www.ecsnetwork.nhs.uk
Guidelines for the administration of sub cutaneous furosemide
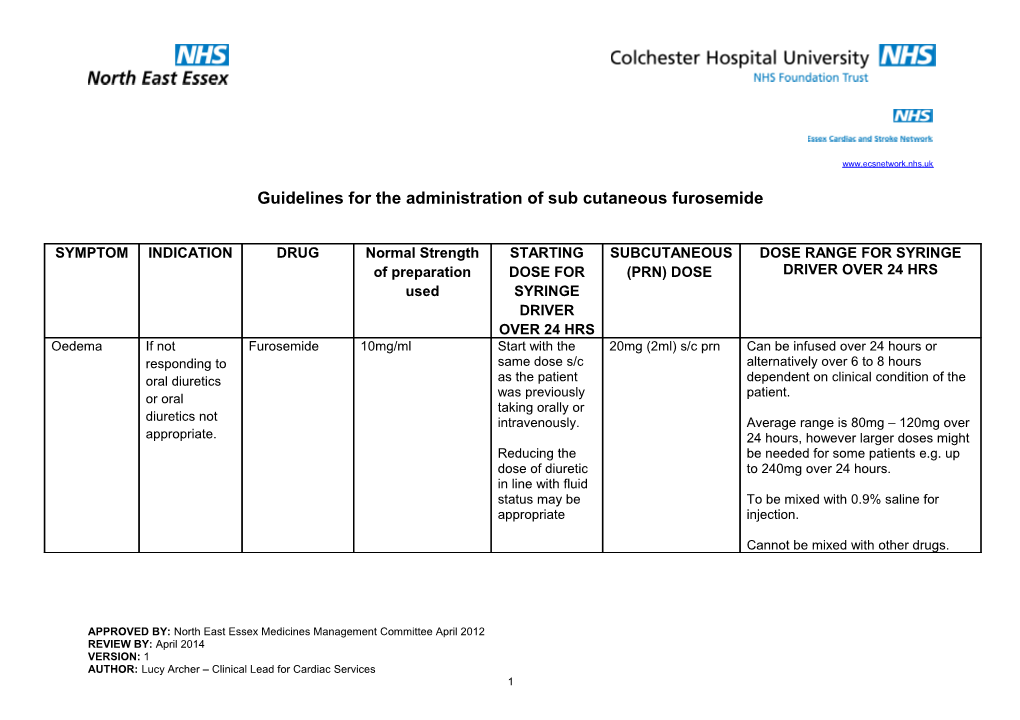
SYMPTOM INDICATION DRUG Normal Strength STARTING SUBCUTANEOUS DOSE RANGE FOR SYRINGE of preparation DOSE FOR (PRN) DOSE DRIVER OVER 24 HRS used SYRINGE DRIVER OVER 24 HRS Oedema If not Furosemide 10mg/ml Start with the 20mg (2ml) s/c prn Can be infused over 24 hours or responding to same dose s/c alternatively over 6 to 8 hours oral diuretics as the patient dependent on clinical condition of the was previously patient. or oral taking orally or diuretics not intravenously. Average range is 80mg – 120mg over appropriate. 24 hours, however larger doses might Reducing the be needed for some patients e.g. up dose of diuretic to 240mg over 24 hours. in line with fluid status may be To be mixed with 0.9% saline for appropriate injection.
Cannot be mixed with other drugs.
APPROVED BY: North East Essex Medicines Management Committee April 2012 REVIEW BY: April 2014 VERSION: 1 AUTHOR: Lucy Archer – Clinical Lead for Cardiac Services 1 Cautions in Use Use with caution with impaired micturition, gout and diabetes. Avoid using oedematous areas as infusion sites due to possible reduced absorption.
Relative Contraindications Hypovolaemia, dehydration, severe hyponatraemia or hypokalaemia. Comatose or precomatose states associated with liver cirrhosis. Renal failure due to nephrotoxic or hepatotoxic drugs. Anuria.
Monitoring Monitor clinical symptoms and signs (breathlessness, weight, oedema) as normal. Adjust the dosage accordingly. Measuring serum urea and electrolytes only if worsening renal function would change your management. Monitor the site for signs of irritation or infection.
Drug Interaction Diuretic effect may be antagonised by corticosteroids. Diuretic effect may be antagonised by Ketorolac. Increase risk of nephrotoxicity with NSAIDs.
Side Effects Mild gastrointestinal disturbances, hyperglycaemia, electrolyte disturbances, tinnitus and deafness. Hypersensitivity reactions including rashes and anaphylaxis.
Cost 10mg/ml amp. 2ml = 30p 5ml= 38p 25ml=£2.50
APPROVED BY: North East Essex Medicines Management Committee April 2012 REVIEW BY: April 2014 VERSION: 1 AUTHOR: Lucy Archer – Clinical Lead for Cardiac Services 2 References British National Formulary Fonzo-Christe C, Vukasovic C, Wasilewski-Rasca A-F, Bonnabry P. Subcutaneous administration of drugs in the elderly: survey of practice and systemic literature review. Palliative Medicine 2005; 19: 208-219 Palliativedrugs.com website bulletin board, search term “furosemide” http://www.palliativedrugs.com/pdi.html accessed 21/04/06 The use of drugs beyond licence in palliative care and pain management. A position statement prepared on behalf of the Association for Palliative Medicine and The Pain Society. http://www.palliative-medicine.org/resources/images/Drugs_doc.pdf . accessed 26/05/06 Twycross R, Wilcock A Ed. Palliative Care Formulary 4th Edition (PCF 4). Verma AK, da Silva JH, Kuhl DR. Diuretic effects of subcutaneous furosemide in human volunteers: a randomized pilot study. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2004 April; 38: 544-549 Zacharias H, Johnson M et al. Is there a role for sub cutaneous furosemide in the community and hospice management of end stage heart failure? Palliative Medicine. 2011 25(6)
Ackowledgements: Dr Shamsul shah – Consultant in Palliative Care, St Helena Hospice Dr Allan Harkness – Consultant Cardiologist, CHUFT Leicestershire Medicines Strategy Group Palliative Care guidelines Halton and St Helens Clinical Guidelines for the use of Furosemide in End of Life Care
APPROVED BY: North East Essex Medicines Management Committee April 2012 REVIEW BY: April 2014 VERSION: 1 AUTHOR: Lucy Archer – Clinical Lead for Cardiac Services 3