Brainy Biologist ______DUE the day of your midterm---Monday, 3/25! Unit 1: Introduction (Chapter 1) & Molecular Biology 1. What is biology? 2. Seeing the color blue usually makes people calm and relaxed. Make a hypothesis about why this occurs.
3. How could you test your hypothesis (remember, it has to be testable!)?
4. What characteristics do all living things have in common?
5. What do you think is the #1 safety rule for the lab? Explain why.
6. You want to see if anti-bacterial soap really works. You decide to grow some bacteria in the lab, on two different plates. You keep the plates at the same temperature, lighting, etc. After 4 days when the bacteria have grown a lot and are spread over the entire plates, you smear anti-bacterial soap inside one of the plates. You count the bacteria on each plate for 3 days. a. Make a hypothesis—what do you think the results of the experiment will be?
b. What is the independent/manipulated variable? c. What is the dependent/responding variable? d. Why did you only put anti-bacterial soap on one of the plates?
e. Do you think you should have put something on the other plate too? Why/why not?
f. Do you think you should have used more plates, or is two enough? Why/why not?
7. For each example, list which piece of lab equipment is most useful for the task. (5 pts) a. Pouring 35 mL of vinegar into a beaker ______b. Measuring 100 grams of baking soda ______c. Making sure that the vinegar is 30ºC ______d. Observing the movement of plankton in a drop of pond water ______8. What type of graph (circle, bar, line) would you use to show each of the following: a. Temperature increases during the afternoon hours of the day ______b. 20% of the students in biology want to be a marine biologist ______c. students in the class range from 5’ to 6’ tall ______
