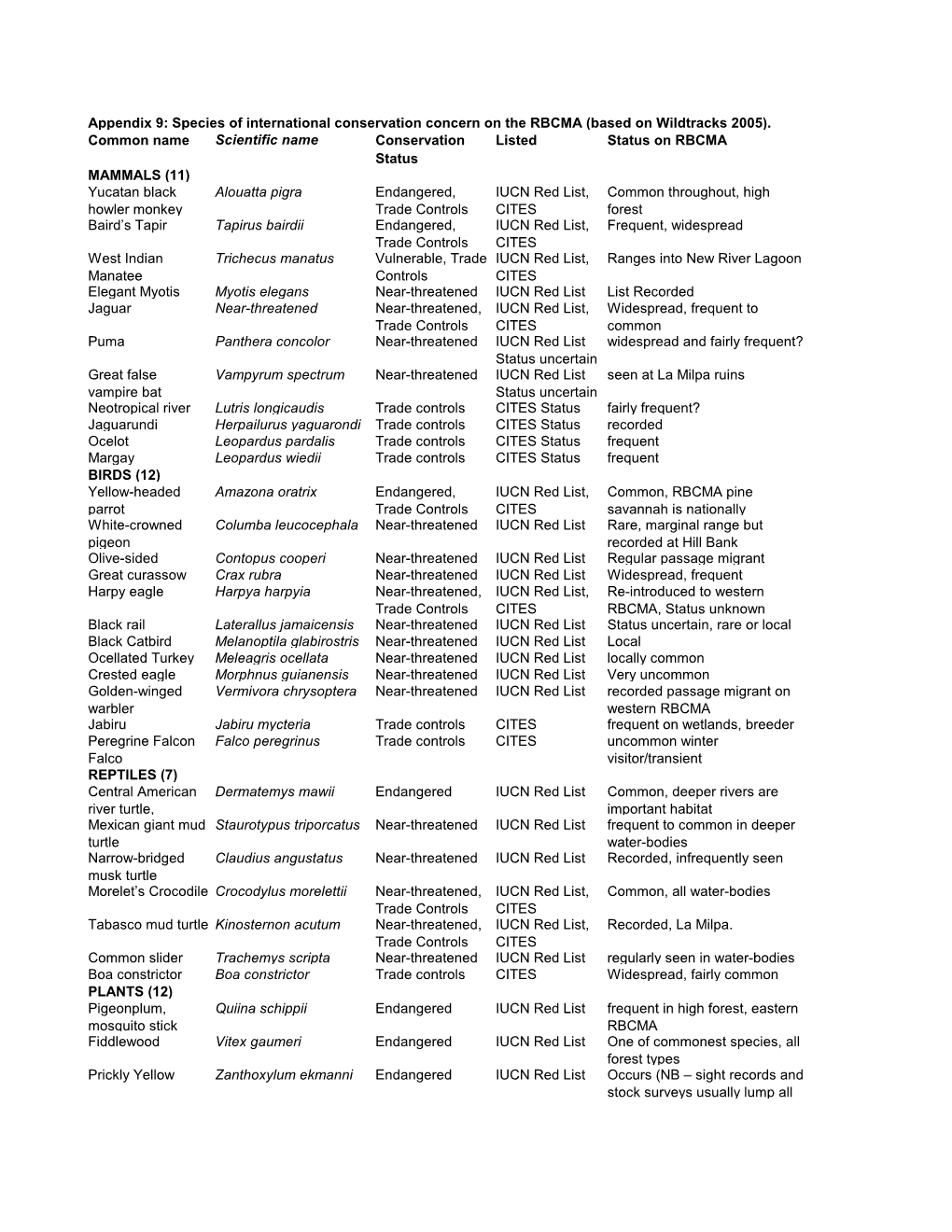
Species of International Conservation Concern on the RBCMA (Based on Wildtracks 2005)
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

