1 of Table 2 Synthesis Table 2: General Information
Practice Area: General –Drugs Needlesticks/Procedures
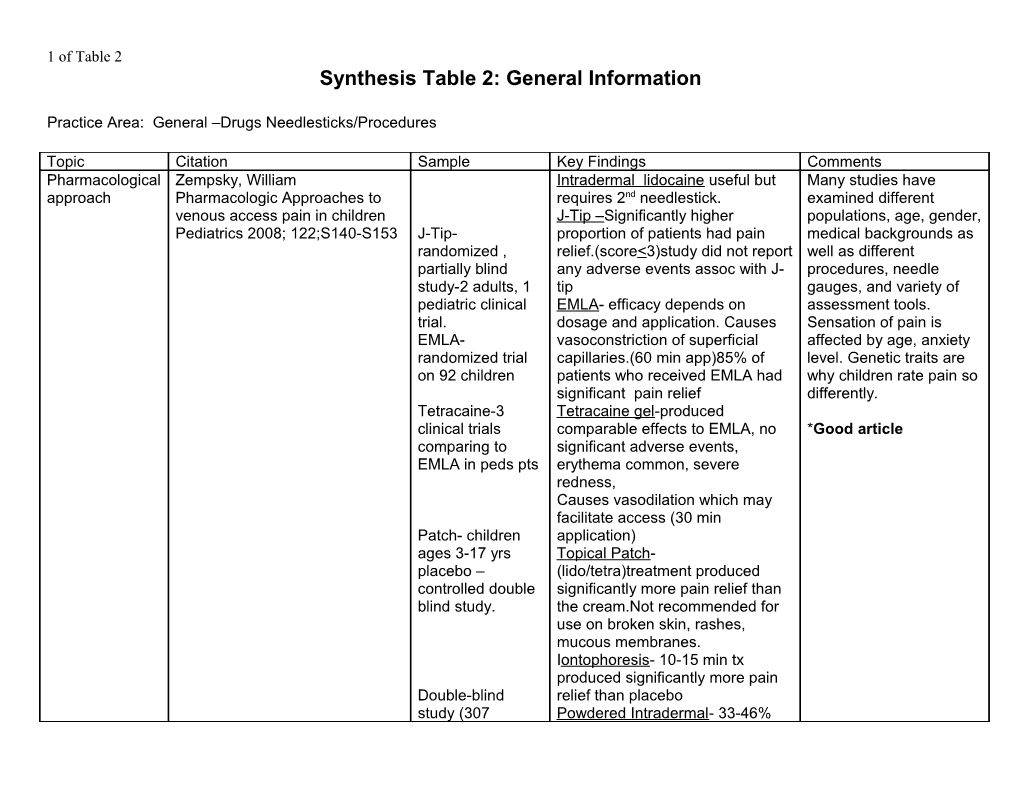
Topic Citation Sample Key Findings Comments Pharmacological Zempsky, William Intradermal lidocaine useful but Many studies have approach Pharmacologic Approaches to requires 2nd needlestick. examined different venous access pain in children J-Tip –Significantly higher populations, age, gender, Pediatrics 2008; 122;S140-S153 J-Tip- proportion of patients had pain medical backgrounds as randomized , relief.(score<3)study did not report well as different partially blind any adverse events assoc with J- procedures, needle study-2 adults, 1 tip gauges, and variety of pediatric clinical EMLA- efficacy depends on assessment tools. trial. dosage and application. Causes Sensation of pain is EMLA- vasoconstriction of superficial affected by age, anxiety randomized trial capillaries.(60 min app)85% of level. Genetic traits are on 92 children patients who received EMLA had why children rate pain so significant pain relief differently. Tetracaine-3 Tetracaine gel-produced clinical trials comparable effects to EMLA, no *Good article comparing to significant adverse events, EMLA in peds pts erythema common, severe redness, Causes vasodilation which may facilitate access (30 min Patch- children application) ages 3-17 yrs Topical Patch- placebo – (lido/tetra)treatment produced controlled double significantly more pain relief than blind study. the cream.Not recommended for use on broken skin, rashes, mucous membranes. Iontophoresis- 10-15 min tx produced significantly more pain Double-blind relief than placebo study (307 Powdered Intradermal- 33-46% 2 of Table 2 children) Reduction compared to placebo Pharmacological Fetzer, SJ Coolant: Ethyl Chloride – 10 Description of discomfort interventions for Reducing the Pain of second spray lasts 5 seconds- from IVs venipuncture Venipuncture Article child has sense of control if asked-78% reported less pain Lidocaine-intradermal injection * Good review of skin- EMLA30-60 minutes – last 85 pain with needlestick minutes, remain on skin fro 5 hrs Non- Carlson, KL ` Review Article Acute pain Multi-component pharmacological Pediatric Nonpharmacological 20 articles Multi-component was Cognitive packages result in lower pain Pain Management; A Review of between 1984- Behavioral interventions. self-reports of pain management Intervention Research 1995 Most studies focused on neonates perception and Capsules and Comments in and preschool to school aged decreased behavioral Pediatric Nursing 1996 2(4): 269- General principles distress. How these 277. Nonpharmacological interventions work alone techniques help control pain, or in combination Focus the child’s attention remains unkown away from the event Non pharmacological interventions can be used independently or with drugs. Pharmacological Doeliman, D Article Topics covered: preparation, Good table of Age and Non- Pharmacological Techniques in Distraction, guided Imagery, Appropriate care Pharmacological Reducing Venipuncture modeling, music, Massage. Psychological Trauma in Pediatric Patients Cultural aspects included Journal of Infusion Nursing2003, 26(2):103-109 Pediatric Schechter, NL, Zempsky, WT, Review article Sections: Effect of reassurance Immunization Cohen, LL, McGrath, PJ, Preparation Nurse behavior – McMurtry, Bright, NS Mayday Fund – Technique increases coping skills Pain Reduction During Pediatric hosted a Location Parent behaviors related Immunization : Evidence-Based consensus Needle length to distress Review and Recommendations conference Local Anesthetic use Excellent article Expert panel Local anesthetic for reviewed highly anxious and 3 of Table 2 literature phobic chidlren Immunizations- Shah, V, Taddio, A & Rieder, MJ Systematic review Topical local anesthetics, sweet- Very detailed review and Pharmacological Effectiveness and tolerability of and Meta- tasking solutions and combined analysis and combined pharmacologic and combined analysis analgesic interventions including interventions interventions for reducing 32 studies breastfeeding were associated injectionpPain during routine 3856 subjects 2 with reduced pain childhood immunizations: weeks to 15 yrs in Systematic review and Meta- the review analyses 23 of the trials Clinical Therapeutics 2009 31 included in the (B): s104-S151 meta-analysis Mother and staff Sweet, SD and McGrath, PJ 60 patient Mother’s distress-promoting Reassurance and behavior and Relative importance of mothers’ 6 tp 18 months behaviors predicted increased comforting – distress infant pain versus medical staffs’ behaviors Video taped infant behavior while staff promotoing behavior in the prediction of infant coping-promoting behaviors immunization pain behavior. predicted decreased pain Distraction- coping- Journal of Pediatric behavior promoting behaviors Psychology1998 23(4) : 2249- ( baseline, injection, 256. recovery)