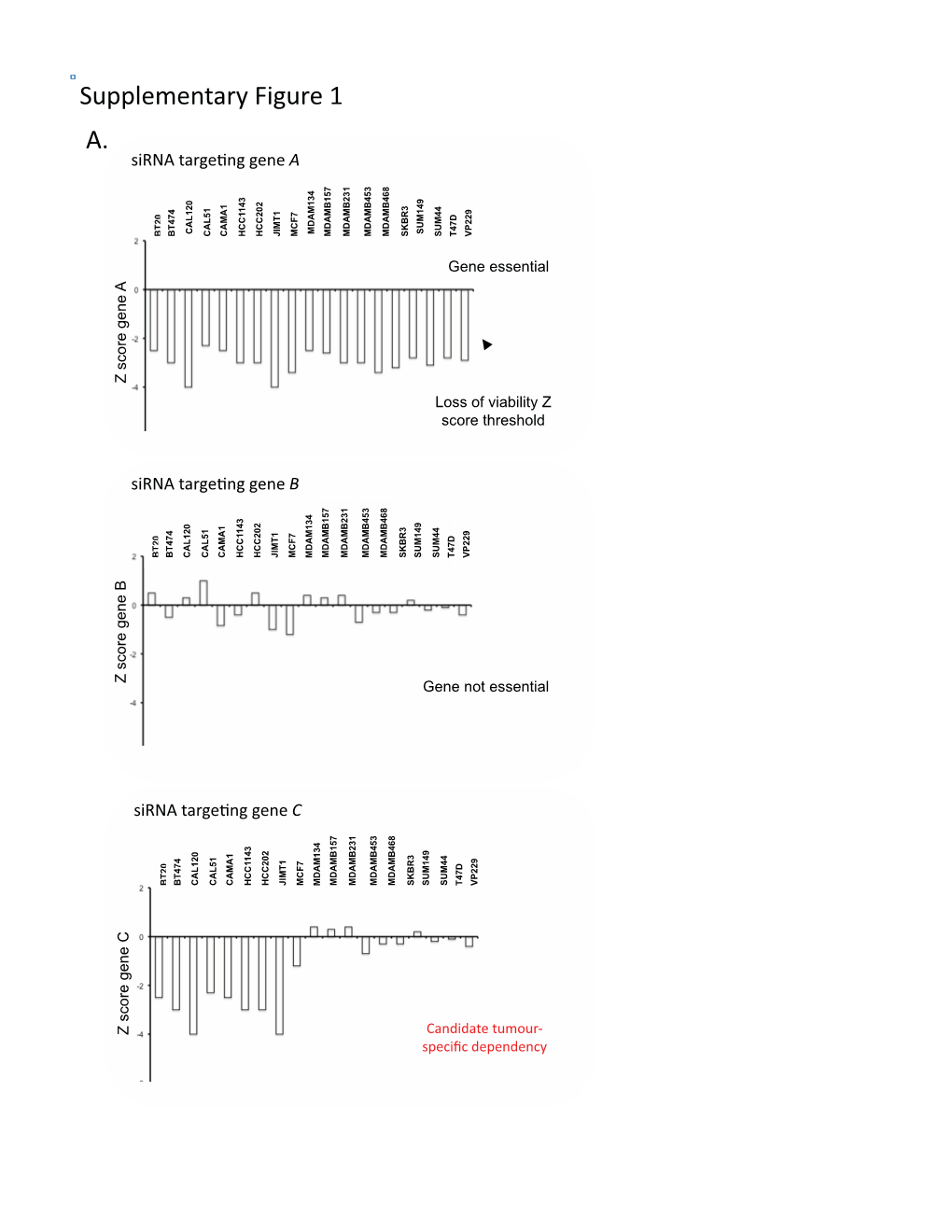
A. Supplementary Figure 1
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Deregulated Gene Expression Pathways in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Leukemia (2010) 24, 756–764 & 2010 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0887-6924/10 $32.00 www.nature.com/leu ORIGINAL ARTICLE Deregulated gene expression pathways in myelodysplastic syndrome hematopoietic stem cells A Pellagatti1, M Cazzola2, A Giagounidis3, J Perry1, L Malcovati2, MG Della Porta2,MJa¨dersten4, S Killick5, A Verma6, CJ Norbury7, E Hellstro¨m-Lindberg4, JS Wainscoat1 and J Boultwood1 1LRF Molecular Haematology Unit, NDCLS, John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, UK; 2Department of Hematology Oncology, University of Pavia Medical School, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, Pavia, Italy; 3Medizinische Klinik II, St Johannes Hospital, Duisburg, Germany; 4Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden; 5Department of Haematology, Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Bournemouth, UK; 6Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA and 7Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK To gain insight into the molecular pathogenesis of the the World Health Organization.6,7 Patients with refractory myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), we performed global gene anemia (RA) with or without ringed sideroblasts, according to expression profiling and pathway analysis on the hemato- poietic stem cells (HSC) of 183 MDS patients as compared with the the French–American–British classification, were subdivided HSC of 17 healthy controls. The most significantly deregulated based on the presence or absence of multilineage dysplasia. In pathways in MDS include interferon signaling, thrombopoietin addition, patients with RA with excess blasts (RAEB) were signaling and the Wnt pathways. Among the most signifi- subdivided into two categories, RAEB1 and RAEB2, based on the cantly deregulated gene pathways in early MDS are immuno- percentage of bone marrow blasts. -

