DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION OF SPHERE STUDY Information and communication safety s t
Number i d e
r Distribution by c of f semester o
r e
the b
The humanities and social-economic subjects m s u n
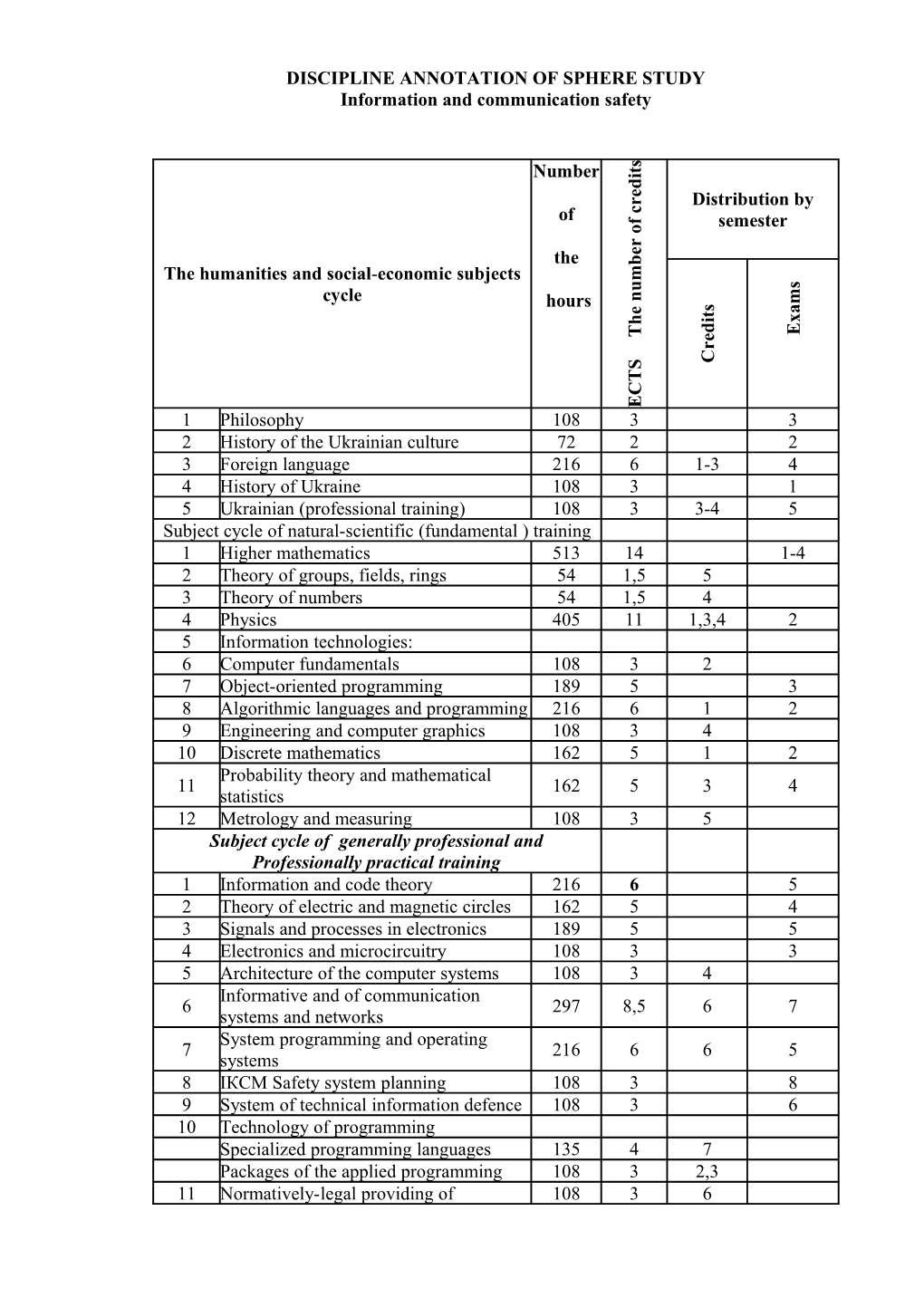
cycle m hours s a e t i x h d E T e r C S T C E 1 Philosophy 108 3 3 2 History of the Ukrainian culture 72 2 2 3 Foreign language 216 6 1-3 4 4 History of Ukraine 108 3 1 5 Ukrainian (professional training) 108 3 3-4 5 Subject cycle of natural-scientific (fundamental ) training 1 Higher mathematics 513 14 1-4 2 Theory of groups, fields, rings 54 1,5 5 3 Theory of numbers 54 1,5 4 4 Physics 405 11 1,3,4 2 5 Information technologies: 6 Computer fundamentals 108 3 2 7 Object-oriented programming 189 5 3 8 Algorithmic languages and programming 216 6 1 2 9 Engineering and computer graphics 108 3 4 10 Discrete mathematics 162 5 1 2 Probability theory and mathematical 11 162 5 3 4 statistics 12 Metrology and measuring 108 3 5 Subject cycle of generally professional and Professionally practical training 1 Information and code theory 216 6 5 2 Theory of electric and magnetic circles 162 5 4 3 Signals and processes in electronics 189 5 5 4 Electronics and microcircuitry 108 3 3 5 Architecture of the computer systems 108 3 4 Informative and of communication 6 297 8,5 6 7 systems and networks System programming and operating 7 216 6 6 5 systems 8 ІКСМ Safety system planning 108 3 8 9 System of technical information defence 108 3 6 10 Technology of programming Specialized programming languages 135 4 7 Packages of the applied programming 108 3 2,3 11 Normatively-legal providing of 108 3 6 informative safety 12 Applied cryptology 270 7,5 5 6 Safety of the informative and of 13 243 7 8 7 communication systems and networks Complex systems of information 14 108 3 8 defence 15 Management informative safety 81 2 7 principles of personal and social safety 16 108 3 4 and labour protection 17 Physical education 378 10,5 2,6,7 Disciplines of educational institution
independent choice Organization of databases and 1 162 4,5 6 knowledge 2 Introduction to the profession 81 2 1 3 Basis of informative safety of the country 54 1,5 2 4 Ecology 54 2 7 Free choice student`s disciplines 1 Military training 1044 29 5-7 8 Subject cycle of of generally professional and Professionally practical training 1 Management 81 2 8 Mathematical modelling of complex 2 189 5 7 systems 3 Parallel systems and calculations 108 3 8 Information defence to management of 4 243 7 7 8 complex system 5 Optoinformatics 72 2 5 Organizing providing of information 6 81 2,5 8 defence 7 Economic security 54 1,5 6 8 Industrial practice 162 5 7 9 Pre-dimploma practice 216 12 8 PHYSICS Lecturer: Full Professor Girka Volodymyr Oleksandrovich Prior reqqirements: general educational course in the secondary educational institutions Aim of the course: To form students` scientific view of the physical processes in the world, to leave theoretical bases of classic mechanics and molecular physics ,basic methods of experimental research of mechanical motion characteristics in their consciousness . To master theoretical bases of molecular physics. To teach students the basic methods of solution of tasks from classic mechanics and molecular physics, using basic methods of differential and integral calculation and also to the basic methods of experimental research of mechanical motion characteristics, and processes in the thermodynamics systems. To make the students form a general and subject competence in the fields of mechanics and molecular physics. Task: 1. To form the scientific world-view of specialists in computer sciences, on the basis of theoretical knowledge ?mechanic laws and molecular physics, practical skills of tasks solutions and implementation of the experimental parameter measuring of mechanical and thermodynamics processes; 2. As the mathematical apparatus of foregoing sections about mechanics and molecular physics is most developed, their study is very important from the viewpoint of fixing knowledge about bases of calculus and vector algebra in practice of solving particular tasks that describe mechanical and thermodynamic processes. 3. To show an interconnection between the mechanic laws and molecular physics. Taking into consideration broad use of analogy methods, and also from the viewpoint of mathematical methods similarity that describe physical processes, it is useful for studying other sections of classic physics. As a study result of this course a student must Know: classic mechanic laws and molecular physics, be able to use them for solving theoretical tasks, be able and to apply these laws for procedure of physical parameters measuring, that mechanics and molecular physics operate, to explain experimental results that is received at implementation of laboratory works Be able to : to execute basic physical parameters measurement in laboratory works. 1. Discipline description: The subject of discipline are basic laws of classic mechanics and molecular physics. It is connected with that physics is main natural discipline in vocational training of computer sciences specialist, without knowledge of which the conscious, qualitative use of mathematical knowledge and actually special computer disciplines, which is the basis of future education of computer sciences specialist , is impossible. During the first two semesters two sections of physics are studied: mechanics and molecular physics, that are base component parts of classic physics. 2. The form of control: written tests after completion of the thematic modules, current control of independent task implementation, written reports of laboratory works, written final test in 1 semester and written examination in 2 semester. Basic literature: 1. Савельев И.В. Куpс общей физики. - М.: Hаука, 1966. -т.1. 2. Ландау Л.Д., Ахиезеp А.И., Лифшиц Е.М. Механика и молекуляpная физика(Mechanics and molecular physics). -М.: Hаука, 1965. 3. Дущенко В.П., Кучерук І.М. Загальна фізика:Фізичні основи механіки. Молекулярна фізика і термодинаміка (General physics: physical bases of mechanics. Molecular physics and thermodynamics). - К.: Вища школа, 1993.- 431 с. 4. Дутчак Я.Й. Молекулярна фізика(Molecular physics). - Видавництво Львівського університету, 1973. С. 264. 5. Савельев И.В. Сбоpник вопросов и задач по общей физике ( Collection of questions and tasks on general physics). -М.: Hаука, 1982. 6. Волькенштейн В.С. Сбоpник задач по общему курсу физики.(Collection of tasks on general course of physics) -М.: Hаука, 1985. 7. Иpодов И.Е. Задачи по общей физике.(Tasks on general physics) -М.: Hаука, 1988. 8. Гірка В.О., Гірка І.О., Кондратенко А.М., Методичні поради до розв'язання домашніх завдань з курсу “Фізика” для студентів першого курсу факультету комп'ютерних наук. (Methodical advises to solving home tasks from the course of “Physics” for first-year- students of computer science faculty) – Харків.: Просвіта, 2005. 9. Гірка В.О., Гірка І.О., Кондратенко А.М., Методичні вказівки до виконання лабораторних робіт з курсу “Механіка” для студентів першого курсу факультету комп’ютерних наук. (Methodical instructions to implementation of laboratory works from the course of "Mechanic" for first-year-students of computer sciences faculty) – Харків.: Просвіта, 2004. 10. Гірка В.О., Гірка І.О., Кондратенко А.М., Методичні вказівки до виконання лабораторних робіт з курсу “Молекулярна фізика” для студентів першого курсу факультету комп’ютерних наук. (Methodical instructions to implementation of laboratory works from the course of "Molecular physics" for first-year-students of computer sciences faculty )– Харків.: Просвіта, 2004. 11. Гірка В.О., Гірка І.О., Кіндратенко А.М. Методичні поради до виконання фізичного практикуму студентами першого курсу Інституту високих технологій. (Methodical advises to implementation of practical work on physics for first-year-students of High Technologies Institute)Харків, 2005. SUPPLEMENTARY 1. Біленко І.І. Фізичний словник(Physical vocabulary).-К.: Вища школа, 1993. 2. Телеснин Р.В. Молекуляpная физика.(Molecular physics) -М.: Высш. школа, 1973. 3. Кучерук І.М., Горбачук І.Т., Луцик П.П. Механіка. Молекулярна фізика і термодинаміка.(Mechanics. Molecular physics and thermodynamics) Том 1. -К.: Техніка, 1999. 4. Иpодов И.Е., Савельев И.В., Замша О.И. Сборник задач по общей физике.(Collection of tasks on general physics) DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION Probability theory and mathematical statistics
1. Lecturer: Kabalyants Petro Stepanovych, the Assistant Professor of the Mathematical Simulation and Computer Software Department 2.Status: Obligatory 3.Year,semester: I and II years, 2 and3 semesters. 4.Amount of credits: 5; all amount of academic hours -162; 52 hours of lectures 52 hours of workshops, 58 hours of independent work. 1 semester – 2,5 credits: chapters 1,2,3 – written test + credit; 2 semester – 2,5 credits: chapters 4,5,6 – written test + credit; 5. Prior requirements: subjects of “ Discrete mathematics” and “Mathematical analysis” 6. Subject description (content, aims, structure):The subject of discipline is theoretical- and mathematical statistics methods. The methods of mathematical models building of probabilistic experiment, imitation of random variable by the methods of statistic evaluation theory, correlative and regressive analysis, are thoroughly studied. The asymptotic probabilistic methods of analysis are survey studied. The aim of the course: Aim of course consists in giving the future specialists with knowledge in the sphere of modern probability theory and mathematical statistics and use of its methods in modeling and analyzing the real objects and processes. The discipline program consists of ?educational schedule, thematic plan that contains 6 chapters, and list of basic literature. 7. Forms of teaching: lectures, workshops, independent work. Methods of teaching: elements of problem lectures, individual tasks for independent work. 8. Assessment forms: written control of individual tasks, written tests, written credit and written examination in 2 and 3 semesters accordingly. Assessment Criteria: Only those students who received more than 35% by all forms of current control from general amount of points are admitted to the examination; the students who received more than 91% by all forms of current control from general amount of points won’t have to take examination. 9 Supportive materials: Program. Calendar plan of studying the discipline. Textbooks. Educational manuals of the department. Collection of tasks. Sets of individual tasks for current control of knowledge. Tasks for rectorial control works. Examination paper
10.Language of Instruction: Russian 11. List of Recommended Literature: Basic Literature 1. Гихман И.И., Скороход А.В., Ядренко М.И. Теория вероятностей и математическая статистика(Probability theory and mathematic statistics). К., Вища школа, 1979. 2. Климов Г.П.. Теория вероятностей и математическая статистика (Probability theory and mathematic statistics)М., Издательство Московского университета, 1983. 3. Коваленко И.Н., Гнеденко Б.В. Теория вероятностей К. (Probability theory), Вища школа ,1990. 4. Розанов Ю.А. Теория вероятностей случайные процессы и математическая статистика. (Probability theory ,stochastic processes and mathematical statistics)М., Наука, 1985. 5. Крамер Г. Математические методы статистики.(Mathematical methods of statistics) М., Мир, 1975. 6. Шметтерер Л. Введение в математическую статистику(Introduction to mathematical statistics). М., Наука, 1976. 7. Закс Ш. Теория статистических выводов(Statistic inferences theory). М., Мир,1975. 8. Кендалл М.Д., Стюарт А. Статистические выводы и связи.(Statistic inferences and connections) М., Наука, 1973. 9. Боровков А.А. Математическая статистика.(Mathematical statistics) М., Наука, 1984. 10. Леман Э. Проверка статистических гипотез(Statistical hypothesis testing). М., Наука, 1979. 11. Бикел П., Доксам К. Математическая статистика.(Mathematical statistics) М., Финансы и статистика, 1983. 12. Ермаков С.М., Михайлов Г.А. Курс статистического моделирования. (Statistical modeling course)М., Наука, 1976. 13. Сборник задач по теории вероятностей математической статистике и теории случайных функций.(Collection of tasks on probability theory, mathematical statistics and stochastic processes) Под ред. А.А. Свешникова, М., Наука,1970. Educational manuals and workbooks. 1. Учебно-методическое пособие “Теория вероятностей и математическая статистика”. Сост. Рофе-Бекетов (Probability theory and mathematical statistics)Ф.С., Подцыкин Н.С. – Харьков, 2001. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION Mathematical analysis and differential equations Lecturer: Nikolenko Irina Gennadiyevna, PhD(physic and mathematic), Associate Professor Status: Obligatory Years, semesters: 1-2 years, 1-3 semesters Aim of the course is to provide future specialists with knowledge in the field of mathematical analysis and differential equation. Prior requirements: “Higher mathematics”, 1 semester, “Analytic geometry”, 1 semester. Subject objective: According to the results of studying the discipline the students must: Know: Properties of infinitely small sequences or functions rules of differentiation theories of Roll, Lagrange, L'Hopital indispensable and sufficient conditions of functions extremum characteristics of antiderivative and indefinite integral calculus rules of Riemann definite integral calculation rules of figures plane, line length, object volumes formulas of differential function of two variable and derivative of compound function least squares method linear operations above rows conditions of the convergence or divergence of series theorems of Leibniz, Abel, Taylor and McLaren series formulas of Euler, Fourier series for a periodic function and Fourier’s integrals of Fourier and Laplace for derivatives calculation formulas of curvilinear, double an triple integral Green’s theorem Formulas of vector field flow through the surface Taylor’s series Methods of solving first-order differential equation Calculation of characteristic polynomial of differential equation, use of Wronskian determinant setting and determination of Cauchy` s function technology of integrating the system of first-order linear equation to the one second-order equation theorems about existence of Laplace’s image representation formulas of derivatives and convolution integral of originals Euler-Puasson and Ostrogradsky equations To group the heuristic formulas for natural variable functions by the methods of mathematical induction Theorem proving
Be able to: To calculate bounds and derivatives of simple and compound functions of one and few variables investigate the functions set directly, indirectly and by means of parameters, to build their graphs to find definite and indefinite Riemann’s integrals to calculate figures area, line length, object volumes to solve differential equation and systems of differential equations to use differential and integral calculation for physical tasks to investigate the numerical, power series and unusual integrals on convergence to develop the functions of the real variable in the Taylor’s , McLaren` s and Fourier` s series to find the function extremums of many variables to calculate curvilinear, double, triple integrals to find the vector field flow through the surface to use formulas of Stokes and Gaus-Ostrogradskiy to calculate integrals by means of beta- and gamut- functions
