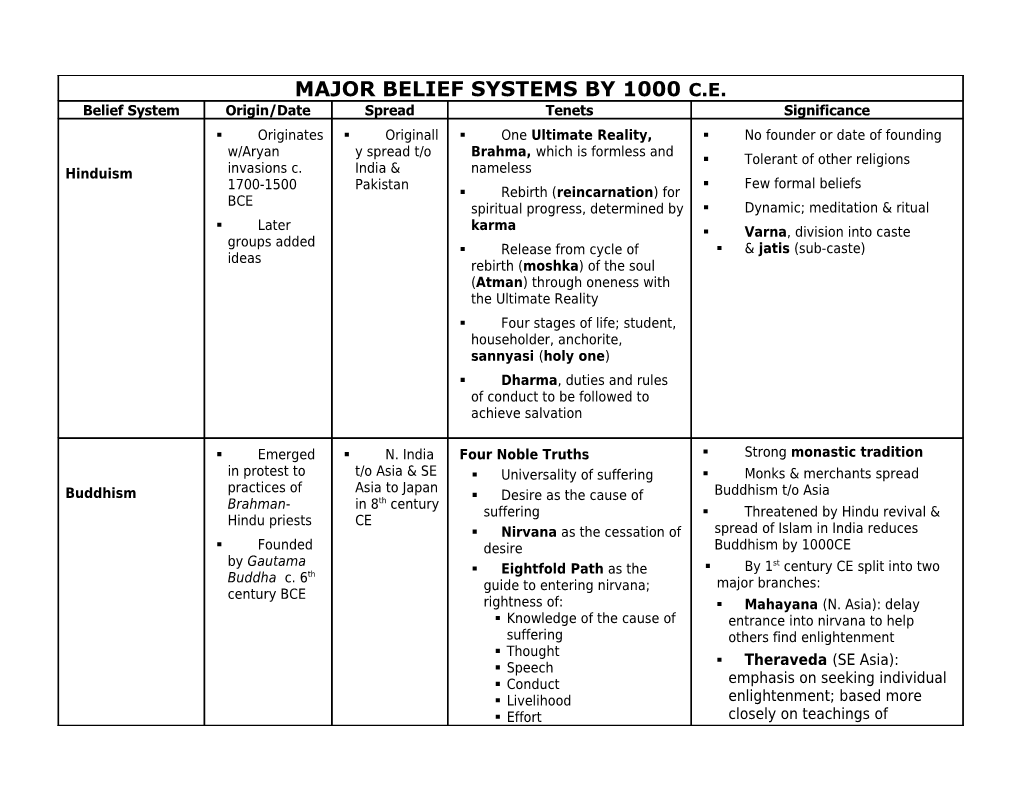
MAJOR BELIEF SYSTEMS BY 1000 C.E. Belief System Origin/Date Spread Tenets Significance . Originates . Originall . One Ultimate Reality, . No founder or date of founding w/Aryan y spread t/o Brahma, which is formless and . Tolerant of other religions Hinduism invasions c. India & nameless 1700-1500 Pakistan . Few formal beliefs . Rebirth (reincarnation) for BCE spiritual progress, determined by . Dynamic; meditation & ritual . Later karma . Varna, division into caste groups added . Release from cycle of . & jatis (sub-caste) ideas rebirth (moshka) of the soul (Atman) through oneness with the Ultimate Reality . Four stages of life; student, householder, anchorite, sannyasi (holy one) . Dharma, duties and rules of conduct to be followed to achieve salvation
. Emerged . N. India Four Noble Truths . Strong monastic tradition in protest to t/o Asia & SE . Universality of suffering . Monks & merchants spread practices of Asia to Japan Buddhism . Desire as the cause of Buddhism t/o Asia Brahman- in 8th century suffering . Threatened by Hindu revival & Hindu priests CE . Nirvana as the cessation of spread of Islam in India reduces . Founded desire Buddhism by 1000CE by Gautama st . Eightfold Path as the . By 1 century CE split into two Buddha c. 6th guide to entering nirvana; major branches: century BCE rightness of: . Mahayana (N. Asia): delay . Knowledge of the cause of entrance into nirvana to help suffering others find enlightenment . Thought . Theraveda (SE Asia): . Speech . Conduct emphasis on seeking individual . Livelihood enlightenment; based more . Effort closely on teachings of . Mind, and Gautama Buddha . Meditation . Zen Buddhism: c. 700 CE in China & c. 1200CE in Japan, sudden enlightenment through meditation. .
