Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5: Geometry Unit 5 Three Dimensional Shapes
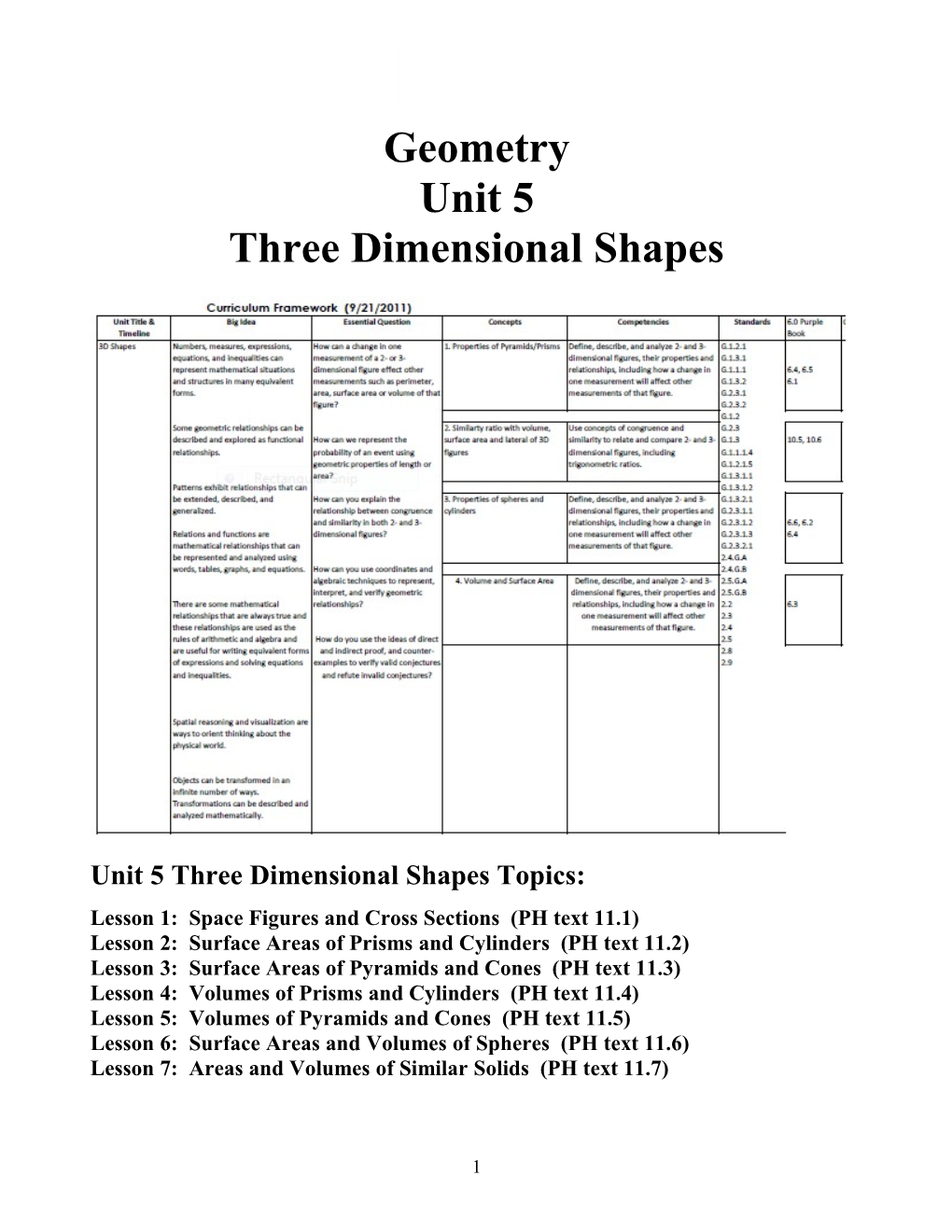
Unit 5 Three Dimensional Shapes Topics: Lesson 1: Space Figures and Cross Sections (PH text 11.1) Lesson 2: Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders (PH text 11.2) Lesson 3: Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones (PH text 11.3) Lesson 4: Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders (PH text 11.4) Lesson 5: Volumes of Pyramids and Cones (PH text 11.5) Lesson 6: Surface Areas and Volumes of Spheres (PH text 11.6) Lesson 7: Areas and Volumes of Similar Solids (PH text 11.7)
1 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Lesson 1: Space Figures and Cross Sections (PH text 11.1) Objective: to recognize polyhedral and their parts to visualize cross sections of space figures polyhedron – a three-dimensional figure, or space figure, whose sides are all polygons face –
edge –
vertex –
net – a two-dimensional pattern that you can fold to form a three-dimensional figure. (Packagers use nets to design boxes.)