Subject description: Sets and functions; operation with sets; sets mapping; bounded sets, exact bounds of numerical sets; Kantor` s principle of nested intervals: equivalent sets; counted and uncounted sets; bounds theory: bound of sequence, bound of function; partial, upper and lower bound of function. Function continuity: local features of function continuity, features of function continuity on a segment. Differential calculation of one variable functions: derivatives and differentials of random order, features of differential functions; Taylor formula; research on extremum and construction function graphs. Indefinite integral: antiderivative and indefinite integral, their features; replacement of variable and partly integration; Tabular integrals; methods of integration: of rational functions. Ostrogradsky method; irrationalities; rational functions from trigonometric; some transcendent functions; Integral of Riemann: features of integrated functions; geometrical and physical use of integral; nonintrinsic Riemann integral. Nonintrinsic integrals: on an infinite interval and from a boundless function on a finite interval; convergence tests of nonintrinsic integrals; absolute and conditional convergence. Series: convergence tests of series, absolute and conditional convergences. Space n : Metrical space, open and closed sets, their features; compacts in metrical space and in n ; sequences in n , their convergence; features of compactness. Differential calculation of many variables functions: derivatives and differentials of random order, features of differential functions; formula of Taylor; implicit function theorem; extremum research and conditional extremum of functions. Functional sequences and series: signs of uniform convergence of functional series; theorems about termwise differentiation and integration of functional series; power series and Taylor series. Riemann integral that depends on parameter; integrals of Euler, method of Laplace; Multiple integral of Riemann: features of integrated functions on series, measured by Jordan; theorems of Fubini and about substitution of variables. Nonintrinsic integrals, geometrical and physical use of multiple integrals. Curvilinear and surface integrals: calculation of first kind surface integrals and their features, calculation of second kind surface integrals; General theorem of Stokes and its classic separate cases; elements of field theory. Fourier`s series: Fourier`s series relatively to ortogonal system of vectors; trigonometric series of Fourier and their pointwise convergence. Fourier integral: features of Fourier transformation and pointwise convergence of the Fourier integral. Differential equations of n-order; Cauchy task of differential equation (DE); geometrical interpretation of first find order DE; normal system (NS) of DE, integration of DE to NS; Cauchy task of NS; equations of separating variables and variables integrated to them; differential equations of higher order that assume the decline of order. Linear differential equations: linear differential equations of first-order, methods of integrating multiplier and variations of random constant, equations in complete differentials, linear differential equation of higher order, theorems of solving linear DE, linear differential equations with constant coefficients; Euler equations; variation method of random constant; differential equations of string vibration; Linear systems of differential equations : linear systems of differential equations with variable coefficients; the linear systems of differential equations with constant coefficients. Laplace transform and use of operating calculation for differential equations. Assessment forms: calculation tasks, tests, exam.
Supportive materials: methodical manuals, methodical guides and calculative- graphical (test) tasks. List of recommended literature: 1. Карташев А.П., Рождественский Б.Л. Математический анализ(Mathematical analysis). - М.: Наука, 1984. 2. Кудрявцев Л.Д. Краткий курс математического анализа(Brief course of mathematical analysis). - М.: Наука, 1989. 3. Зорич В.А. Математический анализ. (Mathematical analysis) - М.: Наука, 1984 (I, II т.). 4. Фихтенгольц Г.М. Основы математического анализа. (Bases of mathematical analysis) - М.: Наука, 1964 (I, II т.). 5. Кудрявцев Л.Д., Кутасов А.Д., Чехлов В.И., Шабунин М.И. Сборник задач по математическому анализу. (Collection of tasks on mathematical analysis) - М.: Наука, 1984. - I т. (Предел, непрерывность, дифференцируемость). 6. Кудрявцев Л.Д., Кутасов А.Д., Чехлов В.И., Шабунин М.И. Сборник задач по математическому анализу(Collection of tasks on mathematical analysis). - М.: Наука, 1984. - II т. (Интегралы, ряды). 7. Демидович Б.П. Сборник задач и упражнений по математическому анализу. (Collection of tasks on mathematical analysis) - М.: Наука, 1966. 8. Петровский И.Г. Лекции по теории обыкновенных дифференциальных уравнений. (Lectures about theory of simple differential equations) М., Изд-во Моск. Ун-та, 1984. 9. Степанов В.В. Курс дифференциальных уравнений.(Course of differential equations) - М.: Гостехиздат, 1953. 10.Понтрягин Л.С. Обыкновенные дифференциальные уравнения.(Simple differential equations) - М.: Наука, 1974. 11.Филиппов А.Ф. Сборник задач по дифференциальным уравнениям.(Collection of tasks on differential equations) - М.: Наука, 1973(1979). DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION Discrete Mathematics . Lecturer: Kabalyants Petro Stepanovych, the Assistant Professor of the Mathematical simulation and Computer Software Department 1.Status: Obligatory 2.Year,semester: I year, 1 and 2 semesters. 3.Amount of credits: 5; all amount of academic hours -162; 52 hours of lectures 52 hours of workshops, 58 hours of independent work. 1 semester – 2,5 credits: chapters 1,2,3 – written test + credit; 2 semester – 2,5 credits: chapters 4,5, – written test + credit; 4. Prior requirements: basic school course of mathematics 5. Subject description (content, aims, structure): The subject of discipline is the methods of discrete mathematics, methods of set theory. methods of theory of sets, theory of the graphs, combinatorics, logic, theory of numbers and coding theories. The methods of sets theory and theory of the graphs are thoroughly studied. The methods numbers theory and coding methods are review studied. The separate chapter is dedicated to combinatorial analysis. The aim of ?course is studying the basic mathematical methods of discrete mathematics : theories of the graphs, theory of sets, combinatorics, logic, theories of automata and grammars. Considerable attention is paid to the matrix, numeral and general methods of algebra, effective in computer realization. The program of discipline consists of educational schedule, thematic plan that contains 4 chapters with 45 topics, and list of supportive materials. 6. Forms of teaching: lectures, workshops, independent work. Methods of teaching: elements of problem lectures, individual tasks for independent work. 7. Assessment forms: written control of individual tasks, written tests, written credit and written examination in 1 and 2 semesters accordingly.
Assessment Criteria: Only those students who received more than 35% by all forms of current control from general amount of points are admitted to the examination; the students who received more than 91% by all forms of current control from general amount of points won`t have to take examination. 8.Supportive materials: Program. Calendar plan of studying the discipline. Textbooks. Educational manuals of the department. Collection of tasks.(with printed material to the chapter of “Combinatorics”) Electronic compendium Sets of individual tasks for current control of knowledge. Tasks for rectorial control works. Examination tickets 9.Language of Instruction: Russian 10.The list of recommended literature: Basic Literature
1. Берж К. Теория графов и ее применение(Theory of graphs and its use). – М.: ИЛИ, 1962. – 320с. 2. Оре О. Теория графов(Theory of graphs). – М.: Наука, 1968. – 352с. 3. Сешу С., Рид М.В. Линейные графы и электрические цепи(Linear graphs and electric circuit). – М.: Высшая школа,1971. – 448с. 4. Харари Ф. Теория графов(Theory of graphs). – М.,Мир,1973. – 304с. 5. Басакер Р.,Саати Т. Конечные графы и сети(Finite graphs and networks). – М.:Наука,1974. – 336с. 6. Кристофидес Н. Теория графов (алгоритмический подход). (Theory of graphs(algorithmic approach)) – М.: Мир, 1978. – 432с. 7. Майника Э. Алгоритмы оптимизации на графах и сетях.(Algorithms of optimization on graphs and networks) – М.: Мир, 1981. – 323с. 8. Свами М., Тхуласираман Н. Графы, сети и алгоритмы.(Graphs,networks and algorithms) – М.: Мир, 1984. – 454с. 9. Филлипс Д., Гарсиа-Диас А. Методы анализа сетей(Methods of networks analysis). – М.: Мир, 1984. – 496с. 10. Кук Д., Бейз Г. Компьютерная математика.(Computer mathematics) – М.: Наука,1990. – 384с. 11. Колмогоров А.Н., Драгалин А.Г. Введение в математическую логику(Introduction to mathematical logic). Учеб пособие для вузов. – М.: Изд.-во МГУ, 1982. – 120с. 12. Сигорский В.П. Математический аппарат инженера (Mathematical apparatus of engineer). – Киев, Техника, 1977. – 766с. 13. Кузнецов ОЛ.П., Адельсон-Вельский Г.М. Дискретная математика для инженера(Descrete mathematics for engineer). – М.: Энергия, 1980. – 342с. 14. Яблонский С.В. Введение в дискретную математику.(Introduction to discrete mathematics) – М.: изд. МГУ, 1986. – 384с. 15. Виноградов И.М. Основы теории чисел(Bases of numbers theory). – М.: Наука 1965. – 172с. 16. Гускин В.М., Цейтлин Г.Е., Ющенко Е.Л. Алгебра, язык, программирование.(Algebra, language, programming) – К.: Наукова думка, 1978. – 318с. Educational manual and methodical instructions 1. Руткас А.Г. Введение в теорию графов. Учебное пособие (Introduction to graph theory. Educational manual). – Х.: ХГУ, 1993. – 63с. 2. Дюбко Г.Ф. Введение в формальные системы.(Introduction to formal systems) – Х.: ХИРЭ, 1992. – 170с. 3. Бондаренко М.Ф., Білоус Н.В., Шубін І.Ю. Збірник тестових завдань з дискретної математики.(Collection of tasks on discrete mathematics) – Х.: ХДТУРЕ, 2000. – 156с. 4. Бондаренко М.Ф., Білоус Н.В., Руткас А.Г. Комп'ютерна дискретна математика: Підручник для ВУЗів(Computer discrete mathematics. Manual for Universities). – Х.: Компания СМІТ, 2004. – 479с. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION Economics Lecturer: Shedyakova Tatyana Evgeniyivna, Associate Professor of the Economic Theory Department Status: Obligatory Year,semester: I year, 2 semester. Prior requirements: Higher Mathematics and Philosophy Subject description : The subject of the discipline is studying economical regularities of public production development, grounding the choice of optimal using means of limited resources by economic agent, with the aim of full satisfaction of people growing needs. The aim of course is forming of the system of knowledge about economic relations in society, problems of the effective use of the limited resources, functioning of basic components of the economic system, development the economical thinking of the students, and also training for further studying the bases of other economic disciplines and possible use of economic knowledge in future professional activity. Know: the basic stages of economic idea development, problems and regularities of public production functioning and development, property relations, economic systems, commodity-money relations, basis of demand and supply in market economy, rational consumer choice, functioning of companies, markets of resources and market structures, regularities of national economy functioning, money-and-credit and financial systems, formation of macroeconomic balance and forms of macroeconomic instability, the basis of government management of economy and international economic relations. Theoretical material, that is studied by students, is divided into 16 topics. Forms of teaching: lectures, workshops, independent work. Assessment forms: written module tests as a current control, and also questioning on workshops on the studied theoretical material; written examination as a final control. Assessment criteria: The knowledge evaluation of students is implemented according to the Bologna system. After all types of works a student can get at most 100 points, from which 60- is current work in a semester, and 40 - is final control. A course is divided into 3 module tests, each of them permits to get 1/3 from general amount of points that are due to current work. The knowledge evaluation of students is implemented on the basis of average rating calculation after each module test and exam separately, with next re-calculation of these ratings into a sum of gained points by means of special coefficients as ratio of maximum possible number of points, which can be gained within the module tests or exams, to the maximum of the scale, in which average rating is determined .Average rating calculation is implemented according to the 5 point scale. For the evaluation of students work on workshops and on examinations there is a scale from 0 to 5 points with the division value of 0, 5 point. For the evaluation of current module tests a 5 point scale is also used, but ?mark is given as a quotient from the division of sum of the points gained by a student during implementation of test, on the coefficient of re-calculation that is determined as quotient from the division questions amount that were in the 5 point test . Writing of all tests is obligatory. If a student doesn’t write a test he will gain 0 points for it. ? Average rating calculation of current work during the semester is implemented according to the formula of arithmetic mean, which is considered as weighting coefficient 2- for module test, 1 or 0,5 (subject to the weight of the student’s work and his activity )- for workshop. The examination passed by a student is estimated as arithmetic mean for every question that contains in the ticket, separately. Thereby, gained average rating re-calculated into number of points gained on the exam, according to the described procedure. Final mark is determined on the basis of the sum of the points gained by a student, according to this scale. Supportive materials: - The program; - textbooks and manuals on economic theory; - regulatory-legal documents that regulate running of economical processes in society: - collections of tasks on micro-and macro-economics: - an electronic compendium of lectures, that is given to the students at the beginning of ? semester; - Tasks for current module control of knowledge; - examination paper. Language of instruction: Ukrainian, Russian, English (within the bounds of micro-and macro- economics terminology, that has ?English origin). Recommended literature: 1. Экономическая теория (политэкономия)(Economical theory(political economy)) Учебник / Под общей ред. заслуженных деятелей науки Российской Федерации, профессоров В.И. Видяпина, Г.П. Журавлевой. – М.: Изд-во Рос. экон. акад., 2000. – 529 с. 2. Курс экономической теории: учебник (Course of economical theory)/ Под общей редакцией проф. Чепурина М.Н., проф. Киселевой Е.А. – Киров: «АСА», 2000. – 752 с. 3. Основи економічної теорії: політекономічний аспект: Підручник (Basis of economical theory.The of political economy aspect: Textbook)/ Відп. ред. Г.Н. Климко. – К.: Знання- Прес, 2002. – 615 с. 4. Політична економія: Навч. Посібник(Political economy.Educational manual) / К.Т. Кривенко, В.С. Савчук, О.О. Бєляєв та ін.; За ред. д-ра екон. наук, проф. К.Т. Кривенка. – К.: КНЕУ, 2001. – 508 с. 5. Економічна теорія: Політекономія: Підручник (Economical theory.Political economy:Textbook) / За ред. В.Д. Базилевича. – 3-тє вид., перероб. і доп. – К.: Знання-Прес, 2004. – 615 с. 6. Иохин В.Я. Экономическая теория: Учебник.(Economical theory.Textbook) – М.: Экономистъ, 2004. – 861 с. 7. Політична економія. Навчальний посібник для студентів вищих навчальних закладів (Political economy. Educational manual fo students of Universities)/ За ред. В.