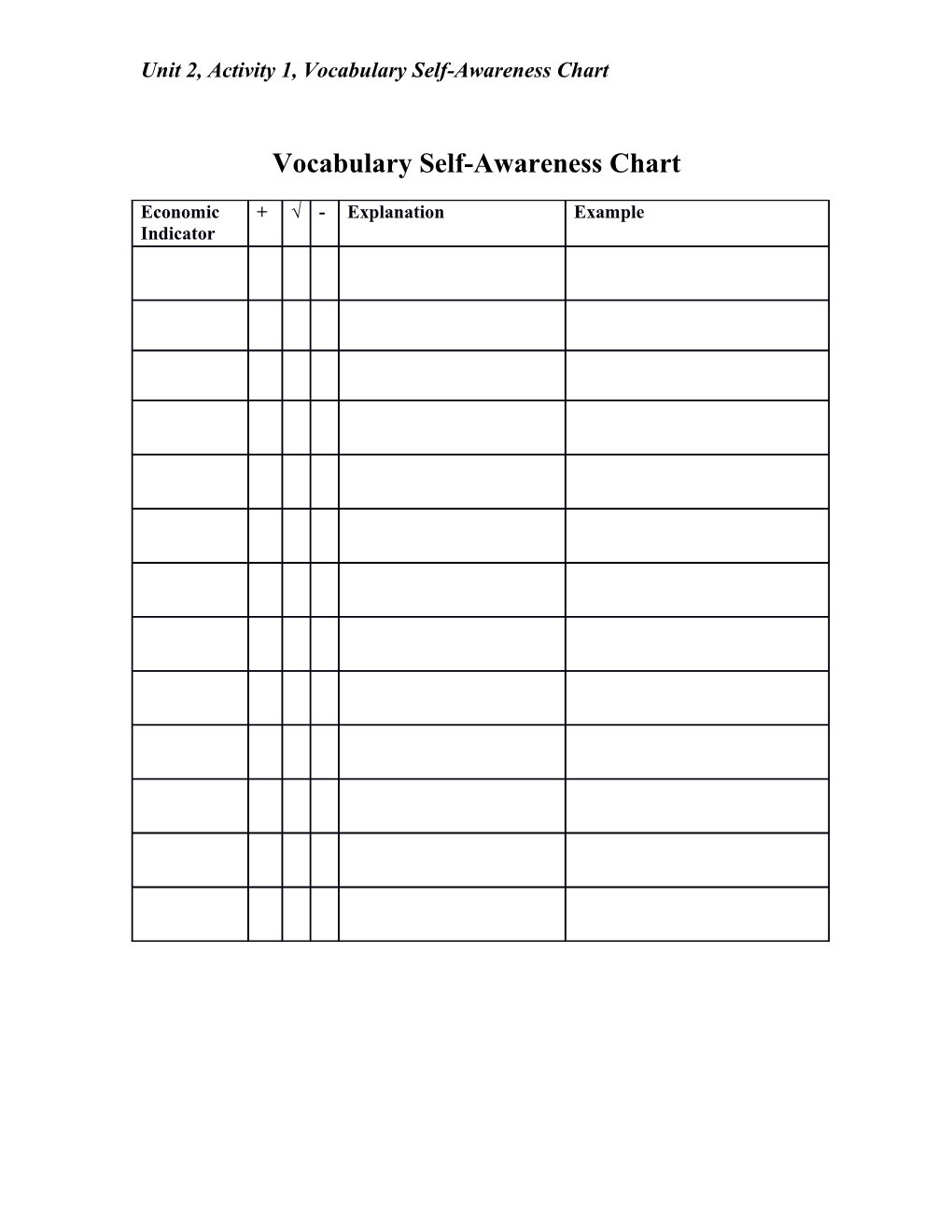
Unit 2, Activity 1, Vocabulary Self-Awareness Chart
Vocabulary Self-Awareness Chart
Economic + √ - Explanation Example Indicator Unit 2, Activity 3, Making Effective Economic Decisions
Making Effective Economic Decisions
Louisiana has experienced an abnormal seasonal drought that is depleting water sources. Your community is having difficulty in replenishing potable water at the current rate of consumption. You are asked to serve on a citizen’s committee to provide suggestions for conserving the town’s water supply.
