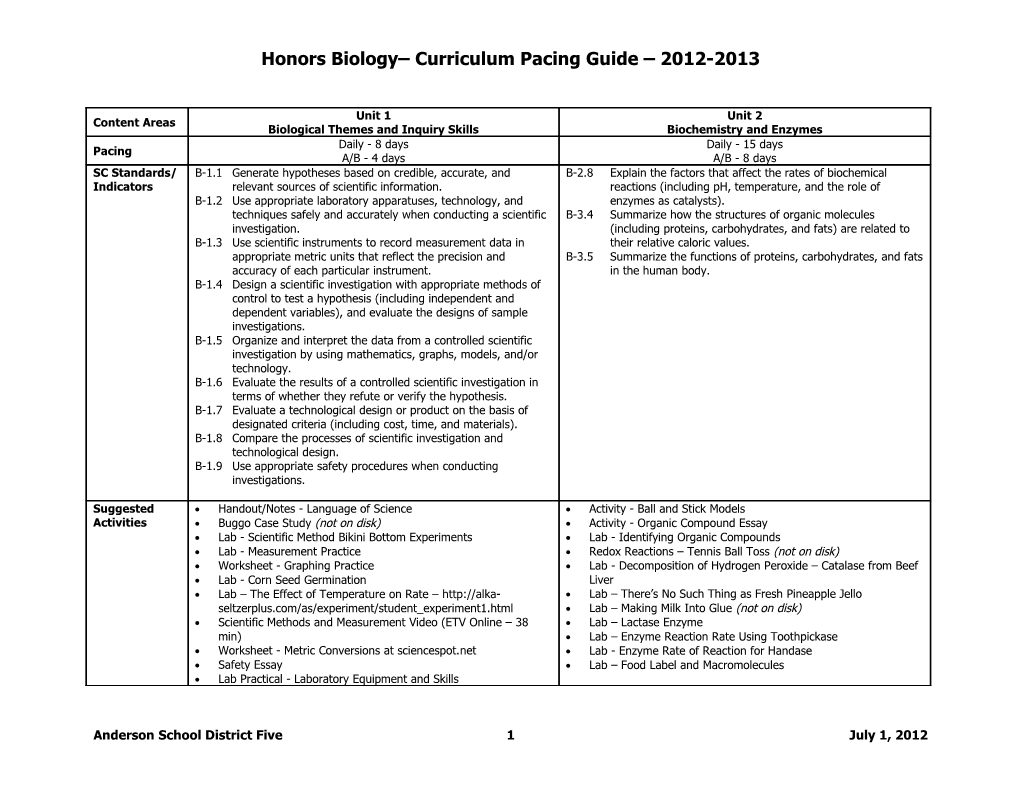
Honors Biology– Curriculum Pacing Guide – 2012-2013
Unit 1 Unit 2 Content Areas Biological Themes and Inquiry Skills Biochemistry and Enzymes Daily - 8 days Daily - 15 days Pacing A/B - 4 days A/B - 8 days SC Standards/ B-1.1 Generate hypotheses based on credible, accurate, and B-2.8 Explain the factors that affect the rates of biochemical Indicators relevant sources of scientific information. reactions (including pH, temperature, and the role of B-1.2 Use appropriate laboratory apparatuses, technology, and enzymes as catalysts). techniques safely and accurately when conducting a scientific B-3.4 Summarize how the structures of organic molecules investigation. (including proteins, carbohydrates, and fats) are related to B-1.3 Use scientific instruments to record measurement data in their relative caloric values. appropriate metric units that reflect the precision and B-3.5 Summarize the functions of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats accuracy of each particular instrument. in the human body. B-1.4 Design a scientific investigation with appropriate methods of control to test a hypothesis (including independent and dependent variables), and evaluate the designs of sample investigations. B-1.5 Organize and interpret the data from a controlled scientific investigation by using mathematics, graphs, models, and/or technology. B-1.6 Evaluate the results of a controlled scientific investigation in terms of whether they refute or verify the hypothesis. B-1.7 Evaluate a technological design or product on the basis of designated criteria (including cost, time, and materials). B-1.8 Compare the processes of scientific investigation and technological design. B-1.9 Use appropriate safety procedures when conducting investigations.