О. Рибалкіна, В.Г. Бодрова. – К.: Академвидав, 2004. – 672 с. 8. Бутук А.И. Экономическая теория: (Economical theory)Учеб. пособие. – 2-е изд., перераб. и доп. – К.: Вікар, 2003. – 668 с. 9. Економічна теорія. Посібник вищої школи(Economical theory. (Manual fo higher school) (Воробйов Є.М., Грищенко А.А., Лісовицький В.М., Соболєв В.М.) / Під загальною редакцією Воробйова Є.М. – Харків-Київ, 2003. – 704 с. 10. Киреев А.П. Международная экономика. В 2-х ч. – Ч. I. Международная экономика: движение товаров и факторов производства. Учебное пособие для вузов. (international economy. Movement of goods and factors of production Educational manual for universities)– М.: Междунар. отношения, 2000. – 416 с. 11. Киреев А.П. Международная экономика. В 2-х ч. – Ч. II. Открытая экономика и макроэкономическое программирование. Учебное пособие для вузов. –(international economy. Open economy and macro economical programming Educational manual for Universities) М.: Междунар. отношения, 2000. – 488 с. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION Economics and manufacture organization Lecturer: Kuklin Vladimir Mikhaylovich, Doctor of Science (Physics and mathematics), Full Professor 1.Knowledge: Tasks on organization principles and management of production; productive process, its organizations and structures, types of productions; structure and features of productive funds; mechanisms of pricing; forms of property, influence on organization and on functioning of enterprise; mechanisms and organization principles of production sale and supply of material and technical resources; principle of financial plan development of enterprises, principles of accounting on an enterprise; methods of planning and analysis of enterprise business activity; legislative control of enterprise activity; principles of the tax system functioning; financial mutual relations of enterprise with a budget; to distinguish business processes, know principles of transfer prices calculation, to organize budgeting. 2.Skills: To calculate the value of assets; cost price of production and its price; estimate quality of products and his competitiveness; to use the indexes system of economic efficiency financial assessment, to make quantitative and qualitative analyses of enterprise functioning efficiency; To calculate income, funds, efficiency, profitability, return on assets, funding capacity, material capacity, to forecast prognosis of production development; to determine a requirement in material, manpower resources; to use the methods of account of business hours charges; to use the methods of a labor productivity measuring; to develop the financial plan of enterprise; to analyze the account posting at the account of economic activity; to develop the plan of economic and social development of enterprise; to develop the operatively-calendar plan of production; to be able to calculate taxes. 3.Subject description: the study of accounting at enterprise; methods of planning and analysis of enterprise business activity; legislative control of activity; principles of tax system functioning; financial mutual relations of enterprise with a budget; to distinguish business processes. 4.Forms of Teaching: lectures, workshops, independent work. Methods of Teaching: elements of problem lectures, individual tasks for independent work. 5.Assessment Forms: written control over the individual tasks, written test, written credit. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION Mathematical statistics in Computer-aided System Lecturer: Podtsykin Mikola Serafimovich, Associate Professor of Mathematical Simulation and Software of Mechanic and Mathematics Department. Prior Requirements: knowledge of courses: Mathematical analysis. Measure theory and Lebesgue integral. Probability theory. Subject description (content, aims, structure): random quantity modeling. Point estimations of distribution parameters. Interval estimations of parameters. Statistical hypotheses verification. Linear regression. Use of methods of statistics in the construction of stochastic mathematical models. Assessment Forms: credit Subject aim: the aim of the course is to provide future specialists with knowledge in the field of modern probability theory and mathematical statistics and use of its methods in modeling and analyzing of real objects and processes. Knowledge of the discipline: As a result of discipline studying students must: Know: Basic laws of probability theories and mathematical statistics Determination of empirical distributions, moments. To build histograms To model random quantities Features of point estimations Methods of contraction obtaining Methods of interval estimations receipt To Check statistical hypotheses Elements of regressive analysis
Be able to: To use basic laws of probability theories and mathematical statistics for analysis of real stochastic objects and processes.
Subject description: Tasks of mathematical statistics. Statistical structure. Determination of empiric distribution. Glivenko–Cantelli theorem. Sample characteristics. Construction of histograms. Modeling of discrete random quantity.Uniform sensor. Design of continuous random quantitives. Methods of estimation receipt moments. Function of authenticity. Method of maximal authenticity of point estimations receipt. Cramér–Rao bound. Effective estimations. Necessary and sufficient condition of bottom bound achievement in inequality of Cramér–Rao. Supereffective estimations. Sufficient statistics. Neumann- Fischer theory. Determination of exact Confidence interval by means of the set statistics. Interval estimations of normal distribution parameters. construction of interval estimations of distributions parameters on the big amount of samples. Simple and difficult hypotheses. Statistical criteria for verification of hypotheses. Criteria of consent c2. Verification of two simple hypotheses. Theorem of Neumann and Pearson . Linear regression. Estimations of regression parameters by least-squares method. Basic literature 1. Гихман И.И., Скороход А.В., Ядренко М.И. Теория вероятностей и математическая статистика. (Probability theory and mathematical statistics)К., Выща школа, 1979. 2. Климов Г.П.. Теория вероятностей и математическая статистика (Probability theory and mathematical statistics)М., Издательство Московского университета, 1983. 3. Коваленко И.Н., Гнеденко Б.В. Теория вероятностей (Probability theory)К., Выща школа ,1990. 4. Розанов Ю.А. Теория вероятностей случайные процессы и математическая статистика. (Probability theory, random processes and mathematical statistics)М., Наука, 1985. 5. Крамер Г. Математические методы статистики. (mathematical methods and statistics)М., Мир, 1975. 6. Закс Ш. Теория статистических выводов. (Statistical inferences theory)М., Мир,1975. 7. Кендалл М.Д., Стюарт А. Статистические выводы и связи. (Statistical inferences and connections)М., Наука, 1973. 8. Боровков А.А. Математическая статистика.( Mathematical statistics) М., Наука, 1984. 9. Леман Э. Проверка статистических гипотез. (Statistical hypothesis verification )М., Наука, 1979. 10. Бикел П., Доксам К. Математическая статистика. .( Mathematical statistics)М., Финансы и статистика, 1983. 11. Ермаков С.М., Михайлов Г.А. Курс статистического моделирования. (Statistical modeling course)М., Наука, 1976. 12. Сборник задач по теории вероятностей математической статистике и теории случайных функций. (Collection of tasks on probability theory and random function theory)Под ред. А.А. Свешникова, М., Наука,1970. Supportive materials 1. Учебно-методическое пособие “Теория вероятностей и математическая статистика”(Educational manual “Probability theory and mathematical statistics”). Сост. Рофе-Бекетов Ф.С., Подцыкин Н.С. – Харьков, 2001 DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION System modeling Lecturer: Podtsykin Mikola, Associate Professor of Mathematical Modeling and Software of Mechanic and Mathematics Department. Year, semester: 4 year, 8 semester Prior Requirements: knowledge of courses: Mathematical analysis. Probability theory and mathematical analysis. Subject description (content, aims, structure): Determined and stochastic systems modeling. Aims and tasks of design. Modeling of the queuing systems. Modeling of the large homogeneous and heterogeneous systems. Modeling of technical systems reliability. Imitation design. AIMS AND TASK OF DISCIPLINE: the aim of the “Modeling system” discipline is the studying by student types of mathematical models, techniques of construction and research of models for the tasks of optimization and management of productive and socio-economic processes. Discipline Tasks studying of basic concepts of modeling, classification of models, general techniques of modeling; Revision and study of mathematical divisions possibilities for the tasks of objects modeling; study and acquisition of practical skills in the algorithmization of difficult systems functioning for the tasks of simulation models construction study of methods of modeling authenticity estimation; and receipt of corresponded practical skills; construction of models with the use of queuing systems devices calculation of middle descriptions of large stochastic dynamic systems As the result of studying the discipline, students must: Know: Existent methods of determined and stochastic systems modeling. Drafting of Kolmogorov equations for states probabilities of stochastic objects. Methods of queuing systems modeling. Method of middle dynamics for a calculation of large stochastic systems descriptions. Be able to: To build the models of the determined and stochastic objects. To use an imitation design for the analysis of the difficult stochastic systems. To use the method of middle dynamics for a calculation of the large stochastic systems descriptions. Assessment Forms: exam Supportive Materials: 1. Бусленко Н.П. Моделирование систем.(System modeling) - М.: Наука, 1978. 2. Бусленко Н.П. Метод статистического моделирования.(Statistical modeling method) - М.: Статистика, 1970. 3. Полляк Ю.Г. Вероятностное моделирование на ЭВМ.(Probable modeling on EVM) - М.: Статистика, 1971. 4. Снапелев Ю.М., Старосельский В.А. Моделирование и управление в сложных системах. (Modeling and management in difficult systems)- М.: Советское радио, 1974. 5. Срагович В.Г. Теория адаптивных систем. (Adaptive systems theory)- М.: Наука, 1976.6. Варшавский В.И. Коллективное поведение автоматов(Collective conduct of automations). - М.: Наука, 1973. 7. Клейнрок Л. Теория массового обслуживания.( Queuing theory) М.: Машиностроение, 1979. 432 с. 8. Саати Т.Л. Элементы теории массового обслуживания и ее приложения.(Elements of queing theory and its application) М.:Сов. радио, 1971. 520 с. 9. Вентцель Е.С. Теория вероятностей.(Probability theory) М.: Наука, 1969. 576 с. 10. Вентцель Е.С. Исследование операций(Operation study). М.: Сов. радио, 1972. 552 с. 11. Смирнов Б.Я., Дунин-Барковский И.В. Краткий курс математической статистики для технических предложений(Brief course of mathematical statistics for technical suggestions ). -М.,: Физматгиз, 1959.- 436 с. 12. Голенко Д.И. Моделирование и статистический анализ псевдослучайных чисел на ЭВМ.(Modeling and statistical analysis of pseudorandom numbers on EVM) - М.: Наука, 1965. - 228 с. 13. Советов Б.Я. Моделирование систем. (System modeling)- М.: Высшая школа, 1985. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION The basic methods of mathematical optimization
Lecturer: Smortsova Tetyana Ivanivna, Assistant Professor Aim of the course: to teach prospective specialist the basic methods of mathematical optimization. Prior requirements: to study the course “The basic methods of mathematical optimization” is based on the knowledge gained from the study “Mathematical Analysis” Tasks: following the completion of the study a student must: know: different types of variational calculus tasks and the simplest numerical optimization methods. To be able to: to use the learnt types of problem tasks and methods in resolving specified tasks. Description of the course: The subject and tasks of the course. Examples. The simplest variational calculus task. The first variation, its calculation and the application of Euler equations. The first integral of Euler equations in different cases. Examples. Brachistochrone problem. Newton aerodynamic problem. Weierstrass-Erdmann condition. Regular functional. Second variation, its calculation and its application. Legendre necessary condition. Yakobi necessary condition. The task about calculation of Euler buckling force. Yakobi sufficient condition. The simplest vector task of variational calculation. Bolza problem with variable end-points. Transversability conditions. Task with the degree of differentiability of function. Isoperimetric problem. The task about rope stability mode, Dido problem. Numerical solution methods of function of one variable minimization. Forms of control: during semester a student has the following forms of control: Module control; Final control (exam). Supportive materials: 1. Ahizer N.I. Variational calculus. 2. Gelfand, Fomin. Variational calculus. 3. Elsholts. Differential equations and Variational calculus. 4. Gill, Murray, Wright. Practical optimization. 5. Sukharev, Timohov, Fedorov. The course of optimization methods. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION Optimal statistic decision procedures in simulation and control problems. Lecturer: Podtsykin Mykola Serafimovitch, Associate Professor of Mathematical Modeling and Computer Software Department of Mechanical-Mathematical Faculty. Aim of the course: to give the students knowledge in the sphere of modern theory of making the optimal statistic decisions in the stochastic management structures: economic, technical and others. Prior requirements: acquaintance with the courses: Mathematical Analysis. Probability calculus and Mathematical statistics. Tasks: following the completion of the study a student must: Know: Classical and Bayesian approach to the estimations of parameters in statistics. Construction and analysis of utility function. Bayesian risk and Bayesian decision determination. The rule of construction of Bayesian decision functions in statistical problem decision. Determination and construction of conjugate family of distributions. Convergence property of posteriori distribution To be able to: To construct and analyze the utility function in case of money income. To calculate Bayesian decision function in the problems with inquiry and known price of inquiry. To find conjugate family of distributions parameter for different inquiry distribution. To apply practically the theory of static decisions in economics, psychology, engineering. Basic Literature 1.Де Гроот М. Оптимальные статистические решения. (Optimal Static Solution) М., Мир. 1974. Ширяев А.Н. Статистический последовательный анализ. (Static Sequential Analysis)М., Наука. 1969. 2 Чжоу Й., Роббинс Х. Об оптимальных правилах остановки. Математика. (Best stopping rule. Mathematics) 9:3, 1965. 3. Чернов Г., Мозес Л. Элементарная теория статистических решений. (Elementary statistical decision theory)М. 1962. 4. Ченцов Н.Н. Статистические решающие правила и оптимальные выводы.(Decision rules and optimal conclusions) М., Наука, 1972. 5. Управление риском: Риск. Устойчивое развитие. (Risk management: Risk. Sustainable development) М., Наука, 2002. 6. Городецкий А.Я. Информационные системы. Вероятностные модели и статистические решения. (Information systems. Chance models and Statistic decisions) СПб, изд-во СПбГПУ, 2003 . Supplementary 1. Гихман И.И., Скороход А.В., Ядренко М.