Page 1 of 4 MSP 3111 SECTION A – ANSWER IN A SEPARATE ANSWER BOOK
CONVENTIONAL DIRECT STAINING HISTOCHEMISTRY
1. A 43-year old male patient has repeatedly elevated transferrin saturation. His serum ferritin is elevated (> 1000ng/mL) and DNA analysis reveals a C282Y mutation. A liver biopsy is taken and sent to the histology laboratory for processing.
1.1 What stain/s will be performed on sections from this specimen? (2) 1.2 What is the rationale behind the method of the special stain used? (3) 1.3 What is the significance of using distilled water? (1) 1.4 What is the histological appearance of the tissue? (6) 1.5 What diagnosis do you think the attending physician is investigating? (1)
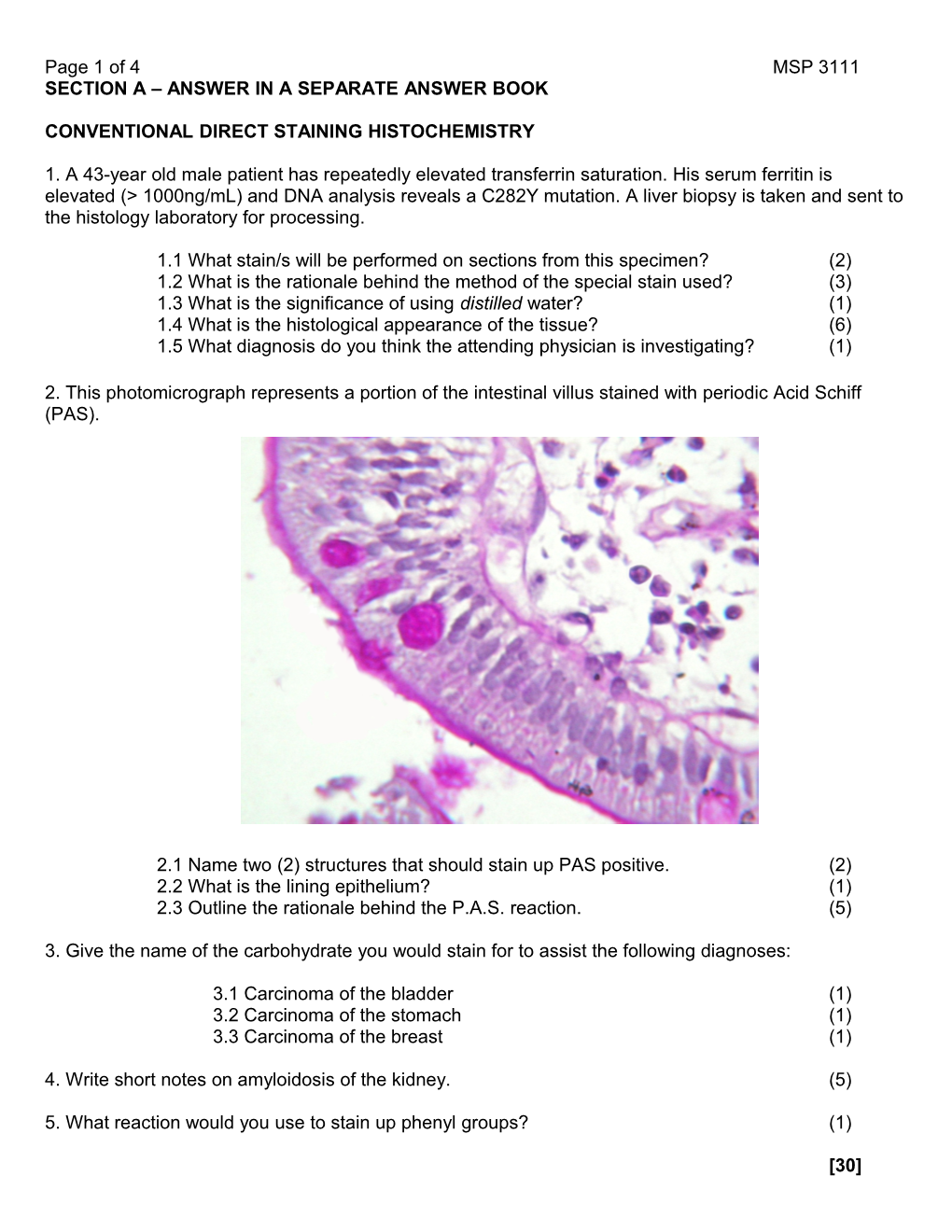
2. This photomicrograph represents a portion of the intestinal villus stained with periodic Acid Schiff (PAS).
2.1 Name two (2) structures that should stain up PAS positive. (2) 2.2 What is the lining epithelium? (1) 2.3 Outline the rationale behind the P.A.S. reaction. (5)
3. Give the name of the carbohydrate you would stain for to assist the following diagnoses:
3.1 Carcinoma of the bladder (1) 3.2 Carcinoma of the stomach (1) 3.3 Carcinoma of the breast (1)
4. Write short notes on amyloidosis of the kidney. (5)
5. What reaction would you use to stain up phenyl groups? (1)
[30] Page 2 of 4 MSP 3111
ENZYME HISTOCHEMISTRY
6. What stains are performed on a muscle biopsy? (7)
7. What are the factors that govern the diffusion of the final reaction product (FRP) in a simultaneous capture reaction? (3)
8. How can a diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s disease be confirmed in a suction biopsy without sufficient submucosa? (2)
9. Discuss jejunal biopsies under the following headings:
9.1 Assists in which diagnoses? (3) 9.2 Enzymes that can be demonstrated. (3) 9.3 Histological appearance of pathology. (5)
10. What stain would you perform to identify possible pathology in muscle mitochondria? (1)
11. What results do you expect from the adenosine triphosphatase stain? (1)
[25]
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY
12. Define the following terms: 12.1 Hybridoma (1) 12.2 Immunofluorescence (3)
13. By means of a pencil sketch outline the peroxidase-anti-peroxidase immunohistochemistry method. (5)
14. Explain how you would go about checking the antibody specificity. (4)
15. List three (3) disadvantages of immunofluorescence. (3)
16. How would the immunohistochemistry results sheet look for a squamous cell carcinoma? (9)
[25]
GENETIC TECHNIQUES
17. Match the words / phrases in column A with the correct option in column B.
A B 1. Method for determining evolutionary (a) transcription factor relatedness of two bacterial species 2. Uses a heat stabile DNA polymerase (b) Sticky ends 3. Also known as the TATA box (c) Nuclear acid hybridization 4. Binds to DNA and initiates transcription (d) Polymerase Chain Reaction Page 3 of 4 MSP 3111