MAJOR BELIEF SYSTEMS BY 1000 C.E. Belief System Origin/Date Spread Tenets Significance . Philosophical and ethical system . . China . Based on jen, the quality of conduct China/Confuciu that relates all people to one . Dominant influence in Chinese s, 500s B.C.E. another, sympathy Confucianism government, education, and and Mencius, . Humaneness scholarship for 2,000 years 300s B.C.E. . Filial piety; family as the . Knowledge of Confucianism teacher of social roles; family as basis of civil service extension of the state; five . Conservative influence, relationships acceptance of the status quo . But the right to overthrow a . Superior man; only the ruler who did not govern for the educated should govern good of the ruled, mandate form heaven . Ancestor Worship . Social conventions such as . Traditiona . China, . Tao meaning “The Way”; Confucian rituals unnatural lly attributed second most indefinable but like nature, . Became mixed with peasant to Lao- influential naturalness Daoism belief in spirits and over time tzu/400s and system after . Live in accord with one’s became polytheistic religion 300s B.C.E. Confucianis nature . Interest in nature greatly m . Oneness with everything influenced Chinese arts through the tao; meditation. . Interaction of yin and yang, passive and active principles, as influences on everything that happens . First monotheistic religion . Hebrews, . Land of . One God . Greatly influenced Christianity ancient Canaan, . Chosen people through a and Islam Israelites/first ancient Judaism special relationship with God. . No widespread hierarchical historical Israel; structure writings Disapora . Messiah to come between 1000 130s C.E. by . Beliefs set forth in the and 800 B.C.E. the Romans; Torah, Mosaic Law, and Middle East, Talmud, collection of oral laws. North Africa, and Europe MAJOR BELIEF SYSTEMS BY 1000 C.E. Belief System Origin/Date Spread Tenets Significance . Persecuted by Romans . Teachings . From . One God . Legalized by Constantine in of Jesus/ 30s Palestine . Jesus as the Messiah late 300s C.E. throughout Christianity . Strong monastic element; the Roman . Through God’s grave people monks preserved much of ancient world, are saved through the gift of Greek and Roman learning after including the faith in Jesus Christ the breakup of the Roman Empire Byzantine . Through this faith sins are . Strong missionary outreach Empire and forgiven; receive new and . Strong, universal hierarchical northern eternal life. structure and discipline Europe . Gospels as main source of . As Roman Catholic Church early teachings of Jesus. power of the papacy came to rival that of European emperors and . Large body of later writings kings developed to interpret and build on original teachings . Split into Sunni and Shi’is sects . Muhamm . From . One God, Allah . Sunni: modern majority, ad/ Early 600s Arabian . Muhammad as the Seal of originally adherents of the C.E. Peninsula Islam the Prophets (Jewish Abraham Ymayyad spread and Moses; Christian Jesus; . Shi’is: originally followers f Ali through Muhammad) . Development of the Sharia, Middle East legal code for many Islamic nations to western . Five Basic Pillars: . Lack of hierarchical structure India, . “There is no God but western Allah and Muhammad is His China, sub- Prophet.” Saharan Africa, and . Prayer five times a day Moorish facing Mecca enclaves in . Charity Spain. . Fasting during Ramadam Pilgrimage to Kaaba, shrine in Mecca. . Original teachings recorded in the Quran . Examples: Sumerian, Shang, . Earliest . Continu . Belief in many gods/spirits Greek, Roman, Germanic, Mayan, religions ed in areas . Gods as personifications of Aztec, and African religions across all that had not Polytheism nature . Modern religion: Hinduism culture regions been evangelized . Animism by Christianity and Islam.