И. Теория вероятностей и математическая статистика. (Probability theory and Mathematical statistics) К., Выща школа, 1979. 2. Крамер Г. Математические методы статистики. (Mathematical methods of statistics) М., Мир, 1975. 3. Леман Э. Проверка статистических гипотез. (Verification of statistical hypothesis) М., Наука, 1979. 4. Бикел П., Доксам К. Математическая статистика. (Mathematical statistics) М., Финансы и статистика, 1983. 5. Ермаков С.М., Михайлов Г.А. Курс статистического моделирования. (The course of statistical modeling ) М., Наука, 1976. 6. Зельнер Ф. Байесовские методы в эконометрике. (Bayesian methods in Econometric theory) М.,: Статистика, 1980. 7. Розен В.В. Цель, оптимальность, решение. Математические модели принятия оптимальных решений. (Aim, Optimality, Decision. Mathematical models of optimal resolution) М. Радио и связь. 1982. 8. Фишберн П. Теория полезности для принятия решений. (The theory of utility for decision making) М., Наука, 1978. OPTOINFORMATICS Lecturer: Dolya Grigoriy Mykolayovytch, Full Professor, Doctor of Science Aim of the course: Acquisition of the basis of optoelectronic devices construction, which used in computer equipment. Generation of the systematized idea about the operation processes of optical and optoelectrical devices of information processing. Getting the practice in the engineering analysis of the main parameters of optical and optoelectrical devices of computer equipment. Tasks: following the completion of the study a student must: Know: The main characteristics and principles of construction and functioning of lazer and optoelectrical devices in computer equipment. Structural, functional, optical-mechanical schemes of typical lazer and optoelectrical devices in computer equipment. Operating instructions and safety technology when using lazer and optoelectrical devices in computer equipment. The main directions of improvement, updating and development prospects of lazer and optoelectrical devices in computer equipment. Factors that limit assessed abilities of the systems mentioned above. To be able to: To substantiate and calculate the main technical characteristics of lazer and optoelectrical devices in computer equipment. To master material equipment, to study the structure of updated, modern and prospective lazer and optoelectrical devices in computer equipment on their own. To find the defects in the elements and devices of optoelectrical devices while operating with them, to choose the best operating mode. To evaluate and analyze the operational capabilities of optical systems in different conditions. Discipline description: The receiving set of optical radiation. Elements of lazer construction. Generation of lazer irradiance. Optical modulator. Optical periphery of PC. Memory devices on the optical discs. Holographic memory devices. Analogue optical processors. Digital optical processors. Supportive materials: 1. Доля Г.Н. Чудовская Е.С. Методические материалы по учебной дисциплине «Оптоинформатика». Часть 1. «Основы фотоники». (Methodological materials for classroom discipline “Optoinformatics”. Part 1. “Photonics Basics”) Харьков – 2008. 2. Доля Г.Н. Чудовская Е.С. Методические материалы по учебной дисциплине «Оптоинформатика». Часть 2. «Оптические технологии в вычислительной технике». (Methodological materials for classroom discipline “Optoinformatics”. Part 2. “Optics technologies in Computer Science”)) Харьков – 2008 Recommended literature Basic. 1. Справочник по лазерной технике. (Optoelectronics guidance) Киев, „Техника”, 1978. 2. Г. Боухьюз и др. Оптические дисковые системы. (Disc optical systems) – М., Радио и связь, 1991. 3. Акаев А.А., Майоров С.А. Оптические методы обработки информации. (Optical methods of data processing) - М.: Высшая школа, 1988. 4.Д. Гринфилд. Оптические сети. (Optical Networks) – К., ООО «ТИД ДС», 2002 5. М.Янг. Оптика и лазеры, включая волоконную оптику и оптические волноводы: Пер. с англ. (Optics and Lasers: Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides) - М.: Мир, 2005 Supplementary 1. Новые физические принципы оптической обработки информации/ (New physical principles of optical data processing) Сборник статей под ред. С.А. Ахманова , 1990 . 2.Р. Фриман. Волоконно- оптические системы связи. (Fiber-optic communication systems) – М., Техносфера. 2004 3. Оптическая голография /(Optical holography) Под ред. Г.Колфилда. – М., Мир, 1982 4. Справочник по лазерам/(Laser Guidance) Под ред. А.М. Прохорова. В 2-х томах. – М. Сов радио, 1978. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION Philosophy Lecturer: Ukrainetc Liliya Viktorivna, PhD (Philosophy), Associate Professor. Aim: to ensure students` acquisition of the main problems and achievements of philosophy from the ancient times and up to nowadays. To form students` mindset guidelines on reasonable and reflexive level. To review with the students the problems and achievements of philosophical ideas from the ancient times and up to nowadays, to form the person who is able to resist external influence, particularly manipulation of a person. The course is aimed to form the rational, independent, responsible, thoughtful person, who meets requirements of present time. Pedagogical strategy is aimed to the development of critical thinking skills of a person, who has the maximum amount of philosophical “instruments” for civilized resolve of critical situations, conflicts, unconventional problems of the time being. To develop critical attitude not only towards the opinion of other people, but also towards the students` opinion. It means that the aim of the course is the development of cultural immunity particularly from laxity and at the same way from the non-violence attitude. Tasks: Approaches that go back to European cultural tradition are considered to be methodological background of the material examination that has to be learnt by students. On the one hand it is cultural-informative approach, that is based on “dialogue with history”, particularly acquisition of intellectual tradition, information about philosophy; on the other hand – problematic, pragmatic approach, that is aimed to the time being (modern methods and the ways of solution, ideas of philosophers that work up to now). The usage of these pedagogical strategies, paradigms is helpful in acquisition of thorough knowledge of educational material and it is also helpful when displaying many-sidedness of philosophical knowledge, answering the question “what can philosophy do nowadays for contemporaneity?” The course is created being orientated to the imperatives of modern culture and civilization of XX century. Following the study of the course “Philosophy” a student must know: the structure of philosophical knowledge (ontology, epistemology, logics, philosophical anthropology, ethics, aesthetics, social philosophy and other); fundamental concept of philosophy; character and content of philosophical terms of reference; main stages of philosophy development and representatives of philosophical knowledge in Ukraine and in the world; historical types of philosophy, main paradigms of philosophy dominant strategies, conditions for the development of thoughtful, independent, responsible person; Following the study of the course “Philosophy” a student must be able to: analyze philosophical literature, interpret philosophical texts and find their ideological meaning; acquire the skills of thoughtful thinking (linguistic, research, cognitive, ethic, social- psychological, social), particularly as the main factor of thoughtful, responsible social and ethical behavior; operate definitions, to define their meaning, the role of metaphors and analogies, to conduct a dialogue; form and outline the problem, analyze information, ask and prepare questions in the context of philosophical range of problems; see the difference, to make connections in different verbal expressions, to operate the facts, to outline strong and weak points, to think logically and so on; listen and to take into account opinions of other people, to be open for criticism in dialogue, to ask questions, draw an analogy, express an opinion, analyze and what is very important to speak in public fluently. Trust and care should influence the development of sympathy, commonality, loyalty to the group, responsible for yourself and others. make the difference between moral, legal and social problems; find the way in the present situation, ideology and activity of social organizations, analyze the facts and phenomena, that happen in society. Assessment forms: In order to learn the subject there should be assessment of 2 modules within the total amount of hours, 1 test and final test in the form of examination. Supportive materials: 1. Texts of lectures (printed and electronic variant) 2. Plans of practical lessons organization (printed and electronic variant) 3. Course schedule 4. Tasks for the test and 2 module assessments 5. Examination paper Basic Literature Філософія. Курс лекцій. (Philosophy. Course of lectures) К., 1993. Философия. Учебник для вузов. (Philosophy. High School text-book) Ростов- на-Дону, 1995. Философия ХХ века. (Philosophy of XX century) М., 1997. Supplementary Реале Дж.,Антисери Д. Западная философия от истоков до наших дней. В 4- х т. (Western philosophy ab initio till this days) С.-Пб.,1994 Соціальна філософія. (Social philosophy) К., 1994. История философии в кратком изложении.(Abridged history of philosophy) -М.,1991 Введение в философию. (Introduction to philosophy) В 2-х ч. М., 1990. Человек. Мыслители прошлого и настоящего о его жизни, смерти и бессмертии. (Human. Thinkers from the past and present about human life, death and immortality) - М.,1991 Історія філософїї на Україні. (The history of philosophy in Ukraine) К.,1987. Мир философии. Книга для чтения. (The world of philosophy. The reading book.) В 2-х ч. М., 1991. Фрейд З. Психология бессознательного (Depth psychology) М,1989. Фромм Э. Анатомия человеческой деструктивности. (Anatomy of human disruptiveness) М. ,1994 Штанько В.И. Основные направления современной философии. Философия науки ХХ века. Конспект лекций. (The main trends in modern philosophy. Philosophy of science of the 20th century ) Х., 1993. Штанько В.І., Сумятін В.М.Філософія в запитаннях і відповідях.. Учбово- методичні матеріали для студентів заочної форми навчання. (Philosophy in the form of question and answers. Educational materials for the students of part-time education dpt.) Харків, 1999. THE HISTORY OF UKRAINIAN CULTURE Lecturer: Marynyak Ruslana Stepanivna, Assosiate Professor Prior requirements: acquisition of the subject is based on the knowledge gained from learning the general course of the “History of Ukraine” Aim: to extend students knowledge of Ukrainian history and theory, to introduce students to the main problems of historical- cultural process in Ukraine in world and European context. Tasks: following the completion of the study a student must: know modern interpretation of the culture history and to be able to use it on Ukrainian material; understand the principles of interdisciplinary approach to the history of Ukrainian culture acquisition. know historical functioning conditions, the main stages of development and main events, phenomena, personalia of Ukrainian cultural process; have the idea of ethnic and national cultures in the territory of Ukraine. To be able to: discuss problematic and disputable questions of Ukrainian cultural process; to prepare an individual essay on the certain topic about the history of Ukrainian culture; to define structural-morphological peculiarities of Ukrainian culture. Discipline description: the subject, aim, tasks and structure of the course. Ukrainian and world culture. Periodization of the history of Ukrainian culture. Research of Ukrainian culture: M.Grushevski, D.Antonovytch, D.Chizhevski, I.Ogienko, I.Lysyak-Rudnitski, O.Pritsak, G.Grabovitch, O.Zabuzhko, M.Popovitch. The definition of the notion “Culture”: historism, human dimension, correlation with the definition “civilization”. Cultural-historical epochs. Cultural dominants in the Ukrainian culture history. Discretisation of Ukrainian culture. Cultural-historical regions of Ukraine and Europe. The main directions of modern historical-cultural researches. Social and intellectual history. Constructivism. Cultural turnaround in the historical science of the second half of XX century. School of “Annals”. The culture of everyday life. Assessment forms: acquisition of the subject presupposes assessment of 2 modules within the total amount of hours, 1 test and final test in the form of examination. Workbooks: 1. Історія української культури: Зб.матеріалів і документів / Упоряд. Білик Б. та ін. (The history of Ukrainian Culture: Source-book) – К., 2000. 2. Історія української культури: Побут.Письменництво. Мистецтво. Театр.Музика. / За ред. І.Крип'якевича. (The history of Ukrainian Culture: Household. Creative Writing. Art. Theatre. Music.) К., 1994. 3. Культура і побут населення України- 2-е вид., доп. та перероблене. .(Culture and Household of Ukrainian people) - К., 1993. 4. Культурологія: Українська та зарубіжна культура: Навч.посіб./ За ред М.М.Заковича.- (Cultural studies: Ukrainian and Foreign culture) К., 2004. 5. Мєднікова Г.С. Українська і зарубіжна культура ХХ століття: Навч. посіб.- (Ukrainian and Foreign culture of XX century) К., 2002. 6. Попович М. В. Нарис історії культури України.- (An Essay of Ukrainian World Culture) - К., 1999. 7. Терещенко Ю.І. Україна і європейський світ: Нарис історії від утворення старокиївської держави до кінця ХVІ ст.: Навч.посібник.- (Ukraine and European world: An essay of the history from the time of Old Kievan Power to the end of XVI century) К., 1996. 8. Українознавство: Хрестоматія – посібник: У 2 кн.- (Ukrainian Studies: Reading book – reference book) К., 1997. 9. Українська культура: історія і сучасність: Навч.посібник для студентів університетів і пед.інститутів /Черепахова С.О., Скотний В.Г., Бичко І.В., Біленко Т.І. та ін. – (Ukrainian culture: history and Contemporaneity) Львів, 1994. 10. Українська та зарубіжна культура: Навч.посіб./За ред. М.Заковича. – (Ukrainian and Foreign culture: Workbook) К., 2001, 2002. 11. Українська культура: Лекції / За ред Д.Антоновича.- (Ukrainian culture: Lectures) К., 1993. 12. Українська художня культура: Навч.посіб. – (Ukrainian artistic culture: Workbook) К., 1996. Literature to the whole course Андерсон Б. Уявлені спільноти. Міркування щодо походження й поширення націоналізму. – (Imaginary communities. thoughts about origin and spread of nationalism) К., 2001. Войтович В. М. Українська міфологія. – (Ukrainian mythology) К.: Либідь, 2002. Горєлов М. Є., Моця О. П., Рафальський О. О. Цивілізаційна історія України / НАН України; Інститут політичних і етнонаціональних досліджень; Інститут археології. — (Civilizational history of Ukraine) К., 2005. Гриценко О. Своя мудрість. Національні міфології та громадянська релігія в Україні. (Insider wisdom. National mythologies and civil religions in Ukraine) - К., 1998. Грушевський М.С. Історія української літератури: В 6 т., 9 кн. – (The history of Ukrainian Literature) К., 1993-1996. Грушевський М. С. Історія України- Руси: В 11 т. 12 кн.- (The history of Ukraine-Rus) К., 1991-2000. Забужко О. С. Філософія української ідеї та європейський контекст: франківський період. – (The philosophy of Ukrainian Idea and European context: the period of Franko) К., 1993. Історія релігії в Україні. У 10 т., -Т.1. -К., 1996, Т.2. – (The history of religion in Ulraine) К., 1997. Історія української культури : В 5-ти тт.- (The history of Ukrainian culture) К., 2001-2005. Історія української літератури: У 8 т. – (The history of Ukrainian literature) К., 1967-1971. Історія українського мистецтва: У 6-ти т.