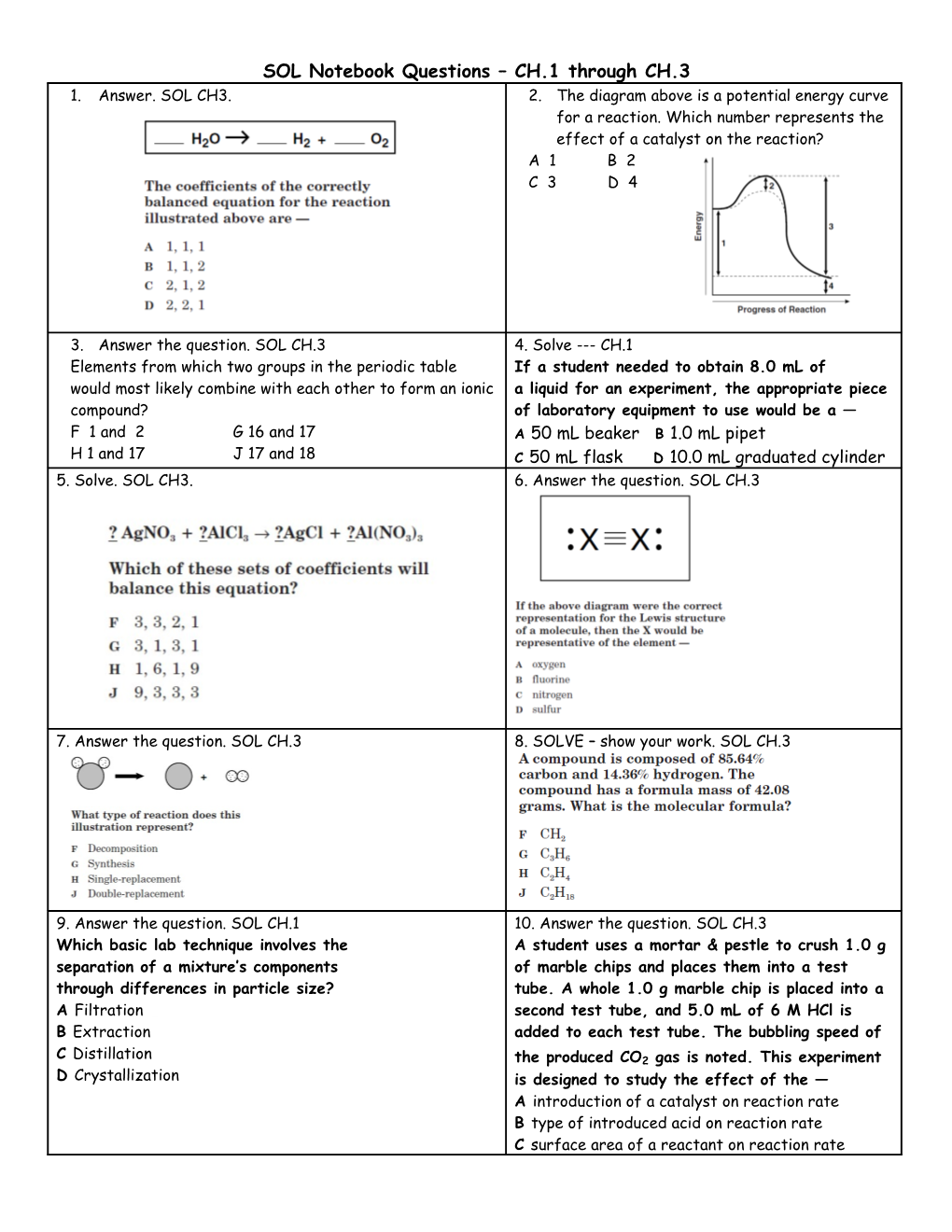
SOL Notebook Questions – CH.1 through CH.3 1. Answer. SOL CH3. 2. The diagram above is a potential energy curve for a reaction. Which number represents the effect of a catalyst on the reaction? A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4
3. Answer the question. SOL CH.3 4. Solve --- CH.1 Elements from which two groups in the periodic table If a student needed to obtain 8.0 mL of would most likely combine with each other to form an ionic a liquid for an experiment, the appropriate piece compound? of laboratory equipment to use would be a — F 1 and 2 G 16 and 17 A 50 mL beaker B 1.0 mL pipet H 1 and 17 J 17 and 18 C 50 mL flask D 10.0 mL graduated cylinder 5. Solve. SOL CH3. 6. Answer the question. SOL CH.3
7. Answer the question. SOL CH.3 8. SOLVE – show your work. SOL CH.3
9. Answer the question. SOL CH.1 10. Answer the question. SOL CH.3 Which basic lab technique involves the A student uses a mortar & pestle to crush 1.0 g separation of a mixture’s components of marble chips and places them into a test through differences in particle size? tube. A whole 1.0 g marble chip is placed into a A Filtration _ second test tube, and 5.0 mL of 6 M HCl is B Extraction added to each test tube. The bubbling speed of
C Distillation the produced CO2 gas is noted. This experiment D Crystallization is designed to study the effect of the — A introduction of a catalyst on reaction rate B type of introduced acid on reaction rate C surface area of a reactant on reaction rate _ D temperature of a reactant on reaction rat 11. The figure to the right shows an 12. A student uses a mortar & pestle to crush experimental setup used to separate 1.0 g of marble chips and places them into a the components of a colored ink sample. test tube. A whole 1.0 g marble chip is placed Which of the following describes this into a second test tube, and 5.0 mL of 6 M HCl laboratory technique? is added to each test tube. The bubbling speed