First Record of an Extinct Marabou Stork in the Neogene of South America
First record of an extinct marabou stork in the Neogene of South America JORGE IGNACIO NORIEGA and GERARDO CLADERA Noriega, J.I. and Cladera, G. 2008. First record of an extinct marabou stork in the Neogene of South America. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 53 (4): 593–600. We describe a new large species of marabou stork, Leptoptilus patagonicus (Ciconiiformes, Ciconiidae, Leptoptilini), from the late Miocene Puerto Madryn Formation, Chubut Province, Argentina. The specimen consists mainly of wing and leg bones, pelvis, sternum, cervical vertebrae, and a few fragments of the skull. We provisionally adopt the traditional system− atic scheme of ciconiid tribes. The specimen is referred to the Leptoptilini on the basis of similarities in morphology and intramembral proportions with the extant genera Ephippiorhynchus, Jabiru,andLeptoptilos. The fossil specimen resembles in overall morphology and size the species of Leptoptilos, but also exhibits several exclusive characters of the sternum, hu− merus, carpometacarpus, tibiotarsus, and pelvis. Additionally, its wing proportions differ from those of any living taxon, providing support to erect a new species. This is the first record of the tribe Leptoptilini in the Tertiary of South America. Key words: Ciconiidae, Leptoptilos, Miocene, Argentina, South America. Jorge I. Noriega [[email protected]], Laboratorio de Paleontología de Vertebrados, CICYTTP−CONICET, Matteri y España, 3105 Diamante, Argentina; Gerardo Cladera [[email protected]], Museo Paleontológico Egidio Feruglio, Avenida Fontana 140, 9100 Trelew, Argentina. Introduction Institutional abbreviations.—BMNH, Natural History Mu− seum, London, UK; CICYTTP, Centro de Investigaciones The stork family (Ciconiidae) is a well−defined group of Científicas y Transferencia de Tecnología a la Producción, waterbirds, traditionally divided into three tribes: the Myc− Diamante, Argentina; CNAR−KB3, collections of locality 3 of teriini, the Ciconiini, and the Leptoptilini (Kahl 1971, 1972, the Kossom Bougoudi area, Centre National d’Appui à la 1979). -

Jabiru Mycteria (Jabiru Stork)
UWI The Online Guide to the Animals of Trinidad and Tobago Ecology Jabiru mycteria (Jabiru Stork) Family: Ciconiidae (Storks) Order: Ciconiiformes (Storks, Herons and Ibises) Class: Aves (Birds) Fig. 1. Jabiru stork, Jabiru mycteria. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jabiru#/media/File:Jabiru_(Jabiru_mycteria)_2.JPG, downloaded 1 March 2017] TRAITS. Jabiru mycteria is one of the largest flying birds on earth, being the largest in the Americas and one of the three stork species found there. Adult jabiru storks can reach 1.2m tall with a wing span of 2.6m. Their bill is large and black, somewhat upturned, with lengths of up to 30cm (Fig. 1). Males are larger than females, and both sexes can be identified by the band of red skin at the base of the neck. Adult storks possess all-white plumage on the body. The head and neck lacks feathers except for a cluster of grey feathers on the back of the head. The juveniles have white feathers with greyish-brown edges (McKinley, 2006; Borjas, 2004). DISTRIBUTION. Jabiru mycteria is native to South American countries such as Argentina, Brazil, Belize, Colombia, Guyana, Honduras, Nicaragua and Venezuela (Fig. 2). Jabirus can have also been sighted in Mexico, Panama, Trinidad and Tobago, Grenada, United States and Uruguay (IUCN, 2016). UWI The Online Guide to the Animals of Trinidad and Tobago Ecology HABITAT AND ACTIVITY. Jabiru storks are diurnal birds and often feed singly or in pairs but can also be found feeding in large groups (Kahl, 1973). They can be found around coastal lagoons, savannas, marshes and also ponds (Belize Zoo, 2017; Pantanal, 2006). -

Neotropical News Neotropical News
COTINGA 1 Neotropical News Neotropical News Brazilian Merganser in Argentina: If the survey’s results reflect the true going, going … status of Mergus octosetaceus in Argentina then there is grave cause for concern — local An expedition (Pato Serrucho ’93) aimed extinction, as in neighbouring Paraguay, at discovering the current status of the seems inevitable. Brazilian Merganser Mergus octosetaceus in Misiones Province, northern Argentina, During the expedition a number of sub has just returned to the U.K. Mergus tropical forest sites were surveyed for birds octosetaceus is one of the world’s rarest — other threatened species recorded during species of wildfowl, with a population now this period included: Black-fronted Piping- estimated to be less than 250 individuals guan Pipile jacutinga, Vinaceous Amazon occurring in just three populations, one in Amazona vinacea, Helmeted Woodpecker northern Argentina, the other two in south- Dryocopus galeatus, White-bearded central Brazil. Antshrike Biata s nigropectus, and São Paulo Tyrannulet Phylloscartes paulistus. Three conservation biologists from the U.K. and three South American counter PHIL BENSTEAD parts surveyed c.450 km of white-water riv Beaver House, Norwich Road, Reepham, ers and streams using an inflatable boat. Norwich, NR10 4JN, U.K. Despite exhaustive searching only one bird was located in an area peripheral to the species’s historical stronghold. Former core Black-breasted Puffleg found: extant areas (and incidently those with the most but seriously threatened. protection) for this species appear to have been adversely affected by the the Urugua- The Black-breasted Puffleg Eriocnemis í dam, which in 1989 flooded c.80 km of the nigrivestis has been recorded from just two Río Urugua-í. -

