RELATIVE PRONOUNS AND CLAUSES
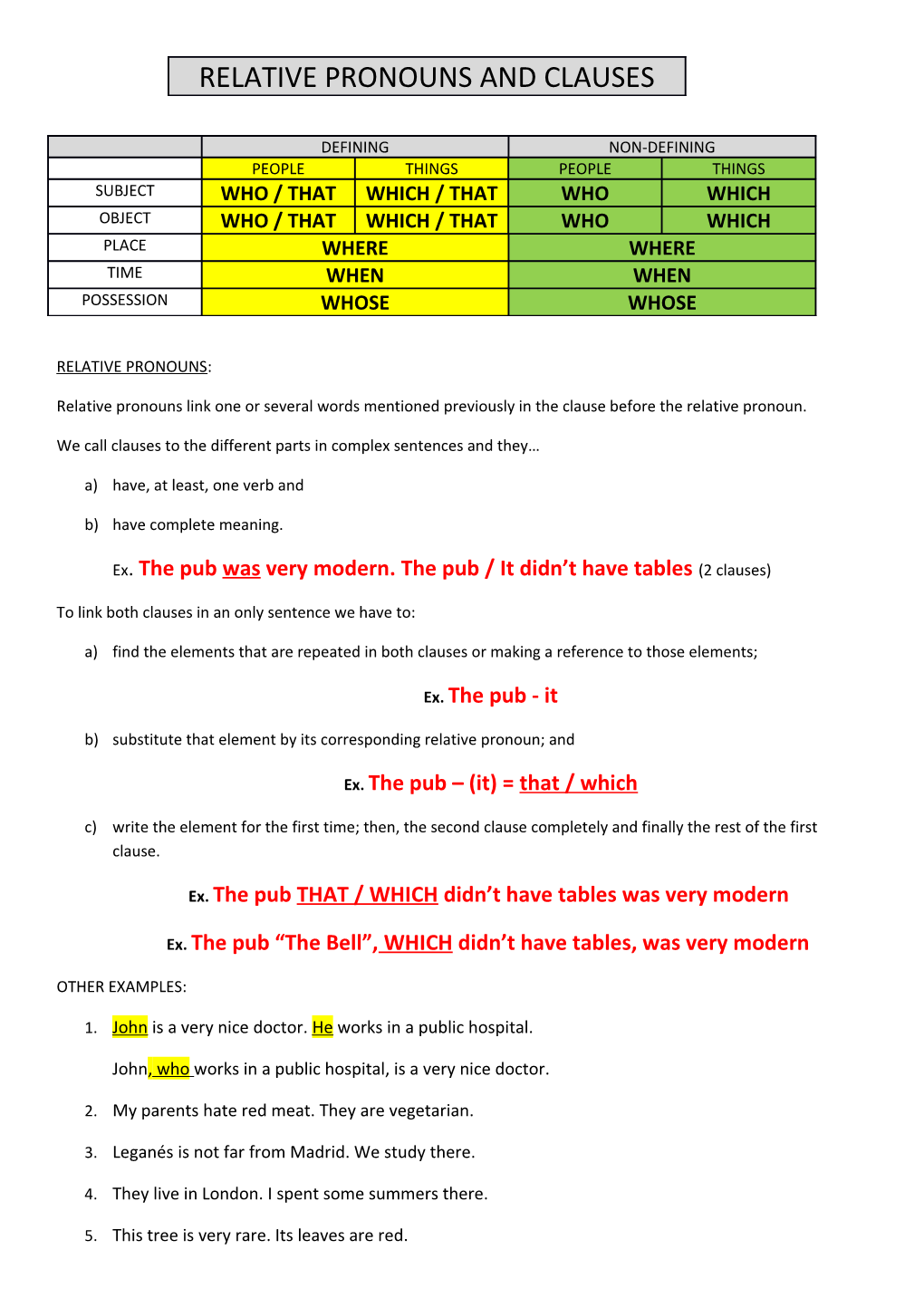
DEFINING NON-DEFINING PEOPLE THINGS PEOPLE THINGS SUBJECT WHO / THAT WHICH / THAT WHO WHICH OBJECT WHO / THAT WHICH / THAT WHO WHICH PLACE WHERE WHERE TIME WHEN WHEN POSSESSION WHOSE WHOSE
RELATIVE PRONOUNS:
Relative pronouns link one or several words mentioned previously in the clause before the relative pronoun.
