Teacher Resource 4 Expected answers to Learner Resource 4
Task 1
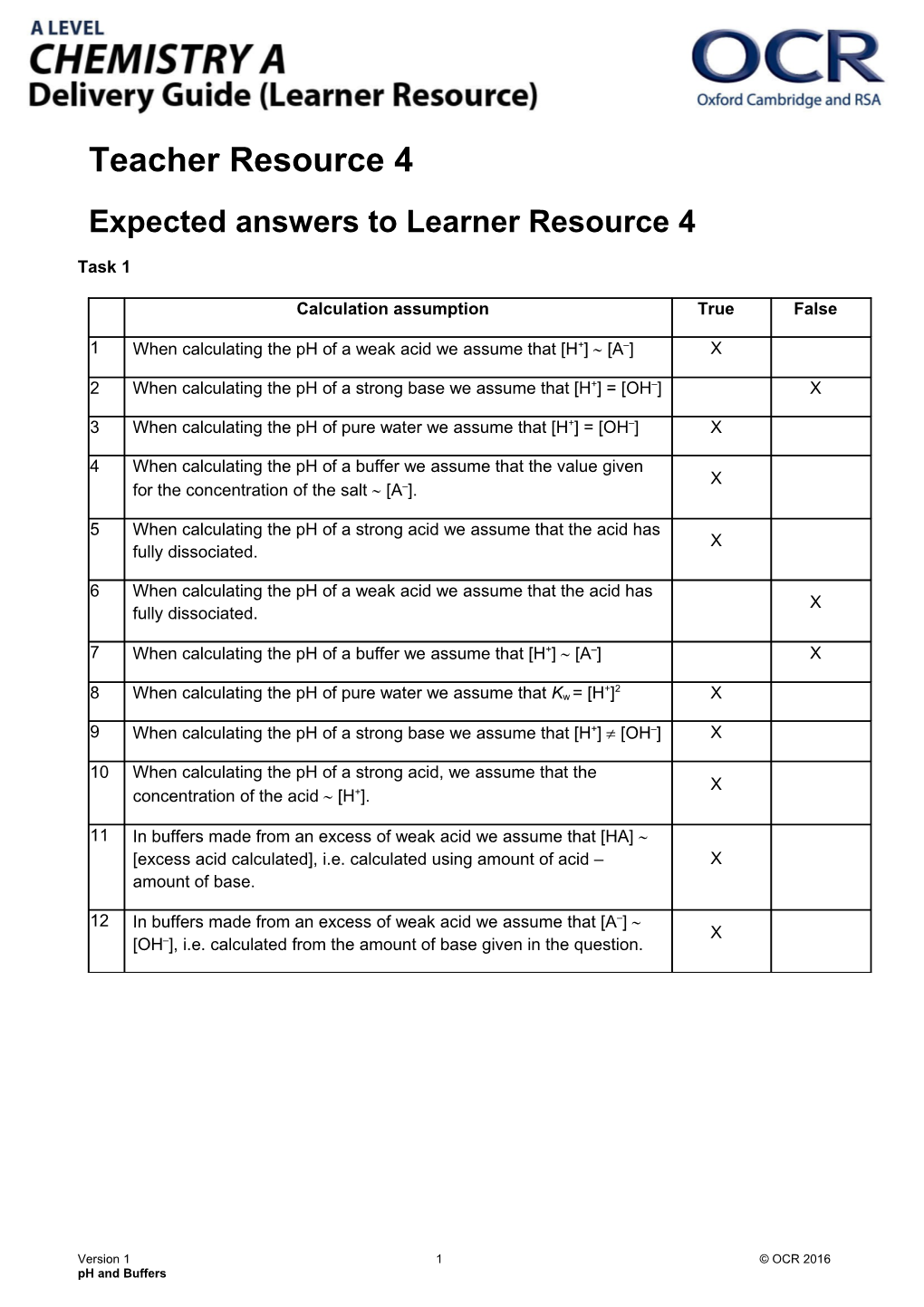
Calculation assumption True False
1 When calculating the pH of a weak acid we assume that [H+] [A–] X
2 When calculating the pH of a strong base we assume that [H+] = [OH–] X
3 When calculating the pH of pure water we assume that [H+] = [OH–] X
4 When calculating the pH of a buffer we assume that the value given X for the concentration of the salt [A–].
5 When calculating the pH of a strong acid we assume that the acid has X fully dissociated.
6 When calculating the pH of a weak acid we assume that the acid has X fully dissociated.
7 When calculating the pH of a buffer we assume that [H+] [A–] X
+ 2 8 When calculating the pH of pure water we assume that Kw = [H ] X
9 When calculating the pH of a strong base we assume that [H+] [OH–] X
10 When calculating the pH of a strong acid, we assume that the X concentration of the acid [H+].
11 In buffers made from an excess of weak acid we assume that [HA] [excess acid calculated], i.e. calculated using amount of acid – X amount of base.
12 In buffers made from an excess of weak acid we assume that [A–] X [OH–], i.e. calculated from the amount of base given in the question.
Version 1 1 © OCR 2016 pH and Buffers Task 2 and Task 3
Statements in italics are rewritten from false statements.
Weak acid When calculating the pH of a weak acid we assume that [H+] [A–]
When calculating the pH of a weak acid we assume the acid has not fully dissociated.
Strong acid When calculating the pH of a strong acid we assume that the acid has fully dissociated.
When calculating the pH of a strong acid, we assume that the concentration of the acid [H+].
Strong base When calculating the pH of a strong base we assume that [H+] [OH–]
Water When calculating the pH of pure water we assume that [H+] = [OH–]
+ 2 When calculating the pH of pure water we assume that Kw = [H ]
Buffer When calculating the pH of a buffer we assume that the value given for the concentration of the salt [A–].
In buffers made from an excess of weak acid we assume that [HA] [excess acid calculated], i.e. calculated using amount of acid – amount of base.
In buffers made from an excess of weak acid we assume that [A–] [OH–], i.e. calculated from the amount of base given in the question.
When calculating the pH of a buffer we do not assume that [H+] [A–]
OCR Resources: the small print
OCR’s resources are provided to support the teaching of OCR specifications, but in no way constitute an endorsed teaching method that is required by the Board, and the decision to use them lies with the individual teacher. Whilst every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the content, OCR cannot be held responsible for any errors or omissions within these resources. © OCR 2016 - This resource may be freely copied and distributed, as long as the OCR logo and this message remain intact and OCR is acknowledged as the originator of this work.
Please get in touch if you want to discuss the accessibility of resources we offer to support delivery of our qualifications: [email protected]
Version 1 2 © OCR 2016 pH and Buffers