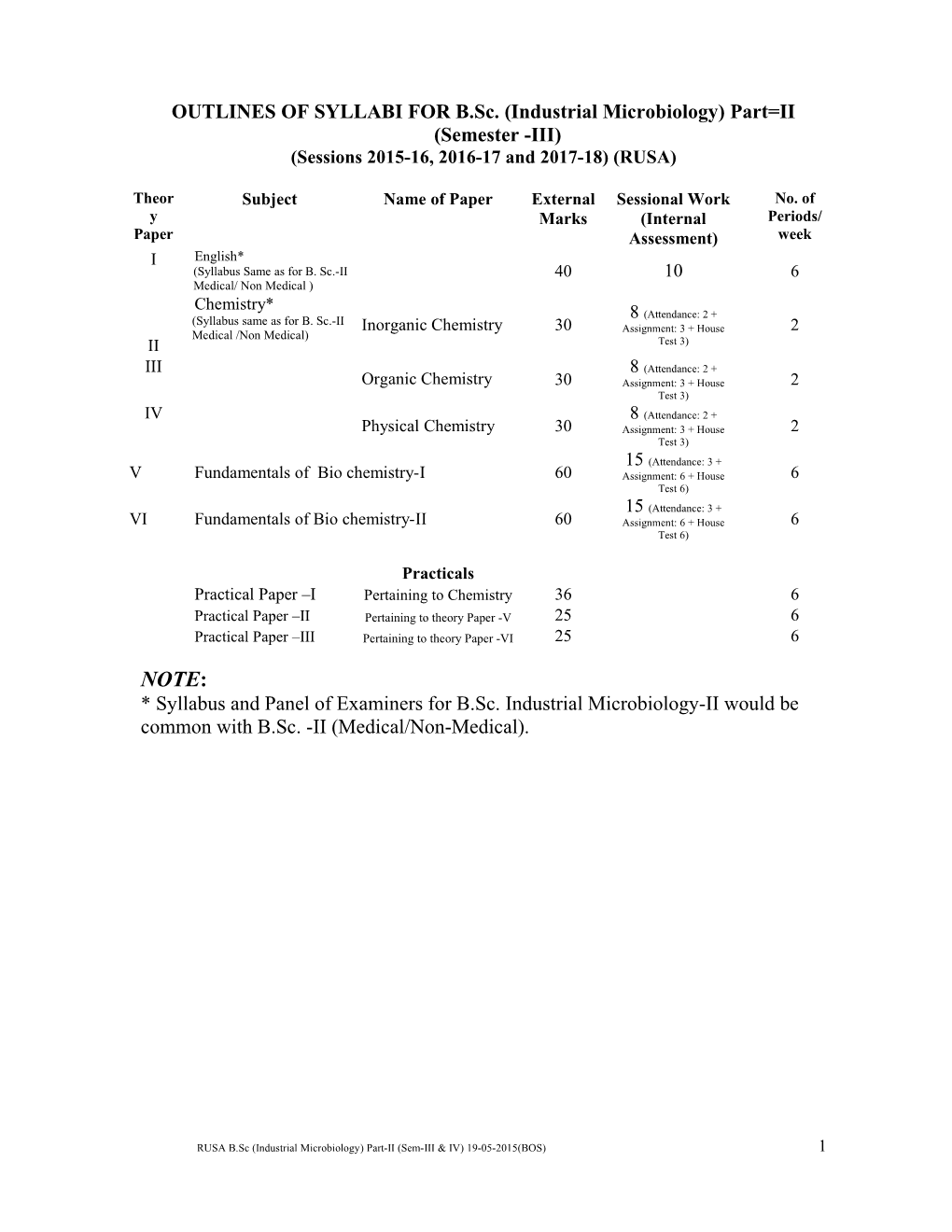
OUTLINES OF SYLLABI FOR B.Sc. (Industrial Microbiology) Part=II (Semester -III) (Sessions 2015-16, 2016-17 and 2017-18) (RUSA)
Theor Subject Name of Paper External Sessional Work No. of y Marks (Internal Periods/ Paper Assessment) week I English* (Syllabus Same as for B. Sc.-II 40 10 6 Medical/ Non Medical ) Chemistry* (Attendance: 2 + (Syllabus same as for B. Sc.-II 8 Inorganic Chemistry 30 Assignment: 3 + House 2 Medical /Non Medical) II Test 3) III 8 (Attendance: 2 + Organic Chemistry 30 Assignment: 3 + House 2 Test 3) IV 8 (Attendance: 2 + Physical Chemistry 30 Assignment: 3 + House 2 Test 3) 15 (Attendance: 3 + V Fundamentals of Bio chemistry-I 60 Assignment: 6 + House 6 Test 6) 15 (Attendance: 3 + VI Fundamentals of Bio chemistry-II 60 Assignment: 6 + House 6 Test 6)
Practicals Practical Paper –I Pertaining to Chemistry 36 6 Practical Paper –II Pertaining to theory Paper -V 25 6 Practical Paper –III Pertaining to theory Paper -VI 25 6
NOTE: * Syllabus and Panel of Examiners for B.Sc. Industrial Microbiology-II would be common with B.Sc. -II (Medical/Non-Medical).
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 1 B.Sc. (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Semester-III)
PAPER TITLE: FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOCHEMISTRY-I
Max. Marks: 60 Lectures to be delivered: 75 Pass Marks: 35% (Each of 45 minutes duration) Time Allowed: 3 Hours
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE PAPER SETTER
The question paper will consist of three sections A, B and C. Section A and B will have four questions from the respective section of syllabus and will carry 9 marks each. Section C will consist of 12 short-answer type questions of 2 marks each which will cover the entire syllabus uniformly and will carry 24 marks in all. INSTRUCTIONS FOR CANDIDATES Candidates are required to attempt two questions from each section A and B and the entire section C, which is compulsory.
SECTION-A