5. Binding increases the rate of transcription of a (e) Basal promoter gene 6. the favorable results of endonuclease digestion (f) enhancer 7. Enables the transfer of DNA fragments from gel (g) Raf kinase to a membrane 8. Activates mitogen-activated protein kinase (h) mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 9. Activates ribosomal S6 protein kinase (i) Recomdinant DNA 10. A method of amplifying a DNA segment using (j) Southern Blot vectors
[10]
SECTION TOTAL [90]
SECTION B – ANSWER IN A SEPARATE ANSWER BOOK
QUESTION 1
1.1 The body has 3 cavities in which effusions develop. Name the 3 cavities and state which effusion is relevant for which cavity. (6)
1.2 Describe the serous cavity, referring to the membrane lining and cells found and the role of this lining in the human body. (1/2 x 4=2)
1.3 Describe the preparation of an effusion including instruments used and stains used. (1/2x4=2)
1.4. a) An effusion showing characteristics of low protein content and scant cellularity, is called ______. (1)
b) An effusion showing characteristics of high specific gravity and has the tendency to clot more often, is called ______. (1)
1.5 Describe a cytological picture of cirrhosis. (3)
1.6 a) Referring to reactive mesothelial cells describe the nucleus and the cytoplasm. (1/2x4=2)
b) Which special stain is used to identify mesothelial cells? (1)
1.7 By means of a table compare benign mesothelial cells to cells of a malignant mesothelioma referring to the nuclei only, including the chromatin features, the presence of nucleoli or not and the shape of the nuclei. (1/2x8=4) [20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 List 4 types of cells found in the respiratory tract. (4) Page 4 of 4 MSP 3111 2.2 Describe a Curschmann's spiral found in sputum specimens. (3)
2.3 a) If you saw the presence of a scolex of a parasite together with hooklets in the background, which parasite would you be identifying? (1) b) The presence of bi-pyramidal or needle like red crystals composed of condensed granules derived from eosinophils would signify which acellular material in a smear? (1)
2.4 Describe a cytological picture indicative of tuberculosis. (3)
2.5 a) Squamous metaplasia occurs when ______is replaced by stratified squamous epithelium. (1)
b) The presence of creola bodies is indicative of ______. (1)
2.6 By means of a table compare a small cell carcinoma and an adenocarcinoma. Refer to nuclear and cytoplasmic changes. (6) [20]
QUESTION 3
3.1 a) Which epithelium is almost exclusively confined to the urinary tract? (1) b) Which epithelium lines the urethra? (1)
3.2 Name 3 types of cells encountered in a normal urine specimen. (3)
3.3 By means of a table describe the a) physiologically exfoliated superficial transitional cells and b) the traumatically exfoliated deep transitional cells. Refer to amount of cells exfoliated, their shape, cytoplasm and nuclei. (1/2x8=4)
3.4 Name 2 parasites that can be found in a urine specimen. (2)
3.5 a a) What are crystals that may be found in a urine specimen? (1)
b) Of the following crystals state whether they are found in an acid or alkaline urine.
CRYSTAL ACID OR ALKALINE URINE Calcium sulfate A. Calcium carbonate B. Amorphous urate C. Phosphate crystals D. (4) c) Give 4 examples of urinary casts. (4) [20]
SECTION TOTAL [60] EXAM TOTAL [150]