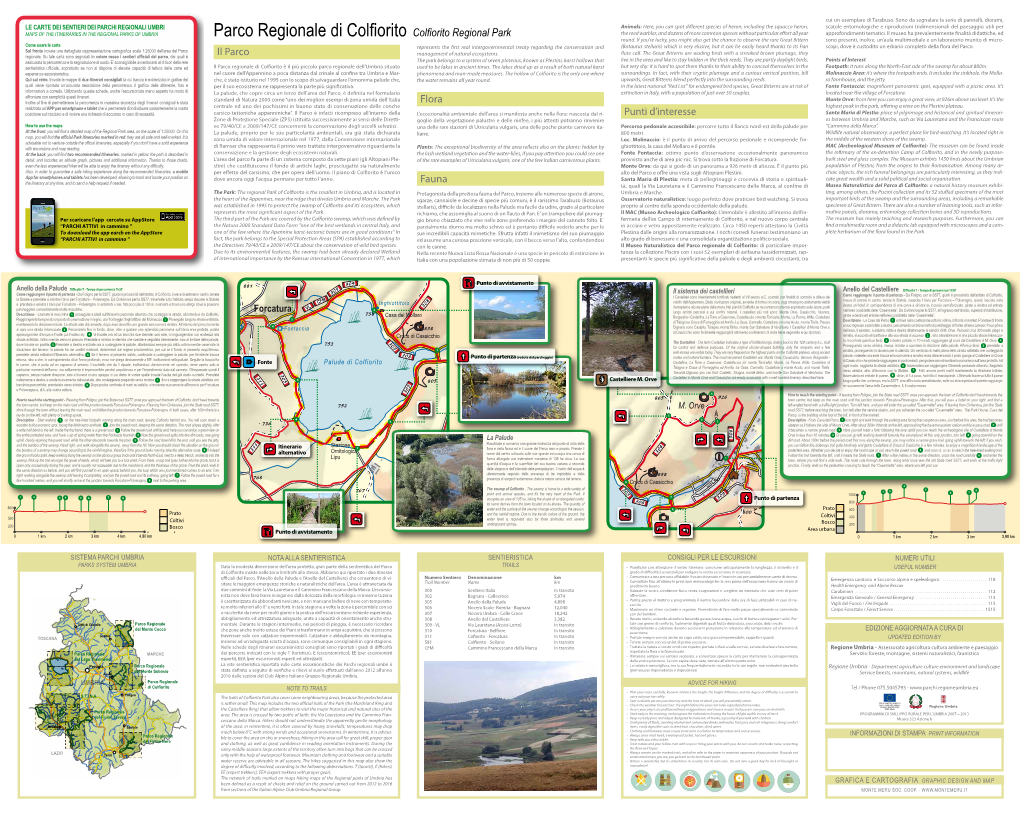
Parco Colfiorito
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Umbria from the Iron Age to the Augustan Era
UMBRIA FROM THE IRON AGE TO THE AUGUSTAN ERA PhD Guy Jolyon Bradley University College London BieC ILONOIK.] ProQuest Number: 10055445 All rights reserved INFORMATION TO ALL USERS The quality of this reproduction is dependent upon the quality of the copy submitted. In the unlikely event that the author did not send a complete manuscript and there are missing pages, these will be noted. Also, if material had to be removed, a note will indicate the deletion. uest. ProQuest 10055445 Published by ProQuest LLC(2016). Copyright of the Dissertation is held by the Author. All rights reserved. This work is protected against unauthorized copying under Title 17, United States Code. Microform Edition © ProQuest LLC. ProQuest LLC 789 East Eisenhower Parkway P.O. Box 1346 Ann Arbor, Ml 48106-1346 Abstract This thesis compares Umbria before and after the Roman conquest in order to assess the impact of the imposition of Roman control over this area of central Italy. There are four sections specifically on Umbria and two more general chapters of introduction and conclusion. The introductory chapter examines the most important issues for the history of the Italian regions in this period and the extent to which they are relevant to Umbria, given the type of evidence that survives. The chapter focuses on the concept of state formation, and the information about it provided by evidence for urbanisation, coinage, and the creation of treaties. The second chapter looks at the archaeological and other available evidence for the history of Umbria before the Roman conquest, and maps the beginnings of the formation of the state through the growth in social complexity, urbanisation and the emergence of cult places. -