1. Introduction to Biochemistry: Water as a biological solvent, dissociation of water, pH, buffer solutions, Handerson -Hasselbalch equation. Amino acids: amino acids titration curves, physical and chemical properties of amino acids. 2. Peptides and Peptide bonds, rigid and planar nature of a peptide bond. Protein architecture, Ramachandran Plot, folding of peptide chains into regular repeating structure (helix, pleated sheets).β. turns in polypeptides, amino acid sequencing of poly peptides. Forces stabilizing different lavels of folding, super secondary structures. 3. Carbohydrates: Fisch and Hawarth structures of carbohydrates, stereoisomerism and mutarotation, anomeric forms of monosaccharides, reactions of monosaccharides, characteristics of the aldehyde, ketones and hydroxyl groups, glycosidic bonds, 4. Structure of oligo and polysaccharides, amylose, amylopectin, starch, cellulose, chitin, pectins, glycosaminoglycans, mucopolysaccharides.
SECTION-B
5. Structure and functions of lipids, fatty acids, triacylglycerols, glycerophospholipids, sphingomyelins, lipoproteins, liposomes, biological membranes and micelles. 6. Nucleic Acids: Structure and properties of purine and pyrimidine bases. Nucleosides and nucleotides, biological functions of DNA and RNA species. Double helical model of DNA and forces responsible for it. Short hand representation of nucleic acid back bone, denaturation of DNA, methods for isolation and purification of nucleic acids. 7. Introduction to enzymes and coenzymes, units of enzyme activity, enzyme nomenclature and classification. Enzyme kinetics, effect of substrate concentration on Michaelis- Menten equation, determination of Km and its significance, effect of pH and temperature on rates of enzymes catalyzed reaction.
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 2 8. Enzyme inhibitors and their importance, chemical methods of active site studies, Introduction of multi substrate enzymes, allosteric enzyme and enzyme regulation, iso enzymes, enzyme immobilization.