- (The history of Ukrainian art) К.,1966-1970. Історія української музики: В 6 т. – (The history of Ukrainian music) К., 1989-1992.- Тт. 1-4. Історична міфологія в сучасній українській культурі. (Historical mythology in the present-day Ukrainian culture) - К., 1998. Кінан Е. Російські історичні міфи. (Russian historical myths) - К.,2001. Кравець О.М. Сімейний побут і звичаї українського народу: Іст.-етногр.нарис. (Family household activities and customs of Ukrainian people) - К., 1966. Кульчицький О. Український персоналізм. Філософська й етнопсихологічна синтеза. (Ukrainian personalism. Philosophical and ethnic-psychological synthesis) - Мюнхен-Париж, 1985. Липа Ю.І. Призначення України. (The Function of Ukraine) Львів, 1992. Лисяк-Рудницький І.П. Історичні есе. В 2-х тт. (A Historical essay) - К., 1994. Маланюк Є. Ф. Книга спостережень. (A book of notes) К., 1995. Маланюк Є. Нариси з історії нашої культури. (An essay on the history of our culture) - К., 1995. Нагорна Л. П. Політична культура українського народу: історична ретроспектива і сучасні реалії / Інститут політичних і етнонаціональних досліджень НАН України. — (Political culture of Ukrainian people: historical retrocpective and present-day realias) К. : Стилос, 1998. Наливайко Д. С. Рецепція України в Західній Європі XVI-ХVIII ст. Perception of Ukraine in Western Europe in XVI-XVIII cent. - К., 1998. Нариси з історії українського мистецтва.- (An essay on the history of Ukrainian Art) К., 1966. Нечуй -Левицький І.С. Світогляд українського народу: Ескіз української міфології. - 2-е вид.- (The worldview of Ukrainian people: a sketch of Ukrainian mythology) К., 1992. Павленко Ю.В. Історія світової цивілізації. Соціокультурний розвиток людства. – (The history of Ukrainian civilization. Sociocultural development of the mankind) К.,1996. Розвиток філософії в Українській РСР. – (The development of Ukrainian RSR) К., 1968. Семчишин М. Тисяча років української культури (історичний огляд українського культурного процесу). – (Thousand years of Ukrainian culture (a historical essay on Ukrainian cultural process)) К., 1993. Український драматичний театр: Т.1-2. – (Ukrainian Drama Theatre) К., 1959-1967. Українці: народні вірування, повір’я , демонологія. – (Ukrainians: national faiths, beliefs, demonology) К., 1991. Феномен української культури. Методологічні засади осмислення. – (The phenomenon of Ukrainian culture: Methodological basics of reasoning) К., 1991. Шевченко Ігор. Україна між Сходом і Заходом. Нариси з історії культури до початку ХУШ століття. Пер. з англ. (Ukraine between East and West. A historical essay on culture till the beginning of XVIII century.) - Львів, 2001. Яковенко Н.М. Нарис історії середньовічної та ранньомодерної України. Вид. 2-е, перероблене та розширене. (Historical essays on medieval and premodern Ukraine) - К., 2005. Literature for lectures and seminars Асеєв Ю.С. Джерела: Мистецтво Київської Русі. – (The Sourses: The art of Kievan Rus) К., 1980. Білецький О.І. Від давнини до сучасності: Вибрані праці: В 2-х тт. – (From Old Times to Modernity: Selected Works) К., 1960. Білецький П.О. “Козак Мамай” – українська народна картина. (“Kozak Mamai” – Ukrainian national picture) - Львів, 1960. Білецький П.О. Українське мистецтво другої половини ХVІІ-ХVІІІ століття. – (Ukrainian Art of the second part of XVII-XVIII century) К., 1981. Білецький О.І., Дейч О.Й. Тарас Григорович Шевченко. Літературний портрет. - 2-е вид. – (Taras Grigorovitch Shevchenko. Character scetch) К., 1961. Боровский Я.Е. Мировоззрение древних киевлян. – (The world view of ancient kievans) К., 1982. Булашев Г.О. Український народ у своїх легендах, релігійних поглядах та віруваннях: космогонічні українські народні погляди та вірування. (Ukrainian people in their legends, religious views and beliefs: cosmogonic Ukrainian national views and beliefs) - К.,1993. Вишенський І. Твори. – (Works) К., 1959. Высоцкий С.А. Средневековые надписи Софии Киевской ( По материалам граффити ХІ- ХVІІ в.в). (Medieval inscriptions of Sophia Cathedral (Based on the materials of graffiti XI-XVII centuries.) ) - К., 1976. Головко А.Б. Древняя Русь в историко-культурном развитии славянских народов // Культурные и общественные связи Украины со странами Европы: Сб. науч. тр. (Ancient Rus in the historical-cultural development of Slavonic nations // Cultural and public relations of Ukraine with the countries of Europe - К., 1990.- С.16-34. Горленко В.Ф., Бойко І.Д., Куницький О.Г. Народна землеробська техніка українців. (Folk agricultural equipment of ukranian people) - К., 1971. Горский В.С. Философские идеи в культуре Киевской Руси. (Philosophical ideas in the culture of Kievan Rus) - К., 1988. Грабович Г.Ю. До історії української літератури: Дослідження, есе, полеміка . (To the history of Ukrainian literature: Research, essay, polemics) - К., 1997. Грабович Г. Ю.Шевченко як міфотворець: Семантика символів у творчості поета. (Shevchenko as like myth-maker: Semantics of symbols in the works of the poet) - К., 1991. Грабович Г.Ю. Шевченко, якого ми не знаємо (з проблематики символічної автобіографії та сучасної рецепції поета). (Shevchenko who we do not know (regarding the topicality of symbolic autobiography and present-day perception of the poet)) - К., 2000. Грищенко О.А. Своя мудрість. Національні міфології та громадянська релігія в Україні. (Insider Wisdom. National mythologies and civil religion in Ukraine.) – К., 1998. Даркевич В.П. Единство и многообразие древнерусской культуры (конец Х – ХІІІ вв.) // Вопросы истории. (Unity and variety of Old Russian culture (the end of X-XIII centuries)) - 1997.- № 4. Дзюба І. Інтернаціоналізм чи русифікація? (Internationalism or Russification?) – К., 1998. Духовная культура древних обществ на территории Украины. (Spiritual culture of ancient societies in the territory of Ukraine) - К., 1991. Жаборюк А. А. Український живопис останньої третини ХІХ – поч. ХХ ст. (Ukrainian pictorial art of the last third of XIX- the beginning in XX century) - К.-Одеса, 1990. Жолтовський П.М. Український живопис ХVІІ – ХVІІІ ст. (Ukrainian pictorial art of the XVII-XVIII century) - К., 1978. Забужко О.С. Філософія української ідеї та європейський контекст: франківський період. (Philosophy of Ukrainian Idea and European context: the period of Franko ) - К., 1993. Забужко О.С. Шевченків міф України: Спроба філософського аналізу.- 2-е вид., випр. (Shevchenko`s myth of Ukraine: An attempt of philosophical analysis) – К., 2001. Запаско Я. П.Мистецтво книги на Україні ХVІ – ХVІІІ століть. (The art of book in the Ukraine of XVI-XVIII centuries) -Львів, 1971. Затенацький Я.П. Українське мистецтво першої половини ХІХ ст. (Ukrainian art of the first half of XIX century) – К., 1965. Іван Котляревський у документах, спогадах, дослідженнях. (Ivan Kotlyarevsky in the documents, memories, researches) - К., 1969. Іван Франко. Життя і творчість. (Ivan Franko. The life and Works) - К., 1956. Изборник Святослава 1073 г.: Сб.ст. Svyatoslav`s Collection - М., 1977. Ільєнко І.О. У жорнах репресій: Оповіді про українських письменників (За архівами ДПУ – НКВС). (In the millstones of purges: Stories are about the Ukrainian writers (After the archives of ДПУ - НКВС) - К., 1995. Ільницький О. Український футуризм 1914-1930. (Ukrainian futurism 1914-1930) - Львів, 2003. Ісаєвич Я.Д. Братства та їх роль у розвитку української культури XVII – XVIII ст. (Brotherhood and their roles in the development of Ukrainian culture in the XVII – XVIII century) – К., 1966. Ісаєвич Я. Д. Джерела з історії української культури епохи феодалізму. The sourses from the history of Ukrainian culture of the feudalism era - К., 1972. Касьянов Г. В. Незгодні: Українська інтелігенція в русі опору 1960 - 80-х років. (Discordant: Ukrainian intellectuals of the process of Resistance movement of 1960-80 years) - К., 1995. Кравченко Б. Соціальні зміни і національна свідомість в Україні ХХ ст. (Social changes and national consciousness in Ukraine of the XX century) – К., 1997. Кремень В.Г., Табачник Д.В., Ткаченко В.М. Україна: альтернативи поступу (критика історичного досвіду). (Ukraine: alternatives of expansion (the criticism of historical experience)) - К., 1996. Кувеньова О.Ф. Громадський побут українського селянства. Civil household of Ukrainian peasantry - К., 1966. Культура славян и Русь. (The culture of Slavs and Rus) - М., 1998. Культурне будівництво в УРСР: Найважливіші рішення Комуністичної партії і Радянського уряду. 1917- 1959 : Зб.док. (The cultural building in the USSR: the most important decisions of Communist Party and Soviet government.) – К., 1961. – Т.1-2. Культурное наследие Древней Руси. Истоки,становление, традиции. ( The cultural heritage of Old Rus. Origin, establishment, traditions.) - М., 1976. Курбатов Г.Л., Фролов Э.Д., Фроянов И.Я. Христианство: Античность. Византия. Древняя Русь. (Christianity: Antiquity. Byzantium. Old Rus.) – Л., 1988. Курносов Ю. О. Інакомислення в Україні (60-ті – перша половина 80-х рр. ХХ ст.) (heterodoxy in Ukraine (60-ies - the first half of 80-ies of the XX century)) – К., 1994. Лазарев В.Н. Византийское и древнерусское искусство: Статьи и материалы. (Byzantine and Old Russian Art) - М., 1978. Лелеков Л.А. Искусство Древней Руси и Восток. (The Art of Old Rus and the East) - М., 1978. Лизанчук В.В. Навічно кайдани кували: Факти, документи, коментарі про русифікацію в Україні. (They forged the fetters forever: Facts, documents, comments about Russification in Ukraine) - Львів, 1995. Липинский В. В. Становлення і розвиток нової системи освіти в УСРР у 20-ті роки. (Establishment and development of the new educational system in USSR in the 20-ies.) - Донецьк, 2000. Літературна спадщина Київської Русі і українська література ХVІ – ХVІІІ ст. (The remains of Kievan Rus and Ukrainian Literature of XVI – XVIII cent.) - К., 1981. Лихачев Д. С. « Слово о полку Игореве» и культура его времени. (“The Song of Igor's Campaign” and the culture of its time) - Л., 1985. Логвин Г.Н. З глибин: Давня книжкова мініатюра ХІ – ХVІІІ ст. (From the depth: An old bookish sketch of XI – XVIII cent.) – К., 1974. Мицько І.З. Острозька слов'яно - греко- латинська академія (1576-1636). (Ostrog Slavonic- Greek-Latin Academy (1576-1636)) - К., 1990. Назаренко И.Д. Общественно-политические, философские и атеистические взгляды Т.Г.Шевченка. (Socio-political, philosophical and ateistic views of T.G. Shevchenko) - М., 1961. Наливайко Д.С. Спільність і своєрідність: українська література в контексті європейського літературного процесу. (Similarity and Originality: Ukrainian literature in the context of European literary process) – К., 1988. Наливайко Д.С. Українське барокко в контексті Європейського літературного процесу ХVІІ ст. (Ukrainian baroque in the context of the European literary process) // Радянське літературознавство. - 1972.- № 1. Національні відносини в Україні у ХХ ст.: Зб.док. і матеріалів.(National relationships in Ukraine in the XX century) - К., 1994. Нікітенко Н.М. Собор святої Софії в Києві. (St. Sophia Cathedral in Kiew) - К., 2000. Нічик В.М., Литвинов В.Д., Стратій Я.М. Гуманістичні і реформаційні ідеї на Україні. (Humanistic and reformation ideas in Ulraine) - К., 1990. Овсійчук В.А. Українське мистецтво другої половини ХVІ – першої половини ХVІІ століть. Гуманістичні та визвольні ідеї. (Ukrainian Art of the second half of the XVI – first half of the XVII centuries. Гуманістичні та визвольні ідеї.) - К., 1985. Откович В. П. Народна течія в українському живопису ХVІІ -ХVІІІ століть. (Folk stream in the Ukrainian pictorial art) - К., 1990. Пам’ятки братських шкіл на Україні (кінця ХVІІ – поч. ХVІІІ ст.). (Memorials of the Ukrainian brethren schools (the end of ХVІІ – the beg. of ХVІІІ cent.) - К., 1988. Памятники литературы древней Руси: ХІІ век. (The monuments of the Old Rus literature: XII century) - М., 1980. Піскун В.М., Ціпко А.В., Щербатюк О.В. та ін. Українство у світі: традиційність культури та спільнотні взаємини. Монографія. (Ukrainians in the world: conventionalism of the culture and social relapses) - К., 2004. Погожева А.П. Антроморфная пластика Триполья. (Anthropomorphous plastics of Trypillya) - Новосибирск, 1983. Попович М.В. Мировоззрение древних славян. (The world view of the ancient Slavs) - К., 1999. Попович М.В. Григорій Сковорода: філософія свободи. (Grigory Skovoroda: the philosophy of freedom) - К., 2007. Присяжнюк Ю.П. Українське селянство Наддніпрянської України: сакраментальна історія другої половини ХІХ – початку ХХ ст. (Ukrainian peasantry of Naddnipryanska (trans-Dnieper) part of Ukraine: sacramental history of the second half of XIX – the beg. of XX century) – Черкаси, 2007. Раевский Д.С. Модель мира скифской культуры. (Model of the world of scythian culture) - М., 1985. Репресоване “відродження”: Про трагічну долю української інтелігенції. (Repressed “Renaissance”: About the tragic destiny of Ukrainian intellectuals) – К., 1993. Російщення України. (Russification of Ukraine) - К., 1992. Русалка Дністровая: Документи і матеріали. Mermaid form the Dniester: Documents and materials - К., 1989. “Руська трійця” в історії суспільно-політичного руху і культури України. (Russian trinity in the history of socio-political movement and culture of Ukraine) - К., 1987. Рыбаков Б.А. Язычество Древней Руси. (The Heathendom in the Old Rus) - М., 1987. UKRAINIAN LANGUAGE ACCORDING TO PROFESSIONAL PROFILE Lecturer: Marynyak Ruslana Stepanivna, Assosiate Professor Preliminary conditions: Ukrainian language secondary school course Study description: Structural levels of the language science. Spelling of names and patronymics. The lexis of the modern Ukrainian literary language. Piculiarilies of usage, complex variations. Surzhik. Translingual homonyms. Spelling of capital letters, apostrophe, soft sign. Spelling of prefixes, suffixes, reduction in consonant groups, reduplication, lengthening. Morphological standarts. Noun. Division on case, conjugation, peculiarities of gender definition, pluralia tantum, singularia tantum. Adjective. Peculiarities of degree of comparison formation. Possessive adjectives. Formative suffixes. Spelling of compound words (nouns, adjectives). Verb forms: gerund, participle I, II. Spelling of adverbs. Conjugation and spelling of pronouns. Conjugation and spelling of numerals. Junction of noun and numeral. Spelling of link words. Stylistic piculiarities of prepositions and particles in science and official styles. Punctuation. Separating characters in expletives, collocations, sentences. Peculiarities of sentence structure with direct and indirect quotation. Direct speech. Punctuation in constructions with direct speech. Noun in apposition. Complex cases of translation of sentences with participles and gerund. Notion of a document: details of documents, classification, a requirement for page format, form, data sheet. Documents regarding individual filling in: principles of drafting. Administrative documents. Communication documents. Documents of personnel matters. Assessment forms: tests in the 2nd semester, credits – 3, 5 semesters, exam – 4th semester. The English language of special usage Lecturer: Motornyuk Tetyana Mykolayivna, lecturer of English language department. Aim: acquisition of learning course “The English language” is the formation of foreign communicative competence and practicing in the process of teaching activity upbringing, education and development of student personality. Tasks: the task of this academic subject is the acquisition of the language, linguistic and cultural knowledge and formation of language system of skills in speaking, reading and auding. Following the completion of the study a student must: Know: The rules of English phonetics Grammatical material: Participle I і Participle II (forms and functions). Participle I і Participle II complexes. Independent Participle complex. Infinitive, its forms and functions. Objective infinitive complex. Gerund, its forms and functions. Gerundial complexes. Modal words. If- clauses. Most commonly used lexis and jargon. To be able to: to follow the conversation and to keep up the conversation on familiar topic, or to take part in the conversation on general topics. to look through the texts looking for necessary information and to understand detailed instructions or advice. to make notes during conversation of other people or to write a letter with nonstandard request, to write annotations for scientific articles. Assessment forms: 1. Method of oral control: individual and group questioning. 2. Methods of written control: test, dictation-translation, translation, written exam 3. Method of test control (written) 4. Method of self-control 1-4 semesters, 5semester – exam Forms of controlling student’s progress and evaluation criteria: oral interpreting, written translation. Topic 1 – written test control Topic 1 and Topic 2 - lexico-grammatical translation Topic 3 – oral questioning Topic 4 – oral or written questioning – in the form of annotation to scientific article according to the profession. Grades distribution: Grades: 1 1. Total Module Grades: final test Practical studies 60 40*** 100 (30*+30**) (current progress + module test) * current progress = average score х 6 **written control ***final test = average score х 8 Written control