The Umbria (Central Italy) Earthquake Series of September 26,1997 E
Transactions on Ecology and the Environment vol 24, © 1998 WIT Press, www.witpress.com, ISSN 1743-3541 The Umbria (Central Italy) earthquake series of September 26,1997 E. Lekkas & I. Fountoulis Division of Dynamic, Tectonic Applied Geology, Department of Geology University of Athens, GR-157 84 Athens, Greece, e-mail: [email protected], [email protected] Abstract The earthquake of 26th September 1997 caused reactivation of NNW-SSE striking faults, much destruction in buildings, and the deaths of 11 people. The site effects observed in the affected area were seismic fractures, landslides, rockfalls, local aquifer level changes, as well as damages to buildings. The site effects extended over a significant area. The type of damage for various types of buildings is described. 1 Introduction, On Friday 26* September 1997, at 9:40 (GMT), a strong earthquake of Ms=5.9 magnitude, produced severe damage and casualties in the area of Umbria, Central Italy. The epicentre of the quake was 43.DON and 12.80E; the focus was 10 km deep, and was located in the broad area of Cesi- Colfiorito villages, which suffered severe damages (Fig. 1). The villages are 50 km east of the town of Perugia (Central Italy). Moreover the populated areas that suffered most damages were Colfiorito, Annifo, Collecurti, Costa, San Martino, Verchiano, Arvello, Aggi, Casenove, etc., which the intensity exceeded the IX of EMS 1992 (Fountoulis,*). According to official information, 11 people were killed, 150 injured, while about 10,000 people became homeless and 100,000 temporarily homeless. The total number of populated areas that suffered significant Transactions on Ecology and the Environment vol 24, © 1998 WIT Press, www.witpress.com, ISSN 1743-3541 94 Risk Analysis damages exceed 60, which are scattered in a mountainous area and which stretches roughly l,000km^. -

45Th Congress of the European Regional Science
A Service of Leibniz-Informationszentrum econstor Wirtschaft Leibniz Information Centre Make Your Publications Visible. zbw for Economics Gualtieri, Alessia; Romano, Bernardino Conference Paper Appennines settlement evolution and transformation analysis with GIS instrument 45th Congress of the European Regional Science Association: "Land Use and Water Management in a Sustainable Network Society", 23-27 August 2005, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Provided in Cooperation with: European Regional Science Association (ERSA) Suggested Citation: Gualtieri, Alessia; Romano, Bernardino (2005) : Appennines settlement evolution and transformation analysis with GIS instrument, 45th Congress of the European Regional Science Association: "Land Use and Water Management in a Sustainable Network Society", 23-27 August 2005, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, European Regional Science Association (ERSA), Louvain-la-Neuve This Version is available at: http://hdl.handle.net/10419/117558 Standard-Nutzungsbedingungen: Terms of use: Die Dokumente auf EconStor dürfen zu eigenen wissenschaftlichen Documents in EconStor may be saved and copied for your Zwecken und zum Privatgebrauch gespeichert und kopiert werden. personal and scholarly purposes. Sie dürfen die Dokumente nicht für öffentliche oder kommerzielle You are not to copy documents for public or commercial Zwecke vervielfältigen, öffentlich ausstellen, öffentlich zugänglich purposes, to exhibit the documents publicly, to make them machen, vertreiben oder anderweitig nutzen. publicly available on the internet, or to distribute or otherwise use the documents in public. Sofern die Verfasser die Dokumente unter Open-Content-Lizenzen (insbesondere CC-Lizenzen) zur Verfügung gestellt haben sollten, If the documents have been made available under an Open gelten abweichend von diesen Nutzungsbedingungen die in der dort Content Licence (especially Creative Commons Licences), you genannten Lizenz gewährten Nutzungsrechte. -

Earthquake Colfiorito in September 1997; a Single Case Study
Animals 2014, 4, 292-312; doi:10.3390/ani4020292 OPEN ACCESS animals ISSN 2076-2615 www.mdpi.com/journal/animals Case Report Cows Come Down from the Mountains before the (Mw = 6.1) Earthquake Colfiorito in September 1997; A Single Case Study Cristiano Fidani 1,2,*, Friedemann Freund 3,4,5 and Rachel Grant 6 1 Osservatorio Sismico “Andrea Bina”, Borgo XX Giugno 74, 06121 Perugia, Italy 2 Central Italy Electromagnetic Network (CIEN), Via Fosso del Passo 6, 63847 San Procolo, Fermo, Italy 3 Ames Research Center, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), Earth Science Division, Code SGE, Moffett Field, CA 94035, USA; E-Mail: [email protected] 4 Department of Physics, San Jose State University, San Jose, CA 95192, USA 5 Carl Sagan Center, SETI Institute, 189 Bernardo Ave., Mountain View, CA 94043, USA 6 Department of Life Sciences, Anglia Ruskin University, East Rd., Cambridge, CB1 1PT, UK; E-Mail: [email protected] * Author to whom correspondence should be addressed; E-Mail: [email protected]. Received: 7 January 2014; in revised form: 13 May 2014 / Accepted: 19 May 2014 / Published: 3 June 2014 Simple Summary: Recent reports from several countries such as China, Italy and Japan support the existence of strange animal behaviour before strong earthquakes. However, the stimuli to which animals are sensitive preceding seismic activity are still not completely understood. Here we report the case of a herd of cows (reported by an entire village) leaving the hill pasture and descending near to the village streets two days before a strong earthquake. -