RECOMMENDED BOOKS
1. Champe, P.C. and Harvey, R.A. 1994. Biochemistry, 2nd Edition, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 2. Jain, J.L. 2000. Fundamentals of Biochemistry, 5th ed., S. Chand and Co., New Delhi. 3. Lubert Streyer 1995. Biochemistry, 4th ed., W.H. Freeman and Company. 4. Nelson, D.L. and Cox, M.M. 2005. Principles of Biochemistry, 4th Edition, W.H. Freeman and Co. 5. Plummer, D.T. 1988. An introduction to practical Biochemistry (3rd) Tata Mc Graw Hill. 6. Rao, K. Rangnathan 1986: Text book of Biochemistry, 3rd ed., Prantice Hall, New Delhi. 7. Raymond Chang 1989. Physical Chemistry with application to Biological systems:, 2nd Ed. MacMillan Publishing Co., New York. 8. Upadhyay and Nath 2002. Biophysical Chemistry- Principles and Techniques , 3rd ed. Himalaya Publishing House. PRACTICALS
Practical Exercise for Fundamentals of Biochemistry-I
1. Preparation of solutions and buffers. 2. Protein estimation by Lowry's method and Pyne's method. 3. Estimation of carbohydrates (glucose, fructose, lactose) 4. TLC of amino acids. 5. Estimation of titrable acidity of given food smaple. 6. Immobilization of enzyme/bacterial cells in calcium-alginate beads.
NOTE:
Candidates will be required to submit their original notebook of lab work initialed with date by their teacher at the time of practical examination. Practical examination shall be held in a single morning session from 9:00 a.m. to 1:00 p.m. Practical examination is to be conducted by the two external examiners. Guideline pattern for the conduct of practical examination. Max. Marks: 25 Time Allowed: 8 Periods/week Practical exercises : 18marks Practical records: 04 marks Viva voice: 03 marks
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 3 B.Sc. (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Semester-III)
Paper Title: FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOCHEMISTRY -II
Max. Marks: 60 Lectures to be delivered: 75 Pass Marks: 35% (Each of 45 minutes duration) Time Allowed: 3 Hours
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE PAPER SETTER
The question paper will consist of three sections A, B and C. Section A and B will have four questions from the respective section of syllabus and will carry 9 marks each. Section C will consist of 12 short-answer type questions of 2 marks each which will cover the entire syllabus uniformly and will carry 24 marks in all. INSTRUCTIONS FOR CANDIDATES Candidates are required to attempt two questions from each section A and B and the entire section C, which is compulsory.
SECTION – A
1. Bioenergetics: Biological system and general laws of thermodynamics, concept of entropy, high energy bonds, biological energy transducers and redox potentials. 2. Metabolic pathways: Basic concept and design, glycolysis, TCA cycle, Pentose phosphate pathway, gluconeogenesis and glycogen metabolism, mitochondrial electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation. 3 β-Oxidation of fatty acids, formation of ketone bodies, Biosynthesis and catabolism of triglycerides, phosphoglycerides and sphingolipids, synthesis of cholesterol and fatty acids 4. Deamination, Transamination, decarboxylation reaction, hormones and vitamins, Urea cycle, biosynthesis and degradation of purines and pyrimidines.
SECTION-B 5. Protein Metabolism: Introduction, protein synthesis and hydrolysis. 6. Nucleotide Metabolism: Synthesis of purine and pyrimidine and their degradation 7. Spectroscopic techniques: - Beer’s Lambert Law, U .V. Visible spectrophotometery, IR spectroscopy and spectrofluorimetry; Principal and biological applications. ORD and CD spectroscopy, NMR and mass spectrometry: Principal and biological application. 8. Electrophoretic techniques: Principle and applications of electrophoretic techniques in purification and characterization of biomolecules, isoelectric focusing, and immunoelectrophoresis, SDS-PAGE and agarose gel electrophoresis RECOMMENDED BOOKS 1. Champe, P.C. and Harvey, R.A. 1994. Biochemistry, 2nd Edition, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 2. Jain, J.L. 2000. Fundamentals of Biochemistry, 5th ed., S. Chand and Co., New Delhi. 3. Lubert Streyer 1995. Biochemistry, 4th ed., W.H. Freeman and Company.
