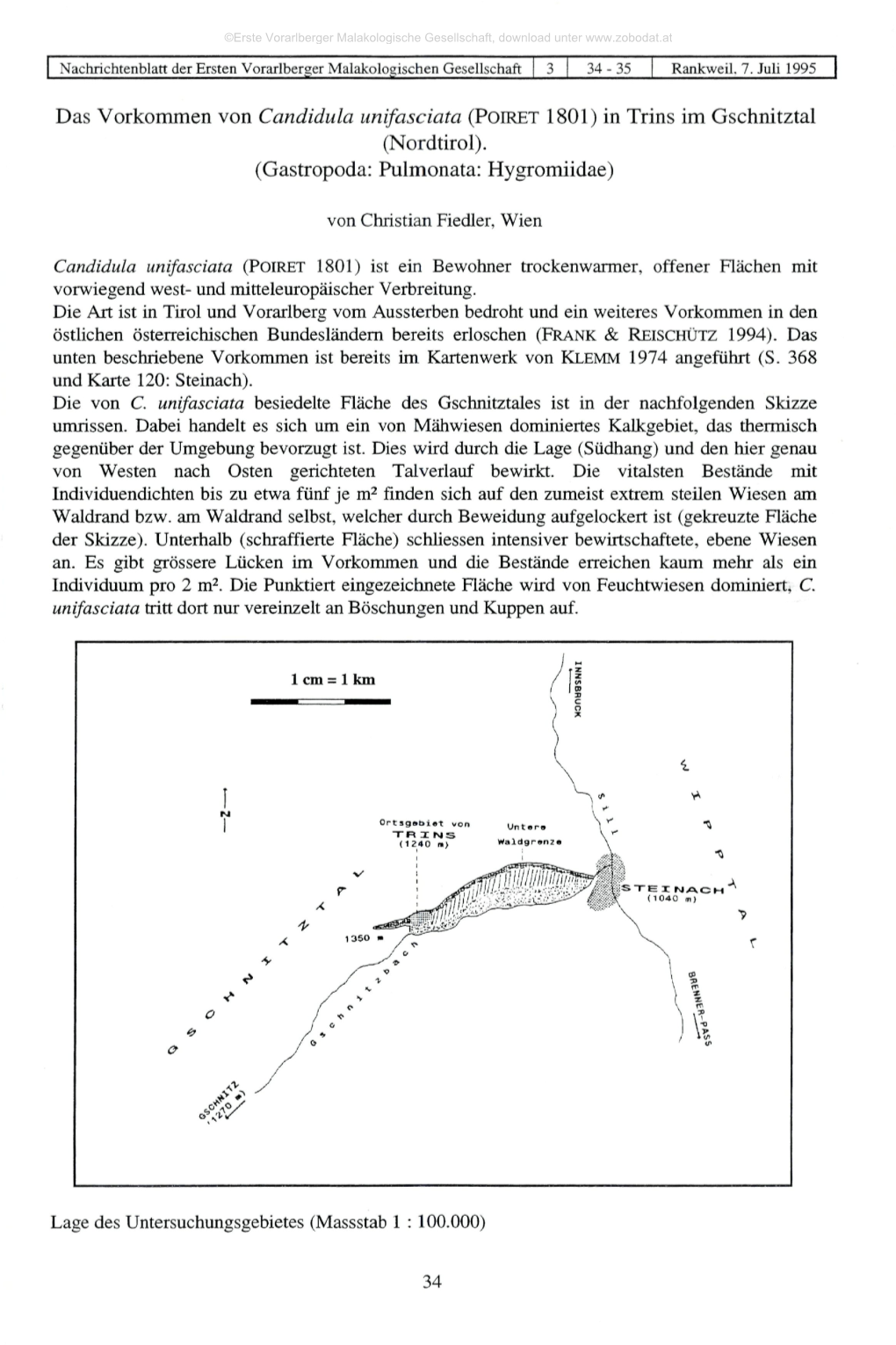
Das Vorkommen Von Candidula Unifasciata (POIRET 1801) in Trins Im Gschnitztal (Nordtirol)
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

