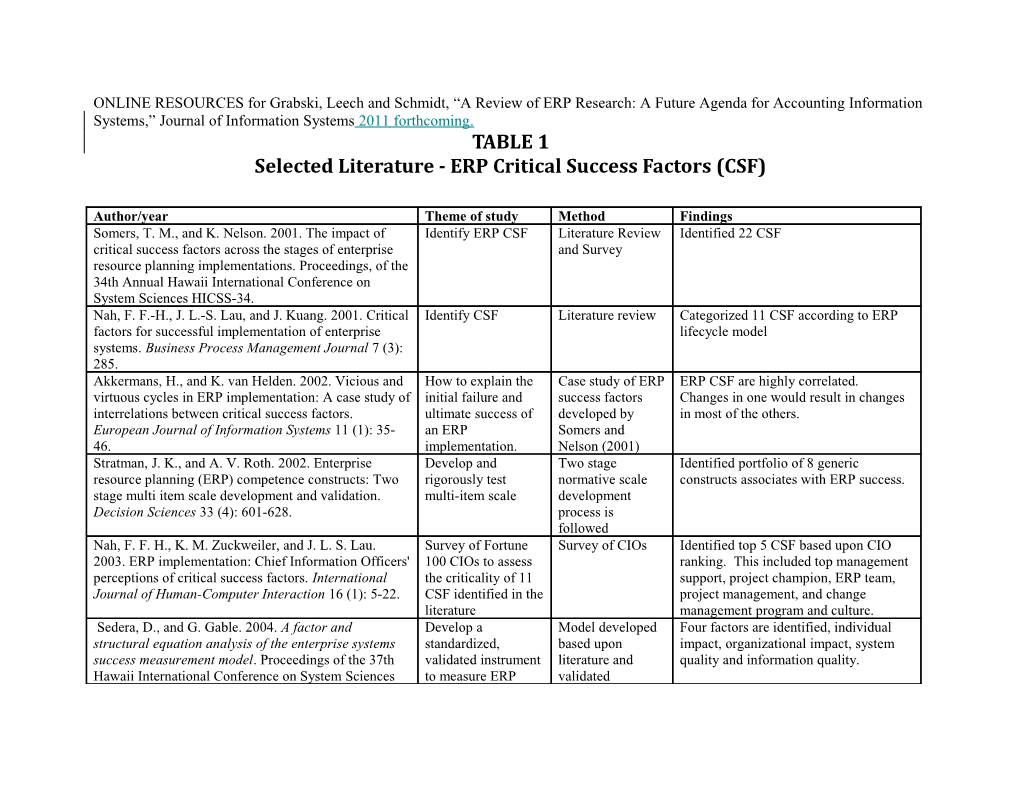
ONLINE RESOURCES for Grabski, Leech and Schmidt, “A Review of ERP Research: A Future Agenda for Accounting Information Systems,” Journal of Information Systems 2011 forthcoming. TABLE 1 Selected Literature - ERP Critical Success Factors (CSF)
Author/year Theme of study Method Findings Somers, T. M., and K. Nelson. 2001. The impact of Identify ERP CSF Literature Review Identified 22 CSF critical success factors across the stages of enterprise and Survey resource planning implementations. Proceedings, of the 34th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences HICSS-34. Nah, F. F.-H., J. L.-S. Lau, and J. Kuang. 2001. Critical Identify CSF Literature review Categorized 11 CSF according to ERP factors for successful implementation of enterprise lifecycle model systems. Business Process Management Journal 7 (3): 285. Akkermans, H., and K. van Helden. 2002. Vicious and How to explain the Case study of ERP ERP CSF are highly correlated. virtuous cycles in ERP implementation: A case study of initial failure and success factors Changes in one would result in changes interrelations between critical success factors. ultimate success of developed by in most of the others. European Journal of Information Systems 11 (1): 35- an ERP Somers and 46. implementation. Nelson (2001) Stratman, J. K., and A. V. Roth. 2002. Enterprise Develop and Two stage Identified portfolio of 8 generic resource planning (ERP) competence constructs: Two rigorously test normative scale constructs associates with ERP success. stage multi item scale development and validation. multi-item scale development Decision Sciences 33 (4): 601-628. process is followed Nah, F. F. H., K. M. Zuckweiler, and J. L. S. Lau. Survey of Fortune Survey of CIOs Identified top 5 CSF based upon CIO 2003. ERP implementation: Chief Information Officers' 100 CIOs to assess ranking. This included top management perceptions of critical success factors. International the criticality of 11 support, project champion, ERP team, Journal of Human-Computer Interaction 16 (1): 5-22. CSF identified in the project management, and change literature management program and culture. Sedera, D., and G. Gable. 2004. A factor and Develop a Model developed Four factors are identified, individual structural equation analysis of the enterprise systems standardized, based upon impact, organizational impact, system success measurement model. Proceedings of the 37th validated instrument literature and quality and information quality. Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences to measure ERP validated (HICSS-37 2004), Big Island, Hawaii success Song, M., and W. M. P. Van der Aalst. 2008. Towards Applied TAM to Survey of 320 Perceived fit, compatibility of an ERP comprehensive support for organizational mining. investigation of ERP managers and system and change management Decision Support Systems 46 (1): 300-317. CSF structural equation influence user adoption; top management support is critical to change management, business process and communication. Snider, B., G. J. C. da Silveira, and B. Jeep. 2009. ERP Explore CSF of Case study of five Identified six CSF and four distinctive implementation at SMEs: Analysis of five Canadian SMEs SMEs in Canada factors associated with SMEs. cases. International Journal of Operations & Production Management 29 (1): 4. TABLE 2 Selected Literature - ERP Domain Specific (Country, Culture and Industry) Author/year Theme of study Method Findings Everdingen, Y. V., J. V. Hillegersberg, and To learn about 1998 large European European SME market in 1998 was a nascent E. Waarts. 2000. ERP adoption by European developments and multi-country/multi- but promising market projected at $50 midsize companies. Association for drivers for ERP industry survey on billion/year. There is a lack of homogeneity in Computing Machinery. Communications of adoption decisions in adoption & adoption the European mid-sized ERP market. CSFs the ACM 43 (4): 27. European mid-market. plans. include fit with current business processes, low price and short implementation times. Hayes, D. C., J. E. Hunton, and J. L. Reck. Capital market study Cross-industry event Support for firm size, firm financial strength & 2001. Market reactions to ERP of reactions to initial study measuring vendor prominence influencing reactions to implementation announcements. Journal of ERP announcements. abnormal market ERP announcements. Most positive for Information Systems 15 (1): 3. returns. small/healthy firms. Reactions most positive to prominent vendors. Huang, Z., and P. Palvia. 