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 4 4. Nelson, D.L. and Cox, M.M. 2005. Principles of Biochemistry, 4th Edition, W.H. Freeman and Co. 5. Plummer, D.T. 1988. An introduction to practical Biochemistry (3rd) Tata Mc Graw Hill. 6. Rao, K. Rangnathan 1986: Text book of Biochemistry, 3rd ed., Prantice Hall, New Delhi. 7. Raymond Chang 1989. Physical Chemistry with application to Biological systems:, 2nd Ed. MacMillan Publishing Co., New York. 8. Upadhyay and Nath 2002. Biophysical Chemistry- Principles and Techniques , 3rd ed. Himalaya Publishing House.
PRACTICALS
Practical Exercise for Fundamentals of Biochemistry-II
1. SDS- PAGE for protein analysis 2. Qualitative estimation of Lipids in a given sample. 3. To study enzyme activity and enzyme kinetics 4. Agarose gel electrophoresis for nucleic acids. 5. Isolation of DNA and RNA 6. To Determine saponification and iodine value of given fat and oil sample
NOTE: Candidates will be required to submit their original notebook of lab work initialed with date by their teacher at the time of practical examination. Practical examination shall be held in a single morning session from 9:00 a.m. to 1:00 p.m. Practical examination is to be conducted by the two external examiners.
Guideline pattern for the conduct of practical examination
Max. Marks: 25 Time Allowed: 8 Periods/week Practical exercises: 18 marks Practical records: 04 marks Viva voice: 03 marks
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 5 OUTLINES OF SYLLABI FOR B.Sc. (Industrial Microbiology) Part=II (Semester -IV) (Sessions 2015-16, 2016-17 and 2017-18) (RUSA)
Theor Subject Name of Paper External Sessional Work No. of y Marks (Internal Periods/ Paper Assessment) week I English* (Syllabus Same as for B. Sc.-II 40 10 6 Medical/ Non Medical ) Chemistry* (Attendance: 2 + (Syllabus same as for B. Sc.-II 8 Inorganic Chemistry 30 Assignment: 3 + House 2 Medical /Non Medical) II Test 3) III 8 (Attendance: 2 + Organic Chemistry 30 Assignment: 3 + House 2 Test 3)
IV 8 (Attendance: 2 + Physical Chemistry 30 Assignment: 3 + House 2 Test 3)
15 (Attendance: 3 + V Microbial Structure and Physiology 60 Assignment: 6 + House 6 Test 6) 15 (Attendance: 3 + VI Microbial Genetics 60 Assignment: 6 + House 6 Test 6) VII Environmental and Road Safety Awareness 100
Practicals Practical Paper –I Pertaining to Chemistry 36 6 Practical Paper –II Pertaining to theory Paper -V 25 6 Practical Paper –III Pertaining to theory Paper -VI 25 6
NOTE: * Syllabus and Panel of Examiners for B.Sc. Industrial Microbiology-II would be common with B.Sc. -II (Medical/Non-Medical).
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 6 B.Sc. (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Semester- IV)
PAPER TITLE: - MICROBIAL STRUCTURE AND PHYSIOLOGY
Max. Marks: 60 Lectures to be delivered: 75 Pass Marks: 35% (Each of 45 minutes duration) Time Allowed: 3 Hours
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE PAPER SETTER
The question paper will consist of three sections A, B and C. Section A and B will have four questions from the respective section of syllabus and will carry 9 marks each. Section C will consist of 12 short-answer type questions of 2 marks each which will cover the entire syllabus uniformly and will carry 24 marks in all. INSTRUCTIONS FOR CANDIDATES Candidates are required to attempt two questions from each section A and B and the entire section C, which is compulsory.
Section – A 1) Classification of microorganisms. General properties and physiology of archaebacteria including thermophiles, halophiles and methanogens. 2) General properties and physiology of eubacteria. 3) Biochemical components of microbial cell – structure and functions of organelles of microbial cell, 4) Role of cell wall and cell membrane in form and functions of microbial cells. Transportation – passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport and group translocation.