Gene Essentiality Landscape and Druggable Oncogenic Dependencies in Herpesviral Primary Effusion Lymphoma
ARTICLE DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05506-9 OPEN Gene essentiality landscape and druggable oncogenic dependencies in herpesviral primary effusion lymphoma Mark Manzano1, Ajinkya Patil1, Alexander Waldrop2, Sandeep S. Dave2, Amir Behdad3 & Eva Gottwein1 Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) is caused by Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Our understanding of PEL is poor and therefore treatment strategies are lacking. To address this 1234567890():,; need, we conducted genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 knockout screens in eight PEL cell lines. Integration with data from unrelated cancers identifies 210 genes as PEL-specific oncogenic dependencies. Genetic requirements of PEL cell lines are largely independent of Epstein-Barr virus co-infection. Genes of the NF-κB pathway are individually non-essential. Instead, we demonstrate requirements for IRF4 and MDM2. PEL cell lines depend on cellular cyclin D2 and c-FLIP despite expression of viral homologs. Moreover, PEL cell lines are addicted to high levels of MCL1 expression, which are also evident in PEL tumors. Strong dependencies on cyclin D2 and MCL1 render PEL cell lines highly sensitive to palbociclib and S63845. In summary, this work comprehensively identifies genetic dependencies in PEL cell lines and identifies novel strategies for therapeutic intervention. 1 Department of Microbiology-Immunology, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL 60611, USA. 2 Duke Cancer Institute and Center for Genomic and Computational Biology, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708, USA. 3 Department of Pathology, Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL 60611, USA. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to E.G. (email: [email protected]) NATURE COMMUNICATIONS | (2018) 9:3263 | DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05506-9 | www.nature.com/naturecommunications 1 ARTICLE NATURE COMMUNICATIONS | DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05506-9 he human oncogenic γ-herpesvirus Kaposi’s sarcoma- (IRF4), a critical oncogene in multiple myeloma33. -

Identification of Hub Genes Involved in the Occurrence and Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Via Bioinformatics Analysis
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 20: 1695-1708, 2020 Identification of hub genes involved in the occurrence and development of hepatocellular carcinoma via bioinformatics analysis NINGNING MI1,2*, JIE CAO1-6*, JINDUO ZHANG2-5, WENKANG FU1-5, CHONGFEI HUANG1-5, LONG GAO1-5, PING YUE2-5, BING BAI2-5, YANYAN LIN1-5, WENBO MENG1-5 and XUN LI4,5,7 1The First Clinical Medical School, Lanzhou University; 2Department of Special Minimally Invasive Surgery, The First Hospital of Lanzhou University; 3Institute of Genetics, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Lanzhou University; 4Gansu Province Institute of Hepatopancreatobiliary; 5Gansu Province Key Laboratory Biotherapy and Regenerative Medicine; 6Laboratory Department; 7The Fifth Department of General Surgery, The First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu 730000, P.R. China Received September 28, 2019; Accepted May 7, 2020 DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.11752 Abstract. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a heterogeneous cyclin B1 (CCNB1), cell-division cycle protein 20 (CDC20), malignancy, which is a major cause of cancer morbidity and cyclin-dependent kinase 1, BUB1 mitotic checkpoint serine/ mortality worldwide. Thus, the aim of the present study was threonine kinase β (BUB1B), cyclin A2, nucleolar and spindle to identify the hub genes and underlying pathways of HCC associated protein 1, ubiquitin‑conjugating enzyme E2 C via bioinformatics analyses. The present study screened three (UBE2C) and ZW10 interactor. Furthermore, upregulated datasets, including GSE112790, GSE84402 and GSE74656 CCNB1, CDC20, BUB1B and UBE2C expression levels from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, and indicated worse disease-free and overall survival. Moreover, downloaded the RNA-sequencing of HCC from The Cancer a meta-analysis of tumor and healthy tissues in the Oncomine Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. -

