Mr. Chapman Biology 30 Genes, Heredity & Punnett Squares Genes, Heredity & Punnett Squares
Mendel’s Units of Heredity
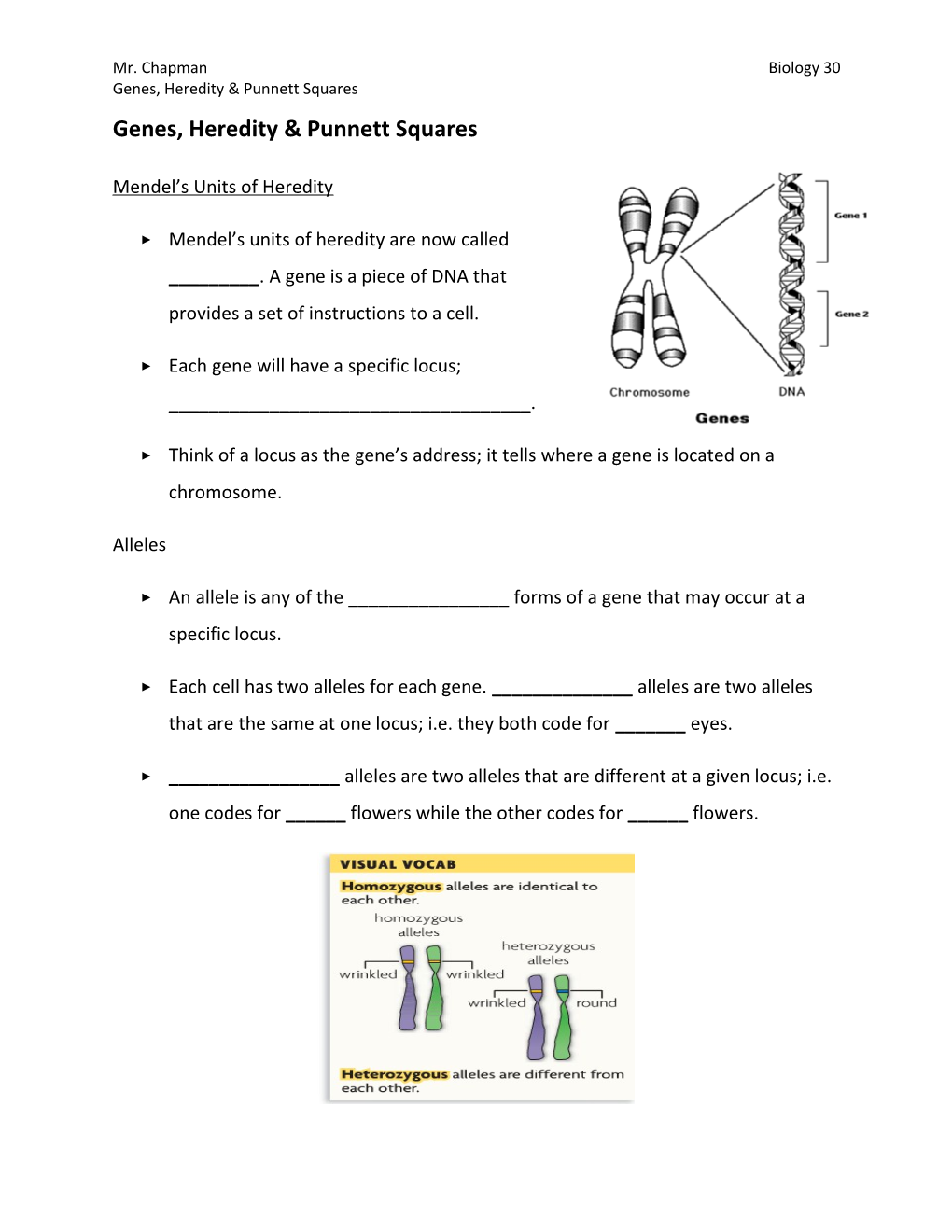
▸ Mendel’s units of heredity are now called ______. A gene is a piece of DNA that provides a set of instructions to a cell.
▸ Each gene will have a specific locus; ______.
▸ Think of a locus as the gene’s address; it tells where a gene is located on a chromosome.
Alleles
▸ An allele is any of the ______forms of a gene that may occur at a specific locus.
▸ Each cell has two alleles for each gene. ______alleles are two alleles that are the same at one locus; i.e. they both code for ______eyes.
▸ ______alleles are two alleles that are different at a given locus; i.e. one codes for ______flowers while the other codes for ______flowers. Mr. Chapman Biology 30 Genes, Heredity & Punnett Squares Genotype and Phenotype
▸ ______is the genetic makeup of a specific set of genes.
▸ For every trait there is a genotype.
▸ Example: the genotype for blue eyes is ______.
▸ ______is the ______makeup or characteristics of an organism.
▸ Depending on the genotype, people express a certain phenotype.
▸ Example: a person with genotype BB has ______eyes.
Important Point!
▸ You have ______genes for ______that you have. One gene comes from your ______, and the other gene comes from your ______.
▸ Therefore, ______are always expressed by two ______. Each letter represents a ______. We use different letters to represent different genes.
▸ The blue eyed gene is symbolized by a ______. A person with blue eyes has two of them, and their genotype is ______.
Dominant and Recessive Alleles
▸ When two different alleles are present in a genotype, one of them tends to dominate the other.
▸ Example: If someone receives an allele symbolized by “B” for eye colour from their mother and an allele symbolized by “b” for eye colour from their father, one dominates the other. ______Mr. Chapman Biology 30 Genes, Heredity & Punnett Squares
▸ In this case, the person would have the physical trait represented by the “____”, which is ______.
Defintions
Dominant Allele: ______
______.
Recessive Allele: ______
______. Mr. Chapman Biology 30 Genes, Heredity & Punnett Squares
Questions
1. A person has the genotype Bb for eye colour. What colour are the person’s eyes?
2. Someone has blonde hair. What are their possible genotypes for hair colour?
3. John goes hitchhiking, and notices that he has the thumb for it. What genotype does he have for this trait?
Punnett Squares
▸ Punnett Squares are a method of predicting the ______of the ______between two ______organisms.
▸ If we know the ______of the parents for a particular ______, we can predict the ______of different genotypes in the ______.
▸ We can perform both ______(one trait) and ______(two traits) ______using Punnett Squares. Mr. Chapman Biology 30 Genes, Heredity & Punnett Squares
One allele from each parent is written in one grid box. Each possible genetic combination is shown and has a specific probability.
Steps to Using a Punnett Square
1. ______
______
2. ______
______
3. ______
______
4. ______
______
Examples Mr. Chapman Biology 30 Genes, Heredity & Punnett Squares
▸ A green flower (GG) is crossed with a white flower (gg). Determine the probability that the offspring will be green.
▸ The allele that represents eye colour is symbolized by the letter “b,” and the dominant allele codes for brown eyes. If two heterozygous (for eye colour) humans mate and produce offspring, what is the probability of each possible genotype?