9. Metric conversions: khdbdcm a. 50 g = ______Hg b. 0.75 Dm = ______km
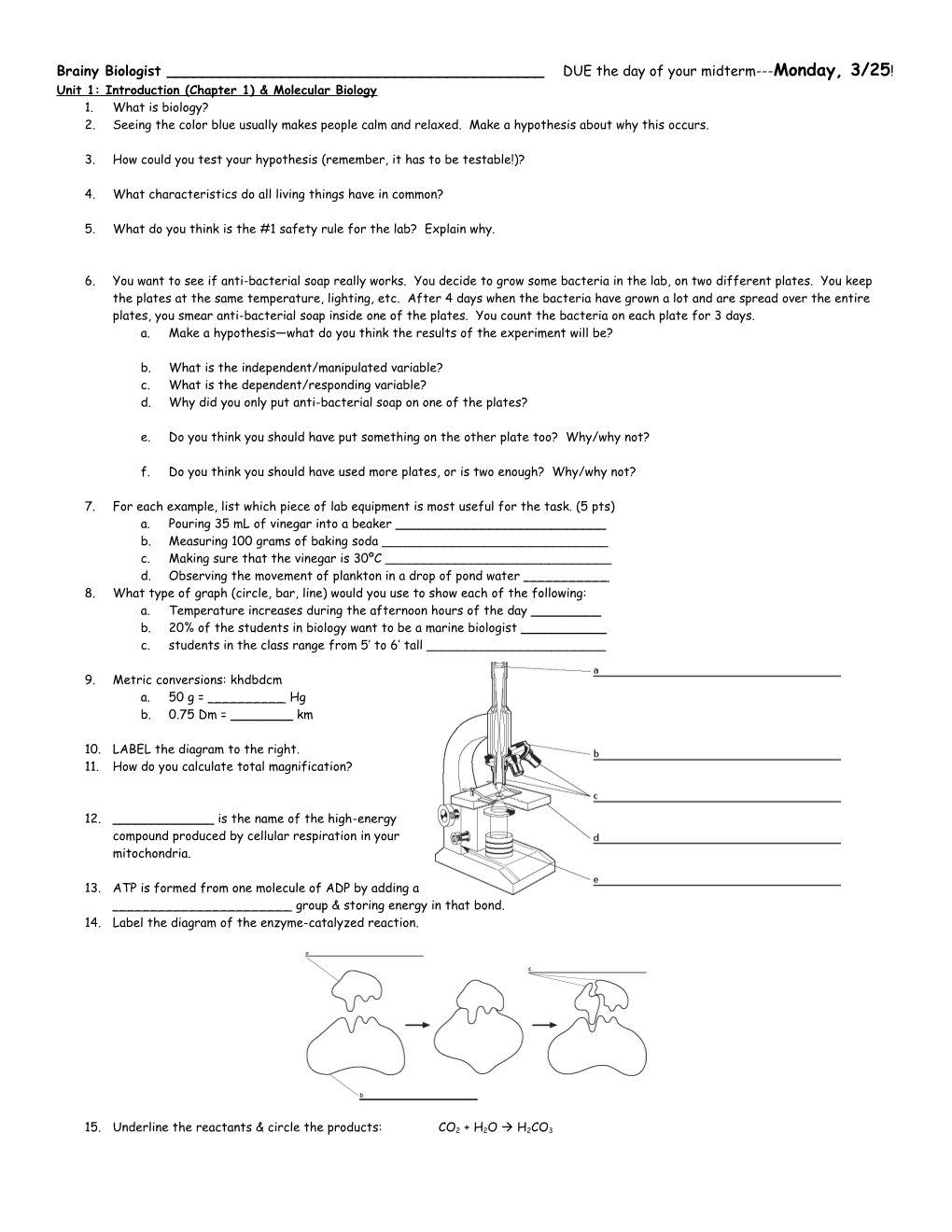
10. LABEL the diagram to the right. 11. How do you calculate total magnification?
12. ______is the name of the high-energy compound produced by cellular respiration in your mitochondria.
13. ATP is formed from one molecule of ADP by adding a ______group & storing energy in that bond. 14. Label the diagram of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
15. Underline the reactants & circle the products: CO2 + H2O H2CO3 16. Label each of the following graphs: exothermic reaction, endothermic reaction, reactants, products, activation energy
17. A reaction that releases energy is ______, and a reaction that absorbs energy is ______.
18. The energy released during a chemical reaction comes from the ______that are broken during the reaction. 19. How do catalysts (enzymes) decrease the amount of time (rate) a reaction takes to finish?
20. Are catalysts carbs, lipids, or proteins? 21. Label the lines on the graph: reaction with enzyme, reaction without enzyme ---- 22. Draw another water molecule bonded to the one below, label the bond and the parts of the water atom.
23. Is water a polar or non-polar molecule? ______What does this mean?
24. Explain the difference between cohesion and adhesion.
25. ______are solutions with a low pH, while ______have a high pH (>7). 26. Redox reactions occur when one molecule is reduced, or ______electrons, and the other is oxidized, or ______electrons. Unit 2: Ecology 1. List the ecological levels of organization with an example of each.
Heterotroph Autotroph
Textbook’s definition 2. 3.
Define in your OWN words
Create an ICON (small picture) to describe it. 4. Draw a food chain to show the following relationships: A maple tree is an autotroph, which is eaten by a grasshopper as it hops from leaf to leaf. A bluejay sees the grasshopper bouncing around & catches it for dinner. The quick red fox has been watching this whole scenario, and while the bluejay’s eating the grasshopper, he pounces on the bluejay and has a dinner of his own. Be sure to place your arrows in the proper direction. Also be sure to label the producers and consumers (including primary, secondary, etc.) as well as the trophic levels (1, 2, etc.).
Energy Pyramid Biomass Pyramid Pyramid of Numbers Define in your own 5. 6. 7. words—what’s it used for? Draw & label an example of each.
Water Cycle Nitrogen Cycle Carbon Cycle Why’s it important? 8. 9. 10. List the main steps or processes involved.
Which parts of the ecosystem are involved?
ABIOTIC BIOTIC Define in your own words. 11. 12.
List 3 examples of each.
13. What’s the difference between a habitat and a niche? Give an example of each.
Competition Predation Symbiosis Define in your own words. 14. 15. 16.
Give 2 examples of each.
3 types of symbiosis: Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Define in your own words. 17. 18. 19.
1 example of each:
Identify who’s being helped or harmed in the example. Primary Succession Secondary Succession Define in your own words. 20. 21.
What’s the “starting” material (soil, rocks, etc.)?
2 examples of each:
22. Draw a logistic growth curve and an exponential growth curve (label each). Which one has carrying capacity?
23. A colony of bacteria reproduce very quickly and never run out of resources because they’re super resistant to everything. Which type of growth curve would theirs look like? Why?
24. What’s the competitive exclusion principle?
Limiting Factors for a Population: Density-Dependent Density-Independent Define in your own words. 25. 26.
Explain one example of each.