2001. ERP Explores differences Global trends in ERP systems encounter many challenges in implementation issues in advanced and in ERP adoption developing (China, developing countries related to economic, developing countries. Business Process between advanced and India & Brazil) cultural, & infrastructure issues. Management Journal 7 (3): 276-284. developing countries. verses advanced Conceptualizes a framework categorized into countries (USA/CA, national/environmental and Europe & Japan). organizational/internal factors with 5 variables per category. Hunton, J. E., B. Lippincott, and J. L. Reck. Cross-industry study Survey of financial No difference between adoptors & non- 2003. Enterprise resource planning systems: of supply chain key performance adoptors but longer ERP experience revealed Comparing firm performance of adoptors process performance. indicators for higher overall performance. Only ERP and nonadoptors. International Journal of business processes- adopters with SCMS had higher performance Accounting Information Systems 4 165-184. supply chain. at the business process level. Laukkanen, S., S. Sarpola, and P. Finland Small firms were found to have significant Hallikainen. 2007. Enterprise size matters: knowledge constraints, while large firms have Objectives and constraints of ERP adoption. challenges relating to organizational changes. Journal of Enterprise Information Management 20 (3): 319 Mabert, V. A., A. Soni, and M. A. Chronicle growth of Case study and The key finding from this study is that Venkataramanan. 2003. The impact of ERP use in survey methodologies companies of different sizes approach ERP organization size on enterprise resource manufacturing in a phased approach. implementations differently across a range of planning (ERP) implementations in the US industry to current issues. Also, the benefits differ by company manufacturing sector. Omega 31 (3): 235- pervasive levels. size. 246. Olhager, J., and E. Seldin. 2003. Enterprise Studies Swedish Survey of Swedish firms preferred to use European and resource planning: Survey of Swedish manufacturing firms professional members Swedish ERP vendors. US firms provided manufacturing firms. European Journal of for ERP penetration, of PLAN (Swedish more economic justification and were more Operational Research 146 (2): 365-373. pre-implementation & Production & optimistic about economic returns associated experiences, Inventory with the ERP systems. configuration, benefits Management & future. Society). Rasmy, M. H., A. Tharwat, and S. Ashraf. CSF & Egyptian A cross-sectional Organizational & ERP package fit was most 2005. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) culture influences ERP survey of Egyptian important factor. Egyptian organizational implementation in the Egyptian implementation. ERP adopters, PLS. culture hindered ERP success. organizational context. Paper presented at European and Mediterranean Conference on Information Systems, Cairo, Egypt. Rikhardsson, P., and P. Kræmmergaard. Denmark Exploratory research Find ERP facilitates change in the basic 2006. Identifying the impacts of enterprise design, based upon assumptions (e.g., predominant language, system implementation and use: Examples on the case study value, culture, etc.), processes, rules and from Denmark. International Journal of methodology & procedures of organization. Organizational Accounting Information Systems 7 (1): 36- grounded theory outcomes based on use. 49. Schoenherr, T., M. A. Venkataramanan, A. Culturalcharacteristics A field study of 18 German SME’s are more representative of Soni, V. A. Mabert, and D. Hilpert. 2005. of German SMEs SME’s (revenues large firs than small.. They prefer a phased The ”new” users: SMEs and the Mittelstand related to their use of from $29-$460 approach, like to customize to own business experience. Strategic ERP: Extension and ERP. million) using needs and, not surprisingly, SAP is the vendor use. Bendoly, E., and Jacobs, F. R. Stanford, interviews. of choice. CA, Stanford University Press. 36-51. Sia, S. K., M. Tang, C. Soh, and W. F. Boh. Explores ERP as an Case study ERP facilitates both empowerment & panoptic 2002. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) ambivalent technology (implementation control. Employees empowered by ERP but systems as a technology of power: of power in a phase) & survey management put efforts to regaining their lost Empowerment or panoptic control? Singapore Hospital. study (after control. New panoptic visibility was easily Database for Advances in Information implementation) learned & accepted. Systems 33 (1): 23.