New Records of Cracids Along a Fragmented Landscape in Cen- Tral
Biodiversity Journal , 2018, 9 (4): 339–344 DOI: 10.31396/Biodiv.Jour.2018.9.4.339.344 New records of Cracids along a fragmented landscape in Cen - tral Mexico (Aves Cracidae) Lorena Silverio-Polo 1, O. Eric Ramírez-Bravo 2* , Casimiro Ordóñez-Prado 3 & Guillermo Ortega Vázquez 4 1Sitio Experimental Las Margaritas, Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Forestales, Agrícolas y Pecuarias, Km 9.5 Carretera Hueytamalco-Tenampulco, Las Margaritas Hueytamalco, Puebla, 73580 México 2Grupo de Investigación en Biodiversidad, Alimentación y Cambio Climático, Instituto de Ciencias de la Benemérita Uni - versidad Autónoma de Puebla, Edificio IC 10 Ciudad Universitaria Colonia San Manuel, Puebla, 72570 México 3Campo Experimental San Martinito, Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Forestales, Agrícolas y Pecuarias, Km 56.5 Car - retera Federal México-Puebla, San Martinito Puebla, 74100 México 4Instituto Tecnológico Superior de Zacapoaxtla, Carretera Acuaco-Zacapoaxtla km 8, Colonia Totoltepec, Zacapoaxtla Pue - bla, 73680 México *Corresponding author, e-mail: [email protected] ABSTRACT The pava cojolita or crested guan ( Penelope purpurascens Wagler, 1830) and the great curas - sow ( Crax rubra Linnaeus, 1758) (Aves Cracidae) inhabit mature rainforests with low or null perturbation, making them potential indicator species. We report actual records of both species obtained through biodiversity monitoring undertaken in the Experimental Site “Las Margar - itas” in the municipality of Hueytamalco at the Sierra Nororiental in the State -

Brazil Pantanal: Jaguars! & More … with Naturalist Journeys & Caligo Ventures
Brazil Pantanal: Jaguars! & More … With Naturalist Journeys & Caligo Ventures July 18 – 27, 2018 With Atlantic Forest Extension July 14 – 18 866.900.1146 800.426.7781 520.558.1146 [email protected] www.naturalistjourneys.com or find us on Facebook at Naturalist Journeys, LLC Brazil’s Pantanal: A place of superlatives. Home to the world’s largest fresh-water wetlands, the Pantanal is ten- times the size of the Everglades, draining into a single channel: the Paraguay River. We venture deep into this world-class wildlife hotspot on a long road that bisects the Transpantaneira wilderness, in search of an adventure that can’t be missed. In this famed region, we discover wildlife thriving in a mix of savanna, forest, and wetland habitats. Even a relaxed day can yield more than 100 species of birds and dozens of mammals — Capybara are everywhere! Brazilian Tapir, Maned Wolf, Giant Anteater, Giant Otter, and yes, Jaguar (we saw four on our 2016 trip!), are five of many incredible mammals we seek, while Harpy Eagle, Greater Rhea, Hyacinth Macaw, Toco Toucan, and Helmeted Manakin top the list of impressive bird sightings. The rare Green Anaconda, the world’s largest snake, may be a lucky find, while the small crocodilian Yacaré can be seen by the thousands. For many, it is the sheer number and variety of species that leaves the most lasting impression. Naturalist Journeys, LLC / Caligo Ventures PO Box 16545 Portal, AZ 85632 PH: 520.558.1146 / 800.426.7781 Fax 650.471.7667 naturalistjourneys.com / caligo.com [email protected] / [email protected] Brazil Pantanal: Jaguars! & More … With Naturalist Journeys & Caligo Ventures Charming (and working) cattle ranches provide our accommodations, each with its own impressive and distinctive wildlife community. -

