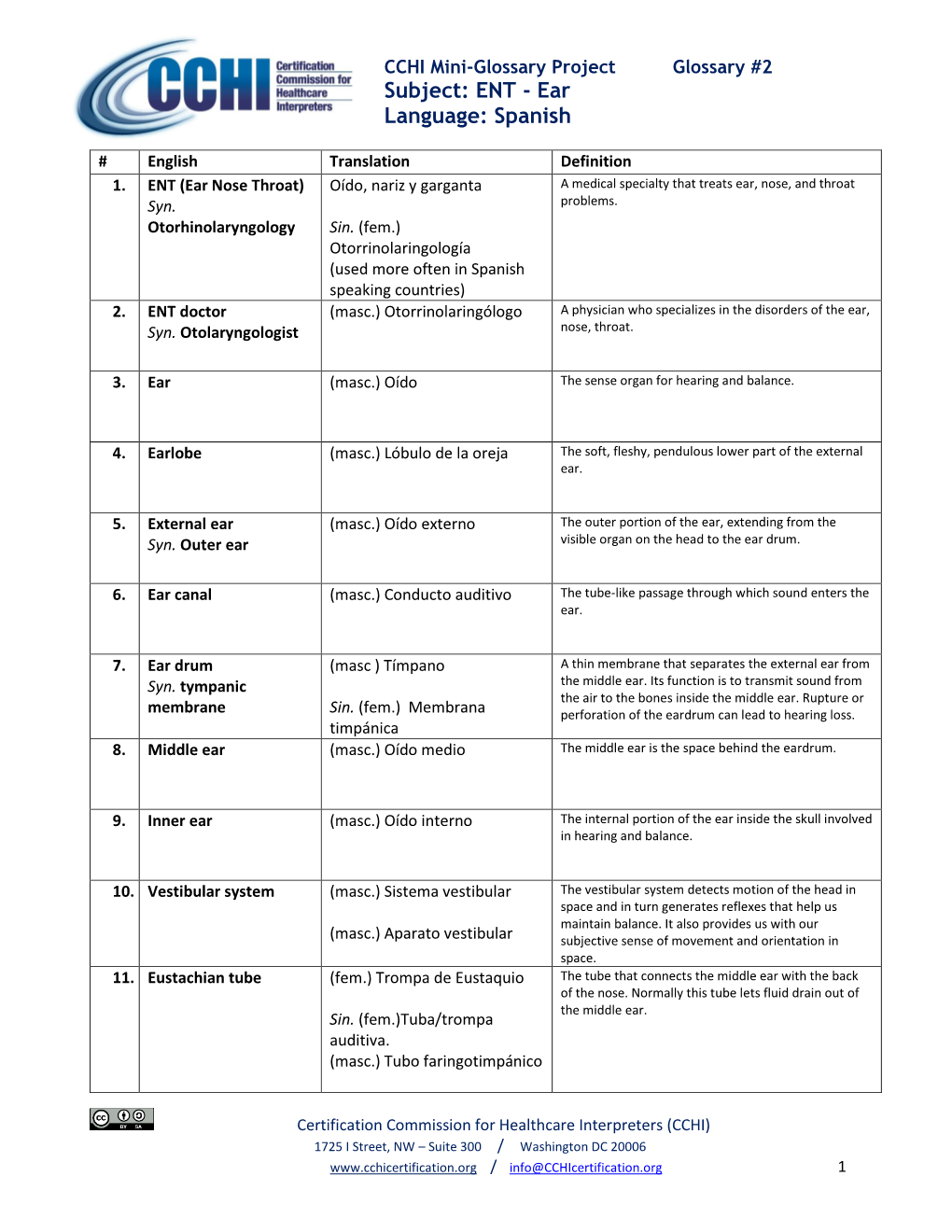
Subject: ENT - Ear Language: Spanish
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Otorhinolaryngology (Ear, Nose and Throat Surgery, ENT)
Published on Health Careers (https://www.healthcareers.nhs.uk) Home > Explore roles > Doctors > Roles for doctors > Surgery > Otorhinolaryngology (ear, nose and throat surgery, ENT) Otorhinolaryngology (ear, nose and throat surgery, ENT) Otorhinolaryngologists (also known as otolaryngologists or ear, nose and throat or ENT Surgeons) are surgical specialists who diagnose, evaluate and manage a wide range of diseases of the head and neck, including the ear, nose and throat regions. This page provides useful information on the nature of the work, the common procedures/interventions, sub-specialties and other roles that may interest you. Nature of the work ENT surgeons often treat conditions that affect the senses such as hearing and balance disorders or smell and taste problems. They also treat patients with conditions that affect their voice, breathing and swallowing as well as those with head and neck tumours including the skull base and interface with the brain. ENT surgeons may treat people of all ages from newborn babies to elderly people. They see more children than most other surgeons, apart from paediatric surgeons. One of the attractions is that they treat a wide spectrum of ages and diseases. A proportion of an ENT surgeon’s time is spent in outpatient clinics and managing conditions medically without the need for surgery. The use of microscopes & endoscopes in outpatients allows treatment/ diagnosis in the clinic. ENT has possibly the widest range of operations of any speciality from major head & neck procedures with flaps & complex -

