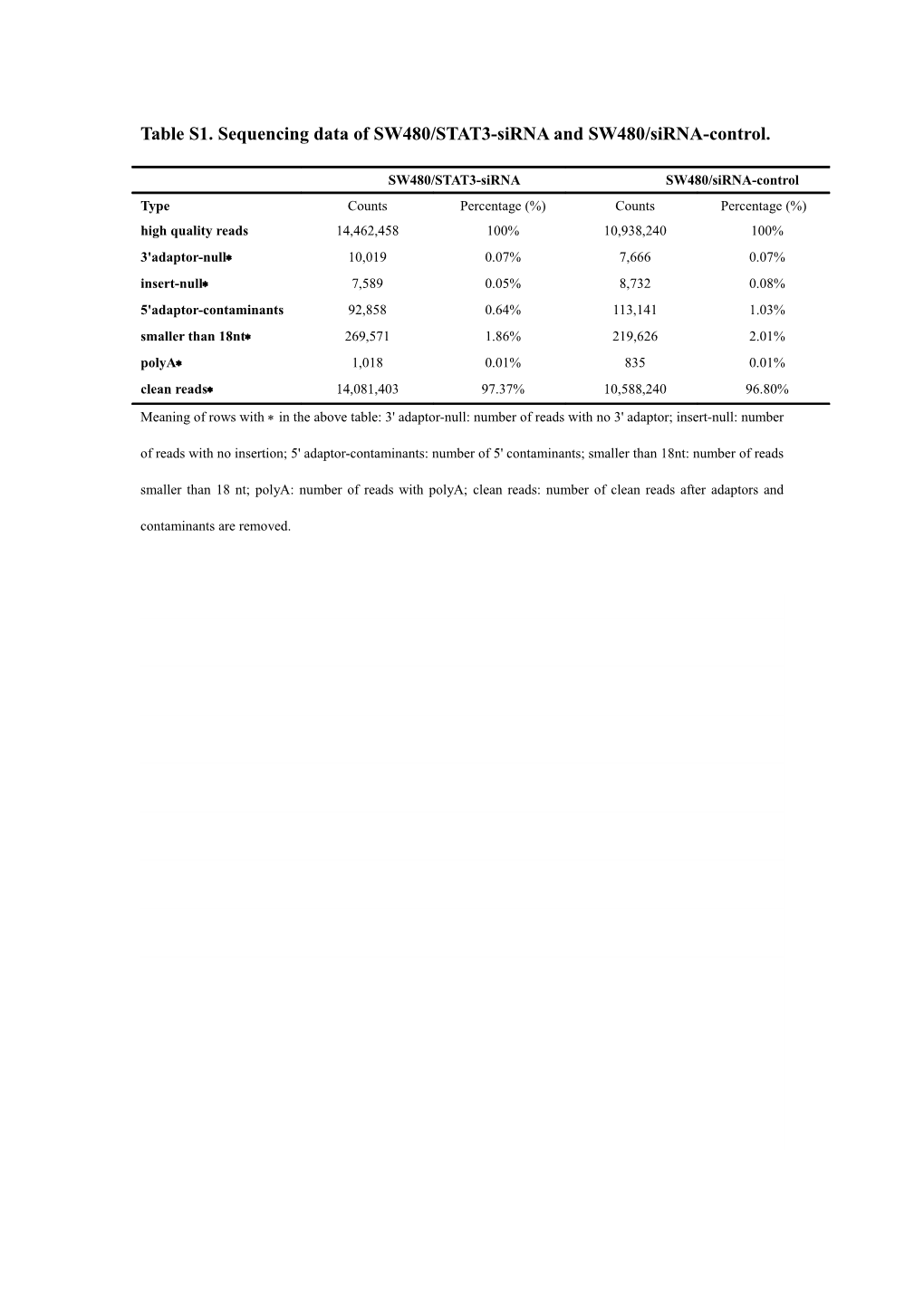
Table S1. Sequencing data of SW480/STAT3-siRNA and SW480/siRNA-control.