We call clauses to the different parts in complex sentences and they…
a) have, at least, one verb and
b) have complete meaning.
Ex. The pub was very modern. The pub / It didn’t have tables (2 clauses)
To link both clauses in an only sentence we have to:
a) find the elements that are repeated in both clauses or making a reference to those elements;
Ex. The pub - it
b) substitute that element by its corresponding relative pronoun; and
Ex. The pub – (it) = that / which
c) write the element for the first time; then, the second clause completely and finally the rest of the first clause.
Ex. The pub THAT / WHICH didn’t have tables was very modern
Ex. The pub “The Bell”, WHICH didn’t have tables, was very modern
OTHER EXAMPLES:
1. John is a very nice doctor. He works in a public hospital.
John, who works in a public hospital, is a very nice doctor.
2. My parents hate red meat. They are vegetarian.
3. Leganés is not far from Madrid. We study there.
4. They live in London. I spent some summers there.
5. This tree is very rare. Its leaves are red. 6. The car doesn’t work properly. It is Czech.
7. The lady is an actress. She is not very old.
8. The students always want to work. They are quite clever.
9. Michael Jackson is having problems in USA. He is very rich.
10. His father likes gardening. He is a lawyer.
THE USE OF RELATIVE PRONOUNS
1. DIFFERENT USES:
A B
Peter: Rod Hudson has died. ROD HUDSON DIES Jane: Who? The actor Rod Hudson, who starred in films such as “Giant” and P.: You know. The film star who played the tough husband in “Written on the Wind”, has died after a long illness. Rod “Giant”. Hudson’s most famous role was as a tough husband in the film J.: I don’t think I’ve seen that. “Giant”, which broke all box-office records. P.: Yes, you have. It’s the film (which/that) we saw on TV last night. J: Oh, I remember.
A: These clauses identify which film star and which film the speaker means. They are called: DEFINING / IDENTIFYING.
B: These clauses add extra information about Rod Hudson and “Giant”. They are called NON-DEFINING / ADDING
2. SOME EXAMPLES:
The woman who always wears a yellow dress is my sister. María, who always wears a yellow dress, is my sister. The river which flows through Madrid is the Manzanares. The Manzanares, which flows through Madrid, is a beautiful The place where we usually go is not far from here. river. Madrid, where we usually go, is not far from here.
A: These clauses identify which one we mean. For example, the clause “who always wears a yellow dress tells us which woman”- Without the relative clause the sentence would be incomplete.
The defining clause does not have commas.
Most relative clauses are defining.
They are common in speech and writing.
B: These clauses add extra information to something already identified. For example, the clause “who always wears a yellow dress” adds information about María. – The sentence is complete and the relative clause only adds extra information. The non-defining clause has commas round it.
They can be rather formal.
They are common in news reports.
3. RELATIVE PRONOUNS:
In defining clauses we can use: In non-defining clauses we can use: Who – whom – which – whose – where – when – Who – whom – which – whose – where when – that (but not that) You know that person who/that invited us. Peter, who invited us, is a nice person. The person whom/that we invited hasn’t come. John, whom we invited yesterday, didn’t come to the party. Towns which/that attract tourists are usually crowded. Madrid, which attracts many tourists, is usually crowded. The man whose car was stolen had to buy a new one. Jane, whose car was stolen, had to buy a new one. The city where we live is very crowded. Leganés, where we live, is also very crowded. Sometimes we can leave out the pronouns: Ex. The man (who) we saw yesterday is my neighbor.
A: Sometimes we can leave out / omit the pronoun in defining object clauses:
Ex. The man (who-m) we saw yesterday is my neighbour. / This is my neighbor. We saw him yesterday.
Have you seen the book (that) I was reading? / I was reading a book. Have you seen it?
B: We cannot leave out / omit the pronoun
Ex. Sam, whom we saw yesterday, is my neighbor.
The book “El Quijote”, which I was reading is really good.
RELATIVE CLAUSES – EXERCISES
1. Write a sentences with WHO or THAT as an OBJECT of the underlined part.
Ex. The shirt doesn’t fit. Which shirt? Peter’s. He bought it yesterday.