A New Approach to an Old Conundrumdna Barcoding Sheds
Molecular Ecology Resources (2010) doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02937.x DNA BARCODING A new approach to an old conundrum—DNA barcoding sheds new light on phenotypic plasticity and morphological stasis in microsnails (Gastropoda, Pulmonata, Carychiidae) ALEXANDER M. WEIGAND,* ADRIENNE JOCHUM,* MARKUS PFENNINGER,† DIRK STEINKE‡ and ANNETTE KLUSSMANN-KOLB*,† *Institute for Ecology, Evolution and Diversity, Siesmayerstrasse 70, Goethe-University, 60323 Frankfurt am Main, Germany, †Research Centre Biodiversity and Climate, Siesmayerstrasse 70, 60323 Frankfurt am Main, Germany, ‡Biodiversity Institute of Ontario, University of Guelph, 50 Stone Road West, Guelph, ON N1G 2V7, Canada Abstract The identification of microsnail taxa based on morphological characters is often a time-consuming and inconclusive process. Aspects such as morphological stasis and phenotypic plasticity further complicate their taxonomic designation. In this study, we demonstrate that the application of DNA barcoding can alleviate these problems within the Carychiidae (Gastro- poda, Pulmonata). These microsnails are a taxon of the pulmonate lineage and most likely migrated onto land indepen- dently of the Stylommatophora clade. Their taxonomical classification is currently based on conchological and anatomical characters only. Despite much confusion about historic species assignments, the Carychiidae can be unambiguously subdi- vided into two taxa: (i) Zospeum species, which are restricted to karst caves, and (ii) Carychium species, which occur in a broad range of environmental conditions. The implementation of discrete molecular data (COI marker) enabled us to cor- rectly designate 90% of the carychiid microsnails. The remaining cases were probably cryptic Zospeum and Carychium taxa and incipient species, which require further investigation into their species status. Because conventional reliance upon mostly continuous (i.e. -

Conservation Status of a Recently Described Endemic Land Snail, Candidula Coudensis, from the Iberian Peninsula
RESEARCH ARTICLE Conservation Status of a Recently Described Endemic Land Snail, Candidula coudensis, from the Iberian Peninsula Francisco Moreira1,2,3☯*, Gonçalo Calado1☯, Susana Dias1,3☯ 1 Department of Life Sciences, Lusófona University, Campo Grande, Lisbon, Portugal, 2 REN Biodiversity Chair, CIBIO/InBIO Associate Laboratory, Uxniversidade do Porto, Campus Agrário de Vairão, Vairão, Portugal, 3 Centro de Ecologia Aplicada Prof. Baeta Neves/InBIO Associate Laboratory, Instituto Superior de Agronomia, Universidade de Lisboa, Tapada da Ajuda, Lisbon, Portugal ☯ These authors contributed equally to this work. * [email protected] Abstract We assessed the distribution, population size and conservation status of Candidula cou- densis, a recently described endemic land snail from Portugal. From March 2013 to April 2014, surveys were carried out in the region where the species was described. We found an extent of occurrence larger than originally described, but still quite small (13.5 km2). The species was found mainly in olive groves, although it occurred in a variety of other habitats OPEN ACCESS with limestone soils, including grasslands, scrublands and stone walls. Minimum population – Citation: Moreira F, Calado G, Dias S (2015) estimate ranged from 110,000 311,000 individuals. The main identified potential threats to Conservation Status of a Recently Described the species include wildfires, pesticides and quarrying. Following the application of IUCN Endemic Land Snail, Candidula coudensis, from the criteria, we advise a conservation status of either “Least Concern” or “Near-threatened” Iberian Peninsula. PLoS ONE 10(9): e0138464. under criterion D (restricted population). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0138464 Editor: Donald James Colgan, Australian Museum, AUSTRALIA Received: May 13, 2015 Accepted: August 31, 2015 Introduction Published: September 17, 2015 Land snails of the Iberian Peninsula are quite diverse, with some clades reaching high levels of Copyright: © 2015 Moreira et al. -