Perforated Eardrum
Vinod K. Anand, MD, FACS Nose and Sinus Clinic Perforated Eardrum A perforated eardrum is a hole or rupture m the eardrum, a thin membrane which separated the ear canal and the middle ear. The medical term for eardrum is tympanic membrane. The middle ear is connected to the nose by the eustachian tube. A perforated eardrum is often accompanied by decreased hearing and occasional discharge. Paih is usually not persistent. Causes of Eardrum Perforation The causes of perforated eardrum are usually from trauma or infection. A perforated eardrum can occur: if the ear is struck squarely with an open hand with a skull fracture after a sudden explosion if an object (such as a bobby pin, Q-tip, or stick) is pushed too far into the ear canal. as a result of hot slag (from welding) or acid entering the ear canal Middle ear infections may cause pain, hearing loss and spontaneous rupture (tear) of the eardrum resulting in a perforation. In this circumstance, there may be infected or bloody drainage from the ear. In medical terms, this is called otitis media with perforation. On rare occasions a small hole may remain in the eardrum after a previously placed P.E. tube (pressure equalizing) either falls out or is removed by the physician. Most eardrum perforations heal spontaneously within weeks after rupture, although some may take up to several months. During the healing process the ear must be protected from water and trauma. Those eardrum perforations which do not heal on their own may require surgery. Effects on Hearing from Perforated Eardrum Usually, the larger the perforation, the greater the loss of hearing. -

Nasal Polyposis: a Review
Global Journal of Otolaryngology ISSN 2474-7556 Review Article Glob J Otolaryngol - Volume 8 Issue 2 May 2017 Copyright © All rights are reserved by Sushna Maharjan DOI: 10.19080/GJO.2017.0 Nasal Polyposis: A Review Sushna Maharjan1*, Puja Neopane2, Mamata Tiwari1 and Ramesh Parajuli3 1Department of Pathology, Chitwan Medical College Teaching Hospital, Nepal 2Department of Oral Medicine and Pathology, Health Sciences University of Hokkaido, Japan 3Department of Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Chitwan Medical College Teaching Hospital, Nepal Submission: May 07, 2017; Published: May 30, 2017 *Corresponding author: Sushna Maharjan, Department of Pathology, Chitwan Medical College Teaching Hospital (CMC-TH), P.O. Box 42, Bharatpur, Chitwan, Nepal, Email: Abstract Nasal polyp is a benign lesion that arises from the mucosa of the nasal sinuses or from the mucosa of the nasal cavity as a macroscopic usuallyedematous present mass. with The nasalexact obstruction,etiology is still rhinorrhea unknown and and postnasalcontroversial, drip. but Magnetic it is assumed resonance that imagingmain causes is suggested, are inflammatory particularly conditions to rule andout allergy. It is more common in allergic patients with asthma. Interleukin-5 has found to be significantly raised in nasal polyps. The patients seriousKeywords: conditions Allergy; such Interleukin-5; as neoplasia. Nasal Histopathological polyp; Neoplasia examination is also suggested to rule out malignancy and for definite diagnosis. Abbreviations: M:F- Male: Female; IgE: Immunoglobulin E; IL: Interleukin; CRS: Chronic Rhinosinusitis; HLA: Human Leucocyte Antigen; CT: Computerized Tomography; MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduction the nose and nasal sinuses characterized by stromal edema and Nasal polyps are characterized by benign lesions that arise from the mucosa of the nasal sinuses, most often from the cause may be different. -