Section – B 5) Mode of nutrition in microbes, growth factors affecting growth of microorganisms: phases of growth, parameters for measuring growth. 6) Resting structures in microorganisms, physiology of endospore formation and its generation, control of microbial growth. 7) Nitrogen fixation, mechanism and energetics. 8) Regulation of metabolism: Enzyme induction, catabolite repression, feed- back inhibition and repression
Recommended Books
1. Alcamo, I.E. 2001. Fundamentals of Microbiology, John & Barlett Publishers. 2. Gottschalk. G Microbial metabolism Springer verlag. 3. Moat, A.G. and Foster, J.W. Microbial Physiology John Wiley and sons. 4. Pelczer, M.J.; Chan, E.C.S. and Krieg, N.R. 2003. Microbiology, Vth Ed., McGraw Hill. 5. Prescot, L.M.; Harley, J.P. and L. Kleig, D.A. 2005. Microbiology, WBC Publishers. 6. Stanier, R.Y.; Abelberg, E.A. and Ingraham, J.L. 2004. General Microbiology, IVth Ed., Mac Millan Press.
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 7 PRACTICAL
Practical Exercises for theory paper Microbial Structure and Physiology
1. Morphological and cultural characterization of bacteria. 2. Bacterial growth curve and measurement of bacterial growth. 3. IMViC Test. 4. Enumeration of bacteria based on their temperature optima. 5. Bacterial Motility using hanging drop technique. 6. To study antibiotic sensitivity profile of microbial isolates.
NOTE:
Candidates will be required to submit their original notebook of lab work initialed with date by their teacher at the time of practical examination. Practical examination shall be held in a single morning session from 9:00 a.m. to 1:00 p.m. Practical examination is to be conducted by the two external examiners.
Guideline pattern for the conduct of practical examination
Max. Marks: 25 Time Allowed: 8 Periods/week Practical exercises: 18 marks. Practical Records: 04 marks Viva Voice: 03 marks
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 8 B.Sc. (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Semester- IV)
Max. Marks: 60 Lectures to be delivered: 75 Pass Marks: 35% (Each of 45 minutes duration) Time Allowed: 3 Hours
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE PAPER SETTER
The question paper will consist of three sections A, B and C. Section A and B will have four questions from the respective section of syllabus and will carry 9 marks each. Section C will consist of 12 short-answer type questions of 2 marks each which will cover the entire syllabus uniformly and will carry 24 marks in all. INSTRUCTIONS FOR CANDIDATES Candidates are required to attempt two questions from each section A and B and the entire section C, which is compulsory.
Section – A 1) Structure and replication of nucleic acids. 2) Gene concept, genetic code, overlapping genes. Split genes, Transposons. 3) Types of mutations, mutagenesis, spontaneous mutation and induced mutation, 4) DNA damage and repair, frame shift mutations, mis-sense, non-sense mutation, Reversion and suppression.
Section – B 5) Bacterial genetics: conjugation, transformation, transduction and sexduction, plasmids.
6) Bacteriophage : General properties, structure and life cycle of T4 and -Phage 7) Gene regulation: operon model, tryptophan and Lac- operon 8) Microbes in genetic engineering and role of genetic engineering in molecular biology.
Recommended Books
1. Bainbridge BW. 1987. Genetics of Microbes, Blackic: Chapman and Hall, glasgow: New York. 2. Friefelder D. 1987. Microbial Genetics. Boston: Jones & Barlett Publ. 3. Friefelder D., Malay S.R. and Cronan J.E. 1994. Microbial Genetics. Jones and Bartlet Pub. New York.
PRACTICALS
Practical Exercise for Microbial Genetics 1) Estimation of total DNA in given suspension by spectroscopy. 2) Isolation of spontaneous mutants for antibiotic resistance. 3) To study replica plating. 4) To carry out isolation of (induced) mutants using UV. 5) Isolation of Genomic DNA from microorganisms.