Price List for Out-Of-State Patients (Jul 2017 – Dec 2017)
Department of Diagnostic Genomics QEII Medical Centre PRICE LIST FOR OUT-OF-STATE PATIENTS (JUL 2017 – DEC 2017) What methods of testing do we employ? Available Methods PCR and/or Sanger DNA Sequencing for predictive testing and familial cascade screening. Targeted Massive Parallel Sequencing (MPS) panels and Sanger sequencing to analyse large genes. MLPA to detect larger deletions and duplications. MS-MLPA to detect methylation changes in addition to deletions and duplications. If you are unsure which method is appropriate for your patient, please contact us by phone on 08 6383 4223 or email on [email protected]. Who do we accept testing requests from? Requesting Clinicians Diagnostic testing can only be requested by a suitably qualified clinician – we do not provide a service direct to the public. For some tests, we will only accept requests once the patient has undergone genetic counselling from a recognised genetic counsellor, due to the clinical sensitivity of these tests. What types of sample(s) are required for testing? Sample requirements for each test are listed below. EDTA Samples Most tests will require a single 2-4mls sample of blood collected with an EDTA preservative. EDTA samples must arrive at our lab within 5 days of phlebotomy, and must be sent at room temperature. Tissue 10-50mg of tissue is required for DNA extraction DNA 1-5µg of extracted DNA (depending on test request) in place of EDTA blood Predictive Testing We recommend testing two separate EDTA blood samples collected from the patient at least 10 minutes apart. Familial Cancer and We recommend testing a second EDTA blood sample in cases where a pathogenic variant is found. -

GUCY2D Cone-Rod Dystrophy-6 Is a ‘Phototransduction Disease’ Triggered by Abnormal Calcium Feedback on Retinal Membrane Guanylyl Cyclase 1
This Accepted Manuscript has not been copyedited and formatted. The final version may differ from this version. Research Articles: Neurobiology of Disease GUCY2D Cone-Rod Dystrophy-6 is a ‘Phototransduction Disease’ Triggered by Abnormal Calcium Feedback on Retinal Membrane Guanylyl Cyclase 1 Shinya Sato1, Igor V. Peshenko2, Elena V. Olshevskaya2, Vladimir J. Kefalov1 and Alexander M. Dizhoor2 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO 63110 2Pennsylavania College of Optometry, Salus University, Elkins Park, PA 19027 DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2985-17.2018 Received: 17 October 2017 Revised: 19 January 2018 Accepted: 24 January 2018 Published: 12 February 2018 Author contributions: S.S., I.V.P., E.V.O., and A.M.D. performed research; S.S., I.V.P., V.J.K., and A.M.D. analyzed data; V.J.K. and A.M.D. designed research; V.J.K. and A.M.D. wrote the paper. Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no competing financial interests. This work was supported by NIH grants EY11522 (AMD), EY19312, EY25696, and EY27387 (VJK), EY02687 (Washington University, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences), Pennsylvania Department of Health Formula Grant (AMD) and by Research to Prevent Blindness. Correspondence should be addressed to Co-corresponding authors: Alexander M. Dizhoor, Pennsylvania College of Optometry, Salus University, Elkins Park, PA 19027, [email protected]; Vladimir J. Kefalov, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO 63110, [email protected] Cite as: J. Neurosci ; 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2985-17.2018 Alerts: Sign up at www.jneurosci.org/cgi/alerts to receive customized email alerts when the fully formatted version of this article is published. -