Draft Carpathian Red List of Forest Habitats
CARPATHIAN RED LIST OF FOREST HABITATS AND SPECIES CARPATHIAN LIST OF INVASIVE ALIEN SPECIES (DRAFT) PUBLISHED BY THE STATE NATURE CONSERVANCY OF THE SLOVAK REPUBLIC 2014 zzbornik_cervenebornik_cervene zzoznamy.inddoznamy.indd 1 227.8.20147.8.2014 222:36:052:36:05 © Štátna ochrana prírody Slovenskej republiky, 2014 Editor: Ján Kadlečík Available from: Štátna ochrana prírody SR Tajovského 28B 974 01 Banská Bystrica Slovakia ISBN 978-80-89310-81-4 Program švajčiarsko-slovenskej spolupráce Swiss-Slovak Cooperation Programme Slovenská republika This publication was elaborated within BioREGIO Carpathians project supported by South East Europe Programme and was fi nanced by a Swiss-Slovak project supported by the Swiss Contribution to the enlarged European Union and Carpathian Wetlands Initiative. zzbornik_cervenebornik_cervene zzoznamy.inddoznamy.indd 2 115.9.20145.9.2014 223:10:123:10:12 Table of contents Draft Red Lists of Threatened Carpathian Habitats and Species and Carpathian List of Invasive Alien Species . 5 Draft Carpathian Red List of Forest Habitats . 20 Red List of Vascular Plants of the Carpathians . 44 Draft Carpathian Red List of Molluscs (Mollusca) . 106 Red List of Spiders (Araneae) of the Carpathian Mts. 118 Draft Red List of Dragonfl ies (Odonata) of the Carpathians . 172 Red List of Grasshoppers, Bush-crickets and Crickets (Orthoptera) of the Carpathian Mountains . 186 Draft Red List of Butterfl ies (Lepidoptera: Papilionoidea) of the Carpathian Mts. 200 Draft Carpathian Red List of Fish and Lamprey Species . 203 Draft Carpathian Red List of Threatened Amphibians (Lissamphibia) . 209 Draft Carpathian Red List of Threatened Reptiles (Reptilia) . 214 Draft Carpathian Red List of Birds (Aves). 217 Draft Carpathian Red List of Threatened Mammals (Mammalia) . -

Guía De Los Caracoles Terrestres De Andalucía
El presente trabajo se enmarca en el Programa de Actuaciones para la Conservación y Uso sostenible de los caracoles terrestres de Andalucía, en el que colaboran, desde 2002, la Consejería de Medio Ambiente de la Junta de Andalucía y el Departamento de Fisiología y Zoología de la Universidad de Sevilla. La edición de la obra es fruto de la colaboración entre la Fundación Gypaetus y la Consejería de Medio Ambiente. Edición: Fundación Gypaetus. Dirección facultativa: Fernando Ortega Alegre. Autores: Antonio Ruiz Ruiz, Ángel Cárcaba Pozo, Ana I. Porras Crevillen y José R. Arrébola Burgos. Fotografía: Antonio Ruiz Ruiz, Alberto Martínez Ortí (págs. 211, 241). Diseño gráfico y maquetación: Carlos Manzano Arrondo y Juan A. Martínez Camúñez. I.S.B.N.: 84-935194-2-1. Depósito legal: 4 Sumario Presentación . 6 1. Introducción a la Guía de los caracoles terrestres de Andalucía a. La Guía y su estructura . 12 b. Uso de la guía . 22 c. Morfología de la concha en los caracoles terrestres . 26 d. Biología y ecología de los caracoles terrestres . 36 e. Normativa ambiental . 45 f. Localización, observación, estudio, identificación y conservación de caracoles terrestres . 49 2. Ordenación sistemática y catálogo de especies . 58 3. Glosario de términos . 278 4. Abreviaturas . 283 5. Indice de nombres científicos. 284 6. Bibliografía . 290 7. Agradecimientos . 299 8. Claves de símbolos . 300 5 Presentación de la Consejera de Medio Ambiente. Uno de los términos claves en Conservación es el de Biodiversidad o Diversidad Biológica. Alude a la gran variedad de formas y patrones de vida existente sobre el planeta y a los complejos ecológicos en los que se integran. -

Candidula (Gastropoda: Hygromii- Dae) in Northern Portugal?
© Sociedad Española de Malacología Iberus, 15 (1): 1-4, 1997 How many species of Candidula (Gastropoda: Hygromii- dae) in northern Portugal? ¿Cuantas especies de Candidula (Gastropoda: Hygromiidae) habitan en el norte de Portugal? Cristian R. ALTABA* Recibido el 6-II-1996. Aceptado el 24-IV-1996 ABSTRACT Two species of Candidula Kobelt, 1871 (Pulmonata: Hygromiidae) endemic to Portugal are reported from the northern part of the country. C. belemensis (Servain, 1880) is consi- dered a valid species similar to, but different from the widespread C. intersecta (Poiret, 1801). C. olisippensis (Servain, 1880) is distinctive, having a shell with very small, round umbilicus, a long spermathecal duct, and a short flagellum. RESUMEN Se citan para el norte de Portugal dos especies endémicas en este país pertenecientes al género Candidula Kobelt, 1871 (Pulmonata: Hygromiidae). C. belemensis (Servain, 1880) es considerada como una especie válida similar, pero diferente, a la ampliamente distribuidaC. intersecta (Poiret, 1801). C. olisippensis (Servain, 1880) es de fácil distin- ción, al tener una concha con un ombligo redondeado y pequeño, un largo conducto de la espermateca y un corto flagelo. KEY WORDS: Gastropoda, Hygromiidae, Candidula, Portugal, distribution, taxonomy. PALABRAS CLAVE: Gastropoda, Hygromiidae, Candidula, Portugal, distribución, taxonomía. INTRODUCTION The genus Candidula Kobelt, 1871 the internal anatomy or in the shells. comprises several species of hygromiid The species of Candidula living in Portu- land snails living in Western Europe. In gal are still poorly known, yet this the Iberian Peninsula this genus has un- country has at least four endemics (AL- dergone a remarkable diversification, TIMIRA, 1969; GITTENBERGER, 1985, 1993). particularly along the Atlantic drainages This note is a contribution towards a re- (ALTONAGA, GÓMEZ, MARTÍN, PRIETO, vision of the genus in the Iberian Penin- PUENTE AND RALLO, 1994). -

