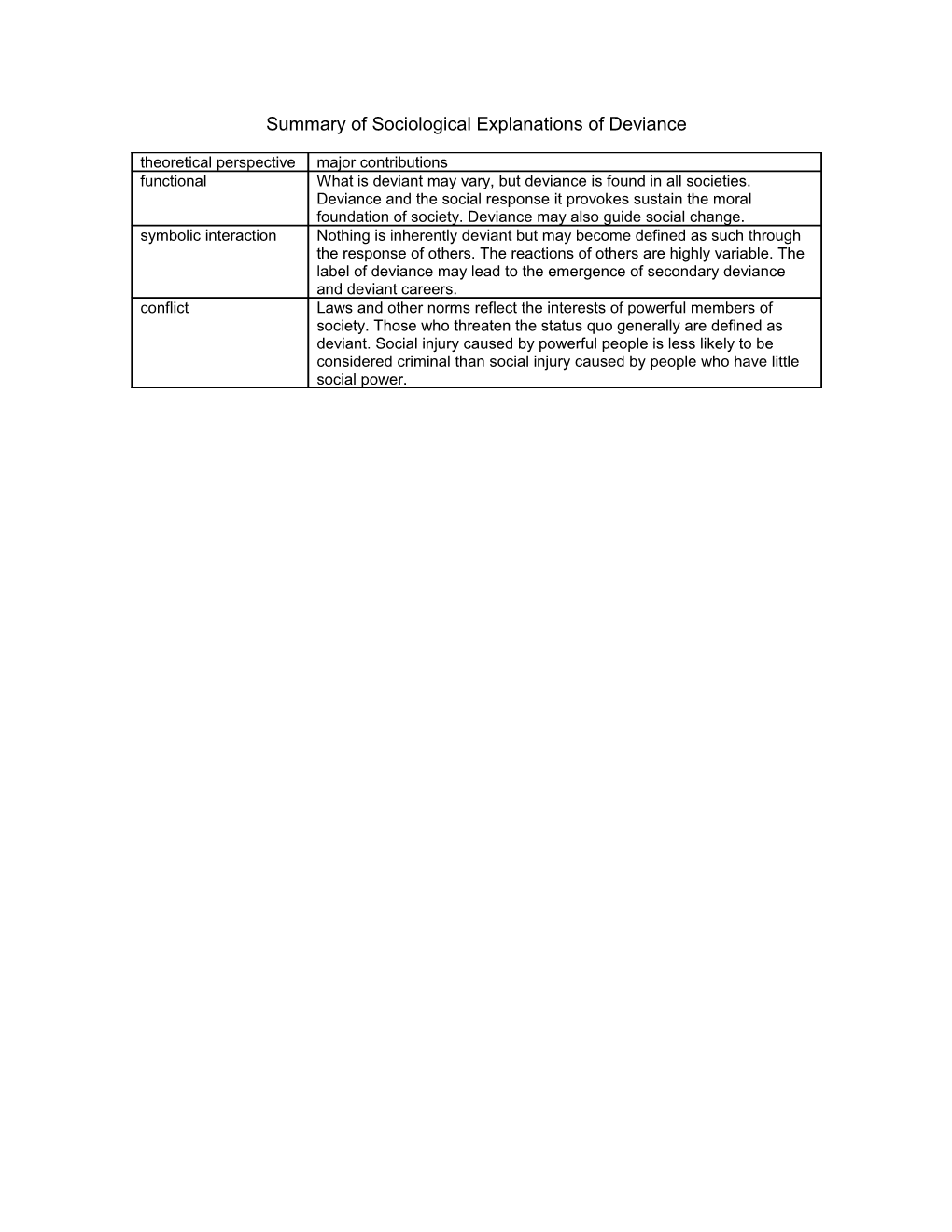
Summary of Sociological Explanations of Deviance theoretical perspective major contributions functional What is deviant may vary, but deviance is found in all societies. Deviance and the social response it provokes sustain the moral foundation of society. Deviance may also guide social change. symbolic interaction Nothing is inherently deviant but may become defined as such through the response of others. The reactions of others are highly variable. The label of deviance may lead to the emergence of secondary deviance and deviant careers. conflict Laws and other norms reflect the interests of powerful members of society. Those who threaten the status quo generally are defined as deviant. Social injury caused by powerful people is less likely to be considered criminal than social injury caused by people who have little social power.
Summary of Sociological Explanations of Deviance
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Recommended publications