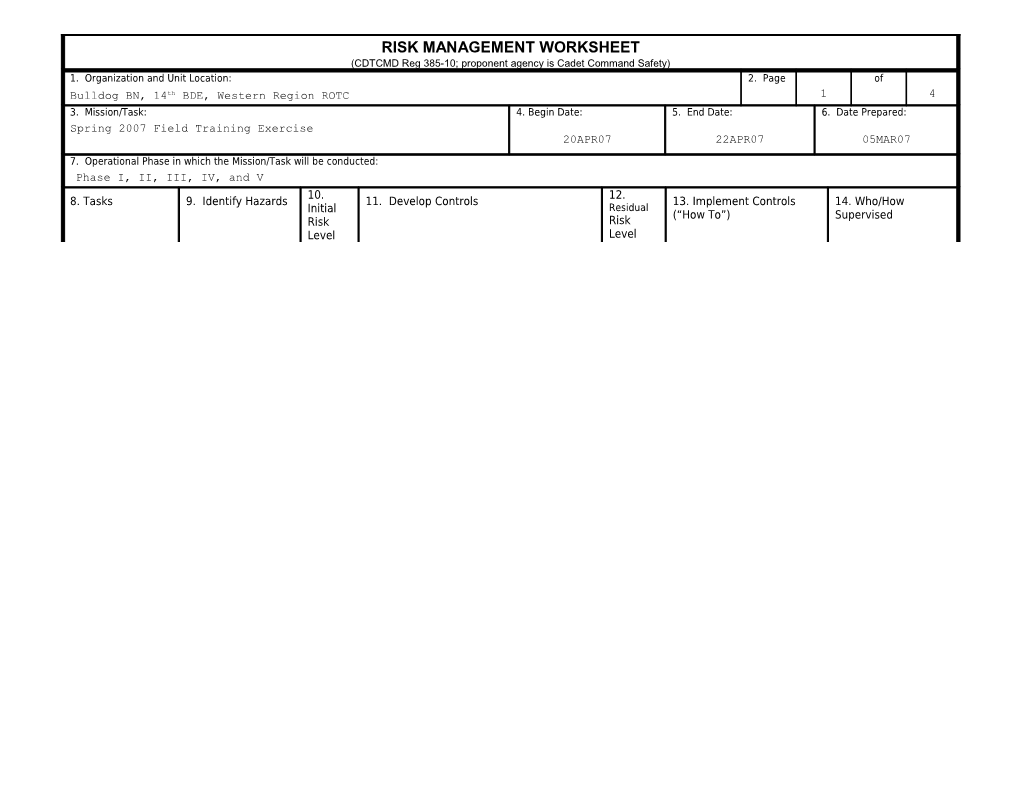
RISK MANAGEMENT WORKSHEET (CDTCMD Reg 385-10; proponent agency is Cadet Command Safety) 1. Organization and Unit Location: 2. Page of Bulldog BN, 14th BDE, Western Region ROTC 1 4 3. Mission/Task: 4. Begin Date: 5. End Date: 6. Date Prepared: Spring 2007 Field Training Exercise 20APR07 22APR07 05MAR07
7. Operational Phase in which the Mission/Task will be conducted: Phase I, II, III, IV, and V 10. 12. 8. Tasks 9. Identify Hazards 11. Develop Controls 13. Implement Controls 14. Who/How Initial Residual (“How To”) Supervised Risk Risk Level Level RISK MANAGEMENT WORKSHEET (CDTCMD Reg 385-10; proponent agency is Cadet Command Safety) 1. Organization and Unit Location: 2. Page of Bulldog BN, 14th BDE, Western Region ROTC 1 4 3. Mission/Task: 4. Begin Date: 5. End Date: 6. Date Prepared: Spring 2007 Field Training Exercise 20APR07 22APR07 05MAR07
7. Operational Phase in which the Mission/Task will be conducted: Phase I, II, III, IV, and V -Transpo -Traffic (L) -Seat belt and spatial (L) -CSUF/FCC Cadre will Cadre to/from Ft Accident awareness; all Cadets travel in provide ground Hunter Liggett to/from FHL GSA vans and commercial buses. transpo to/from FHL. (FHL) -Seat belts worn by all Cadre -OIC will ensure all OIC and Cadets, no exceptions. seat belts are worn -Before, during, and after PMCS. before operating GSA -Conduct safety briefing. vehicle. -OIC will ensure OIC -Accident from (L) -Ground guides will be used (L) before, during and putting vehicle every time vehicle is put into after PMCS are in reverse and reverse and backed, no performed. backing up exceptions. -OIC will conduct OIC safety briefing prior to vehicle movement. -OIC will ensure that ground guides are OIC used at all times.