Molecular Profile of Tumor-Specific CD8+ T Cell Hypofunction in a Transplantable Murine Cancer Model
Downloaded from http://www.jimmunol.org/ by guest on September 25, 2021 T + is online at: average * The Journal of Immunology , 34 of which you can access for free at: 2016; 197:1477-1488; Prepublished online 1 July from submission to initial decision 4 weeks from acceptance to publication 2016; doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600589 http://www.jimmunol.org/content/197/4/1477 Molecular Profile of Tumor-Specific CD8 Cell Hypofunction in a Transplantable Murine Cancer Model Katherine A. Waugh, Sonia M. Leach, Brandon L. Moore, Tullia C. Bruno, Jonathan D. Buhrman and Jill E. Slansky J Immunol cites 95 articles Submit online. Every submission reviewed by practicing scientists ? is published twice each month by Receive free email-alerts when new articles cite this article. Sign up at: http://jimmunol.org/alerts http://jimmunol.org/subscription Submit copyright permission requests at: http://www.aai.org/About/Publications/JI/copyright.html http://www.jimmunol.org/content/suppl/2016/07/01/jimmunol.160058 9.DCSupplemental This article http://www.jimmunol.org/content/197/4/1477.full#ref-list-1 Information about subscribing to The JI No Triage! Fast Publication! Rapid Reviews! 30 days* Why • • • Material References Permissions Email Alerts Subscription Supplementary The Journal of Immunology The American Association of Immunologists, Inc., 1451 Rockville Pike, Suite 650, Rockville, MD 20852 Copyright © 2016 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc. All rights reserved. Print ISSN: 0022-1767 Online ISSN: 1550-6606. This information is current as of September 25, 2021. The Journal of Immunology Molecular Profile of Tumor-Specific CD8+ T Cell Hypofunction in a Transplantable Murine Cancer Model Katherine A. -

GSK3 Is a Negative Regulator of the Thermogenic Program in Brown Adipocytes
GSK3 is a negative regulator of the thermogenic program in brown adipocytes Markussen, Lasse K.; Winther, Sally; Wicksteed, Barton; Hansen, Jacob B. Published in: Scientific Reports DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-21795-y Publication date: 2018 Document version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Document license: CC BY Citation for published version (APA): Markussen, L. K., Winther, S., Wicksteed, B., & Hansen, J. B. (2018). GSK3 is a negative regulator of the thermogenic program in brown adipocytes. Scientific Reports, 8, 1-12. [3469]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598- 018-21795-y Download date: 01. okt.. 2021 www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN GSK3 is a negative regulator of the thermogenic program in brown adipocytes Received: 16 January 2017 Lasse K. Markussen1, Sally Winther1, Barton Wicksteed2 & Jacob B. Hansen 1 Accepted: 9 February 2018 Brown adipose tissue is a promising therapeutic target in metabolic disorders due to its ability to Published: xx xx xxxx dissipate energy and improve systemic insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis. β-Adrenergic stimulation of brown adipocytes leads to an increase in oxygen consumption and induction of a thermogenic gene program that includes uncoupling protein 1 (Ucp1) and fbroblast growth factor 21 (Fgf21). In kinase inhibitor screens, we have identifed glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) as a negative regulator of basal and β-adrenergically stimulated Fgf21 expression in cultured brown adipocytes. In addition, inhibition of GSK3 also caused increased Ucp1 expression and oxygen consumption. β-Adrenergic stimulation triggered an inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK3 in a protein kinase A (PKA)- dependent manner. Mechanistically, inhibition of GSK3 activated the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase 3/6-p38 MAPK-activating transcription factor 2 signaling module. -

MAP2K3 (Human) Recombinant Protein (Q01)
MAP2K3 (Human) Recombinant phosphorylates and thus activates MAPK14/p38-MAPK. Protein (Q01) This kinase can be activated by insulin, and is necessary for the expression of glucose transporter. Expression of Catalog Number: H00005606-Q01 RAS oncogene is found to result in the accumulation of the active form of this kinase, which thus leads to the Regulation Status: For research use only (RUO) constitutive activation of MAPK14, and confers oncogenic transformation of primary cells. The inhibition Product Description: Human MAP2K3 partial ORF ( of this kinase is involved in the pathogenesis of Yersina AAH32478, 1 a.a. - 100 a.a.) recombinant protein with pseudotuberculosis. Multiple alternatively spliced GST-tag at N-terminal. transcript variants that encode distinct isoforms have been reported for this gene. [provided by RefSeq] Sequence: MESPASSQPASMPQSKGKSKRKKDLRISCMSKPPAP NPTPPRNLDSRTFITIGDRNFEVEADDLVTISELGRGAY GVVEKVRHAQSGTIMAVKRIRATVN Host: Wheat Germ (in vitro) Theoretical MW (kDa): 36.63 Applications: AP, Array, ELISA, WB-Re (See our web site product page for detailed applications information) Protocols: See our web site at http://www.abnova.com/support/protocols.asp or product page for detailed protocols Preparation Method: in vitro wheat germ expression system Purification: Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow Storage Buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCI, 10 mM reduced Glutathione, pH=8.0 in the elution buffer. Storage Instruction: Store at -80°C. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. Entrez GeneID: 5606 Gene Symbol: MAP2K3 Gene Alias: MAPKK3, MEK3, MKK3, PRKMK3 Gene Summary: The protein encoded by this gene is a dual specificity protein kinase that belongs to the MAP kinase kinase family. This kinase is activated by mitogenic and environmental stress, and participates in the MAP kinase-mediated signaling cascade. -