Diurnal Birds of Prey of Belize
DIURNAL BIRDS OF PREY OF BELIZE Nevertheless, we located thirty-four active Osprey by Dora Weyer nests, all with eggs or young. The average number was three per nest. Henry Pelzl, who spent the month The Accipitridae of June, 1968, studying birds on the cayes, estimated 75 Belize is a small country south of the Yucatán to 100 pairs offshore. Again, he could not get to many Peninsula on the Caribbean Sea. Despite its small of the outer cayes. It has been reported that the size, 285 km long and 112 km wide (22 963 km2), southernmost part of Osprey range here is at Belize encompasses a great variety of habitats: Dangriga (formerly named Stann Creek Town), a mangrove cays and coastal forests, lowland tropical little more than halfway down the coast. On Mr pine/oak/palm savannas (unique to Belize, Honduras Knoder’s flight we found Osprey nesting out from and Nicaragua), extensive inland marsh, swamp and Punta Gorda, well to the south. lagoon systems, subtropical pine forests, hardwood Osprey also nest along some of the rivers inland. Dr forests ranging from subtropical dry to tropical wet, Stephen M. Russell, author of A Distributional Study and small areas of elfin forest at the top of the highest of the Birds of British Honduras, the only localized peaks of the Maya Mountains. These mountains are reference, in 1963, suspects that most of the birds seen built of extremely old granite overlaid with karst inland are of the northern race, carolinensis, which limestone. The highest is just under 1220 m. Rainfall winters here. -

Biodiversity of the Pantanal: Response to Seasonal Flooding Regime and To
Biodiversity of the Pantanal: response to seasonal flooding regime and to environmental degradation Alho, CJR.* Pós-graduação em Meio Ambiente e Desenvolvimento Regional, Universidade Para o Desenvolvimento do Estado e da Região do Pantanal – UNIDERP, Rua Ceará, 333, CEP 79003-010, Campo Grande, MS, Brazil *e-mail: [email protected] Received December 27, 2007 – Accepted December 27, 2007 – Distributed November 30, 2008 (With 1 figure) Abstract Seasonal flooding is the most important ecological phenomenon in the Pantanal. Every year many parts of the biome change from terrestrial into aquatic habitats and vice-versa. The degree of inundation creates a range of major habi- tats. Flooding occupies about 80% of the whole Pantanal. In contrast, during the dry season, most of the flooded areas stay dry, when the water returns to the river beds or evaporates. The Pantanal is a large continental savanna wetland (147,574 km2 in Brazil), touching Bolivia to the north and Paraguay to the south. The maze of fluctuating water levels, nutrients, and biota forms a dynamic ecosystem. The vegetation comprises 1,863 phanerogam plant species listed for the floodplain and 3,400 for the whole basin and 250 species of aquatic plants. The complex vegetation cover and sea- sonal productivity support a diverse and abundant fauna within the floodplain: 263 species of fish, 41 of amphibians, 113 of reptiles (177 for the basin), 463 of birds and 132 mammal species. Many endangered species occur, including jaguar (Panthera onca Linnaeus, 1758). Waterfowl are exceptionally -

GREAT CURASSOW Galliformes Family: Cracidae Genus: Crax Species: Rubra
GREAT CURASSOW Galliformes Family: Cracidae Genus: Crax Species: rubra Range: Southern Mexico to Western Ecuador Habitat: Tropical and sub-tropical forests Niche: Arboreal, omnivorous, diurnal Wild diet: Seeds, fruits and invertebrates Zoo diet: Seeds and fruits Life Span: (Wild) (Captivity) Sexual dimorphism: M is black with yellow knob on upper mandible, F is rust-colored and somewhat smaller Location in SF Zoo: South American Tropical Rainforest and Aviary APPEARANCE & PHYSICAL ADAPTATIONS: The plumage of the female is rust to yellowish whereas the male is black with white ventral areas. Female has black and white bared markings on head while the male is predominantly black with a shaggy semi-erect crest with forward curling feathers. The male also has a yellow knob on its upper mandible. Overall their bodies are Weight: 10 - 10.6 lbs slender with long broad, flat tails, which are slightly longer than their wings. Wings are short and rounded. The feet have well developed Length: 37 inches hind toes “pigeon footed” that allows them to walk easily along tree Wingspan: 15.7 inches limbs. Curassow have large muscular gizzard but also two ceca for hindgut fermentation. STATUS & CONSERVATION The rapid destruction of tropical forest is the greatest threat to this species. They are hunted for food and sport since their inability to fly fast makes them an easy target. Listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List with decreasing population numbers. COMMUNICATION AND OTHER BEHAVIOR They utter one or two booming or whistling notes. Their voice is amplified by means of an extended windpipe (trachea). A system of air chambers in the neck also serves to amplify the voice, which is loud and raucous. -