Tasks for control test Amount of Amount of Score Time tasks control elements
30 30 30 45 minutes (1 point for every correct answer)
Criteria for evaluating written control test Amount of Criteria for Penalty Penalty Penalty active moments evaluating oral points for "good points for points for interpreting "satisfactory "unsatisfactory 30 0 -3 4-8 9-15 16 and more
Final test 1. Translation of the sentences from foreign language into native language. Type of task Amount of Amount of Time of control elements points fulfillment
Translation of 10 20 45 hours the sentences
2. Lexico-grammatical translation Type of task Amount of tasks Amount of Time of points fulfillment
Translation of the sentences from 10 20 45 minutes foreign language into native language. Evaluation scale (according to the national system) Amount of penalty points Amount of Criteria for Penalty points Penalty points Penalty points active evaluating oral for "good for for moments interpreting "satisfactory "unsatisfactory Translation 40 0– 4 4,5 - 12 12,5 – 20 20,5 and more
Minimal number of points that a student must get to pass each module is 30 points (50%) The student must have 30 points to be admitted to semester control. 10. Supportive materials 10.1. Recommended literature Basic: 1. English for Computer Science Students. Навчальний посібник під ред. Т.В. Смирнової. М.: Флінта: Наука, 2004. 2. Dinos Demetriades. Information Technology. – Oxford University Press. – 2003. – 40p. 3. Пройдаков Э., Теплицкий Л.М. Словарь компьютерной (вычислительной) и бытовой техники., (Dictionary of computer technologies and household appliances) М. 2004. 4. Аутентичні тексти з фаху з іноземних джерел. (Authentic texts from foreign sources) Supplementary : 1. Raymond Murphy. English Grammar In Use For Elementary Students. – Cambridge University Press. – 1990. – 259 p. 2. Raymond Murphy. English Grammar In Use For Intermediate Students. – Cambridge University Press. – 1994. – 350 p. 3. Swan C. Walter. How English Works. – Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997. – 358 p. 4. Michael McCarthy, Felicity O’Dell. English Vocabulary In Use. - Cambridge University Press. – 2005. – 309 p. 5. Филюшкина Л.Т., Фролова М.П. Сборник упражнений. (Exercise book) – Москва: Международные отношения, 1995. – 157 с. 6. Голицынский Ю. Сборник упражнений. (Exercise book) – Санкт-Петербург: Каро, 2004. – 537 с. 7. Газети “the Day”, “the Kyiv Post”. 10.2. Іnformation resources Basic: 1. Bell English Online http://www.bellenglish.com/ 2. English with the BBC Service http://www.bbc.co.uk/worldservice/learningenglish/index.shtml 3. Oxford University Press http://www.oup.co.uk/ 4. OUP online http://www.oup.com/online/ Oxford DNB, online references, etc. 5. Longman Dictionary http://www.ldoceonline.com/ 6. Internet Grammar of English (very academic) http://www.ucl.ac.uk/internet-grammar/home.htm 7. English Grammar and Writing online http://www.edufind.com/english/grammar/ 8. Good tests and exercises in English Grammar http://www.usingenglish.com/online-tests.html 9. Vocabulary and Grammar Exercises online http://www.roseofyork.co.uk/learning.html 10. English for learners http://www.churchillhouse.com/english/learners.html
Supplementary: 1. What is the latest news in the Guardian? British Press online http://www.wrx.zen.co.uk/britnews.htm 2. What is the word of the day? Oxford Dictionaries online… http://www.askoxford.com/ 3. Enjoy English idioms with Cambridge University Press CUP Activity Page http://www.dictionary.cambridge.org/activity.htm 4. Find the script of your favourite movie Scripts online http://www.joblo.com/moviescripts.php 5. What’s new in Headway? Phrase builder with Headway http://www.oup.com/elt/global/products/headway/everydayenglish/ 6. Can you sing All My Loving with us? Song Lyrics site for educational purposes http://www.lyricz.org/search INFORMATION SECURITY Lecturer : Yesin Vitaliy Ivanovych, PhD (Engineering), Associate Professor Aim : To lay terminological grounds, to teach students to carry out an accurate analysis of data security threats, to teach basic techniques, principles and algorithms of protecting information in computer systems considering present conditions and outlook on development of the potential intruders’ theatening techniques, systems and means. Tasks : During this course students should acquire certain skills and abilities in data guard theoretical and practical aspects. Following the completion of the course students must : KNOW : modern threats to information system security ;
data guard methods and facilities ;
data guard cryptographic techniques ;
security program techniques and methods ;
data guard techniques in distributed information systems ;
information security organizational and legal policy. BE ABLE TO : analyse possibilities of unauthorized information extracting by potential intruders;
analyse computer viruses and malicious software influence on computer system security ;
study secret cryptographic systems strength;
study assymetry of cryptographic system;
detect viruses in Windows OS by means of proceeding processes analysis, suspect routine codes analysis and antivirus programmes.
organize and exercise activities of data guard department officials according to the instructions and duties.
Subject Description: Data guard cryptographic techniques. Information security fundamentals. Information protectiom in computer systems from accidental threats. Data guard facilities and methods. Safety program techniques and methods. Data guard techniques in distributed information systems. Information security organizational and legal policy.
Assessment Forms : During the semester students take the following tests :
module test (2 modules) ;
final test (examination).
Supportive Materials : 1. Lecture materials (printed and electronic variants). 2. Workshop and seminar schedule (printed and electronic variants). 3. Discipline schedule. 4. Tasks for two module tests. 5. Examination questions. Recommended literature Basic 1. Есин В. И., Кузнецов А. А., Сорока Л. С. Безопасность информационных систем и технологий (Information System and Technology Security)– Х.:ООО «ЭДЭНА», 2010.-656с. 2. Горбенко І. Д. Гриненко Т. О. Захист інформації в інформаційно- телекомунікаційних системах (Information Protection in Information and Telecommunication Systems): Навч. посібник. Ч.1. Криптографічний захист інформації - Харків: ХНУРЕ, 2004 - 368 с. 3. Домарев В. В. Безопасность информационных технологий (Information Technology Security): Системный подход: - К.: ООО "ТИД ДС", 2004. – 992с. 4. Конев И. Р., Беляев А. В. Информационная безопасность предприятия (Enterprise Information Security).- СПб.: БХВ - Петербург, 2003, 752с.: ил. Supplementary 1. Белов Е. Б., Лось В. П., Мещеряков Р. В., Шелупанов А. А. Основы информационной безопасности (Information Security Fundamentals). Учебное пособие для вузов - М.: Горячая линия - Телеком, 2006. - 544 с: ил. 2. Биячуев Т. А. / под ред. Л. Г.Осовецкого Безопасность корпоративных сетей (Coorporate Network Security). – СПб: СПб ГУ ИТМО, 2004.- 161 с. 3. Завгородний В. И. Комплексная защита информации в компьютерных системах (Complex Information Protection in Computer Systems): Учебное пособие. - М.: Логос, 2001. - 264 с : ил. 4. Зегжда Д. П., Ивашко А. М. Основы безопасности информационных систем (Foundations of Information System Security). – М.: Горячая линия – Телеком, 2000. 452с., ил. 5. Малюк А. А. Информационная безопасность: концептуальные и методологические основы защиты информации (Information Security: Conceptual and Methodological Data Guard Fundamentals) . Учеб. пособие для вузов. - М: Горячая линия-Телеком, 2004. -280 с. ил. 6. Малюк А. А., Пазизин С. В., Погожин Н.С. Введение в защиту информации в автоматизированных Системах (Introduction to Information Protection in Automated Systems). - М.: Горячая линия-Телеком, 2001. - 148 с: ил. 7. Мамаев М., Петренко С. Технологии защиты информации в Интернете (Technologies of Information Protection on the Internet). Специальный справочник. – СПб.: Питер, 2002.- 848 с.: ил. 8. Мельников В. В. Защита информации в компьютерных системах (Data Guard in Computer Systems). – М.: Финансы и статистика; Электронинформ, 1997.- 368с.:ил. 9. Шеннон К. Работы по теории информации и кибернетике (Works on Information Theory and Cybernetics), М., ИЛ, 1963, с. 333-369 (Перевод В.Ф.Писаренко) 10. Козлов Д. А., Парандовский А. А., Парандовский А. К. Энциклопедия компьютерных вирусов (Encyclopedia of Computer Viruses). - М.: «СОЛОН-Р», 2001. 11. Романец Ю. В., Тимофеев П. А., Шаньгин В. Ф. Защита информации в компьютерных системах и сетях (Protection of Information in Computer Systems and Networks)/ Под ред. В. Ф. Шаньгина.-2-е изд., перераб. и доп.-М.: Радио и связь, 2001.-376 с: ил. 12. Фергюсон Н., Шнайер Б. Практическая криптография (Practical Cryptography). : Пер. с англ. — М.: Издательский дом "Вильямс", 2005. — 424 с. : ил. 13. Хорошков В. А., Чекатков А. А. Методы и средства защиты информации (Data Guard Methods and Facilities) / Под ред. Ю. С. Ковтанюка – К.: Издательство Юниор, 2003.- 504с., ил. 14. Шнайер Б. Прикладная криптография: Протоколы, алгоритмы, исходные тексты на языке Си (Applied Cryptography: Protocols, Algorithms, C-based Source Texts). - М.: "Триумф", 2002 Information Resources 1. Закон України від 25.06.93 № 3323-XII-ВР "Про науково-технічну інформацію" (The Law of Ukraine on Scientific and Technical Information). 2. Закон України "Про інформацію" (The Law of Ukraine on Information). Із змінами, внесеними згідно із Законом від 07.02.2002 № 3047-III-ВР. 3. Закон України "Про Державну таємницю" (The Law of Ukraine on State Secret). Із змінами і доповненнями, внесеними Законом України від 21.09.1999 №1079-XIV. 4. Закон України від 05.07.94 № 80/94-ВР "Про захист інформації в автоматизованих системах” (The Law of Ukraine on Information Protection in Automated Systems). 5. Закон України "Про Національну програму інформатизації" (The Law of Ukraine on National Informatization Programme) Із змінами, внесеними згідно із Законом від 13.09.2001 № 2684-III-ВР. 6. Закон України "Про зв’язок" (The Law of Ukraine on Communication) Із змінами, внесеними згідно із Законом від 04.07.2002 № 36-IV-ВР. 7. Закон України від 15 грудня 2005 року № 3200-IV "Про основи національної безпеки України" (The Law of Ukraine on Foundations of National Security of Ukraine). 8. Введение в криптографию под ред. В. В. Ященко (Introduction to Cryptography under the Editorship of V. V. Yaschenko) // http://nature.web.ru/db/msg.html? mid=1157083&uri=node1.html 9. Казарин О. В. Безопасность программного обеспечения компьютерных систем (Computer Software Security) // http://citforum.ru/security/articles/kazarin 10. Ростовцев А. Г., Михайлова Н. В. Методы криптоанализа классических шифров (Classic Codes Cryptoanalysis Methods) // http :// www . ssl . stu . neva . ru / psw / crypto / rostovtsev / cryptoanalysis .html 11. Федотов Н. Н. Защита информации (Data Guard) (Учебный курс) // http://www.college.ru/UDP/texts/index.html DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION Complex Computer Network Components Lecturer : Rassomakhin Serhiy Hennadiyovych, PhD (Engineering), Full Professor Prior Requirements : The discipline « Management Theory » is based on abilities acquired after a completion of the following courses : « Advanced Mathematics », « Physics », « Metrology and Measurement », « System Analysis », « Algorithmic Languages and Programming », « Computer Fundamentals ». Aim : To learn modern theoretical and practical organization and composition principles of computer system communication channels and links, convertion of data and information representation forms in multilevel digital hierarchy channels, mobile network, personal call and trunked radio system realization principles. Tasks : Following the completion of the course students must : KNOW : basic principles and modern methods of complex computer network elements realization ;
types and features of the physical communication links (wire, optical, radio, radiorelay, satellite) ;
the ways of analog-to-digital data forms convertion ;
modern methods of digital stream compression ;
organization principles of complex computer network multichannel communication and frequency (FDMA), time (TDMA) and code (CDMA) division multiple access ;
principles and norms of plesiochronous and synchronous digital hierarchy network composition ;
methods and systems of realization of the first, second (AMPS, GSM, CDMA) and third (3G) mobile communication generations ;
methods of personal communication satellite system (PCSS) composition ;
basic features and realization methods of trunked radio networks ; BE ABLE TO : make engineering estimations of the communication links of different physical nature ;
make estimation and formation of analog-to-digital data forms convertion systems ;
apply the methods of compact coding and digital stream compression in complex computer systems ;
determine features and make formation of FDMA and TDMA elements ;
make analysis and optimization of code-division broad-band systems ;
apply modern algorithms of multilevel digital hierarchy protocol composition ;
estimate efficiency of mobile network different organization methods ;
conduct basic operations on engineering and optimization of the trunked radio and satellite communication systems’ features ;
Discipline Description: Interaction-between-open-systems model. Classification, types and features of physical communication links. Analog transmission systems. Forms and features of information signal represantation. Mathematic principles of digital source representation optimization. Digital stream compression methods. Multichannel communication and multiple access methods. Frequency division multiple access (FDMA) systems. Time division multiple access (TDMA) systems. Plesiochronous and synchronous hierarchy. Code division multiple access (CDMA) systems. First generation NMT-450, AMPS analog telephony. GSM-standard mobile networks. CDMA (2G, 2.5G, 3G) mobile networks. Satellite communication and personal call systems. Trunked radio data transfer networks. Outlook on development of complex computer networks.