On Trochoidea Geyeri (Soos, 1926) and Some Conchologically Similar Taxa (Mollusca: Gastropoda Pulmonata: Hygromiidae)
On Trochoidea geyeri (Soos, 1926) and some conchologically similar taxa (Mollusca: Gastropoda Pulmonata: Hygromiidae) E. Gittenberger Gittenberger, E. On Trochoidea geyeri (Sods, 1926) and some conchologically similar taxa (Mollusca: Gastropoda Pulmonata: Hygromiidae). Zool. Med. Leiden 67 (19), 30.vii.1993:303-320, figs. 1-29.— ISSN 0024-0672. Key words: Hygromiidae; taxonomy; synonymy; Trochoidea geyeri; France; Spain. To provide background information for a proposal to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature to suppress five subjective senior synonyms of Trochoidea geyeri, the synonymies of this and some other hygromiid species are given. The nominal taxa that are dealt with concern species that are conchologically more or less similar. These species were studied to minimize the risk that even more unused senior synonyms of T. geyeri would be discovered, which would require an additional ruling of the Commission. Distributional data and short conchological diagnoses are added to increase the usefulness of the present paper. E. Gittenberger, Nationaal Natuurhistorisch Museum, Postbus 9517, NL-2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands. Introduction Trochoidea geyeri (Soos, 1926) has frequently been confused with conchologically similar species. Its name, however, is well known. It remained unchallenged since the original description. Therefore, it was rather surprising to discover six senior synonyms, all but one of which available names that remained unused after their introduction. In line with ICZN Article 23 (b), this case is referred to the Commission for a ruling, to conserve the usage of the seventh name (case no. 2870: Gittenberger, in press). In the first part of the present paper, the nominal taxa are listed that apply to T. -

Systema Naturae 250 the Linnaean Ark
Systema Naturae 250 The Linnaean Ark Systema Naturae 250 The Linnaean Ark Edited by Andrew Polaszek Cover image of “La fontaine d’os” by surrealist Wolfgang Paalen (1907–1959) used with permission of Paalen Archiv Berlin. CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group 6000 Broken Sound Parkway NW, Suite 300 Boca Raton, FL 33487-2742 © 2010 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC CRC Press is an imprint of Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business No claim to original U.S. Government works Version Date: 20140515 International Standard Book Number-13: 978-1-4200-9502-9 (eBook - PDF) This book contains information obtained from authentic and highly regarded sources. Reasonable efforts have been made to publish reliable data and information, but the author and publisher cannot assume responsibility for the valid- ity of all materials or the consequences of their use. The authors and publishers have attempted to trace the copyright holders of all material reproduced in this publication and apologize to copyright holders if permission to publish in this form has not been obtained. If any copyright material has not been acknowledged please write and let us know so we may rectify in any future reprint. Except as permitted under U.S. Copyright Law, no part of this book may be reprinted, reproduced, transmitted, or uti- lized in any form by any electronic, mechanical, or other means, now known or hereafter invented, including photocopy- ing, microfilming, and recording, or in any information storage or retrieval system, without written permission from the publishers. For permission to photocopy or use material electronically from this work, please access www.copyright.com (http:// www.copyright.com/) or contact the Copyright Clearance Center, Inc. -