Diet of Ornate Hawk-Eagle (Spizaetus Ornatus)
Revista Brasileira de Ornitologia 27(1): 31–39. ARTICLE March 2019 Diet of Ornate Hawk-Eagle (Spizaetus ornatus) Fagner Daniel Teixeira1,5, Elisa Paraíso Mesquita2, Michele Alves Ferreira3 & Felipe de Carvalho Araújo4 1 Avenida João Gonçalves Teixeira, 22, Bairro Glória, Carmópolis de Minas, MG, Brazil. 2 Rua Coronel Pedro Jorge, 26, Bairro Prado, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil. 3 Rua Gustavo da Silveira, 1000, Bairro Horto Florestal, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil. 4 Departamento de Ciências Florestais, Universidade Federal de Lavras, Lavras, MG, Brazil. 5 Corresponding author: [email protected] Received on 12 November 2018. Accepted on 21 February 2019. ABSTRACT: The Ornate Hawk-Eagle (Spizaetus ornatus) is a top predator and inhabits mainly preserved forests. It occurs from Mexico to Argentina and throughout Brazil, where it is threatened by extinction. It hunts birds, mammals and reptiles, picking up both on the ground and on the branches in the forest. Here we report data on a pair and one young individual of this species registered in the southeast of Minas Gerais state, eastern portion of the Espinhaço Range, Brazil. In addition, a literature review on the diet of the species was carried out aiming gather data on food habits. The nesting territory, as well as the nest was discovered in semi-deciduous seasonal forest area. We recorded predation of a Lesser Yellow-headed Vulture (Cathartes burrovianus) by the young. After two days of observation, the nest was overthrown, what allowed its screening for other food items discovered after analysis of some feathers and bones. Detailed records of predation of S. ornatus were non-existent or inaccurate. -

Bfree Bird List
The following is a list of species of birds that have been recorded in the vicinity of BFREE, a scientific field station in Toledo District, southern Belize. The list includes birds seen on the 1,153 private reserve and in the adjacent protected area, the Bladen Nature Reserve. BFREE BIRD LIST ❏ Neotropic ❏ Double-toothed ❏ Little Tinamou Cormorant Kite ❏ Thicket Tinamou ❏ Anhinga ❏ White Tailed Kite ❏ Slaty-breasted ❏ Brown Pelican ❏ Plumbeous Kite Tinamou ❏ Bare-throated ❏ Black-collared ❏ Plain Chachalaca Tiger-Heron Hawk ❏ Crested Guan ❏ Great Blue Heron ❏ Bicolored Hawk ❏ Great Curassow ❏ Snowy Egret ❏ Crane Hawk ❏ Ocellated Turkey ❏ Little Blue Heron ❏ White Hawk ❏ Spotted ❏ Cattle Egret ❏ Gray Hawk Wood-Quail ❏ Great Egret ❏ Sharp-shinned ❏ Singing Quail ❏ Green Heron Hawk ❏ Black-throated ❏ Agami Heron ❏ Common Bobwhite ❏ Yellow-crowned Black-Hawk ❏ Ruddy Crake Night-Heron ❏ Great Black-Hawk ❏ Gray-necked ❏ Boat-billed Heron ❏ Solitary Eagle Wood-Rail ❏ Wood Stork ❏ Roadside Hawk ❏ Sora ❏ Jabiru Stork ❏ Zone-tailed Hawk ❏ Sungrebe ❏ Limpkin ❏ Crested Eagle ❏ Killdeer ❏ Black-bellied ❏ Harpy Eagle ❏ Northern Jacana Whistling-Duck ❏ Black-and-white ❏ Solitary Sandpiper ❏ Muscovy Duck Hawk-Eagle ❏ Lesser Yellow Legs ❏ Blue-winged Teal ❏ Black Hawk-Eagle ❏ Spotted Sandpiper ❏ Black Vulture ❏ Ornate Hawk-Eagle ❏ Pale-vented Pigeon ❏ Turkey Vulture ❏ Barred ❏ Short-billed Pigeon ❏ King Vulture Forest-Falcon ❏ Scaled Pigeon ❏ Lesser ❏ Collared ❏ Ruddy Yellow-headed Forest-Falcon Ground-Dove Vulture ❏ Laughing Falcon ❏ Blue Ground-Dove -