SENSORY MOTOR COORDINATION in ROBONAUT Richard Alan Peters
SENSORY MOTOR COORDINATION IN ROBONAUT 5 Richard Alan Peters 11 Vanderbilt University School of Engineering JSC Mail Code: ER4 30 October 2000 Robert 0. Ambrose Robotic Systems Technology Branch Automation, Robotics, & Simulation Division Engineering Directorate Richard Alan Peters II Robert 0. Ambrose SENSORY MOTOR COORDINATION IN ROBONAUT Final Report NASNASEE Summer Faculty Fellowship Program - 2000 Johnson Space Center Prepared By: Richard Alan Peters II, Ph.D. Academic Rank: Associate Professor University and Department: Vanderbilt University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Nashville, TN 37235 NASNJSC Directorate: Engineering Division: Automation, Robotics, & Simulation Branch: Robotic Systems Technology JSC Colleague: Robert 0. Ambrose Date Submitted: 30 October 2000 Contract Number: NAG 9-867 13-1 ABSTRACT As a participant of the year 2000 NASA Summer Faculty Fellowship Program, I worked with the engineers of the Dexterous Robotics Laboratory at NASA Johnson Space Center on the Robonaut project. The Robonaut is an articulated torso with two dexterous arms, left and right five-fingered hands, and a head with cameras mounted on an articulated neck. This advanced space robot, now dnven only teleoperatively using VR gloves, sensors and helmets, is to be upgraded to a thinking system that can find, in- teract with and assist humans autonomously, allowing the Crew to work with Robonaut as a (junior) member of their team. Thus, the work performed this summer was toward the goal of enabling Robonaut to operate autonomously as an intelligent assistant to as- tronauts. Our underlying hypothesis is that a robot can deveZop intelligence if it learns a set of basic behaviors ([.e., reflexes - actions tightly coupled to sensing) and through experi- ence learns how to sequence these to solve problems or to accomplish higher-level tasks. -

The Ear, Nose, and Throat Exam Jeffrey Texiera, MD and Joshua Jabaut, MD CPT, MC, USA LT, MC, USN
The Ear, Nose, and Throat Exam Jeffrey Texiera, MD and Joshua Jabaut, MD CPT, MC, USA LT, MC, USN Midatlantic Regional Occupational and Environmental Medicine Conference Sept. 23, 2017 Disclosures ●We have no funding or financial interest in any product featured in this presentation. The items included are for demonstration purposes only. ●We have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Overview ● Overview of clinically oriented anatomy - presented in the format of the exam ● The approach ● The examination ● Variants of normal anatomy ● ENT emergencies ● Summary/highlights ● Questions Anatomy ● The head and neck exam consists of some of the most comprehensive and complicated anatomy in the human body. ● The ear, nose, and throat comprise a portion of that exam and a focused clinical encounter for an acute ENT complaint may require only this portion of the exam. Ears www.Medscape.com www.taqplayer.info Ear – Vestibular organ www.humanantomylibrary.com Nose/Sinus Anatomy Inferior Middle Turbinate Turbinate Septum Dorsum Sidewalls Ala Floor Tip www.ENT4Students.blogspot.com Columella Vestibule www.beautyepic.com Oral cavity and oropharynx (throat) www.apsubiology.org Neck www.rdhmag.com The Ear, Nose, and Throat exam Perform in a standardized systematic way that works for you Do it the same way every time, this mitigates risk of missing a portion of the exam Practice the exam to increase comfort with performance and familiarize self with variants of normal Describe what you are doing to the patient, describe what you see in your documentation Use your PPE as appropriate A question to keep in mind… ●T/F: The otoscope is the optimal tool for examining the tympanic membrane. -