-Crew chief will train all Cadets and -Conduct air -Lack of (H) -Cadets will take all directions (M) Cadre on boarding and Aircraft Crew movement Cadets’ from the crew chief. un-boarding Chief operation to experience with -Cadets will conduct boarding procedures. FHL helicopter and un-boarding procedures -OIC will brief operations -Brief cadets on behavior in Cadets and Cadre on aircraft prior to flight. safety and OIC -Conduct safety briefing prior appropriate behavior to boarding aircraft. for the aircraft.
-Brief Cadets to be drinking water prior -Ruck march -Dehydration (M) -Ensure that Cadets are drinking (L) to FTX and while on Cadet Chain of from bus drop water on bus ride to FHL. buses. Command off point to -Ensure that Cadets have two -PCI Cadets to ensure TA site full canteens prior to start of to full canteens. ruck march. -Brief cadets on foot CO 1SG -Foot (M) -Brief Cadets to wear broken in (L) hygiene at lab. casualties boots. -Brief Cadets to wear thick Cadet COC socks and foot powder. CDTCMD Form 385-2-R-E, Apr 01 Risk Assessment and Risk Management Countermeasure Worksheets in CC Reg 145-3 are OBSOLETE RISK MANAGEMENT WORKSHEET (CDTCMD Reg 385-10; proponent agency is Cadet Command Safety) 1. Organization and Unit Location: 2. Page of Bulldog BN, 14th BDE, Western Region ROTC 4 4 3. Mission/Task: 4. Begin Date: 5. End Date: 6. Date Prepared: Spring 2007 Field Training Exercise 20APR07 22APR07 05MAR06 10. 12. 8. Tasks 9. Identify Hazards 11. Develop Controls 13. Implement Controls 14. Who/How Initial Residual (“How To”) Supervised Risk Risk Level Level -Rappel Tower -Falling from (M) -Three safety checks to ensure (L) -Swiss seat, proper Station 1 and 2 rope due to proper tying and wear of all fit of Kevlar helmet, OIC and Rappel improper wear equipment. and gloves will be Master of equipment. -Conduct a brief on proper way checked at equipment of descending the tower with a station, base of -Contact with (M) demonstration. (L) tower, and by rappel the wall while -One person will be on belay at master before descent descending. all times while another is on of tower. rappel. -Brief Cadets of the -Head injuries (H) -All Cadets will wear Kevlar (M) safety issues of Site OIC sustained from helmets while climbing and rappelling and teach collision with descending the tower. them the correct tower wall. -All Cadets will wear black methods of descending leather gloves while climbing the tower. -Rope burn to (L) and descending the rappel tower. (L) -Certified rappel the hands from -Ensure that rope is properly master will inspect descent from secured to the tower. the rope to ensure Rappel Master tower. that it is secured correctly to the tower.