EXPLORE! Use the templates and models provided to explore polyhedrons and their nets. Record your observations.
Polyhedron (name) # faces (F) # Vertices (V) # edges (E)
Notice the pattern. Write a formula for the number of edges, E, in terms of F and V. The Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler discovered that this relationship is true for any polyhedron, so it is known as Euler’s Formula.
Euler’s Formula-
2 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Verify Euler’s Formula.
Platonic Solids - “regular” polyhedrons:
Tetrahedron
Hexahedron
Octahedron
Dodecahedron
Icosahedron
Note: Plato was a Greek philosopher (427-347 B.C.) who discussed these regular solids extensively, and associated each of the four classical elements (earth, air, water, fire) with one of the regular solids.
Interactive website:
3 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5: http://www.learner.org/interactives/geometry/3d_prisms.html Cross Section – the intersection of a ______and a ______
Practice:
HW: p.691 #5-23, 26, 38, 51-53, define lesson 2 vocabulary
4 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
NOTE: Be sure you can solve literal equations, as in the algebra review on p.698.
5 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Lesson 2: Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders (PH text 11.2) Objective: to find the surface area and lateral area of prisms and cylinders
Vocabulary: prism –
base –
lateral face –
right prism –
oblique prism –
lateral area –
surface area –
Theorem 11-1 Lateral and Surface Areas of a Right Prism The lateral area of a right prism is the product of the perimeter of the base and the height. L. A . = ph The surface area of a right prism is the sum of the lateral area and the areas of the two bases. S. A .= L . A . + 2 B
6 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Examples:
1. Right Triangular Prism: Height is 5 cm. Base is an equilateral triangle with sides 2 cm. Find the lateral area, then the surface area.
2. Cube: Find the lateral area and surface area of a cube with side 5 inches.
More vocabulary: cylinder –
right cylinder – oblique cylinder –
Theorem 11-2 Lateral and Surface Areas of a Right Cylinder The lateral area of a right cylinder is the product of the perimeter of the circumference base and the height of the cylinder. L. A .= 2p rh or L. A . = p dh The surface area of a right cylinder is the sum of the lateral area and the areas of the two bases. S. A .= L . A . + 2 B
7 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Examples: 3. Right Cylinder: Height is 6inches. Radius of the base is 4 in. Find the lateral area, then the surface area.
4. Right Cylinder: A capped section of pipe measures 500 feet in length. Its diameter is 3 ft. Find the lateral area, then the surface area.
Practice:
HW: p.704 #7-21, 23, 38-42 even, define lesson 3 vocabulary 8 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Lesson 3: Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones (PH text 11.3) Objective: to find the surface area of a pyramid and a cone
Vocabulary – pyramid –
base –
lateral face –
vertex –
altitude –
height –
slant height –
regular pyramid –
lateral area –
surface area –
9 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Theorem 11-3 Lateral and Surface Areas of a Regular Pyramid The lateral area of a regular pyramid is half the product of the perimeter of the base and the slant height. 1 L. A . = pl 2 The surface area of a regular pyramid is the sum of the lateral area and the area of the base. S. A .= L . A . + B
Examples:
1. Regular Pyramid with square base Edges of base are 149 feet Slant height of 800 feet Find the lateral area, then the surface area
2. Regular Hexagonal Pyramid Bases edges of 10 meters Slant Height of 35 meters Find the lateral area and the surface area
10 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Vocabulary: cone – right cone – altitude – height – slant height –
Theorem 11-4 Lateral and Surface Areas of a Right Cone The lateral area of a right cone is half the product of the circumference of the base and the slant height. 1 L. A .= 鬃 2p r l or L. A . = p rl 2 The surface area of a right cone is the sum of the lateral area and the area of the base. S. A .= L . A . + B
Examples: 3. Cone: Radius of 10 meters Slant Height of 35 meters Find the lateral area and the surface area
11 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
HW: p.713 #9-22, 26-28
Mini Project: Package Construction Due date: ______(10% will be deducted for each day it is late.) Choose a product that you enjoy using. Design and make a new package for the product. The package must be completely your own creation, made out of a sturdy material (heavier than construction paper). Calculate the surface area and volume of your package, and describe the advantages (at least two) it has over the current package. ______(10 pts) Package sample – basic construction ______(2 pts) Package sample – exceptional neatness ______(2 pts) Package sample – decorated ______(3 pts) Surface area calculated (calculations shown and explained – neatly) ______(3 pts) Volume calculated (calculations shown and explained – neatly) ______(5 pts) Advantages described (in a typed, well constructed, grammatically correct paragraph)
______(25 pts) TOTAL POINTS
12 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Lesson 4: Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders (PH text 11.4) Objective: to find the volume of a prisms and cylinders volume –
Theorem 11-5 Cavalieri’s Principle If two space figures have the same height and the same cross-sectional area at every level, then they have the same volume.