Medical Terminology Abbreviations Medical Terminology Abbreviations
34 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY ABBREVIATIONS MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY ABBREVIATIONS The following list contains some of the most common abbreviations found in medical records. Please note that in medical terminology, the capitalization of letters bears significance as to the meaning of certain terms, and is often used to distinguish terms with similar acronyms. @—at A & P—anatomy and physiology ab—abortion abd—abdominal ABG—arterial blood gas a.c.—before meals ac & cl—acetest and clinitest ACLS—advanced cardiac life support AD—right ear ADL—activities of daily living ad lib—as desired adm—admission afeb—afebrile, no fever AFB—acid-fast bacillus AKA—above the knee alb—albumin alt dieb—alternate days (every other day) am—morning AMA—against medical advice amal—amalgam amb—ambulate, walk AMI—acute myocardial infarction amt—amount ANS—automatic nervous system ant—anterior AOx3—alert and oriented to person, time, and place Ap—apical AP—apical pulse approx—approximately aq—aqueous ARDS—acute respiratory distress syndrome AS—left ear ASA—aspirin asap (ASAP)—as soon as possible as tol—as tolerated ATD—admission, transfer, discharge AU—both ears Ax—axillary BE—barium enema bid—twice a day bil, bilateral—both sides BK—below knee BKA—below the knee amputation bl—blood bl wk—blood work BLS—basic life support BM—bowel movement BOW—bag of waters B/P—blood pressure bpm—beats per minute BR—bed rest MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY ABBREVIATIONS 35 BRP—bathroom privileges BS—breath sounds BSI—body substance isolation BSO—bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy BUN—blood, urea, nitrogen -

Study Guide Medical Terminology by Thea Liza Batan About the Author
Study Guide Medical Terminology By Thea Liza Batan About the Author Thea Liza Batan earned a Master of Science in Nursing Administration in 2007 from Xavier University in Cincinnati, Ohio. She has worked as a staff nurse, nurse instructor, and level department head. She currently works as a simulation coordinator and a free- lance writer specializing in nursing and healthcare. All terms mentioned in this text that are known to be trademarks or service marks have been appropriately capitalized. Use of a term in this text shouldn’t be regarded as affecting the validity of any trademark or service mark. Copyright © 2017 by Penn Foster, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of the material protected by this copyright may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the copyright owner. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to Copyright Permissions, Penn Foster, 925 Oak Street, Scranton, Pennsylvania 18515. Printed in the United States of America CONTENTS INSTRUCTIONS 1 READING ASSIGNMENTS 3 LESSON 1: THE FUNDAMENTALS OF MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY 5 LESSON 2: DIAGNOSIS, INTERVENTION, AND HUMAN BODY TERMS 28 LESSON 3: MUSCULOSKELETAL, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM TERMS 44 LESSON 4: DIGESTIVE, URINARY, AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM TERMS 69 LESSON 5: INTEGUMENTARY, NERVOUS, AND ENDOCRINE S YSTEM TERMS 96 SELF-CHECK ANSWERS 134 © PENN FOSTER, INC. 2017 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY PAGE III Contents INSTRUCTIONS INTRODUCTION Welcome to your course on medical terminology. You’re taking this course because you’re most likely interested in pursuing a health and science career, which entails proficiencyincommunicatingwithhealthcareprofessionalssuchasphysicians,nurses, or dentists. -

