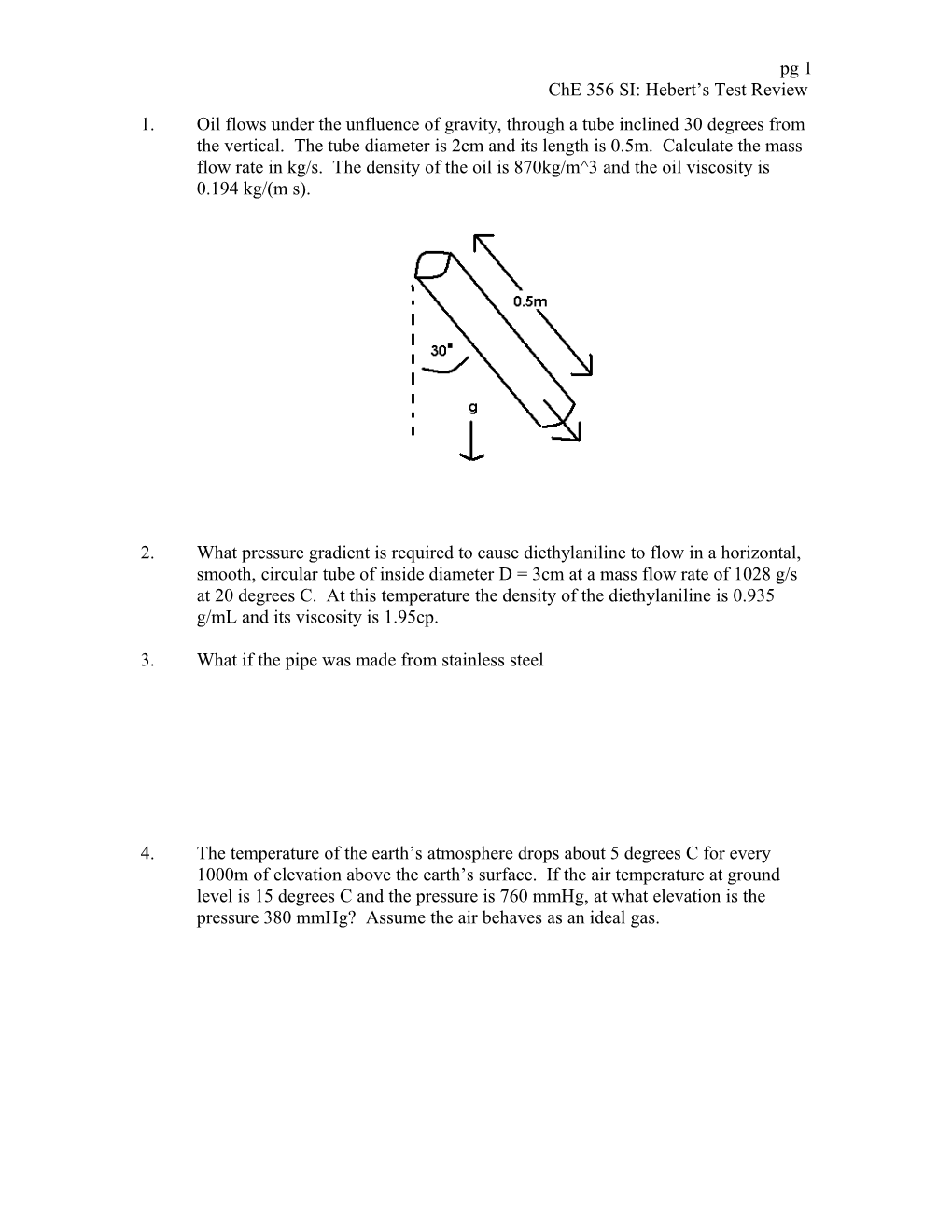
pg 1 ChE 356 SI: Hebert’s Test Review 1. Oil flows under the unfluence of gravity, through a tube inclined 30 degrees from the vertical. The tube diameter is 2cm and its length is 0.5m. Calculate the mass flow rate in kg/s. The density of the oil is 870kg/m^3 and the oil viscosity is 0.194 kg/(m s).
2. What pressure gradient is required to cause diethylaniline to flow in a horizontal, smooth, circular tube of inside diameter D = 3cm at a mass flow rate of 1028 g/s at 20 degrees C. At this temperature the density of the diethylaniline is 0.935 g/mL and its viscosity is 1.95cp.
3. What if the pipe was made from stainless steel
4. The temperature of the earth’s atmosphere drops about 5 degrees C for every 1000m of elevation above the earth’s surface. If the air temperature at ground level is 15 degrees C and the pressure is 760 mmHg, at what elevation is the pressure 380 mmHg? Assume the air behaves as an ideal gas. pg 2 ChE 356 SI: Hebert’s Test Review 5. A flexible tube is connected to the bottom of an old tank. The pressure in the tank is 175 kPa (absolute), and the air pressure is 110 kPa. The density of air is 1.2 kg/m^3, and the density of the oil is 870 kg/m^3. Assume the tube is filled with oil. Calculate the height H of the tube end, at which there is no flow of oil through the tube (H could be negative).
6. Now assume there is an air bubble in the bottom of the tube, as shown below. The height of the bubble on the right side is h, relative to the left side. Again calculate the height H of the tube end, at which there is no flow of oil through the tube (H could be negative). Let h = 1.0m.
7. For Laminar flow through the following pipe, derive an equation for the average velocity in terms of the pressure drop. Use eq. 3.8 along with the concept of the hydraulic diameter. pg 3 ChE 356 SI: Hebert’s Test Review Find Equations for the following. What is the definition of :
laminar(smooth) turbulent(smooth) not smooth f =
What is the cut off number Re = for laminar to turbulent flow?
Visosity of a Newtonian fluid =
Hagen- Poiseuille Eqn (flow in a pipe):
Power Input for a pipe:
Hydraulic Diameter = Hydraulic Radius =
Wetted parameter (for a pipe) = Cross-sectional Area =
Volume of a pipe = Volume of a sphere =
Relate velocity to volumetric flow rate to mass flow rate: