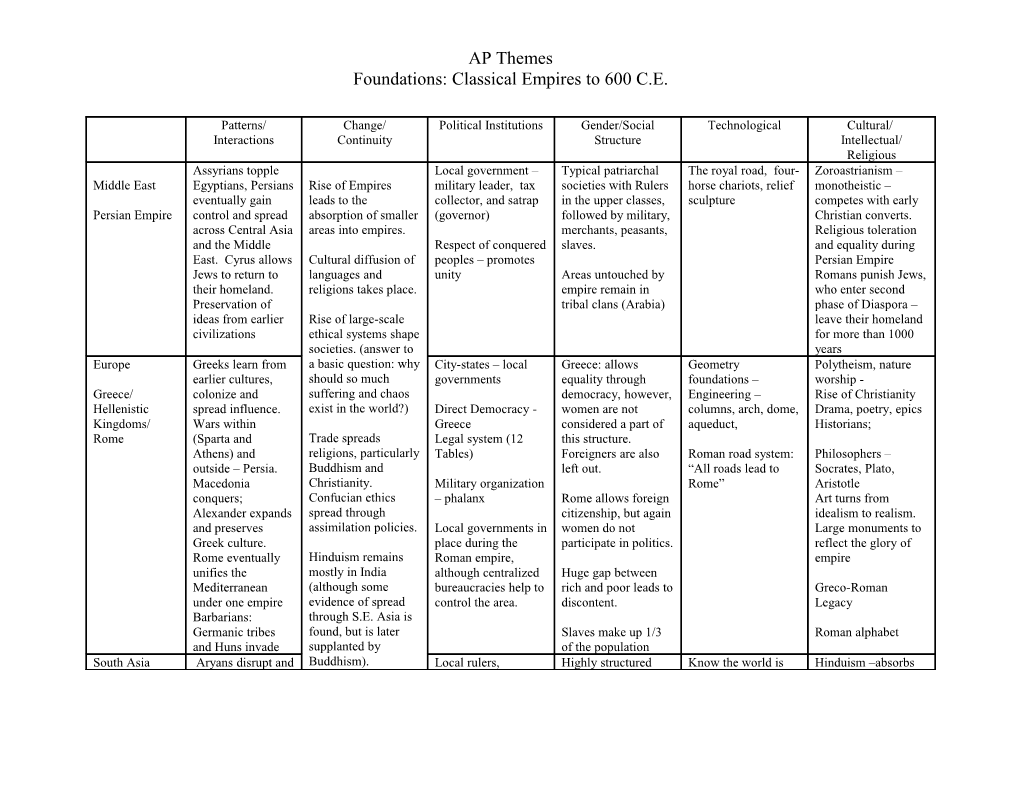
AP Themes Foundations: Classical Empires to 600 C.E.
Patterns/ Change/ Political Institutions Gender/Social Technological Cultural/ Interactions Continuity Structure Intellectual/ Religious Assyrians topple Local government – Typical patriarchal The royal road, four- Zoroastrianism – Middle East Egyptians, Persians Rise of Empires military leader, tax societies with Rulers horse chariots, relief monotheistic – eventually gain leads to the collector, and satrap in the upper classes, sculpture competes with early Persian Empire control and spread absorption of smaller (governor) followed by military, Christian converts. across Central Asia areas into empires. merchants, peasants, Religious toleration and the Middle Respect of conquered slaves. and equality during East. Cyrus allows Cultural diffusion of peoples – promotes Persian Empire Jews to return to languages and unity Areas untouched by Romans punish Jews, their homeland. religions takes place. empire remain in who enter second Preservation of tribal clans (Arabia) phase of Diaspora – ideas from earlier Rise of large-scale leave their homeland civilizations ethical systems shape for more than 1000 societies. (answer to years Europe Greeks learn from a basic question: why City-states – local Greece: allows Geometry Polytheism, nature earlier cultures, should so much governments equality through foundations – worship - Greece/ colonize and suffering and chaos democracy, however, Engineering – Rise of Christianity Hellenistic spread influence. exist in the world?) Direct Democracy - women are not columns, arch, dome, Drama, poetry, epics Kingdoms/ Wars within Greece considered a part of aqueduct, Historians; Rome (Sparta and Trade spreads Legal system (12 this structure. Athens) and religions, particularly Tables) Foreigners are also Roman road system: Philosophers – outside – Persia. Buddhism and left out. “All roads lead to Socrates, Plato, Macedonia Christianity. Military organization Rome” Aristotle conquers; Confucian ethics – phalanx Rome allows foreign Art turns from Alexander expands spread through citizenship, but again idealism to realism. and preserves assimilation policies. Local governments in women do not Large monuments to Greek culture. place during the participate in politics. reflect the glory of Rome eventually Hinduism remains Roman empire, empire unifies the mostly in India although centralized Huge gap between Mediterranean (although some bureaucracies help to rich and poor leads to Greco-Roman under one empire evidence of spread control the area. discontent. Legacy Barbarians: through S.E. Asia is Germanic tribes found, but is later Slaves make up 1/3 Roman alphabet and Huns invade supplanted by of the population South Asia Aryans disrupt and Buddhism). Local rulers, Highly structured Know the world is Hinduism –absorbs AP Themes Foundations: Classical Empires to 600 C.E.