A Chromatography _ of the produced CO2 gas is noted. This B Filtration experiment is designed to study the effect of C Decanting the — D Distillation A introduction of a catalyst on reaction rate B type of introduced acid on reaction rate C surface area of a reactant on reaction rate _ D temperature of a reactant on reaction rate
13. To remove the sand first and then the salt from a 14. What is the name of the mixture of sand and salt water, one combination of lab equipment shown to the techniques you could use would be to first — right? A evaporate and then distill F Watch glass B evaporate and then condense G Crucible _ C filter and then evaporate _ H Beaker D filter and then condense J Evaporating dish
15. Which of the following pieces of glassware can be 16. If a student’s hand is accidentally exposed used to measure the volume of a liquid with the greatest to an acidic solution, what should be done? accuracy? A Rinse the hand in a concentrated base. A Test tube B Cover the hand with oil. B Beaker C Wrap the hand in paper towels. C Flask D Rinse the hand in running water. D Graduated cylinder 17. When examining the physical properties of an 18. Which of the following best describes why unknown substance, which of the following characteristics an experiment should be repeated? is unsafe to observe? A To organize the data A Color B To produce a variety of results B Weight C To include another variable C Taste D To verify the observed results D Form_ 19. Measurement 1: 5.2 g 20. First measurement: 6.293 g Measurement 2: 5.4 g Second measurement: 6.294 g Measurement 3: 3 g Third measurement: 6.295 g Measurement 4: 2.45 g A student obtained these data after measuring These data show repeated measurements of the same the mass of an object three different times. If object which has a known mass of 5.38 grams. Which the true value of the object’s mass is 5.550 g, measurement is most accurate? these data are best described as — A 1 F precise but not accurate _ B 2 _ G accurate but not precise C 3 H accurate and precise D 4 J neither accurate nor precise 22. A compound has 50% sulfur and 50% oxygen. What is 21. Which is an example of a synthesis reaction? its empirical formula?
23. What would be the product(s) of this reaction? 24.
25. 26.
27. 28.