Assessment Forms : Current control of the students’ work is carried out at workshops and laboratory- based work by means of quizzing. Final control is carried out by means of writing semester tests and examination. Supportive Materials :
1. Course of lectures « Complex Computer Network Components », electronic variant. 2. PowerPoint presentation set «Complex Computer Network Components ». 3. Instructive guidelines for workshops and laboratory-based work. Recommended Literature Basic 1. Томаси У. Электронные системы связи (Electronic Communicaton Systems). М.: Техносфера, 2007.–1360 с. 2. Скляр Б. Цифровая связь. Теоретические основы и практическое применение (Digital Communication. Theoretical Fundamentals and Practical Application). Изд-е 2-е, испр.: Пер с англ.–М.: "Вильямс", 2003.–1104 с. 3. Гаранин М.В., Журавлев В.И., Кунегин С.В. Системы и сети передачи информации (Data Transfer Systems and Networks).–М.: Радио и связь,2001.–336 с. Supplementary 1. Вишневский В.М., Ляхов А.И., Портной С.Л., Шахнович И.В. Широкополосные беспроводные сети передачи информации (Broad-Band Wireless Data Transfer Networks). – М.: Техносфера, 2005. –592 с. 2. Шахнович И.В. Современные технологии беспроводной связи (Modern Technologies of Wireless Communication). –М.: Техносфера, 2006.– 288 с. 3. Величко В.В. Передача данных в сетях мобильной связи третьего поколения (Data Transfer in Third Generation Mobile Communication Networks). – М.: Радио и связь,2005.– 332 с.
Information Resources http://www.studfiles.ru/ DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION DATA AND KNOWLEDGE BASE ORGANIZATION Lecturer : Yesin Vitaliy Ivanovych, PhD (Engineering), Associate Professor Prior Requirements : The discipline « Data and Knowledge Base Organization» is based on abilities acquired after the completion of the following courses : « Advanced Mathematics », « Discrete Mathematics », « Physics », « Electronics and Microcircuitry», « Microprocessor and Its Application », « Optical Informatics », « Information Theory », « Computer Fundamentals », « Algorithmic Languages and Programming », « System Programming and Operating Systems ». Aim : To lay terminological grounds, to teach students the foundations of database design and main principles of its exploitation , to teach the language of determination and manipulation of DB information, and knowledge base foundations considering present conditions and outlook on development of information systems. Tasks : During this course students should acquire certain skills and abilities in data and knowledge bases organization. Following the completion of the course students must : KNOW : the history of development, advantages and disadvantages of the DBMS ;
data models ;
DBMS structure architecture ;
main principles, approaches and stages of database design ;
foundations of relational database design using « entity-relationship» model ;
(Structured Query Language) SQL fundamentals ;
main principles of the shareable database parallel transaction processing ;
main principles of DB security ;
main principles of the structure and development of object-oriented DBMS ;
knowledge base fundamentals ; BE ABLE TO : design databases using ER-model ;
design normalization-based relational databases ;
apply SQL for data determination and manipulation in Microsoft Access DBMS ;
install Oracle Client software and configure Oracle Client connection with Oracle Server DB ; Subject Description: Introduction to database. Main principles of database design. SQL fundamentals. Main principles of database exploitation. Introduction to object-oriented DBMS. Database fundamentals. Assessment Forms : The discipline involves writing a term paper, two module tests within the total number of academic hours and a final test in the form of « pass-fail » examination. Supportive Materials :
1. Lecture materials (printed and electronic variants). 2. Workshop and laboratory-based work schedule (printed and electronic variants). 3. Discipline schedule. 4. Tasks for two module tests. 5. Term paper projects. 6. Examination questions. Recommended Literature Basic 1. Дейт К. Введение в системы баз данных (Introduction to Database Systems), 7-е издание.: Пер. с англ. — М.: Издательский дом "Вильямс", 2001. — 1072с.: ил.
2. Коннолли Т., Бегг К. Базы данных. Проектирование, реализация и сопровождение. Теория и практика (Database. Design, Realization and Maintenance. Theory and Practice). 3-е издание. : Пер. с англ. — М.: Издательский дом "Вильямс", 2003. — 1440с. : ил.
3. Хомоненко А. Д., Цыганков В. М-, Мальцев М. Г. Базы данных (Database): Учебник для высших учебных заведений / Под ред. проф. А. Д. Хомоненко. — 4-е изд., доп. и перераб. — СПб.: КОРОНА принт, 2004. — 736 с. Supplementary 1. Крёнке Д. Теория и практика построения баз данных (Theory and Practice of Database Design). 8-е изд.— СПб.: Питер, 2003. — 800 с: ил. — (Серия «Классика computer science»). 2. Райордан Р. Основы реляционных баз данных (Foundations of Relational Databases) / Пер, С Англ. — М.: Издательско-торговый дом «Русская Редакция», 2001. — 384 с.: ил. 3. Цаленко М. Ш. Моделирование семантики в базах данных (Semantics Modeiling in Database). М.: Наука. Гл. ред.физ-мат.лит., 1989.- 288с. 4. Цикритзис Д., Лоховски Ф. Модели данных (Data Models) /Пер. с англ. – М.: Финансы и статистика, 1985. – 344с. Information Resources 1. American National Standards Institute (1975). ANSI/X3/SPARC Study Group on Data Base Management Systems. Interim Report, FDT. ACM SIGMOD Bulletin, 7(2). 2. ГОСТ 34.320-96 Межгосударственный стандарт. Информационные технологии. Система стандартов по базам данных. Концепции и терминология для концептуальной схемы и информационной базы (Information Technology. Database System of Standards) // http://dp-beg.narod.ru/gost1.doc 3. Кузнецов С.Д. Базы данных. Вводный курс (Database. Introductory Course)// http://www.citforum.ru/database/advanced_intro/ 4. Петер Пин-Шен Чен Модель "сущность-связь" – шаг к единому представлению о данных (“Entity-Relationship” Model Is a Step toward Data Single Overview) / Перевод: М.Р. Когаловский, Новая редакция: Сергей Кузнецов, 2009 г. // http://www.citforum.ru/database/classics/chen/ DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION BASIC PRINCIPLES OF THE STATE INFORMATION SECURITY Lecturer : Pievniev Volodymyr Yakovych, PhD (Engineering), Associate Professor Prior Requirements : The course is based on knowledge acquired at school and after the completion of the following courses : « Advanced Mathematics », « Physics », « Introduction to the Occupation ». Aim : To provide guidance on theoretical foundations of information security, basic principles of the state information securing, the ratio between information and state secret, national security information, non-state confidential and unclassified information that requires protection, basic principles of information security structure. Tasks : Following the completion of the course a student must : KNOW : state information security policy ; information security system components ; the process of protecting information in computer systems from unauthorized access ; BE ABLE TO : carry out analysis of regulatory-based technical protection of information ; make up models of security object systems ; estimate information resources risks ; KNOW: modern data acquisition methods and techniques ; main principles of information dessimination. Subject Description: Structure and content of the discipline. Information security components. Information security system. Protection of state information sources in information and telecommunication systems. General characteristic of information security models. Technical protection of information. Cryptographic systems. Assessment Forms : The discipline is given in the second semester and involves lectures, workshops, independent work and writing a module test within the total number of academic hours, « pass-fail » examination. Supportive Materials :
1. Course of lectures «Basic Principles of the State Information Security», electronic variant. 2. Set of slides «Basic Principles of the State Information Security». 3. List of questions for the module test. 4. Instructive guidelines for workshops. Recommended Literature Basic 1. ДОКТРИНА інформаційної безпеки України (Doctrine of Information Security of Ukraine). Указ Президента України від 8 липня 2009 року № 514/2009 2. Безопасность информационных технологий. Методология создания систем защиты (Information Technology Security. Methodology of Protection System Design) / В.В. Домарев. – К.: ООО "ТИД "ДС", 2001. – 688 с. 3. Энциклопедия промышленного шпионажа (Encyclopedia of Industrial Espionage) / Под общ. ред. Е.В. Куренкова – С.-Петербург: ООО "Изд-во Полигон", 1999. – 512 с. 4. Хорев А.А. Способы и средства защиты информации (Data Guard Techniques and Facilities). – М.: МО РФ, 2000. – 316 с. 5. А.Ю.Щербаков. Введение в теорию и практику компьютерной безопасности (Introduction to Theory and Practice of Computer Security). -М.: издатель Молгачева С.В., 2001. 6. Бармен, Скотт. Разработка правил информационной безопасности.(Development of Information Security Regulations): Пер. с англ. – М.: Издательский дом "Вильямс", 2002. 7. С.Л.Емельянов Основы информационной безопасности (Information Security Fundamentals).- Одесса: Юридична література, 2003.- 198с. Supplementary 1. Про державну таємницю (The Law of Ukraine on State Secret). Закон України №3855- XII від 21.01.1994 р. (в редакції Закону № 1079-14 від 21.09.99). 2. Про затвердження зводу відомостей, що становлять державну таємницю (On the Approval of Data List Representing State Secret). Наказ Голови Служби безпеки України від 12.08.2005 р. № 440. 3. НД ТЗІ 1.1 – 002 – 99. Общие положения по защите информации в компьютерных системах от несанкционированного доступа (Normative Document on Technical Protection of Information. General Provisions on Protecting Information from Unauthorized Access in Computer Systems). Нормативный документ ДСТЗИ СБ Украины. Киев, 1999. 4. Про інформацію (The Law of Ukraine on Information). Закон України № 2657-XII від 02.10.92 р. 5. Концепція технічного захисту інформації в Україні (Concept of Technical Protection of Information in Ukraine). Постанова КМУ №1126 8.10.97. 6. Положення про технічний захист інформації в Україні (Provisions on Technical Protection of Information in Ukraine). Указ Президента України №1229/99 від 27.09.99. 7. Тимчасові рекомендації з технічного захисту інформації вид витоку каналами побічних електромагнітних випромінювань і наводок (Temporary Recommendations on Technical Protection of Information from Accidental Electromagnetic and Phantom Emission from Channels). (ТР ТЗІ-ПЕМВН-95). Затверджені наказом ДСТЗІ від 09.06.95р. № 25. 8. НД ТЗІ 1.4-001-2000. Типове положення про службу захисту інформації в автоматизованій системі (Typical Provision about Information Security Service in Automated System). 9. НД ТЗІ 2.5-005-99. Класифікація автоматизованих систем і стандартні функціональні профілі захищеності оброблюваної інформації від несанкціонованого доступу (Classification of Automated Systems and Standard Functional Profiles of Processing Information Security from Unauthorized Access). 10. НД ТЗІ 2.1-001-2001. Створення комплексів технічного захисту інформації. Атестація комплексів. Основні положення. (Development of Information Technical Protection Netwoks. Network Assessment. Basic Principles) 11. НД ТЗІ 3.7-001-99. Методичні вказівки щодо розробки технічного завдання на створення комплексної системи захисту інформації в автоматизованій системі (Instructive Guidelines for the Development of Techniques to Design Complex Data Guard System in Automated System) (Зі зміною № 1, затвердженою наказом ДСТСЗІ СБУ 18.06.02 № 37). 12. НД ТЗІ 2.5-010-2003. Вимоги до захисту інформації WEB-сторінки від несанкціонованого доступу (Requirements for WEB-page Information Protection from Unauthorized Access). 13. ГОСТ Р 51275-99. Защита информации. Объект информатизации. Факторы, воздействующие на информацию. Общие положения (Information Protection. Object of Informatization. Factors Influencing Information. General Provisions). 14. Симонов С.В. Методология анализа рисков в информационных системах (Methodology of Risk Analysis in Information Systems). Журнал "Защита информации. Конфидент", №1, 2001. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION INFORMATION THEORY Lecturer : Soroka Leonid Stepanovych, Doctor of Science (Engineering), Full Professor Aim : The discipline seeks to teach students to make estimations of quantitative characteristics of data transfer, storage and processing processes in information transfer systems, as well as to acquire modern information analysis techniques of signal convertion methods. Tasks : Following the completion of the course a student must : KNOW : 1. Mathematic models of signals, hindrances and communication channels. 2. Basic principles of data exchange in information transfer systems. 3. Signal-to-channel adjustment principles under severe physical resources restrictions. 4. The ways of improving discrete information transfer reliability via application of error control coding and feedback information transfer systems. BE ABLE TO : 1. Determine key information features of message sources. 2. Determine basic information and technological features of information transfer systems. 3. Apply modern information methods of data transfer and processing analysis. 4. Make estimations of channel-to-resource information capacity adjustment. 5. Apply basic principles of information theory to estimate IT features of control and communication system elements. 6. Carry into effect coding and decoding machines of error control codes.