Spathis, C. 2006. Enterprise systems Greece Survey of Greek ERP The main accounting benefits from ERP implementation and accounting benefits. users system adoption are organizational and Journal of Enterprise Information operational. Management 19 (1/2): 67-82. Yeh, C., M. Miozzo, and T. Vurdubakis. Investigate role of Collective case study Domestic ERP vendors have an advantage in 2006. The importance of being local? domestic ERP vendors of 14 ERP firms who meeting special, localized requirements along Learning among Taiwan's enterprise in Taiwan design, deliver and with directly implementing own product, rather solutions providers. Journal of Enterprise support ERP in than having a consultant implement the Information Management 19 (1/2): 30. Taiwan. software. TABLE 3 Selected Literature - ERP Organizational Impact
Author/year Theme of study Method Findings Hunton, J., E. , A. Wright, M. , and S. Wright. Examines financial Experimental method Financial auditors do not see added 2004. Are financial auditors overconfident in their auditor’s assessment where system type reason to assess higher risk for ERP vs. ability to assess risks associated with enterprise of ERP vs. non-ERP (ERP vs. non-ERP) non-ERP systems, nor are they resource planning systems? Journal of risks in the presence of was manipulation. inclined to consult IT specialists more Information Systems 18 (2): 7. a control weakness for ERP systems. IT specialists do over access privileges. assess higher risks to ERP systems. Overall, financial auditors appear to be overconfident in their ability to assess ERP system risks. O'Donnell, E. 2005. Enterprise risk management: Describes a systems- A risk assessment Systems-thinking approach to risk A systems-thinking framework for the event thinking approach to methods paper (non- assessment proposes a) determine the identification phase. International Journal of identify events that empirical). organization's value chain to identify Accounting Information Systems 6 (3): 177-195. should be considered relationships, and (b) use the taxonomy during risk to analyze relationships and identify assessment. events that could threaten business process performance. Debreceny, R. S., G. L. Gray, J. Ng, K. Lee, et al. Assesses the nature of Exploratory paper that Found there was limited support for 2005. Embedded audit modules in enterprise support for embedded addresses the lack of EAMs primarily a due to little demand resource planning systems: Implementation and audit modules (EAMs) ERP research on from the user community. Vendors functionality. Journal of Information Systems 19 from ERP providers. embedded audit were consistent in their view that (2): 7-27. modules. EAMs were technically feasible. Dillard, J., L. Ruchala, and K. Yuthas. 2005. Investigate the This is a non- When all activities are quantified this Enterprise resource planning systems: A physical negative potential of empirical theory in turn dehumanizes actions and manifestation of administrative evil. International instrumental paper. Critical theory individuals resulting in abdication of Journal of Accounting Information Systems 6 rationality acting in is used to evaluate moral responsibility. Management 107– 127. and through advanced dominant ERP should explain how ERP design, IT. ideology and expose application and implementation would underlying be different from an approach assumptions. implemented within a totalitarian regime. Alles, M., G. Brennan, A. Kogan, and M. A. A report on a A case study reporting Concludes that audit procedures & Vasarhelyi. 