29. A compound is composed of 58.8% C, 9.8% H, and 30. 31.4% O, and the molar mass is 102 g/mol. What is the Which reaction type best describes the reaction above? - molecular formula for this compound? Pb(NO3)2 + 2HBr PbBr2 + 2HNO3 A Combination B Single Replacement Reaction C Double Replacement Reaction D Decomposition
31. 32.The empirical formula for butane (C4H10) is The reaction shown below is – A CH A(s) + heat B(s) + D(g) A an endothermic reaction B C2H5 B an exothermic reaction C C1H2.5 C a decomposition reaction D C4H10 D a double-replacement reaction 33. The table below lists the melting and boiling points of some 34. Match the formulas with the names of the following metals. Which metal remains liquid over the widest range of compounds temperature?
__ 341 Ammonium phosphate __ 342 Lead (III) Sulfate __ 343 Potassium permanganate __ 344 Iron (II) oxide A Copper __ 345 Nickel (II) dichromate __ 346 Acetate B Iron __ 347 Silver Bromide __ 348 Tin (II) Chlorite C Lead __ 349 Mercury hydroxide __ 350 Cadmium Nitride D Platinum
35. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a neutral 36. Cations are formed when neutral atoms lose atom of Lithium?
37. 38.
39. 40.
41. 42.
43. Which of the following is a balanced equation? 44.What is the correct formula for Ammonium Phosphate?
45. Which set of coefficients will balance this equation? 46. Which set of coefficients will balance this equation?
47. Which set of coefficients will balance this equation? 48. Which set of coefficients will balance this equation?
49. Which set of coefficients will balance this equation? 50. Which set of coefficients will balance this equation? 51. For an experiment in which you are determining the freezing point 52. Below shows a chemical equation representing a of an unknown chemical, you record the temperature every minute for chemical reaction. The name and mass of each substance 20 minutes. In this example, time is the – involved in the chemical reaction are also shown. Which of a. Control c. Dependent Variable these are the reactants? b. Hypothesis d. Independent Variable
53. Which of these is the ground-state electron configuration for an 54. What is the chemical formula for a compound formed atom of fluorine? (atomic no. = 9) from calcium ions (Ca2+) and chloride ions (Cl-)?
55. What name would be given to the compound PBr5? 56. Which is the correct formula for iron (III) sulfate?
CH.1a Understand designated laboratory techniques CH.1b Safe use of chemicals and equipment CH.1b Proper identification of lab equipment CH.1c Proper response to emergency situations CH.1d Manipulation of multiple variables, using repeated trials CH.1d Precision vs Accuracy CH.1e Accurate recording, organization, and analysis of data through repeated trials CH.1f Mathematical and procedural error analysis CH.1g Mathematical manipulations - SI units, Scientific Notation, & Significant Digits CH.1g Mathematical manipulations - Linear equations, Graphing, Ratio and Gathering Data CH.1g Mathematical manipulations - Proportion & Dimensional analysis CH.1g Scientific Method CH.1h Use of computers & graphing calculators for gathering data & results CH.1h Use of probeware for gathering data CH.1i Construction and defense of a scientific viewpoint (the nature of science).
CH.2a Use Periodic Table to calculate average atomic mass, mass number, and atomic number CH.2b Use Periodic Table to calculate isotopes, half lives, and radioactive decay CH.2c Calculate mass and charge characteristics of subatomic particles CH.2d Use the Periodic Table to recognize trends and patterns in families or groups CH.2e Use the Periodic Table to recognize trends and patterns in series and periods CH.2f Use P.Table to find trends with atomic radii, electronegativity, shielding effect, and ionization energy CH.2g Use P.Table to identify electron configurations, valence electrons, and oxidation numbers CH.2h Identify and distinguish chemical and physical properties CH.2i Identify and distinguish historical and quantum models
CH.3a Chemical formulas and balanced equations & their nomenclature CH.3b Balancing chemical equations CH.3c Writing chemical formulas (molecular, empirical, & ionic) CH.3c Writing chemical formulas (structural & Lewis diagrams) CH.3d Bonding types (ionic and covalent) CH.3e Reaction types (synthesis, decomposition, single and double replacement) CH.3e Reaction types (oxidation-reduction, neutralization, exothermic, and endothermic) CH.3f Reaction rates and kinetics (activation energy, catalysis, and degree of randomness).