SW480/STAT3-siRNA SW480/siRNA-control Type Counts Percentage (%) Counts Percentage (%) high quality reads 14,462,458 100% 10,938,240 100% 3'adaptor-null 10,019 0.07% 7,666 0.07% insert-null 7,589 0.05% 8,732 0.08% 5'adaptor-contaminants 92,858 0.64% 113,141 1.03% sadaptor-contaminantsmaller than 18nt 269,571 1.86% 219,626 2.01% polyA 1,018 0.01% 835 0.01% clean reads 14,081,403 97.37% 10,588,240 96.80% Meaning of rows with in the above table: 3' adaptor-null: number of reads with no 3' adaptor; insert-null: number of reads with no insertion; 5' adaptor-contaminants: number of 5' contaminants; smaller than 18nt: number of reads smaller than 18 nt; polyA: number of reads with polyA; clean reads: number of clean reads after adaptors and contaminants are removed. Table S2. Gene Ontology enrichment analysis of predicted targets of differentially expressed novel miRNAs.
GO ID GO term Bonferroni Correction GO:0022008 neurogenesis 8.92E-09 GO:0048468 cell development 1.28E-08 GO:0006366 transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter 1.80E-08 GO:0006357 regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II 2.78E-08 GO:0048699 generation of neurons 5.47E-08 GO:0048856 anatomical structure development 7.96E-08 GO:0048731 system development 1.13E-07 GO:0007399 nervous system development 1.13E-07 GO:0048869 cellular developmental process 4.83E-07 GO:0007275 multicellular organismal development 4.98E-07 GO:0032502 developmental process 1.28E-06 GO:0019222 regulation of metabolic process 1.32E-06 GO:0030030 cell projection organization 1.73E-06 GO:0030182 neuron differentiation 3.84E-06 GO:0019219 regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and 3.97E-06 nucleic acid metabolic process
GO:0080090 regulation of primary metabolic process 4.63E-06 GO:0080090 regulation of primary metabolic process 4.63E-06 GO:0030154 cell differentiation 5.19E-06 GO:0051171 regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process 5.79E-06 GO:0009889 regulation of biosynthetic process 7.11E-06 GO:0031326 regulation of cellular biosynthetic process 9.59E-06 GO:0031323 regulation of cellular metabolic process 1.18E-05 GO:0048513 organ development 9.95E-05 GO:0065007 biological regulation 1.00E-04 GO:0048666 neuron development 1.20E-04 GO:0009888 tissue development 1.70E-04 GO:0016043 cellular component organization 2.60E-04 GO:0051252 regulation of RNA metabolic process 3.20E-04 GO:0060255 ®ulation of macromolecule metabolic process 3.30E-04 GO:0009653 anatomical structure morphogenesis 5.20E-04 GO:0031175 neuron projection development 5.50E-04 GO:0006355 regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent 6.20E-04 GO:0007417 central nervous system development 6.20E-04 GO:0010556 regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process 6.40E-04 GO:0045449 regulation of transcription 7.40E-04 GO:0010556 regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process 9.20E-04 GO:0050789 regulation of biological process 9.40E-04 GO:0010468 regulation of gene expression 1.13E-03 GO:0060255 regulation of macromolecule metabolic process 1.13E-03 GO:0065008 regulation of biological quality 3.16E-03 GO:0009987 cellular process 3.49E-03 Table S3. The KEGG analysis of predicted targets mediated by novel miRNAs.
Term Pathway Gene Percentage Bonferroni correction count (%) hsa04012 ErbB signaling pathway 288 1.32 2.17E-02 hsa04010 MAPK signaling pathway 736 3.36 2.17E-02 hsa04330 Notch signaling pathway 120 0.55 2.63E-02 hsa05212 Pancreatic cancer 179 0.82 2.88E-02 hsa00514 Other types of O-glycan biosynthesis 109 0.50 3.83E-02 Figure S1. Size distributions of small RNAs in SW480/siRNA-control and
SW480/STAT3-siRNA cells. 22-nucleotide small RNAs are enriched in both samples, which is in line with the typical size of miRNAs. Figure S2. Base compositions of small RNAs in SW480/siRNA-control and
SW480/STAT3-siRNA cells. Each color represents the small RNA tags
whose first base is a certain base. Most 22-nt small RNAs begin with the
base “U”. The 23-nt small RNAs display a bias to “A” and “U” at first base
in SW480/STAT3-siRNA while only “U” in SW480/siRNA-control. Figure S3. The proportions of unique common tags and total common tags of small
RNAs detected in SW480/siRNA-control and SW480/STAT3-siRNA
cells. The very few unique common tags indicate that SW480/STAT3-siRNA
presents a distinctive small RNA profile compared to SW480/siRNA-control. Figure S4. Mapping of small RNAs from SW480/siRNA-control and SW480/STAT3-
siRNA cells onto human chromosomes, respectively. Red lines indicate
miRNAs that are located on the antisense chains of genome while the blue
ones are on the sense chains.