Suggested Handout/Notes - Language of Science Activity - Ball and Stick Models Activities Buggo Case Study (not on disk) Activity - Organic Compound Essay Lab - Scientific Method Bikini Bottom Experiments Lab - Identifying Organic Compounds Lab - Measurement Practice Redox Reactions – Tennis Ball Toss (not on disk) Worksheet - Graphing Practice Lab - Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide – Catalase from Beef Lab - Corn Seed Germination Liver Lab – The Effect of Temperature on Rate – http://alka- Lab – There’s No Such Thing as Fresh Pineapple Jello seltzerplus.com/as/experiment/student_experiment1.html Lab – Making Milk Into Glue (not on disk) Scientific Methods and Measurement Video (ETV Online – 38 Lab – Lactase Enzyme min) Lab – Enzyme Reaction Rate Using Toothpickase Worksheet - Metric Conversions at sciencespot.net Lab - Enzyme Rate of Reaction for Handase Safety Essay Lab – Food Label and Macromolecules Lab Practical - Laboratory Equipment and Skills
Anderson School District Five 1 July 1, 2012 Honors Biology– Curriculum Pacing Guide – 2012-2013
Unit 1 Unit 2 Content Areas Biological Themes and Inquiry Skills Biochemistry and Enzymes Lab Safety Worksheet at http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/safety.html Lab - Is Yeast Alive? Worksheet - Scientific Inquiary Problem Textbook Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Correlation Chapter 1 Chapter 2
Anderson School District Five 2 July 1, 2012 Honors Biology– Curriculum Pacing Guide – 2012-2013
Content Unit 3 Unit 4 Areas Cell Structure and Function Photosynthesis and Cellular Respirations Daily - 18 days Daily - 20 days Pacing A/B - 9 days A/B - 10 days SC B-2.1 Recall the three major tenets of cell theory (all living things B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis Standards/ are composed of one or more cells; cells are the basic converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret Indicators units of structure and function in living things; and all the chemical equation for the process. presently existing cells arose from previously existing B-3.2 Summarize the basic aerobic and anaerobic processes of cells). cellular respiration and interpret the chemical equation for B-2.2 Summarize the structures and functions of organelles cellular respiration. found in a eukaryotic cell (including the nucleus, B-3.3 Recognize the overall structure of adenosine triphosphate mitochondria, chloroplasts, lysosomes, vacuoles, (ATP)—namely, adenine, the sugar ribose, and three ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum [ER], Golgi apparatus, phosphate groups—and summarize its function (including cilia, flagella, cell membrane, nuclear membrane, cell wall, the ATP-ADP [adenosine diphosphate] cycle). and cytoplasm). B-2.3 Compare the structures and organelles of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. B-2.4 Explain the process of cell differentiation as the basis for the hierarchical organization of organisms (including cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems). B-2.5 Explain how active, passive, and facilitated transport serve to maintain the homeostasis of the cell.
Suggested Lab – Using a Microscope Diagram or Model ATP Conversions (not on disk) Activities Lab – Measuring with the Microscope Demo - Chromatography of Plant Pigments Lab – Pond Water Exploration Analogies – Light Dependent Reactions (not on disk) Worksheet – Introduction to the Light microscope Activity - Visualizing the Light Reactions Through Dynamic Cell Tour Project (not on disk) Demonstration Cell Coloring Diagrams (not on disk) Demo – Energy Transfer in Photosynthesis - Chlorophyll Lab – Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Fluorescence Worksheet - Ink Diffusion Lab – Lasting Impressions - Counting Stomata Perfume Diffusion (not on disk) Lab – Examining the Rate of Photosynthesis Demo - Potato Osmosis Lab – What is Needed for Photosynthesis Demo – Osmosis Across a Chicken Egg Membrane Lab – Wavelengths of Light and Photosynthesis Lab – Osmosis/Diffusion Demo – The Effect of Temperature on Yeast Fermentation Lab – Normal and Plasmolyzed Elodea Cells Aerobic Respiration Internet Activity (not on disk) Demo – Observing Water Transport in a Celery Stalk Lab – Photosynthesis - Carbon Dioxide Fixation Lab – Transport Weblab Lab – Sugar Fermentation in Yeast Lab Lab – Organelles Weblab Demo – Yeast Fermentation - Styrofoam/Phospholipl Lab – Clothespin Lab Lab - Cell Volume vs. Surface Area
Anderson School District Five 3 July 1, 2012 Honors Biology– Curriculum Pacing Guide – 2012-2013
Content Unit 3 Unit 4 Areas Cell Structure and Function Photosynthesis and Cellular Respirations - Diffusion wiwth Agar and Phenalpthalein Lab – Compound Light Microscope - Cell Analogies
Textbook Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Correlation Chapter 7 Chapters 8 and 9
Anderson School District Five 4 July 1, 2012 Honors Biology– Curriculum Pacing Guide – 2012-2013
Content Unit 5 Unit 6 Areas Cell Growth and Division Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Daily - 20 days Daily - 5 days Pacing A/B - 10 days A/B - 3 days SC B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase B-4.2 Summarize the relationship among DNA, genes, and Standards/ (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, chromosomes. Indicators metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and B-4.5 Summarize the characteristics of the phases of meiosis I animal cytokinesis. and II. B-2.7 Summarize how cell regulation controls and coordinates cell growth and division and allows cells to respond to the environment, and recognize the consequences of uncontrolled cell division.