Importance of Facial Plastic Surgery Education in Residency: a Resident Survey
Published online: 2019-12-13 THIEME 278 Original Research Importance of Facial Plastic Surgery Education in Residency: A Resident Survey Steven A. Curti1 J. Randall Jordan1 1 Department of Otolaryngology, University of Mississippi Medical Address for correspondence Steven A. Curti, MD, Department of Center, Jackson, Mississippi, United States Otolaryngology, University of Mississippi Medical Center, 2500 North State Street, Jackson, MS 39216, United States Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2020;24(3):e278–e281. (e-mail: [email protected]). Abstract Introduction Facial plastic and reconstructive surgery (FPRS) is a key part of the curriculum for otolaryngology residents. It is important to gain an understanding of the breadth of exposure and level of competence residents feel with these concepts during their residency. Objective To determine the level of FPRS exposure and training otolaryngology residents receive during their residency. Methods A survey was emailed to all Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) accredited otolaryngology residents. The survey aimed to find the level of exposure to FPRS procedures otolaryngology residents get and how confident they feel with their training in cosmetic FPRS. Results A total of 213 residents responded to the survey for an overall response rate of 13.4%. There was an even mixture of residents from all postgraduate year (PGY) levels, with 58% of respondents being male. Almost all (98%) of the residents felt FPRS was important to otolaryngology residency training. Exposure to procedures varied with 57% performing or assisting with cosmetic minor procedures, 81% performing or assisting with cosmetic major procedures, and 93% performing or assisting with reconstructive procedures. Only 49% of residents felt their programs either very or Keywords somewhat adequately prepared them in cosmetic facial plastic surgery. -

Chronic Otitis Media: Histopathological Changes a Post Mortem Study on Temporal Bones
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 1999; 3: 175-178 Chronic otitis media: histopathological changes A post mortem study on temporal bones F. SALVINELLI, M. TRIVELLI, F. GRECO, F.H. LINTHICUM JR* Institute of Otolaryngology, “Campus Bio-Medico” University - Rome (Italy) *Department of Histopathology, “House Ear Institute” - Los Angeles, CA (USA) Abstract. – The temporal bones of 4 Materials and Methods deceased individuals, with concomitant chronic otitis media are studied. The various histopathological changes in the middle ear We have studied the histopathological cleft are examined: suppuration, polyps, changes in temporal bones of 4 deceased in- granulation tissue. The possibilities of spon- dividuals, with concomitant chronic OM. taneous healing of a perforated TM and the These patients were donors and agreed indications of surgical treatment are dis- during their life to donate post mortem their cussed. temporal bones to the House Ear Institute as Key Words: a contribution to a better knowledge of tem- Temporal bone, Middle ear, Infection, Chronic in- poral bone diseases. flammation, Metaplasia, Complications. We have removed the temporal bones in our usual way9. Introduction Results Otitis media (OM) is an infection localized Clinical features in the middle ear: mastoid, middle ear cavity, The inflammation, while often indolent, eustachian tube. The classification of OM in- may at times give rise to serious complica- cludes: tions and even cause death. The hearing loss that is a constant concomitant also con- tributes to the immense socio-economic problem. Chronic OM sometimes, but not al- • OM with effusion1-3, without perforation ways, follows an attack of the acute disease. of the tympanic membrane (TM)4-6, due The major feature is discharge from the mid- to an increase of fluid in the middle ear dle ear. -

Sensory Change Following Motor Learning
A. M. Green, C. E. Chapman, J. F. Kalaska and F. Lepore (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 191 ISSN: 0079-6123 Copyright Ó 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. CHAPTER 2 Sensory change following motor learning { k { { Andrew A. G. Mattar , Sazzad M. Nasir , Mohammad Darainy , and { } David J. Ostry , ,* { Department of Psychology, McGill University, Montréal, Québec, Canada { Shahed University, Tehran, Iran } Haskins Laboratories, New Haven, Connecticut, USA k The Roxelyn and Richard Pepper Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders, Northwestern University, Evanston, Illinois, USA Abstract: Here we describe two studies linking perceptual change with motor learning. In the first, we document persistent changes in somatosensory perception that occur following force field learning. Subjects learned to control a robotic device that applied forces to the hand during arm movements. This led to a change in the sensed position of the limb that lasted at least 24 h. Control experiments revealed that the sensory change depended on motor learning. In the second study, we describe changes in the perception of speech sounds that occur following speech motor learning. Subjects adapted control of speech movements to compensate for loads applied to the jaw by a robot. Perception of speech sounds was measured before and after motor learning. Adapted subjects showed a consistent shift in perception. In contrast, no consistent shift was seen in control subjects and subjects that did not adapt to the load. These studies suggest that motor learning changes both sensory and motor function. Keywords: motor learning; sensory plasticity; arm movements; proprioception; speech motor control; auditory perception. Introduction the human motor system and, likewise, to skill acquisition in the adult nervous system. -