2006. Continuous monitoring of continuous auditing on the experiences audit judgment can be more formally business process controls: A pilot implementation project implementing from a pilot defined than is commonly expected or of a continuous auditing system at Siemens. a monitoring & implementation at one estimated. The management of audit International Journal of Accounting Information control layer to large company alarms and the prevention of the alarm Systems 7 (2): 137-161. continuously monitor floods are found to be critical tasks in business process the continuous auditing controls. implementation process Kumar, V., R. Pollanen, and B. Maheshwari. Investigate enhancing Case studies of 4 In all four companies, existing ERP 2008. Challenges in enhancing enterprise resource ERP systems for medium & large systems did not meet all control planning systems for compliance with Sarbanes- compliance with SOX companies with requirements without modifications or Oxley Act and analogous Canadian legislation. and Canadian operations in the USA add-on applications. Major challenges Management Research News 31 (10): 758. regulatory internal and Canada that all included systems security, the control requirements. use ERP systems. segregation of duties and cultural issues especially resistance to change. Bonson, E., V. Cortijo, and T. Escobar. 2009. Examines if global Results provide guidance on the Towards the global adoption of XBRL using IFRS-GP taxonomy evaluation of IFRS-GP effectiveness international financial reporting standards supports European and provide direction for further (IFRS). International Journal of Accounting firms’ financial improvements of the IFRS-GP Information Systems 10 (1): 46-60. reporting needs. taxonomy. TABLE 4 Selected Literature - ERP Economic Impact
Author/year Theme of study Method Findings Nicolaou, A. I. 2004. Quality of A literature review of Qualitative case study Defines the construct of post- postimplementation review for enterprise ERP implementation of two organizations implementation review (PIR) quality resource planning systems. International studies is used to derive following ERP consisting of five dimensions. Finds that the Journal of Accounting Information Systems factors for ERP implementation. quality of PIR, and not merely the activity 5 (1): 25-49. effectiveness itself, that determines the effect on business implementations over performance. Provides a framework for PIR time. effectiveness research in future ERP studies. Nicolaou, A. I. 2004. Firm performance Investigates how the Compared ERP Found that firms who adopted ERP systems effects in relation to the implementation long-term adoption and adoption firms with a exhibited higher differential performance and use of enterprise resource planning use of ERP affects a matched control group after two years relative to matched firms systems. Journal of Information Systems firm’s financial of non-adoptor firms, that did not implement ERP systems. 18 (2): 79-105. performance. cross-sectionally and longitudinally (before and after adoption). Chand, D., G. Hachey, J. Hunton, V. Proposes an ‘ERP Integrate Zuboff’s Proposes that the ERP scorecard offers Owhoso, et al. 2005. A balanced scorecard Scorecard’ based on the dimensions of advantages including a methodology to based framework for assessing the strategic balanced-scorecard automate, informate assess ERP after implementation, a means impacts of ERP systems. Computers in framework for and transformate into to identify operational automation, new Industry 56 (6): 558-572. evaluating ERP the balanced scorecard informational and innovative system’s strategic framework. (transformational) impacts, & assess ERP at contributions. different stages. Cotteleer, M. J., and E. Bendoly. 2006. The influence of Quantitative: utilized ERP supports significantly reduced order Order lead-time improvement following enterprise systems lead-time information lead times. Pattern of lead times showed enterprise information technology implementation on tracked in ERP (12 that, after ERP implementation, lead time implementation: An empirical study. operational months pre to 24 initially improved, then declined, and then Management Information Systems performance, months post improved again. Study provides empirical Quarterly 30 (3): 643. specifically, order lead implementation) evidence of ERP’s benefits to include swift, times. even production flow. Theory used was a subset of Mooney’s typology. Hendricks, K. B., V. R. Singhal, and J. K. The effect of enterprise Event study of Mixed results related to financial benefits. Stratman. 