Theorem 11-6 Volume of a Prism The volume of a prism is the product of the area of a base and the height of the prism. V= Bh
Examples: 1) Find the volume. 2) Base is an equilateral triangle. Find the volume.
10 cm
12 cm 12 cm 15 cm
5 cm
3) The volume of a triangular prism is 1860 cm3. Its base is a right triangle with legs 24 cm and 10 cm. a) Draw and label a diagram. b) Find the area of the base of the prism. c) Find the height of the prism.
13 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Theorem 11-7 Volume of a Cylinder The volume of a cylinder is the product of the area of a base and the height of the cylinder. V= Bh or V= p r2 h
Examples: 4. For a right cylinder with a diameter of 120 feet and a height of 50 feet, find the volume.
5. Draw an oblique prism with a radius of 8 ft. and height of 12 ft. Find the volume.
6.
Practice:
HW: p.721 #1-25
14 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Lesson 5: Volumes of Pyramids and Cones (PH text 11.5) Objective: to find the volumes of pyramids and cones
Theorem 11-8 Volume of a Pyramid The volume of a pyramid is one third the product of the area of the base and the height of the pyramid. 1 V= Bh 3
Examples:
1. Square Pyramid Base length of 15 cm Height to 22 cm Find the volume
2. Square Pyramid Base length of 16 meters Slant height of 10 m Find the volume
3.
15 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Theorem 11-9 Volume of a Cone The volume of a cone is one third the product of the area of the base and the height. 1 1 V= Bh or V= p r2 h 3 3
Examples:
4. Right cone with radius 5 cm and height of 8 cm Find the volume
5. An oblique cone has a height of 6 m and radius of 2 m. What is its volume?
6.
16 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Practice:
HW: p.729 #6-19, 23-25, 30-32, 37
17 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Lesson 6: Surface Areas and Volumes of Spheres (PH text 11.6) Objective: to calculate the surface area and volume of spheres sphere – center – great circle – circumference of the sphere – hemisphere –
Theorem 11-10 Surface Area of a Sphere The surface area of a sphere is four times the product of p and the square of the radius of the sphere. S. A .= 4p r 2
Example 1: Find the surface area.
18 in
Example 2: A sphere is encased in a cube that has sides 24 cm. The surface of the sphere is tangent to the sides of the cube. Find the surface area of the sphere.
18 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Theorem 6-11 Volume of a Sphere The volume of a sphere is four thirds the product of p and the cube of the radius of the sphere. 4 V= p r 3 3 Examples: 3 & 4) Find the volume of each sphere.
40 cm 23 ft
5) If V= 904.78 cm3 , what is the surface area?
6) A cube with sides 24cm is inscribed within a sphere. All vertices of the cube touch the interior surface of the sphere. Find the volume of the sphere.
19 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Practice:
HW: p.737 #6-25, 30, 49-54
20 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Lesson 7: Areas and Volumes of Similar Solids (PH text 11.7) Objective: to compare and find the areas and volumes of similar solids.
Similar solids have the same shape and all their corresponding dimensions are proportional. The ratio of corresponding linear dimensions (similarity ratio) is the scale factor. Note: Any two cubes are similar. Any two spheres are similar.
Examples:
Theorem 11-12 Areas and Volumes of Solids If the scale factor of two similar solids is a:b, then: a) the ratio of their corresponding areas is a2:b2 b) the ratio of their volumes is a3:b3
These prisms are similar.
The ratio of the side lengths is ______.
The ratio of the surface areas is ______.
The ratio of the volumes is ______.
21 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Examples: 5) The surface areas of two similar cylinders 80 m2 and180 m 2 . The volume of the larger cylinder is324 m3 . Find the volume of the smaller cylinder.
2 2 6) The surface area of two similar solids are 160m and 250m . 3 The volume of the larger one is 250 m . What is the volume of the smaller one?
7) There are 750 toothpicks in a regular-size box. If a jumbo box is made by doubling all the dimensions of the regular box, how many toothpicks will the jumbo box hold?
8) A cylindrical can holds 16 ounces of water. How many gallons of water does a similarly-shaped can hold if its radius and height are four times the radius and height of the smaller can? (1 gal = 128 oz)
9) A regular pentagonal prism with base edges 9 cm long is enlarged to a similar prism with base edges 36 cm long. By what factor is its volume increased?
22 Geometry 2206 Mrs. Bondi Unit 5:
Practice:
HW: p. 746 #5-22, 31-38 23