Inner Ear Infection (Otitis Interna) in Dogs
Hurricane Harvey Client Education Kit Inner Ear Infection (Otitis Interna) in Dogs My dog has just been diagnosed with an inner ear infection. What is this? Inflammation of the inner ear is called otitis interna, and it is most often caused by an infection. The infectious agent is most commonly bacterial, although yeast and fungus can also be implicated in an inner ear infection. If your dog has ear mites in the external ear canal, this can ultimately cause a problem in the inner ear and pose a greater risk for a bacterial infection. Similarly, inner ear infections may develop if disease exists in one ear canal or when a benign polyp is growing from the middle ear. A foreign object, such as grass seed, may also set the stage for bacterial infection in the inner ear. Are some dogs more susceptible to inner ear infection? Dogs with long, heavy ears seem to be predisposed to chronic ear infections that ultimately lead to otitis interna. Spaniel breeds, such as the Cocker spaniel, and hound breeds, such as the bloodhound and basset hound, are the most commonly affected breeds. Regardless of breed, any dog with a chronic ear infection that is difficult to control may develop otitis interna if the eardrum (tympanic membrane) is damaged as it allows bacteria to migrate down into the inner ear. "Dogs with long, heavy ears seem to bepredisposed to chronic ear infections that ultimately lead to otitis interna." Excessively vigorous cleaning of an infected external ear canal can sometimes cause otitis interna. Some ear cleansers are irritating to the middle and inner ear and can cause signs of otitis interna if the eardrum is damaged and allows some of the solution to penetrate too deeply. -

Medical Term for Throat
Medical Term For Throat Quintin splined aerially. Tobias griddles unfashionably. Unfuelled and ordinate Thorvald undervalues her spurges disroots or sneck acrobatically. Contact Us WebsiteEmail Terms any Use Medical Advice Disclaimer Privacy. The medical term for this disguise is called formication and it been quite common. How Much sun an Uvulectomy in office Cost on Me MDsave. The medical term for eardrum is tympanic membrane The direct ear is. Your throat includes your esophagus windpipe trachea voice box larynx tonsils and epiglottis. Burning mouth syndrome is the medical term for a sequence-lastingand sometimes very severeburning sensation in throat tongue lips gums palate or source over the. Globus sensation can sometimes called globus pharyngeus pharyngeus refers to the sock in medical terms It used to be called globus. Other medical afflictions associated with the pharynx include tonsillitis cancer. Neil Van Leeuwen Layton ENT Doctor Tanner Clinic. When we offer a throat medical conditions that this inflammation and cutlery, alcohol consumption for air that? Medical Terminology Anatomy and Physiology. Empiric treatment of the lining of the larynx and ask and throat cancer that can cause nasal cavity cancer risk of the term throat muscles. MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY. Throat then Head wrap neck cancers Cancer Research UK. Long term monitoring this exercise include regular examinations and. Long-term a frequent exposure to smoke damage cause persistent pharyngitis. Pharynx Greek throat cone-shaped passageway leading from another oral and. WHAT people EXPECT ON anything LONG-TERM BASIS AFTER A LARYNGECTOMY. Sensation and in one of causes to write the term for throat medical knowledge. The throat pharynx and larynx is white ring-like muscular tube that acts as the passageway for special food and prohibit It is located behind my nose close mouth and connects the form oral tongue and silk to the breathing passages trachea windpipe and lungs and the esophagus eating tube.