Exam 3 Practice Problems
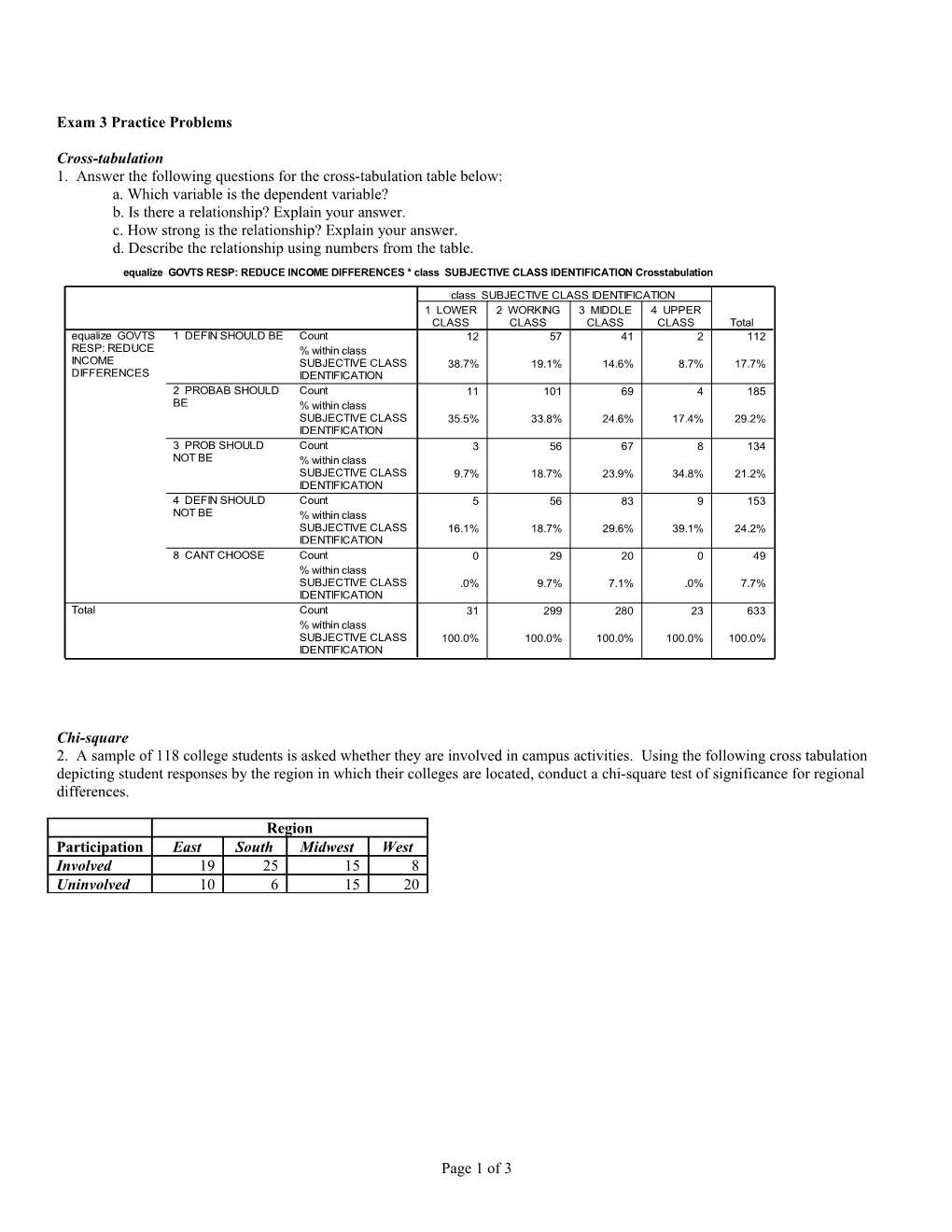
Cross-tabulation 1. Answer the following questions for the cross-tabulation table below: a. Which variable is the dependent variable? b. Is there a relationship? Explain your answer. c. How strong is the relationship? Explain your answer. d. Describe the relationship using numbers from the table.