Candidula Corbellai N
Animal Biodiversity and Conservation 34.1 (2011) 1 A new hygromiid for the Iberian malacofauna: Candidula corbellai n. sp. (Gastropoda, Pulmonata) A. Martínez–Ortí Martínez–Ortí, A., 2011. A new hygromiid for the Iberian malacofauna: Candidula corbellai n. sp. (Gastropoda, Pulmonata). Animal Biodiversity and Conservation, 34.1: 1–10. Abstract A new hygromiid for the Iberian malacofauna: Candidula corbellai n. sp. (Gastropoda, Pulmonata).— We report a new Iberian hygromiid, Candidula corbellai n. sp., and describe its conchological and anatomical charac- teristics. This new species is compared with two other Iberian endemic species, Candidula camporroblensis and C. rocandioi, which present similarities in the reproductive system, such as the long flagellum. The shell of the new species is compared with specimens of the type series of these taxa. The reproductive system of C. corbellai n. sp. is distinguished from C. camporroblensis by its longer male part, although the flagellum is shorter than the penis and epiphallus together and it has a long bursa copulatrix with respect to its duct, which is shorter. The epiphallus and the bursa copulatrix duct are longer in C. rocandioi than in C. corbellai n. sp. A geographical distribution map of the three species in the Iberian peninsula is shown. Key words: Hygromiidae, Candidula corbellai n. sp., Candidula camporroblensis, Candidula rocandioi, Catalonia, Iberian peninsula. Resumen Un nuevo higrómido para la malacofauna ibérica: Candidula corbellai sp. n. (Gastropoda, Pulmonata).— Se describen las características conquiológicas y anatómicas de un nuevo higrómido ibérico, Candidula corbellai sp. n. Se compara con otros dos endemismos ibéricos, Candidula camporroblensis y C. rocandioi, especies con las que presenta similitud en el aparato reproductor, ya que ambos poseen el flagelo largo. -

Kapitel 16 Weichtiere Rote Listen Sachsen-Anhalt 2020
Rote Listen Sachsen-Anhalt Berichte des Landesamtes für Umweltschutz Sachsen-Anhalt 16 Weichtiere (Mollusca) Halle, Heft 1/2020: 367–378 Bearbeitet von Katrin HARTENAUER, Michael UNRUH Anzahl Neunachweise autochtoner Arten, wie Chon- und Andreas STARK drina avenacea, Deroceras rodnae, Vertigo moulin- (4. Fassung, Stand: November 2019) siana, Omphiscola glabra, Gyraulus riparius, Bithynia troschelii, Pisidium hibernicum und Pisidium globulare, welche bisher übersehen worden sind. Hinzu kom- Einleitung men eingeschleppte Neozoen und vor Jahrzehnten ausgesetzte Arten, die stabile Bestände aufbauen Weichtiere sind in fast allen Lebensräumen ver- konnten. Zu letzteren gehören in Sachsen-Anhalt Dro- treten und bieten somit Aussagemöglichkeiten zu bacia banatica und Alopia straminicollis monacha (vgl. verschiedenen Biotoptypen. Neben einer besonders KÖRNIG et al. 2013) sowie Alopia livida und Microponti- hohen Zahl stenöker Arten zeichnen sich Mollusken ca caucasica (vgl. UNRUH & STARK 2018). durch den meist geringen Aktionsradius und stark Gegenüber der letzten Fassung erfolgte bei vier eingeschränkte Ausbreitungsmöglichkeiten aus. Die Arten eine Rückstufung. Bei diesen handelt es sich oftmals hochgradige Spezialisierung führt in Verbin- zum einen um die Wiederfunde der verschollenen dung mit der geringen Mobilität bereits bei geringfü- Anisus vorticulus und Pseudanodonta complanata gig erscheinenden Veränderungen in den besiedelten und zum anderen um die beiden Xerothermarten Habitaten zu merklichen Reaktionen hinsichtlich der Truncatellina -