2007. The impact of enterprise systems (ERP, SCM, & abnormal returns. Regarding ERP systems, some evidence of systems on corporate performance: A study CRM) systems Measures abnormal improvements in profitability were seen, but of ERP, SCM, and CRM system investments on stock performance as change not in stock returns. Found that implementations. Journal of Operations price and profitability. in performance minus improvements in profitability are stronger Management 25 (1): 65-82. the median for early adopters of ERP systems. performance change of comparison group. Wier, B., J. Hunton, and H. R. Links ERP adoption Firms with both non-financial performance HassabElnaby. 2007. Enterprise resource market returns with incentives & ERP obtained significantly planning systems and non-financial non-financial higher short-term & long-term ROA and performance incentives: The joint impact performance incentives stock returns than either of these single on corporate performance. International in executive conditions. Used theory base of cybernetic Journal of Accounting Information Systems compensation. control theory and agency theory. 8 (3): 165-190. Nicolaou, A. I., and S. Bhattacharya. 2008. Explores the nature and Qualitative archival ERP post-implementation activities to Sustainability of ERPs performance timing of post- study using the firm improve subsequent system implementation outcomes: The role of post-implementation implementation sample from Nicolaous planning and business process review quality. International Journal of activities (2004b). Coded improvements are most effective when Accounting Information Systems 9 (1): 43- activities found in ERP undertaken soon. Waiting appears to have 60. PIR announcements. negative short-term financial impact. Roztocki, N., and H. R. Weistroffer. 2008. Examined market Event studies review. Financial markets differentiate among Stock price reactions to investments in EAI reaction to both ERP & technologies in which companies invest to and ERP: A comparative event study. enterprise application integrate their information systems. Proceedings of the 41st Hawaii integration Influential factors include technology International Conference on System announcements across maturity, financial health of the investing Sciences (HICSS-41), Hawaii markets (bull and bear) company, & stock market conditions. & firm financials. Häkkinen, L., and O. Hilmola. 2008. ERP Takes a longitudinal A case study using the Poorest ERP assessments were given early evaluation during the shakedown phase: view (at 0 & 2 years) of DeLone and McLean during shakedown phase but problems Lessons from an after-sales division. the use and evaluation (1992) model to existed after 2 years. Assessments depended Information Systems Journal 18 (1): 73. of an ERP system. evaluate user on user type and the business process(es) in perceptions & use. which they participated. APPENDIX Primary Journals in this Review (Cited two or more times in paper and online materials)
Accounting, Organizations and Society Business Process Management Journal Communications of the ACM Communications of the Association for Information Systems Computers in Industry Decision Support Systems Database for Advances in Information Systems European Accounting Review European Journal of Information Systems Harvard Business Review Proceedings, International Conference on Information Systems 2008 Industrial Management & Data Systems Information & Management Information and Organization Information Management & Computer Security Information Systems Frontiers Information Technology & People International Journal of Accounting Information Systems International Journal of Enterprise Information Systems International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction International Journal of Information Management International Journal of Operations & Production Management International Journal of Production Economics International Journal of Production Research Journal of Enterprise Information Management Journal of Information Systems Education Journal of Information Systems Journal of Information Technology Journal of Management Information Systems Journal of Organizational Change Management Journal of Software Maintenance and Evolution: Research and Practice Journal of Strategic Information Systems Management Accounting Research Management Information Systems Quarterly New Technology Work and Employment Organization Science Proceedings, Hawaii International Conference on Systems Sciences (HICSS) Sloan Management Review Strategic Change Systems Practice The Internal Auditor The Journal of Computer Information Systems