Biallelic TRIP13 Mutations Predispose to Wilms Tumor and Chromosome Missegregation
Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Nat Genet. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2017 July 01. Published in final edited form as: Nat Genet. 2017 July ; 49(7): 1148–1151. doi:10.1038/ng.3883. Europe PMC Funders Author Manuscripts Biallelic TRIP13 mutations predispose to Wilms tumor and chromosome missegregation Shawn Yost#1, Bas de Wolf#2, Sandra Hanks#1, Anna Zachariou1, Chiara Marcozzi3,4, Matthew Clarke1, Richarda de Voer2, Banafsheh Etemad2, Esther Uijttewaal2, Emma Ramsay1, Harriet Wylie1, Anna Elliott1, Susan Picton5, Audrey Smith6, Sarah Smithson7, Sheila Seal1, Elise Ruark1, Gunnar Houge8, Jonathan Pines3,4, Geert J.P.L. Kops2,9,10,+, and Nazneen Rahman1,11,+ 1Division of Genetics and Epidemiology, Institute of Cancer Research, 15 Cotswold Road, London, SM2 5NG, UK 2Hubrecht Institute – KNAW (Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences), Uppsalalaan 8, 3584 CT Utrecht, The Netherlands 3The Gurdon Institute and Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge CB2 1QN, UK 4Division of Cancer Biology, The Institute of Cancer Research, 237 Fulham Road, London SW3 6JB, UK 5Children's and Adolescent Oncology and Haematology Unit, Leeds General Infirmary, Leeds, LS1 3EX, UK 6Yorkshire Regional Clinical Genetics Service, Chapel Allerton Hospital, Chapeltown Road, Leeds, LS7 4SA, UK 7Clinical Genetics Service, St Michael's Hospital, Southwell Street, Bristol, BS2 8EG, UK 8Center for Medical Genetics, Haukeland University Hospital, N-5021 Bergen, Norway 9Cancer Genomics Netherlands, Utrecht, The Netherlands 10Center for Molecular 11 Europe PMC Funders Author Manuscripts Medicine, University Medical Center Utrecht, 3584 CG, Utrecht, The Netherlands Cancer Genetics Unit, Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK SM2 5PT, UK # These authors contributed equally to this work. -

IFT88 Transports Gucy2d, a Guanylyl Cyclase, to Maintain Sensory Cilia Function in Drosophila
bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.15.417840; this version posted December 15, 2020. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. It is made available under aCC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license. Werner S et al. Title: IFT88 transports Gucy2d, a guanylyl cyclase, to maintain sensory cilia function in Drosophila Authors: Sascha Werner1,6, Sihem Zitouni1,4, Pilar Okenve-Ramos1, Susana Mendonça1,5, Anje Sporbert2, Christian Spalthoff3, Martin C. Göpfert3, Swadhin Chandra Jana1,6,7, Mónica Bettencourt-Dias1,6,7 Affiliations: 1- Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência, Rua da Quinta Grande, nº 6, 2780-156 Oeiras, Portugal. 2- Advanced Light Microscopy, Max Delbrück Centrum for Molecular Medicine Berlin in the Helmholtz Association Robert-Rössle-Straße 10, 13125 Berlin, Germany. 3- Department of Cellular Neurobiology, University of Göttingen, 37077 Göttingen, Germany. 4- Present address: Institut de Génétique Humaine (IGH) UMR 9002 CNRS, 141 Rue de la Cardonille, Montpellier, France. 5- Present address: Instituto de Investigação e Inovação em Saúde, Universidade do Porto, Rua Alfredo Allen, 208 4200-135 Porto, Portugal. 6- Correspondence should be addressed to Sascha Werner ([email protected]); Swadhin Chandra Jana ([email protected]); Mónica Bettencourt-Dias ([email protected]) 7- Shared lead authors. 1 bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.15.417840; this version posted December 15, 2020. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. -