27. Why is the human population on earth increasing at such a high rate? 28. Which type of growth curve is it (human population growth)—logistic or exponential? 29. Please explain how the following human activities have changed the environment: a. Agriculture b. Industry c. Technology d. Urban development
30. a. We can plant trees, so they are a ______resource. b. We can’t make fossil fuels, so they’re a ______resource. c. What is sustainability?
d. Although we aren’t required to recycle, why is it a good thing to do?
Human Impacts: Global Warming Ozone depletion Invasive Species Acid Precipitation
What causes it? 31. 32. 33. 34.
What’s the problem?
What can we do to stop it?
35. What are the THREE types of survivorship curves? Draw a graph, label it, give an example of each.
36. What’s biodiversity? How do species richness and species evenness differ?
37. How does biological magnification work? What happens to the pollutant when the producers get “affected” by it? … does it stop there?
Unit 3: Digestion & Energy Macromolecules: 1. “Organic chemistry” is the study of compounds that contain which element?
2. In the equation below, if it proceeds from LEFT TO RIGHT, is this condensation or hydrolysis?
3. Now, circle the polymer(s) & draw a square around the monomer(s).
Please indicate whether the following statements are about Carbs (C), Lipids (L), Proteins (P), or Nucleic Acids (NA):
4. ______monomer: amino acids 10. ______stores long-term energy 5. ______monomer: sugar (ex. Glucose) 11. ______stores short-term energy 6. ______monomer: fatty acid 12. ______beans, tofu, meat 7. ______starches, sugars 13. ______has a phosphate head and fatty acid 8. ______fats, oils, waxes, fatty acids tail 9. ______glucose, fructose, glycogen 14. ______enzymes 15. Label the diagram. Completion 16. ______“CHYME” is produced here & protein digestion begins 17. ______Enzyme secreted by salivary glands, breaks down starch into maltose. 18. ______type of digestion that uses muscles or teeth to break down food 19. ______stores bile 20. ______bile digests these molecules 21. ______organ stores glucose(glycogen),makes proteins & bile, breaks down toxins 22. ______organ that secretes insulin to regulate blood glucose levels 23. ______organ that’s over 21’ long. Nutrient absorption occurs here. 24. ______secretes amylase (carb digestion), trypsin (proteins), and lipase (lipids) 25. ______no nutrient absorption here, but water is absorbed to keep you hydrated 26. ______pepsinogen secreted, converted to pepsin when pH low enough (proteins) 27. ______“wad” of food pushed down esophagus by peristalsis
Energy 28. Photosynthesis is the process by which organisms use energy from ______to make their own food (glucose), inside the ______of the cell. Identify if the process occurs in the Light-Dependent (LD) or Light-Independent (LI) Reactions of photosynthesis: 29. ______CO2 enters the chloroplast and combines with RuBP. 30. ______light hits the chlorophyll in the photosystems 31. ______water is split and oxygen is released 32. ______glucose is made 33. ______electron transport chain passes energy from one protein to another 34. ______NADPH and ATP are made 35. ______NADPH and ATP are used to complete the Calvin Cycle ------36. Please write the chemical equation for photosynthesis:______37. Cellular Respiration is the process that breaks down ______in order to make ______inside the ______of the organism’s cell. Identify if the process occurs in Glycolysis (G), Aerobic Cell Respiration (CR), or Anaerobic Fermentation (F). You may have >1 answer! 38. ______needs oxygen to occur 39. ______does not need oxygen to occur 40. ______pyruvic acid is used to produce CO2, NADH, FADH2, and ATP 41. ______glucose is used to make pyruvic acid 42. ______pyruvic acid is used to produce lactic acid or ethanol + CO2 43. ______electron transport chain is used to make large amounts of ATP 44. ______happens in bacteria and yeast 45. ______happens in animals 46. ______makes a little ATP, but not much ------47. Please write the Chemical equation for respiration:______48. Does photosynthesis occur in animals, plants, or both? 49. Does cellular respiration occur in animals, plants, or both?
NOW THAT YOU’RE FINISHED STUDYING…GET SOME REST! YOU NEED TO “SLEEP ON IT” SO IT WILL SOAK INTO THAT BRAIN OF YOURS!! REALLY!!! GET A GOOD NIGHT’S REST & EAT A YUMMY, CARB & PROTEIN-FILLED BREAKFAST IN THE MORNING! GOTTA FEED THE BRAIN!