15. Determine Overall Mission/Task Risk Level After Countermeasures Are Implemented: LOW (L) MODERATE HIGH EXTREMELY HIGH (E) (Circle Highest Remaining Risk Level) (M) (H) 16. Medical Support: Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) is required within 1 hour. On-site Medical Support provided (Circle one): Medic Combat Lifesaver ARC/NSC First-Aid Responder None 17. Prepared by: (Rank, Last Name, Duty Position) 18. Reviewed by Action Officer/Commander: (Rank, Last Name, Duty Position and CDT Diaz, CDT BN S-3 Signature): LTC Busteed, Professor of Military Science
19. Risk Decision Authority (Signature Block and Signature): Extremely High Risk: Not Applicable for Cadet Command COL Michael R. Johnson, AR, Commanding High Risk: CG or DCG RISK MANAGEMENT WORKSHEET (CDTCMD Reg 385-10; proponent agency is Cadet Command Safety) 1. Organization and Unit Location: 2. Page of Bulldog BN, 14th BDE, Western Region ROTC 4 4 3. Mission/Task: 4. Begin Date: 5. End Date: 6. Date Prepared: Spring 2007 Field Training Exercise 20APR07 22APR07 05MAR06 10. 12. 8. Tasks 9. Identify Hazards 11. Develop Controls 13. Implement Controls 14. Who/How Initial Residual (“How To”) Supervised Risk Risk Level Level Moderate Risk: Brigade Cdr (0-6). At Advanced/Basic Camp – Region Cdr or CofS Low Risk: Battalion Cdr. At Advanced/Basic Camp – Committee Chief or Regimental Cdr/TAC Officer CDTCMD Form 385-2-R-E, Apr 01 Risk Assessment and Risk Management Countermeasure Worksheets in CC Reg 145-3 are OBSOLETE Sample Risk Management Worksheet Need to Risk Manage a METT-T Hazard RISK MANAGEMENT WORKSHEET Hazards not adequately controlled are likely to cause loss of combat power. Answer the (CDTCMD Reg 385-10; proponent agency is Cadet Command Safety) 1. Organization and Unit Location: 2. Page of following questions about each hazard to determine if it is adequately controlled. If not, ROTC Battalion 1 2 3. Mission/Task: 4. Begin Date: 5. End Date: 6. Date Prepared: hazards needs to be risk managed. Conduct Rappel Training (include Transportation to and from Tower) 7. Operational Phase in which the Mission/Task will be conducted: Yes No Throughout training phase Are the Controls Adequate? 10. Initial 12. Residual 8. Tasks 9. Identify Hazards 11. Develop Controls 13. Implement Controls (“How To”) 14. Who/How Supervised Support – Is type/amount/capability/condition of support adequate to carry Risk Level Risk Level Transportation to Driver Fatigue M Ensure driver gets adequate rest. L AR 385-55, Prevention of Driver – Self out the mission? tower. Motor Vehicle Accidents Traffic/Congestion M Drive slower and defensively. L Driver – Self Personnel AR 600-55, Army Driver and Weather Conditions H Drive slower than posted speed limit. M Operator Standardization Driver – Self Supplies (rain/ice on road) Program Equipment/Material Rappelling from a Inexperienced H Instruct and demonstrate: (1) Fundamentals M TSP No.1, Basic Rappelling Qualified Rappel 34-ft Tower cadets of rappelling, (2) How to properly tie knots TC 21-24, Rappelling Master will supervise. Services/Facilities and (3) Safety requirements. Always require use of helmets and gloves. Standards – Is guidance / procedure adequately clear / practical /specific Equipment failure H Conduct a safety inspection of tower and all M TC 21-24, Rappelling Rappel Master will to control hazard? resulting in falls. rappelling equipment prior to training inspect. exercise. Training – Is training adequately thorough and recent to control hazard? Conduct annual safety inspection of tower. M AR 385-10, Safety Program Army Safety Officer, DA Pam 385-1, Unit Safety CDSO, Univ. Safety. Leader – Is leadership ready, willing, and able to enforce standards Heat Injury/ H Monitor Heat Index, advise all to drink M TB MED 507 Cadre monitor required to control hazard? Dehydration sufficient volumes of water at frequent Water buffalo/jugs on site. weather. intervals, carry canteen(s) and know GTA 8-5-50 location of water points. Individual/Unit Self-Discipline – Is performance and conduct sufficiently self-disciplined to control hazard? Wildlife, insects and M Brief cadets to avoid wildlife, insects and L FM 21-10 Cadre monitor Heat plants plants. Use insect repellent. GTAs based on area. Index. Have bee stings kits available. Use buddy system. If all “yes”, no further action required (subject to commander’s risk guidance). If one or more 15. Determine Overall Mission/Task Risk Level After Countermeasures Are Implemented: (Circle Highest Remaining Risk Level) LOW (L) MODERATE (M) HIGH (H) EXTREMELY HIGH (E) “no ”, risk manage this hazard 16. Medical Support: Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) is required within 1 hour. On-site Medical Support provided (Circle one): Medic Combat Lifesaver ARC/NSC First-Aid Responder None 17. Prepared by: (Rank, Last Name, Duty Position) 18. Reviewed by Action Officer/Commander: (Rank, Last Name, Duty Position and Signature):