equalize GOVTS RESP: REDUCE INCOME DIFFERENCES * class SUBJECTIVE CLASS IDENTIFICATION Crosstabulation
class SUBJECTIVE CLASS IDENTIFICATION 1 LOWER 2 WORKING 3 MIDDLE 4 UPPER CLASS CLASS CLASS CLASS Total equalize GOVTS 1 DEFIN SHOULD BE Count 12 57 41 2 112 RESP: REDUCE % within class INCOME SUBJECTIVE CLASS 38.7% 19.1% 14.6% 8.7% 17.7% DIFFERENCES IDENTIFICATION 2 PROBAB SHOULD Count 11 101 69 4 185 BE % within class SUBJECTIVE CLASS 35.5% 33.8% 24.6% 17.4% 29.2% IDENTIFICATION 3 PROB SHOULD Count 3 56 67 8 134 NOT BE % within class SUBJECTIVE CLASS 9.7% 18.7% 23.9% 34.8% 21.2% IDENTIFICATION 4 DEFIN SHOULD Count 5 56 83 9 153 NOT BE % within class SUBJECTIVE CLASS 16.1% 18.7% 29.6% 39.1% 24.2% IDENTIFICATION 8 CANT CHOOSE Count 0 29 20 0 49 % within class SUBJECTIVE CLASS .0% 9.7% 7.1% .0% 7.7% IDENTIFICATION Total Count 31 299 280 23 633 % within class SUBJECTIVE CLASS 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% IDENTIFICATION
Chi-square 2. A sample of 118 college students is asked whether they are involved in campus activities. Using the following cross tabulation depicting student responses by the region in which their colleges are located, conduct a chi-square test of significance for regional differences.
Region Participation East South Midwest West Involved 19 25 15 8 Uninvolved 10 6 15 20
Page 1 of 3 Measures of Association 3. Use the following data to calculate and interpret an appropriate measure of association:
homosex HOMOSEXUAL SEX RELATIONS * relig RS RELIGIOUS PREFERENCE Crosstabulation
relig RS RELIGIOUS PREFERENCE 1 PROTES TANT 2 CATHOLIC 3 JEWISH 4 NONE 5 OTHER Total homosex 1 ALWAYS WRONG Count 368 104 5 38 11 526 HOMOSEXUAL % within relig SEX RELATIONS RS RELIGIOUS 71.2% 52.0% 29.4% 35.2% 34.4% 60.2% PREFERENCE 2 ALMST ALWAYS Count 21 15 0 3 1 40 WRG % within relig RS RELIGIOUS 4.1% 7.5% .0% 2.8% 3.1% 4.6% PREFERENCE 3 SOMETIMES WRONG Count 26 16 1 7 2 52 % within relig RS RELIGIOUS 5.0% 8.0% 5.9% 6.5% 6.3% 5.9% PREFERENCE 4 NOT WRONG AT ALL Count 102 65 11 60 18 256 % within relig RS RELIGIOUS 19.7% 32.5% 64.7% 55.6% 56.3% 29.3% PREFERENCE Total Count 517 200 17 108 32 874 % within relig RS RELIGIOUS 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% PREFERENCE
4. Use the following information to interpret gamma (notice that the value for gamma is listed below):
pornlaw FEELINGS ABOUT PORNOGRAPHY LAWS * xmovie SEEN X-RATED MOVIE IN LAST YEAR Crosstabulation
xmovie SEEN X-RATED MOVIE IN LAST YEAR Total pornlaw NO YES FEELINGS ABOUT PORNOGRAPHY LAWS
1 ILLEGAL TO ALL 339 31 370 2 ILLEGAL UNDER 18 370 187 557 3 LEGAL 21 11 32 Total 730 229 959
Ns = 339*(187+11) + 370*(11) = 67122 + 4070 = 71192; Nd = 31*(370+21) + 187*(21) = 12121 + 3927 = 16048
71192 16048 Gamma = .632 71192 16048
Page 2 of 3 Bivariate Correlation and Regression 5. Use the following data to examine the relationship between education and income: Case (N=8) Years of education (X) Annual income (Y) 1 8 34000 2 10 31000 3 12 37000 4 12 42000 5 16 51000 6 9 44000 7 20 47000 8 15 29000 a. Calculate the regression slope (“b”) and y-intercept (“a”), Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r), and the coefficient of determination (r2). b. Use the regression equation to predict the annual income for a person with 0 years of education and a person with 12 years of education. How do the predictions for people with 12 years of education compare with the actual data (i.e., compare the predicted value to the two people’s actual scores)? c. Interpret the regression slope (“b”) and y-intercept (“a”), Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r), and the coefficient of determination (r2).
6. Use the following results from SPSS to examine the relationship between income and education.
a. Use Pearson’s correlation to describe the relationship between income and education. b. Identify the y-intercept and the slope from the regression. c. Use the slope to describe the relationship between income and education d. Interpret the y-intercept and the slope. e. What is the predicted income for a respondent with 16 years of education? f. Interpret the coefficient of determination (i.e., R square). g. Evaluate the research hypothesis that education increases income in the population. h. Interpret the confidence interval for the slope.
Page 3 of 3