Situation Conservation Plan Consequences
Decorative outdoor fountains attract tourists, but use 1,000s of gallons/day.
Home owners have increased lawn watering due to the drought.
Water consumption at the water park attraction has increased.
Record sales at the local ice house have increased causing an increase in water consumption.
Other plans to conserve water Consequences Unit 2, Activity 4, Pay Me Now, or Pay Me Later
Pay Me Now, or Pay Me Later
High School Vocational University Graduate Certification Degree Average number of years beyond high school 0 2 4 $ investment prior to entering workforce (fulltime) $ 0 $ 3,000 $ 40,000
Entry level annual salary $ 12,000 $ 22,000 $ 30,000
Annual salary after 10 years $ 18,000 $ 35,000 $ 55,000
Total earnings after 20 years $ 300,000 $ 570,000 $ 850,000 (Statistics are estimated averages and should be updated and reflective of regional or state averages.)
After reviewing the chart, answer the following questions:
1. What is the relationship between education and earnings?
2. Why is there such a large increase between years 10 and 20?
3. What could have caused these increases?
Answer these questions in your social studies learning log using economic terms.
Type of Job: Information About the Job
Qualifications Needed (Example: education, experience, skills, etc.)
Starting salary or range Benefits Unit 2, Activity 4, Pay Me Now, or Pay Me Later
Job location Job Search Unit 2, Activity 5, Careers
Careers What jobs/careers require special training?
What percentage of the employment section, roughly, is devoted to the larger specializations? What needs does that speak to in Louisiana?
What jobs might you come to Louisiana for specifically?
What jobs might you have to leave Louisiana to secure? Unit 2, Activity 6, Four Basic Economic Questions
Four Basic Economic Questions
Command Market Traditional
1. What to produce?
2. How to produce it?
3. How much to produce?
4. Who gets what is produced? Unit 2, Activity 6, Economic Systems
Economic Systems
Term Definition Application Which exists in the United States and Louisiana?
Traditional Economic System
Command Economic System
Market Economic System Unit 2, Activity 6, Advantages/Disadvantages of Each Economic System
Advantages/Disadvantages of Each Economic System
Advantages Disadvantages
Command System
Traditional System
Market System Unit 2, Activity 7, Public and Private Sector
Public and Private Sector
Service Public Private Advantage Disadvantage Alternate Service City Bus Parish School 5 Star Hotel State Park City Pool Health Unit Tulane University Country Club Taxi Unit 2, Activity 9, To Tax or Not To Tax
To Tax or Not To Tax
Products Sold Without Tariff Prices and Products Possible Possible Producer’s Consumer’s Reaction Reaction Louisiana crawfish @ $ 5.00 per lb.
Chinese crawfish @ $ 2.00 per lb.
If a tariff is placed on the Chinese crawfish, how will that affect prices?
What is the intent of the tariff regarding consumer response?
Products Sold With Tariff Prices and Products Consumer’s Producer’s Reaction Reaction Louisiana crawfish @ $ 5.00 per lb
Chinese crawfish @ $ 5.50 per lb
Take a stand on either supporting import tariffs or opposing import tariffs. Write “a letter to the editor” expressing your opinion and a justification for your stance. Unit 2, Activity 10, Trade Agreements
Trade Agreements
Trade Agreement GATT NAFTA CAFTA
Official Title
Participating Nations
Basic Terms of the Agreement
Economic Benefits
Economic Set-backs Unit 2, Activity 10, Alliances and International Organizations
Alliances and International Organizations
Trade Agreement NATO United Nations OPEC
Official Title
Participating Nations
Basic Terms of the Agreement
Economic Benefits
Economic Set-backs
Effects on Louisiana Unit 2, Activity 12, Scenario 1: Supply and Demand
Scenario 1: Supply and Demand
Table 1: Supply Schedule of Pralines
Price per Praline Quantity Supplied $ .50 1,000 $ 1.00 2,000 $ 1.50 3,000 $ 2.00 4,000 $ 2.50 5,000
Design a chart labeling the axis with prices (y-axis) and quantity supplied (x-axis) of pralines. Plot the figures to create a supply curve.