19. Risk Decision Authority (Signature Block and Signature): Extremely High Risk: Not Applicable for Cadet Command Risk Assessment Matrix High Risk: CG or DCG Moderate Risk: Brigade Cdr (0-6). At Advanced/Basic Camp – Region Cdr or CofS PROBABILITY Low Risk: Battalion Cdr. At Advanced/Basic Camp – Committee Chief or Regimental Cdr/TAC Officer SEVERITY Frequent Likely Occasional Seldom Unlikely CDTCMD Form 385-1-R-E, Apr 01 Risk Assessment and Risk Management Countermeasure Worksheets in CC Reg 145-3 are OBSOLETE Catastrophic E E H H M Work Sheet Instructions Critical E H H M L Blocks Marginal H M M L L 1 8. Self explanatory Negligible M L L L L 9. Identify Hazards – Review METT-T factors for the mission or task. Additional factors include historical lessons learned, experience, judgment, equipment characteristics and warnings, and PROBABILITY – The likelihood that an event will occur. environmental considerations. FREQUENT – Occurs often, continuously experienced. 10. Initial Risk Level – Assess hazard and determine initial risk for each hazard by applying risk assessment matrix. LIKELY – Occurs several times. 11. Develop Controls – Develop one or more controls for each hazard that will either eliminate the OCCASIONAL – Occurs sporadically. hazard or reduce the risk (probability and/or severity). Specify who, what, where, why, when, and how SELDOM – Unlikely, but could occur at some time. for each control. 12. Residual Risk Level – Determine the residual risk for each hazard by applying the risk UNLIKELY – Can assume it will not occur. assessment matrix, assuming the controls are implemented. 13. Implement Controls – Decide how each control will be put into effect or communicated to the SEVERITY – The expected consequence of an event in terms of degree of injury, property personnel who will make it happen (written or verbal instruction; tactical, safety, garrison SOPs, damage, or other mission-impairing factors. rehearsals). CATASTROPHIC – Death or permanent total disability, system loss, major damage, 14. Who/How Supervised – Who and how will each control be monitored (continuous significant property damage, mission failure. supervision, spot-checks). Evaluate frequently and pass on lessons learned. CRITICAL – Permanent partial disability, temporary total disability in excess of 3 months, 15. Determine Overall Mission/Task Risk – Select the highest residual risk level and circle it. major system damage, significant property damage, significant mission degradation. This becomes the overall mission or task risk level. The commander decides whether the controls MARGINAL – Minor injury, lost workday accident, minor system damage, minor property are sufficient to accept the level of residual risk. If the risk is too great to continue the mission or task, the commander directs development of additional controls or modifies, changes, or rejects the COA. damage, some mission degradation. 16. Medical Support – Select type of on-site medical support provided and circle it. NEGLIGIBLE – First aid or minor medical treatment, minor system impairment, little/no impact on mission accomplishment. 17 & 18. Self explanatory 19. Risk Decision Authority – The decision to accept or not accept the risk(s) associated with an * FM 101-5, 31 May 1997 action is made by the appropriate commander or leader responsible for performing that action. RISK MANAGEMENT WORKSHEET (CDTCMD Reg 385-10; proponent agency is Cadet Command Safety) 1. Organization and Unit Location: 2. Page of Bulldog BN, 14th BDE, Western Region ROTC 2 4 3. Mission/Task: 4. Begin Date: 5. End Date: 6. Date Prepared: Spring 2007 Field Training Exercise 20APR07 22APR07 06MAR07
7. Operational Phase in which the Mission/Task will be conducted: Phase I, II, III, IV, and V 10. 12. 8. Tasks 9. Identify Hazards 11. Develop Controls 13. Implement Controls 14. Who/How Initial Residual (“How To”) Supervised Risk Risk Level Level RISK MANAGEMENT WORKSHEET (CDTCMD Reg 385-10; proponent agency is Cadet Command Safety) 1. Organization and Unit Location: 2. Page of Bulldog BN, 14th BDE, Western Region ROTC 2 4 3. Mission/Task: 4. Begin Date: 5. End Date: 6. Date Prepared: Spring 2007 Field Training Exercise 20APR07 22APR07 06MAR07
7. Operational Phase in which the Mission/Task will be conducted: Phase I, II, III, IV, and V -Day Land -Dehydration (L) -Water points will be placed (L) -Water point S-4 Navigation throughout the Land Nav Course. coordinates will be -Each Cadet will start course made to Cadets. with two full canteens. -Each Cadet will be S-1 checked for water -Twisted ankles (L) -Brief cadets on uneven terrain. (L) during checkout to from uneven start the course. terrain -Safety brief prior XO to training to all -Cadets getting (L) -Inexperienced Cadets will go (L) Cadets. lost out in groups of three or four. -Groups check out S-1 -Establish a panic azimuth. with S-1 prior to training. -Cover in safety XO briefing.