Vegetation of the "Altipiani Di Colfiorito" Wetlands (Central Apennines, Italy)
Plant Sociology 57(2) 2020, 113–132 | DOI 10.3897/pls2020572/04 Società Italiana di Scienza della Vegetazione (SISV) Vegetation of the "Altipiani di Colfiorito" wetlands (central Apennines, Italy) Federico Maria Tardella1, Vincenzo Maria Di Agostino2 1 Herbarium Universitatis Camerinensis, Unit of Plant Diversity and Ecosystems Management, School of Biosciences and Veterinary Medicine, University of Camerino, Via Pontoni 5, I-62032 Camerino, Macerata, Italy 2 School of Biosciences and Veterinary Medicine, University of Camerino, Via Pontoni 5, I-62032 Camerino, Macerata, Italy Corresponding author: Federico Maria Tardella ([email protected]) Subject editor: Daniele Viciani ♦ Received 22 September 2020 ♦ Accepted 16 December 2020 ♦ Published 28 December 2020 Abstract The "Altipiani di Colfiorito" catchment basin in central Italy features a wetland system of great interest for conservation, composed of seven plains. Considering that most of the relevés conducted in the past refer to one plain and date back to the 1960s, the research aim was to widen and update the vegetation knowledge in the whole wetland system. Two hundred and thirty-nine phytosociological relevés were carried out using the Braun-Blanquet method. On the basis of cluster analysis of the species data set and phytosocio- logical interpretation, 39 vegetation types were classified, most of which of high conservation interest in central Italy, referred to the Potamogetonetea (6 communities), Bidentetea (2), Phragmito-Magnocaricetea (21), Molinio-Arrhenatheretea (9), and Epilobietea an- gustifolii (1) classes. The new subassociationPhalaridetum arundinaceae alopecuretosum bulbosi is also described. Twenty-two com- munities found in the past decades by other authors were confirmed, while 17 were new records for the study area. -

Damage Scenarios and Vulnerability Sources in the Not-Aseismic Masonry Buildings
1453 UMBRIA-MARCHES EARTHQUAKE OF 26 SEPTEMBER 1997: DAMAGE SCENARIOS AND VULNERABILITY SOURCES IN THE NOT-ASEISMIC MASONRY BUILDINGS G SARÀ1, G BARBETTI2, A BONI3, F MARILLI4, R NUDO5 And S VITI6 SUMMARY The present investigation concerns the response to the seismic action of the traditional masonry buildings, therefore not provided with aseismic measures, located in the Umbria and Marches places hurt by the double seismic event of 26 September 1997. The investigation, performed on a statistical basis, points out the most frequent types and scenarios of damage. These scenarios are associated, by the individuation of the crisis mechanism, to the vulnerability sources related to the architectonic-structural characteristics of the buildings. That allows to come to useful conclusions about the most appropriate intervention strategies to be adopted referring to the different building situations. INTRODUCTION On 26 September 1997 the Umbria and Marches regions, and in particular the Perugia and Macerata provinces, have experienced a couple of seismic events of medium-high intensity. The two shocks, occurred at 2:33 and 11:40 a.m. with epicentre around Colfiorito (Perugia), had a magnitudo ML of 5.5 and 5.8 respectively, and an average intensity, in the epicentre area, equal to the VII and VIII degree of the MCS scale. While the concrete buildings have been on the whole lightly damaged, the masonry buildings, generally realized by traditional, not aseismic techniques, have been seriously damaged, particularly in the zones near the epicentre. This occurred both to constructions of the historical centres, with or without monumental character, and to the buildings of the most modern city suburbs and of the towns and villages spread in the territory.