Advancing a Clinically Relevant Perspective of the Clonal Nature of Cancer
Advancing a clinically relevant perspective of the clonal nature of cancer Christian Ruiza,b, Elizabeth Lenkiewicza, Lisa Eversa, Tara Holleya, Alex Robesona, Jeffrey Kieferc, Michael J. Demeurea,d, Michael A. Hollingsworthe, Michael Shenf, Donna Prunkardf, Peter S. Rabinovitchf, Tobias Zellwegerg, Spyro Moussesc, Jeffrey M. Trenta,h, John D. Carpteni, Lukas Bubendorfb, Daniel Von Hoffa,d, and Michael T. Barretta,1 aClinical Translational Research Division, Translational Genomics Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ 85259; bInstitute for Pathology, University Hospital Basel, University of Basel, 4031 Basel, Switzerland; cGenetic Basis of Human Disease, Translational Genomics Research Institute, Phoenix, AZ 85004; dVirginia G. Piper Cancer Center, Scottsdale Healthcare, Scottsdale, AZ 85258; eEppley Institute for Research in Cancer and Allied Diseases, Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE 68198; fDepartment of Pathology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98105; gDivision of Urology, St. Claraspital and University of Basel, 4058 Basel, Switzerland; hVan Andel Research Institute, Grand Rapids, MI 49503; and iIntegrated Cancer Genomics Division, Translational Genomics Research Institute, Phoenix, AZ 85004 Edited* by George F. Vande Woude, Van Andel Research Institute, Grand Rapids, MI, and approved June 10, 2011 (received for review March 11, 2011) Cancers frequently arise as a result of an acquired genomic insta- on the basis of morphology alone (8). Thus, the application of bility and the subsequent clonal evolution of neoplastic cells with purification methods such as laser capture microdissection does variable patterns of genetic aberrations. Thus, the presence and not resolve the complexities of many samples. A second approach behaviors of distinct clonal populations in each patient’s tumor is to passage tumor biopsies in tissue culture or in xenografts (4, 9– may underlie multiple clinical phenotypes in cancers. -

Profiling Data
Compound Name DiscoveRx Gene Symbol Entrez Gene Percent Compound Symbol Control Concentration (nM) JNK-IN-8 AAK1 AAK1 69 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(E255K)-phosphorylated ABL1 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(F317I)-nonphosphorylated ABL1 87 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(F317I)-phosphorylated ABL1 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(F317L)-nonphosphorylated ABL1 65 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(F317L)-phosphorylated ABL1 61 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(H396P)-nonphosphorylated ABL1 42 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(H396P)-phosphorylated ABL1 60 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(M351T)-phosphorylated ABL1 81 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(Q252H)-nonphosphorylated ABL1 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(Q252H)-phosphorylated ABL1 56 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(T315I)-nonphosphorylated ABL1 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(T315I)-phosphorylated ABL1 92 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1(Y253F)-phosphorylated ABL1 71 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1-nonphosphorylated ABL1 97 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL1-phosphorylated ABL1 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ABL2 ABL2 97 1000 JNK-IN-8 ACVR1 ACVR1 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ACVR1B ACVR1B 88 1000 JNK-IN-8 ACVR2A ACVR2A 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ACVR2B ACVR2B 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ACVRL1 ACVRL1 96 1000 JNK-IN-8 ADCK3 CABC1 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ADCK4 ADCK4 93 1000 JNK-IN-8 AKT1 AKT1 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 AKT2 AKT2 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 AKT3 AKT3 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ALK ALK 85 1000 JNK-IN-8 AMPK-alpha1 PRKAA1 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 AMPK-alpha2 PRKAA2 84 1000 JNK-IN-8 ANKK1 ANKK1 75 1000 JNK-IN-8 ARK5 NUAK1 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ASK1 MAP3K5 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 ASK2 MAP3K6 93 1000 JNK-IN-8 AURKA AURKA 100 1000 JNK-IN-8 AURKA AURKA 84 1000 JNK-IN-8 AURKB AURKB 83 1000 JNK-IN-8 AURKB AURKB 96 1000 JNK-IN-8 AURKC AURKC 95 1000 JNK-IN-8