-Night Land -Dehydration (L) -Water points will be placed (L) -Water point S-4 Navigation throughout the Land Nav Course. coordinates will be -Each Cadet will start course made to Cadets. with two full canteens. -Each Cadet will be S-1 checked for water -Twisted ankles (L) -Brief cadets on uneven terrain. (L) during checkout to from uneven start the course. terrain -Safety brief prior XO to training to all -Cadets getting (L) -Inexperienced Cadets will go (L) Cadets. lost out in groups of three or four. -Groups check out S-1 -Establish a panic azimuth. with S-1 prior to training. -Cover in safety XO briefing. -Falling down (L) -Each Cadet will have a (L) -PCI Cadets for 1SG due to lack of flashlight on them as part of flashlight and to sight LBE. ensure that it works.
CDTCMD Form 385-2-R-E, Apr 01 Risk Assessment and Risk Management Countermeasure Worksheets in CC Reg 145-3 are OBSOLETE RISK MANAGEMENT WORKSHEET (CDTCMD Reg 385-10; proponent agency is Cadet Command Safety) 1. Organization and Unit Location: 2. Page of Bulldog BN, 14th BDE, Western Region ROTC 3 4 3. Mission/Task: 4. Begin Date: 5. End Date: 6. Date Prepared: Spring 2007 Field Training Exercise 20APR07 22APR07 06MAR07
7. Operational Phase in which the Mission/Task will be conducted: Phase I, II, III, IV, and V 10. 12. 8. Tasks 9. Identify Hazards 11. Develop Controls 13. Implement Controls 14. Who/How Initial Residual (“How To”) Supervised Risk Risk Level Level RISK MANAGEMENT WORKSHEET (CDTCMD Reg 385-10; proponent agency is Cadet Command Safety) 1. Organization and Unit Location: 2. Page of Bulldog BN, 14th BDE, Western Region ROTC 3 4 3. Mission/Task: 4. Begin Date: 5. End Date: 6. Date Prepared: Spring 2007 Field Training Exercise 20APR07 22APR07 06MAR07
7. Operational Phase in which the Mission/Task will be conducted: Phase I, II, III, IV, and V -Squad STX -Dehydration (M) -Two 5 gallon water jugs will be (L) -Place two 5 gallon S-4 utilizing placed at every TAA site. water jugs at TAA paintball -Each Cadet will start each sites. mission with two full canteens. -PCI cadets for full Squad Leader -Patrolling -Twisted ankles (L) -Brief Cadets on uneven terrain. (L) canteens prior to STX utilizing from uneven mission start. paintball terrain -Conduct safety XO briefing prior to -Close (M) -Establish a safety kill zone of (L) training. proximity fires ten meters. -Brief Cadets that XO any shots fired -Shots to the (M) -Wearing of facial protection (L) within 10 meters is a face equipment at all times when safety violation and executing a mission. just call “safety kill”. -Limited (L) -Safety brief given to Cadets (L) -All Cadets will be S-4 visibility due prior to start of training. issued a face mask to wearing of prior to training w/ mask paintball. -O/Cs will be move w/ O/Cs SQDs and will halt training if Cadet is not wearing mask. -Brief Cadets to clean mask prior to XO training and at designated breaks. -Ensure that two 5 -Obstacle -Dehydration (L) -10 gallons of water placed at (L) gallon water jugs are S-4 Course training site. full at training -Falling from (L) -Wear of LBE to ensure that (L) sites. obstacles Cadets have water on them at all -PCI Cadets to ensure times. that they have full Squad Leader -Conduct safety brief prior to canteens. training. -Assign safeties as -Have safeties at all points necessary to spot O/Cs that involve a Cadet’s feet Cadets. leaving the ground. -Assign O/Cs. -Have O/C move with all persons. CO CDTCMD Form 385-2-R-E, Apr 01 Risk Assessment and Risk Management Countermeasure Worksheets in CC Reg 145-3 are OBSOLETE