The shirt that Peter bought yesterday doesn’t fit.
a. He is a millionaire. Who is? Angela knows him.
The man ______
b. The vase was extremely valuable. What vase? You know. John broke it.
The vase______
c. It’s really nice. What is? The jacket. You wore it last night.
The jacket ______2. Complete the advertisements. Use relative clauses without a pronoun.
Ex. Heno de Pravia soap. Beautiful people use it. It’s the soap beautiful people use.
a. A Honda car. You can afford it.
- It’s ______
b. ‘Braveheart’. People want to see this film.
- It’s ______
c. ‘Lindt chocolates’. You enjoy them.
- It’s ______
d. ‘Pronto cleaner’. You can trust it.
- It’s ______
e. ‘ “Muy interesante” magazine’. Clever people read it.
- It’s ______
3. Match the phrases and write the definitions
a. A kitchen a cupboard somebody travels to it.
b. A microphone a piece of furniture you can either sit or sleep on it.
c. A sofa bed an instrument you can make holes with it.
d. A drill a room we keep valuable things in it.
e. A destination a passage you cook in it.
f. A corridor the place people speak into it.
g. A safe a tool people walk along it.
4. Join sentences with a relative pronoun.
a. The coffee shop was very modern. It didn’t have tables.
b. John is a very nice doctor. He works in a public hospital.
c. My parents hate red meat. They are vegetarians.
d. The car doesn’t work properly. It is Japanese.
e. They live in London. I spent some summers there.
f. The students don’t want to work. They are always very lazy.
g. Felipe González likes gardening. He is a lawyer.
h. Thetree is very rare. Its leaves are purple. 5. Join the sentences with a relative pronoun. Omit the relative when possible.
a. He found the letter. He was looking for it.
b. Carlos Arguiñano is a cook. He’s working for TVE now.
c. The hotel is called “The Palace”. Famous politicians go there.
d. Victor Manuel is a singer. His songs are very popular.
e. Where did you buy the jeans? You were wearing them at the party last night.
f. Cela is a writer. He received the Nobel Prize in 1969.
g. Sharon Stone is a famous film star. Everybody knows her.
h. Bon Jovi is a pop group. They will give a concert inSpain next June.
i. We bought a table. It only had three legs.
j. That picture is a Renoir. You are looking at it.
k. Atocha is a railway station. The AVE starts its journey there.
l. This is the school. Its windows are always open.
6. Complete the text, using who, which, where, whose or leaving a blank.
Billie Holiday , American singer (1913-1959)
Billie Holiday is a show-business figure ______will never be forgotten. She was one of the greatest nightclub singers ______the world has ever known. She heard her first jazz music in the Baltimore club ______she used to sing as a child. She became a successful jazz singer and later toured with a man ______band was well-known all over the world – Count Basie.
Holiday had the sort of voice ______mad songs like ‘The Man I love’ unforgettable.
However, her personal life was never happy. The man ______she really loved was her first husband, a heroin addict. It was her attempt to cure him ______caused her own addiction and ______turned her life into a pattern of hospital and prison.
7. What do you know about Charles Dickens? Complete the sentences with who, which or whose. If “ who” and “which” are not necessary, don’t write them in.
Charles Dickens’ biography
Charles Dickens was an English writer ______lived from 1812 to 1870. The books ______he wrote are read in many countries. Dickens, ______family was very poor, had to start work when he was ten years old. In England at that time, people ______could not pay their debts were sent to prison. This happened to Dicken’s father, ______first name was John. This meant that Dickens, ______was only a boy, had to visit his father in prison. Later, Dickens wrote books based on people ______he had known and places ______he had lived in. In ‘David Copperfield’ he wrote about the visits ______he paid to his father inprison. In some of his books he wrote about terrible schools like the one ______he went to himself. In ‘Oliver Twist’ he wrote about children ______were poor and sometimes orphans – children ______parents have died.
Dickens is known for making up characters like Uriah Heep, Fagin and the Artful Dodger, ______names are known even to some people ______have no read the books. Dickens, ______was also a good actor, used to read his stories to audiences in England and America.
He married a woman ______name was Catherine and ______was the daughter of his first publisher.