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 9 NOTE:
Candidates will be required to submit their original notebook of lab work initialed with date by their teacher at the time of practical examination. Practical examination shall be held in a single morning session from 9:00 a.m. to 1:00 p.m. Practical examination is to be conducted by the two external examiners.
Guideline pattern for the conduct of practical examination
Max. Marks: 25 Time Allowed: 8 Periods/week Practical exercises: 18 marks. Practical Records: 04 marks Viva Voice: 03 marks
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 10 B.Sc. Part-II (Sem-IV) Environmental and Road Safety Awareness
Time Allowed: 3 hours Total Marks: 100 Total lectures: 50 Pass marks: 35 Theory Paper: 70 marks+ Internal Assessment 30 marks Instructions: a) The paper has been introduced from the session 2013-14. b) The paper will be taught in the Second year/fourth Semester of all the U.G. Courses (B.A., B.Com., B.Sc., Law, Engineering, Commerce, Agriculture etc.) except L.L.B. three year course and will be a qualifying paper only. The marks of this paper will not be counted towards final score of the under graduate degree. c) This will cover only preliminary and basics of the subject and the paper will be set accordingly. d) The question paper will consist of three sections A, B and C. Section A and B will have four questions in each section from the respective sections of the syllabus and will carry 10 marks each. Section C will consist of 15 short-answer type questions which will cover the entire syllabus uniformly and will carry 30 marks in all. e) Candidates are required to attempt two questions from each section A and B and the entire section C. Section – A Unit 1: The multidisciplinary nature of environmental studies. Definition, scope and importance Concept of Biosphere – Lithosphere, Hydrosphere, Atmosphere. Need for public awareness (6 lectures)
Unit – 2: Natural Resources – Renewable and non-renewable resources. Natural resources and associated problems. a) Forest resources: use and over exploitation, deforestation and its impact. b) Water resources: use and overutilization of surface and ground water and its impact. c) Mineral resources: use and effects on environment on over exploitation. d) Food resources: Effects modern agriculture, fertilizer-pesticide problem, water logging and salinity. e) Energy resources: Growing energy needs, renewable and non-renewable energy sources, use of alternate energy resources. f) Role of an individual in conservation of natural resources for sustainable development. (7 lectures)
Unit 3: Ecosystems Ecosystem and its components: Definition, structure and function; producer, consumer and decomposer. Types of Ecosystem (Introduction only) Food Chains, food web and ecological pyramids (6 lectures)
Unit – 4: Biodiversity and conservation Introduction – Definition: genetic, species and ecosystem diversity, value of biodiversity. Hot spots of biodiversity Threats to biodiversity: habitat loss, poocting of wildlife, man-wildlife conflicts. Endangered and endemic species of India. Conservation of Biodiversity. (6 lectures)
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 11 Section – B Units 5: Environmental Pollution Definition, causes, effects and control measures of a) Air pollution b) Water pollution c) Soil pollution d) Marine pollution e) Noise pollution f) Thermal pollution g) Nuclear hazard
Role of an individual in prevention of pollution. Solid waste management: vermin-composting. Disaster management : Floods, earthquake, cyclone and landslides (7 lectures)
Unit 6: Social Issues and the Environment Urban problems related to energy. Water conservation rain water harvesting, water shed management. Resettlement and rehabilitation of people: its problems and concerns. Climate changes, global warming, acid rain, ozone layer depletion. Consumerism and waste products. Population explosion – Family welfare programme (6 lectures)
Unit 7: Introduction to Environmental Protection Laws in India Environmental Protection Act. Air (Prevention and control of pollution) Act. Water (Prevention and Control of pollution) Act. Wild life Protection Act. Forest Conservation Act. Issues involved in the enforcement of environmental legislation. (6 lectures)
Unit 8: Road safety Awareness Concept and significance of Road safety. Traffic signs. Traffic rules. Traffic Offences and penalties. How to obtain license. Role of first aid in Road Safety. (6 lectures)
RUSA B.Sc (Industrial Microbiology) Part-II (Sem-III & IV) 19-05-2015(BOS) 12