Praline Supply Curve
Quantity Supplied (1 = 1,000) Unit 2, Activity 12, Scenario 1: Supply and Demand with Answers
Scenario 1: Supply and Demand
Table 1: Supply Schedule of Pralines
Price per Praline Quantity Supplied $ .50 1,000 $ 1.00 2,000 $ 1.50 3,000 $ 2.00 4,000 $ 2.50 5,000
Design a chart labeling the axis with prices (y-axis) and quantity supplied (x-axis) of pralines. Plot the figures to create a supply curve.
Praline Supply Curve
Quantity Supplied (1 = 1,000) Unit 2, Activity 12, Scenario 2: Supply and Demand
Scenario 2: Supply and Demand Table 2: Demand Schedule of Pralines
Price per Praline Quantity Supplied $ 4.50 1,000 $ 4.00 2,000 $ 3.50 3,000 $ 3.00 4,000 $ 2.50 5,000
Have students design a chart labeling the axis with prices (y-axis) and quantity supplied (x-axis) of pralines. Have the students plot the figures to create a demand curve.
Praline Demand Curve
QuantityDemanded (1 = 1,000) Unit 2, Activity 12, Scenario 2: Supply and Demand with Answers
Scenario 2: Supply and Demand
Table 2: Demand Schedule of Pralines
Price per Praline Quantity Supplied $ 4.50 1,000 $ 4.00 2,000 $ 3.50 3,000 $ 3.00 4,000 $ 2.50 5,000
Have students design a chart labeling the axis with prices (y-axis) and quantity supplied (x-axis) of pralines. Have the students plot the figures to create a demand curve.
Praline Demand Curve
Quantity Supplied (1 = 1,000) Unit 2, Activity 12, Equilibrium
Quantity Supplied (1 = 1,000) Unit 2, Activity 12, Equilibrium with Answers
Quantity Supplied (1 = 1,000) Unit 2, Activity 12, Making Economic Choices
Making Economic Choices
Complete the chart below listing possible options the bakery could choose and the cost and benefits for each option.
Choice(s) Benefits What are the two (2) choices the bakery can make What are the possible benefits associated with: regarding the rising prices? Choice 1:
Choice 2:
Costs
What are possible economic costs associated with:
Choice 1:
Choice 2: Unit 2, Activity 12, Making Economic Choices with Answers
Making Economic Choices
Complete the chart below listing possible options the bakery could choose and the cost and benefits for each option.
Choice(s) Benefits What are the two (2) choices the bakery can make What are the possible benefits associated with: regarding the rising prices? Choice 1: (e.g., lower production costs, lower price of 1. (e.g., purchase cheaper pecans from out of pralines) state) 2. (e.g., reduce production in order to adjust to demand until pecans become more affordable)
Choice 2: (reducing production lowers cost)
Costs
What are possible economic costs associated with:
Choice 1: (e.g., risks integrity of product – Louisiana Pralines)
Choice 2: (e.g., potential loss of profit and share of market)
Role Audience Form Topic Option 1 College Student Newspaper Readers Classified Ad Searching for Affordable Housing Option 2 Real Estate Agent Potential Customers Newspaper Ad Baton Rouge Unit 2, Activity 12, Making Economic Choices with Answers
Housing Option 3 City Planner City Council Housing Proposal Public Housing Option 4 Evacuee Government Officials Letter Temporary Housing RAFT Options for Housing Shortage Unit 2, Activities 9 and 13, Specific Assessment Rubric
Sample Rubric for Grading Essays
Score Level Description of Score Level 4 The response demonstrates in-depth understanding of the relevant content and/or procedure. The student completes all important components of the task accurately and communicates ideas effectively. Where appropriate, the student offers insightful interpretations and/or extensions. Where appropriate, the student chooses more sophisticated reasoning and/or efficient procedures. 3 The response demonstrates understanding of major concepts and/or processes, although less important ideas or details may be overlooked or misunderstood. The student completes the most important aspects of the task accurately and communicates clearly. The student’s logic and reasoning may contain minor flaws. 2 The student completes some parts of the task successfully. The response demonstrates gaps in conceptual understanding. 1 The student completes only a small portion of the task and/or shows minimal understanding of the concepts or processes. 0 The student’s response is totally incorrect, irrelevant, too brief to evaluate, or blank.