Suggested Cell Surface Area activity (not on disk) Activity - Homologous Shoes Activities Modeling – Chromosomes and Mitosis (not on disk) Crossing Over Coloring Diagram (not on disk) Diagramming the Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis (not on Diagramming Meiosis (not on disk) disk) Activity - Doing the Meiosis Shuffle Activity - Exploring Mitosis through the Learning Cycle Activity - Mitosis and Meiosis Side/Side Coloring Lab – Onion Root Mitosis Lab – Whitefish Blastula Mitosis (not on disk) NIH Cancer Supplements (not on disk) Stem Cell Research Assignment – teacher set parameters (not on disk) - Stem Cell Articles and Presentations
Textbook Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Correlation Chapter 10 Chapter 11 (section 11-4 only)
Anderson School District Five 5 July 1, 2012 Honors Biology– Curriculum Pacing Guide – 2012-2013
Unit 7 Unit 8 Content Areas Mendelian Genetics Protein Synthesis Daily - 12 days Daily - 5 days Pacing A/B - 6 days A/B - 3 days SC Standards/ B-4.6 Predict inherited traits by using the principles of Mendelian B-4.1 Compare DNA and RNA in terms of structure, Indicators genetics (including segregation, independent assortment, nucleotides, and base pairs. and dominance). B-4.2 Summarize the relationship among DNA, genes, and B-4.7 Summarize the chromosome theory of inheritance and chromosomes. relate that theory to Gregor Mendel’s principles of B-4.3 Explain how DNA functions as the code of life and the genetics. blueprint for proteins. B-4.4 Summarize the basic processes involved in protein synthesis (including transcription and translation). B-4.8 Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. B-1.1 Generate hypotheses based on credible, accurate, and relevant sources of scientific information. B-1.2 Use appropriate laboratory apparatuses, technology, and techniques safely and accurately when conducting a scientific investigation. B-1.3 Use scientific instruments to record measurement data in appropriate metric units that reflect the precision and accuracy of each particular instrument. B-1.4 Design a scientific investigation with appropriate methods of control to test a hypothesis (including independent and dependent variables), and evaluate the designs of sample investigations.
Suggested Lab – Probability and Mendelian Genetics Activity - Codon Bingo Activities Genetics Practice Problems – Activity - The Great Codon Mystery www.sciencespot.net/Media/gen_spbobgenetics.pdf Lab - Sci Fly Mutation www.sciencespot.net/Media/gen_spbobgenetics2.pdf Worksheet – Gene Action/Mutations www.nsummi.k12.ut.us/.../PDF/Bikini%20Bottom%20Genetics%20Quiz.pdf Lab – Protein Synthesis Weblab Lab – Genetics Weblab
Textbook Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Correlation Chapter 11 (sections 11-1, 11-2, 11-3, and 11-5) Chapter 12
Anderson School District Five 6 July 1, 2012 Honors Biology– Curriculum Pacing Guide – 2012-2013
Unit 9 Unit 10 Content Areas Genetics Biotechnology Daily - 17 days Daily - 8 days Pacing A/B - 9 days A/B - 4 days SC Standards/ B-4.7 Summarize the chromosome theory of inheritance and B-4.9 Exemplify ways that introduce new genetic Indicators relate that theory to Gregor Mendel’s principles of characteristics into an organism or a population by genetics. applying the principles of modern genetics. B-4.8 Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. B-4.9 Exemplify ways that introduce new genetic characteristics into an organism or a population by applying the principles of modern genetics. (not tested) Suggested Expression of Traits Manipulating DNA Activities Incomplete Dominance Genetic Engineering Codominance Polygenic Traits Multiple Allele Traits Sex Linked Traits Pedigrees Karyotypes Chromosomal Disorders Gene Linkage
Textbook Inheritance Patterns (not on disk) Project - Biotechnology Research Paper Correlation Worksheet - Human Genetic Traits (Exploring Hereditary Project - GMO Research Traits) Activity - The Great Cake Heist Lab – Making a Baby Activity - Forensic Science: A Paternal Case Lab - Drosophila Lab #1 Lab – DNA WHodunit Lab – Drosophila Lab #2 Lab – Paper Restriction Enzyme Lab (not on disk) Activity - Chromosomes and Genetic Mapping Recombinant DNA Paper Lab (not on disk) Sex Linkage Coloring Diagram (not on disk) Activity – Transgenic Activity Lab - Karyotyping Weblab Lab – Gel Electrophoresis Weblabs Worksheet - A Human Pedigree - Hemophilia Lab - Case of the Hooded Murderer Activity - The Ultimate Pedigree Challenge (I’m My Own Grandpa) Lab – Human Karyotyping (not on disk) Lab – Bug Genetics Karyotype Project - Genetic Disorder Research Project