change society. government has social divisions – round, accurate many local gods. Mauryan and Invasions by By the end of the control of trade in caste system. mathematical Buddhism – state Gupta Empires Hellenistic period, most of the some areas Restrictive, racially calculations – extend religion during kingdoms into Eurasian continent, based. Π to four digits, Ashoka’s reign –then northern areas – and Africa move Government employs concept of zero, fades from India linguistic diffusion, toward monotheistic spies. Women are lower accurate surgery. Gupta poetry, drama cultural spread, religious structures. than men and kept Art reflects religion Greeks and there through the Buddhist pillars, Persians, Eastern Asia highly caste system. monuments, rock unification through unified through shelters Ashoka language, ethical Patriarchal systems Merchants engage system, and a policy except in southern in trade along the of assimilation that India, where Silk Road as remains influential matriarchies exist middlemen, Indian for 2000 years. Ocean trade brings Buddhism to S.E. Americas remain in Asia isolation from the East Asia Deal with nomadic rest of the world and Dynasties based on Family important Silk, paper, Ancestor worship invasions by do not develop the the Mandate of Filial piety agricultural Daoism Qin Dynasty constructing the major monotheistic Heaven (emperor) Confucianism: Five improvements: plow, Confucianism and Han China Great Wall. ethical systems and Legalism (Qin) relationships water mills, Spread of Buddhism some of the Peasants in the wheelbarrow, at the end. Expand empire into technology ( notably Highly centralized middle of society compass, roads, North Korea and the wheel). government Merchants at the canals, large-scale Terracotta warriors – Vietnam – bottom agricultural realistic maintain through Government control Women subjugated improvements. assimilation of commerce through Silk policies. Confucianism Confucian scholars – Large gulf between Scholarship is based Trade with Rome merit based officials rich and poor leads to on studying the via the Silk Road rebellion writings of Confucius (also linked to High taxes for the India) poor
Africa Bantu migrations Monarchy in Kush Looser gender Spread of iron, Polytheistic, continue. and Aksum relations continue. terrace farming in animism, belief in a AP Themes Foundations: Classical Empires to 600 C.E.
Kush, Aksum International trade some areas, only sub- single creator-god in Aksum – minted Village Chiefs Most societies are Saharan written Aksum becomes coins – Christianity Clans (extended based on matriarchal language Christian introduced. family units) systems. (hieroglyphs), Griots – oral Camel introduced Basic unit: family historians from Arabia in first century C.E. – stelae (large stone many pillars) TransSaharan Routes established – salt and gold important Indian Ocean trade expands, introduction of bananas Americas Religion-based Religiously linked irrigation and Polytheistic, Influence of No apparent rulers farming techniques ritualistic sacrifice, Continue with mother cultures organization in (cultivation of maize jaguar spirit Olmec, Chavin evident Chavin culture and potatoes) Monumental stone Later: Zapotec, Trade networks Domestication of sculptures, pyramids, Nazca and throughout North llamas and turkeys ball courts, pottery, Moche arise and Mesoamerica – existence of ball courts, precious gems, stones, and spread of maize cultivation