Records of Xerocrassa Muehlfeldtiana (Rossmässler 1837) Refer to X
JOURNAL OF CONCHOLOGY (2014), VOL.41, NO.6 1 RECORDS OF XEROCRASSA MUEHLFELDTIANA (ROSSMÄSSLER 1837) REFER TO X. RHABDOTA (STURANY 1901): REDESCRIPTION OF THE SPECIES AND DETAILED ANATOMICAL DESCRIPTION OF OTHER BALKAN XEROCRASSA SPECIES (GASTROPODA: PULMONATA: HYGROMIIDAE) 1, 2 WILLY DE MATTIA & BARNA PÁLL-GERGELY 1International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) Padriciano, 99. 34149 Trieste, Italy 2Department of Biology, Shinshu University, Matsumoto 390–8621, Japan Abstract The hygromiid land snail Xerocrassa muehlfeldtiana (Rossmässler 1837) was reported from several localities in the western Balkans by previous authors. Evaluation of the taxonomic history of Rossmässler’s name revealed that it is a junior synonym of Helicopsis striata (O. F. Müller 1774), which therefore cannot be applied to populations from the Balkans. There is, however, an available and geographically appropriate name for that species: Xerocrassa rhabdota (Sturany 1901). In this paper, we redescribe the shell and anatomy of X. rhabdota based on newly collected material from Slovenia, Croatia and Bosnia- Herzegovina. Additionally, we compare the anatomy and shell of X. rhabdota with the type species of the genus (X. seetzeni (L. Pfeiffer 1847)), and the three congeners known from the central and the continental part of southeastern Europe (Balkan Peninsula), namely Xerocrassa geyeri (Soós, 1926), Xerocrassa cretica (L. Pfeiffer, 1841) and Xerocrassa poecilodoma (O. Boettger, 1894). Key words drought tolerant land snail species, anatomy, taxonomy, nomenclature, Balkans INTRODUCTION agriculturally important parasites (Anderson, Arid, open areas such as shrublands, rocky 2000; Rommel et al., 2000). Therefore, in order to beaches, grassy slopes and sand dunes are char- get exact information about their distribution, the acteristic habitats of the Mediterranean Region. -

Is Cold Hardiness Size-Constrained? a Comparative Approach in Land Snails Armelle Ansart, Annie Guiller, Olivier Moine, Marie-Claire Martin, Luc Madec
Is cold hardiness size-constrained? A comparative approach in land snails Armelle Ansart, Annie Guiller, Olivier Moine, Marie-Claire Martin, Luc Madec To cite this version: Armelle Ansart, Annie Guiller, Olivier Moine, Marie-Claire Martin, Luc Madec. Is cold hardiness size-constrained? A comparative approach in land snails. Evolutionary Ecology, Springer Verlag, 2013, 28 (3), pp.471-493. 10.1007/s10682-013-9680-9. hal-00909016 HAL Id: hal-00909016 https://hal-univ-rennes1.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00909016 Submitted on 25 Nov 2013 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Ansart, Guiller, Moine, Martin and Madec – CH is size-constrained in land snails Is cold hardiness size-constrained? A comparative approach in land snails ANSART Armelle1*, [email protected] 5 GUILLER Annie2, [email protected] MOINE Olivier3, [email protected] MARTIN Marie-Claire1, marie-claire.martin@univ-rennes1 MADEC Luc1, [email protected] 10 1 Université de Rennes 1, UMR 6553 Ecobio, bâtiment 14A, 263 Avenue du Général Leclerc, -

PDF Scan to USB Stick
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by Hochschulschriftenserver - Universität Frankfurt am Main Phenotypic evolution and hidden speciation in Candidula unifasciata ssp. (Helicellinae, Gastropoda) inf erred by 16s variathn and quantitative shell traits MARKUS PFENNINGER*arid FREDERIC MAGNIN~ *Abteilung Ökologie und Evolution, Zoologisches Institut der J. W. Goethe-Universität, Bio-Campus Siesmayerstra$e, 0-60054 FrankfurtlMain, Germany, tIMEP ESA 6116 Case 461, Facultt?des Sciences et Techniques de St. Jerome, 13997 Marseille Cedex 20, France Abstract In an effort to link quantitative morphometric information with molecular data on the popu- lation level, we have analysed 19 populations of the conchologically variable land snail Candidula unifasciata from across the species range for variation in quantitative shell traits L and at the mitochondrial16S ribosomai (r)DNA locus. In genetic analysis, including 21 additional populations, we observed two fundamental haplotype clades with an average pairwise sequence divergence of 0.209 f 0.009 between clades compared to 0.017 IT 0.012 within clades, suggesting the presence of two different evolution-y lineages. Integrating additional shell material from the Senckenberg Malacological Collection, a highly signific ant discriminant analysis on the morphological sheli traits with fundamental haplotype clades as grouping variable suggested that the less frequent haplotype corresponds to the described subspecies C. U. rugosiuscula, which we propose to regard as a distinct species. Both taxa were highly subdivided genetically (GT= 0.648 and 0.777 P < 0.001). This was contrasted by the partition of morphological variance, where only 29.6% and 21.9% of the variance were distributed among populations, respectively.