The Cracidae – Chachalacas, Guans and Curassows the Cracidae Or
The Cracidae – Chachalacas, Guans and Curassows The Cracidae or cracids are a bird family group of ancient origin going back perhaps some 50 million years and currently inhabiting parts of South and Central America. The Craci are a sub-order of the Galliformes which also contains most of the best known game birds in the sub-order the Phasiani such as pheasants, grouse, guinea fowls, and quails. The other members of the Craci comprise the megapodes of Australasia. Cracids are mostly arboreal (tree-dwelling) species which typically inhabit forest environments and thus their biology and habits are not well known. There is a good deal of debate on how many species the family comprise but there are some 40 – 50 currently extant. Curassows are the largest in size of the birds in this group with measurements generally in the 70-80 cm range; Guans are slightly smaller (+/- 60cm) and Chachalacas the smallest in the group at +/- 50 cm. Chachalacas are all rather similar in appearance Plain Chachalaca Ortalis vetula Chaco Chachalaca Ortalis canicollis Cracids appear to be monogamous and make a rather flat rudimentary nest of sticks with two to four plain white or cream eggs being laid depending on the species; the eggs are quite large relative to the size of the bird although the nests tend to be relatively small. Little Chachalaca Ortalis motmot Rufous-vented Chachalaca Ortalis ruficauda All cracids are typically vegetarian eating fruits, seeds, flowers, buds and leaves but limited evidence shows that some animal matter, especially insects such as grasshoppers are taken. Most cracids are highly vocal and their calls can carry a considerable distance. -

(Crax Fasciolata) Life History Patterns in the Northern
UNIVERZA NA PRIMORSKEM 2020 FAKULTETA ZA MATEMATIKO, NARAVOSLOVJE IN INFORMACIJSKE TEHNOLOGIJE MASTER’S THESIS (MAGISTRSKO DELO) CAMERA TRAP BASED DATA ANALYSIS OF THE BARE-FACED CURASSOW (CRAX FASCIOLATA) LIFE HISTORY PATTERNS IN THE NORTHERN PANTANAL, BRAZIL R'S THESIS (ANALIZA VZORCEV ŽIVLJENJSKE ZGODOVINE MASTE GOLOLIČNE HOKOJKE (CRAX FASCIOLATA) NA OSNOVI PODATKOV PRIDOBLJENIH S FOTOPASTMI NA OBMOČJU SEVERNEGA PANTANALA, BRAZILIJA) MARTIN SENIČ MARTIN SENIČ UNIVERZA NA PRIMORSKEM FAKULTETA ZA MATEMATIKO, NARAVOSLOVJE IN INFORMACIJSKE TEHNOLOGIJE Master's thesis (Magistrsko delo) Camera trap based data analysis of the Bare-faced Curassow (Crax fasciolata) life history patterns in the northern Pantanal, Brazil (Analiza vzorcev življenjske zgodovine gololične hokojke (Crax fasciolata) na osnovi podatkov pridobljenih s fotopastmi na območju severnega Pantanala, Brazilija) Ime in priimek: Martin Senič Študijski program: Varstvo narave, 2. stopnja Mentor: prof. dr. Karl-Ludwig Schuchmann Somentor: doc. dr. Andrej Sovinc Delovna somentorica: mag. Kathrin Burs Koper, maj 2020 Senič M. Camera trap based data analysis of Crax fasciolata life history patterns in the northern Pantanal. Univerza na Primorskem, Fakulteta za matematiko, naravoslovje in informacijske tehnologije, 2020 II Ključna dokumentacijska informacija Ime in PRIIMEK: Martin SENIČ Naslov magistrskega dela: Analiza vzorcev življenjske zgodovine gololične hokojke (Crax fasciolata) na osnovi podatkov pridobljenih s fotopastmi na območju severnega Pantanala, Brazilija Kraj: Koper