Anderson School District Five 7 July 1, 2012 Honors Biology– Curriculum Pacing Guide – 2012-2013
Unit 9 Unit 10 Content Areas Genetics Biotechnology Activity - Cystic Fibrosis Pedigree Case Studies (not on disk) Worksheet - Kansas State Problems Worksheet – Linked Genes Worksheet
Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Chapter 14 Chapter 13
Anderson School District Five 8 July 1, 2012 Honors Biology– Curriculum Pacing Guide – 2012-2013
Unit 11 Unit 12 Content Areas Biological Evolution Ecology Daily - 20 days Daily - 15 days Pacing A/B - 10 days A/B - 8 days SC Standards/ B-5.1 Summarize the process of natural selection. B-3.6 Illustrate the flow of energy through ecosystems Indicators B-5.2 Explain how genetic processes result in the continuity of (including food chains, food webs, energy pyramids, life-forms over time. number pyramids, and biomass pyramids). B-5.3 Explain how diversity within a species increases the B-6.1 Explain how the interrelationships among organisms chances of its survival. (including predation, competition, parasitism, mutualism, B-5.4 Explain how genetic variability and environmental factors and commensalism) generate stability within ecosystems. lead to biological evolution. B-6.2 Explain how populations are affected by limiting factors B-5.5 Exemplify scientific evidence in the fields of anatomy, (including density-dependent, density-independent, embryology, biochemistry, and paleontology that underlies abiotic, and biotic factors). the theory of biological evolution. B-6.3 Illustrate the processes of succession in ecosystems. B-5.6 Summarize ways that scientists use data from a variety of B-6.4 Exemplify the role of organisms in the geochemical sources to investigate and critically analyze aspects of cycles (including the cycles of carbon, nitrogen, and evolutionary theory. water). B-5.7 Use a phylogenetic tree to identify the evolutionary B-6.5 Explain how ecosystems maintain themselves through relationships among different groups of organisms. naturally occurring processes (including maintaining the quality of the atmosphere, generating soils, controlling the hydrologic cycle, disposing of wastes, and recycling nutrients). B-6.6 Explain how human activities (including population growth, technology, and consumption of resources) affect the physical and chemical cycles and processes of Earth.
Suggested Natural Selection Energy in Ecosystems Activities Evidence for Evolution Cycles Population Evolution Community Interactions Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Population Growth Speciation Succession Classification Conservation of Resources Greenhouse Effect
Textbook Handout - Lamarck vs. Darwin Design a Food Chain/Food Web (not on disk) Correlation Fossil Observation (not on disk) Lab - The Lynx Eats the Hare Radiometric Dating Practice (not on disk) Population Ecology Coloring Diagram Fossil Dating (not on disk) Activity - The Lorax Activity - The Molecular Connection Human Impact Essays (not on disk) Activity - Making a Cladogram Activity - Nitrogen Cycle Jigsaw
Anderson School District Five 9 July 1, 2012 Honors Biology– Curriculum Pacing Guide – 2012-2013
Unit 11 Unit 12 Content Areas Biological Evolution Ecology Design a Phylogenetic Tree (not on disk) Lab – Fossil Study Hardy-Weinberg Practice Problems (not on disk) Lab – Establishing Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Lab – Allele Frequency and Sickle Cell Anemia Lab – Jelly Bean and Evolutionary Principles Lab – Peppered Moth Survey in the Classroom Lab – Modeling Selection Lab – Island Biogeography and Evolution Activity – Straw Bird Biochemistry Activity - Breeding Bunnies Activity - Flashy Fish Activity - Speciation Stories
Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Prentice Hall Biology, 2009 Edition Chapters 15, 16, and 18 Chapter 3, Chapter 4 (sections 4-1 Greenhouse Effect only and 4-2), Chapters 5 and 6
Anderson School District Five 10 July 1, 2012