KNOW : Modern development tendencies of information theory and its practical application. Subject Description: Information, message, signal, communication channel, communication system. Classification of information transfer systems. Main features of information transfer system. Hindrances and errors in communication channels. Amount of information and entropy. Entropy of a random experiment with equally and unequally probable consequences. Conditional entropy. Entropy of joint systems. Discrete entropy. Differential entropy. The excessity of message sources. Deterministic and stochastic signals (processes). Stationary stochastic process. Ergodic stochastic process. Fourier transform theory elements. Energy spectrum. Time quantization. Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem. Level quantization. Correlation function of stationary stochastic process. Wiener-Khinchin theorem. Classification of communication channels. Continuous channel model. Discrete channel model. Shannon’s noiseless-channel coding theorem. Efficient coding. Discrete channel capacity. Shannon’s noisy-channel coding theorem. Continuous channel capacity. Message source-to-communication channel adjustment. The ways of improving information reliability. Feedback information transfer systems. Error control coding principles. Classification of error control codes. Key features of error control codes. Basic types of error control codes. Composition methods of error control codes’ coders and decoders. Realization principles of error control codes’ coders and decoders. Assessment Forms : Current control of the students’ work is carried out during workshops by means of quizzing. Final control involves writing semester « pass-fail » examination. Supportive Materials : 1. Course of lectures « Information Theory » , electronic variant. 2. PowerPoint Presentation set « Information Theory ». 3. Instructive guidelines for workshops and students’ independent work. Recommended Literature Basic 1. Сорока Л.С. Основи теорії інформації (Foundations of Information Theory): Навчальний посібник. Х.: ХНУ ім. В.Н. Каразіна, 2007.–264 с. 2. Краснобаєв В.А., Фурман І.А. Теорія інформації (Information Theory): Підручник для ВНЗ / М-во освіти і науки України. – К., 2005. – 160 с. 3. Сорока Л.С. Основы теории минимально-избыточных сигналов. Математические методы и средства обработки: Монография (Foundations of Minimum-Pressure Signals. Mathematic Processing Methods and Techniques. Monography).- Х.: МОУ ОНИИ ВС, 2005.- 280 с. Supplementary 1. А.Н. Колмогоров Избранные труды. III том: Теория информации и теория алгоритмов (Selective Works. Part 3. Information Theory and theory of Algorithms) М., "Наука", 1987, - 303 с. 2. Блейхут Р. Теория и практика кодов, контролирующих ошибки (Theory and Practice of Error-Correction Codes) / Пер. с англ. – М.: Мир, 1986. – 576 с. 3. Кузьмин И.В. Основы теории информации и кодирования (Foundations of Information and Coding Theory)/ И.В. Кузьмин, В.А. Кедрус – К.: Вища школа, 1986. – 238 с. 4. Лосев Ю.И. Основы теории передачи данных (Foundations of Data Transfer Theory). Х.: ВИРТА, 1992. – 233 с. 5. Никитин Г. И. Помехоустойчивые циклические коды (Cycle Error Control Codes): Учеб. пособие. – Санкт-Петербург. – СПбГУАП, 2003. – 33 c. 6. Питерсон У. Коды, исправляющие ошибки (Error-Correction Codes)/ У. Питерсон, Э. Уэлдон.: Пер. с англ. – М.: Мир, 1976. – 600 с. 7. Шульгин В.И. Основы теории передачи информации. Ч. 2. Помехоустойчивое кодирование (Foundations of Data Transfer Theory. Part 2. Error Control Coding): Учеб. пособие. – Харьков: Нац. аэрокосм. ун-т «Харьк. авиац. институт», 2003. – 87 с. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION CONTROL THEORY Lecturer : Yesin Vitaliy Ivanovych, PhD (Engineering), Associate Professor Prior Requirements : The discipline « Control Theory» is based on abilities acquired after a completion of the following disciplines : « Advanced Mathematics », « Physics », « Metrology and Measurement », « System Analysis , « Algorithmic Languages and Programming », « Computer Fundamentals ». Aim : To lay terminological grounds, to teach students to carry out analysis and synthesis of control systems, to teach management principles of technical systems and methods, information technology and projects. Tasks : During this course students should acquire certain skills and abilities in theoretical and practical aspects of technical systems and methods, information technology and projects management. Following the completion of the course students must : KNOW : 1. basic concepts of control theory ; 2. method of dynamic process estimations (Kalman filter) ; 3. calculus of variations method ; 4. Pontryagin’s maximum principle ; 5. method of dynamic programming ; 6. IT control methods ; 7. design control theoretical foundations ; BE ABLE TO : 1. carry out controlability and observability analysis of control systems ;
2. examine dynamic system stability ;
3. analyse methods of solving optimization problems ;
4. solve optimization problems ;
5. synthesize optimal control algorithms ;
6. apply worldwide standards for IT control ;
7. develop software projects. Subject Description: Optimal control theory. IT control. Design control. Assessment Forms : The discipline involves writing two module tests within the total number of academic hours, one control paper and final control in the form of examination. Supportive Materials : 1. Lecture materials (printed and electronic variants). 2. Workshop and seminar schedule (printed and electronic variants). 3. Discipline Schedule. 4. Tasks for a control paper and two module tests. 5. Examination questions. Recommended Literature Basic
1. Михайлов В. С. Теория управления (Control Theory). — К.: Выща шк. Головное изд- во, 1988. — 312 с; 26 табл., 80 ил. 2. Основы теории управления (Foundations of Control Theory) : учеб. пособие /Ю.Ю. Громов, В.О. Драчёв, О. Г. Иванова, Ю.С. Сербулов, К.А. Набатов. – Тамбов : Изд-во Тамб. гос.техн. ун-та, 2008. – 240 с. 3. Певзнер Л. Д. Теория систем управления (Control System Theory). — М.: Издательство Московского государственного горного университета, 2002. — 472 с. Supplementary 1. Александров А. Г. Оптимальные и адаптивные системы (Optimal and Adaptive Systems): Учеб. Пособие для вузов по спец. "Автоматика и упр. в техн. системах". - М.: Высш.шк.,1989.-263 с.: ил. 2. Достаточно общая теория управления (General Control Theory) / Постановочные материалы учебного курса факультета прикладной математики — процессов управления Санкт-Петербургского государственного университета (1997 — 2003 гг.) 3. Основы теории оптимального управления (Foundations of Optimal Control Theory): Учеб. Пособие для экон. вузов / В.Ф. Кротов, Б.А. Лагоша, С.М. Лобанов и др.; Под ред. В.Ф. Кротова.- М.: Высш.шк.,1990.- 430 с.: ил. 4. Сотсков А.И., Колесник Г.В. Оптимальное управление в примерах и задачах (Optimal Control in Illustrations and Schemes). – М.: Российская экономическая школа, 2002 – 58 с. 5. Теория управления (Control Theory): Учебник / Под общ. ред. А. Л. Гапоненко, А. П. Панкрухина.- М.: Изд-во РАГС, 2003.-558с. Information Resources 1. Справочник по прикладной статистике (Reference Book on Applied Statistics). В 2-х т. Т.2: Пер. с англ. / Под ред. Э. Ллойда, У. Ледермана, С.А. Айвазяна, Ю.Н. Тюрина. – М.: Финансы и статистика, 1990. – 526 с.: ил. 2. Справочник по теории автоматического управления (Reference Book on Automatic Control)/ Под ред. А.А. Красовского .- М.: Наука, Гл. ред физ.-мат. Лит., 1987.- 712 с. 3. CobiT 4.1 Российское издание. Методология. Цели контроля. Руководство по управлению. Модели зрелости процессов (CobiT4. Russian Edition. Metodology. Control Targets. Management Directives. Process Completeness Models). - М.: Аудит и контроль информационных систем, 2008 4. С. Гузик Стандарт CobiT. Управление и аудит информационных технологий. Особенности проведения внешнего аудита ИТ (CobiT Standard. IT Management and Audit. Main Principles of IT External Audit) . / http://citforum.nis.nnov.su/consulting/standart_cobit/ 5. Ефремов В.С. Проектное управление: модели и методы принятия решений (Project Control: Decision-Making Techniques and Models)/ http://www.cfin.ru/press/management/1998- 6/11.shtml DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION PROGRAMMING TECHNOLOGY Lecturer : Kuklin Volodymyr Mykhailovych, Doctor of Science (Physics and Mathematics) Organizatinal and Methodical Section. The course is included into general professional training process and it is basic for the speciality 08. 04. 01 – « Information Management Systems and Technologies ». The descipline seeks to introduce students to foundations of programming and software development techniques, considering specific requirements to professional training. The course is comprised of programming theory foundations, information about general requirements to computer software, programming technologies using modern software tools. The discipline can be given after a set of mathematical and general professional disciplines and it aims at : introducing students to foundations of programming theory ;
presenting basic principles of the software organization and its requirements ;
giving knowledge required for professional work within a software designers group ; Following the completion of the discipline students must : be knowledgeable in basic programming theory concepts ;
have a notion about problem modeling, designing and algorithmization and software development ;
be able to carry out basic technological procedures of programming tools development process ;
be experienced in working with corresponding software tools. Recommended Literature 1. Столлингс В. «Операционные системы. Внутреннее устройство и принципы проектирования» (Operating Systems. Interior Arrangement and Design Principles) 4-е изд., М., Издательский дом «Вильямс», 2002. – 848с.. 2. Кессел П., Бикслер Д., Темпестини Р. «Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional. Энциклопедия пользователя» (Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional. User’s Encyclopedia)., К., «ДиаСофт», 2001, - 825с. 3. Андреев А., Беззубов Е., Емельянов М., и др. «Microsoft Windows 2000 Server и Professional», СПб, «БХВ», 2000, - 1055с. 4. Немнюгин С., Чаунин М., Комолкин А. «UNIX» СПб, «Питер», 2001, - 682с. 5. Беляков М. И., Рабовер Ю. И., Фридман А. Л. «Мобильная операционная система» (Mobile Operating System), М., «Радио и связь», 1991, - 208с. 6. Дейтел Г. «Введение в операционные системы» (Introduction to Operating Systems) , в 2-х томах. М., «Мир», 1987, - 758с DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION SPECIALIZED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES Lecturer : Rukkas Kyrylo Markovych, PhD (Engineering), Associate Professor Aim : To master skills of using specialized programming languages. Tasks : Following the completion of the course a student must : KNOW : 1. Principles of distributed client-server programmes development ; 2. Socket operating principle. Socket types and parameters. Socket network programmes development features ; 3. Principle of parallel and serial servers structure. 4. Basic concepts of the .Net Framework. 5. Basic data types and structures of the C# Programming language. 6. Java core libraries. Application principles. 7. Java core libraries for network programmes development. 8. Java servlet development principle. BE ABLE TO : 1. Develop network programmes based on socket mechanism. 2. Develop C#-based application software . 3. Develop C#-based network programmes. 4. Develop Java-based application software . 5. Develop Java-based network programmes. Subject Description: Windows Socket Application Programming Interface (WINSOCK). The C# programming language. Java programming language. Assessment Forms : Control of the students’ work is carried out during workshops and laboratory-based work via writing control papers. Final control is carried out via examination paper. Supportive Materials : 1. Textbook « Computer Networks », electronic form. 2. Multimedia equipment and reference materials in electronic variant. 3. Instructive guidelines for laboratory-based work. Recommended Literature Basic 1. Таненбаум Э. Компьютерные сети (Computer Networks). – С-П.: Питер , 2001. 2. Й. Снейдер. Эффективное программирование TCP/IP (TCP/IP Efficient Programming). С-П.: Питер, 2002. 3. Л. Чепел, Э. Титтел. TCP/IP Учебный курс.//С-П: BHV, 2003 4. Стивенс Р. Протоколы TCP/IP практическое руководство (TCP/IP Protocols. Practical Guidance) С-П.: БХВ-Петербург, 2001. 5. Джонс Э., Оланд Дж. Программирование в сетях Windows (Windoms Network Programming).-Спб.: Питер; М.: Издательско-торговый дом «Русская редакция», 2002.-608 с 6. Павловская Т.А. C#. Программирование на языке высокого уровня (High-Level Language Programming). Питер, 2009. – 432 с. 7. Герберт Шилдт C# .Учебный курс. Питер, 2003.- 512 с 8. Ноутон П., Шилдт Г. Java 2. С-П.: БХВ-Петербург, 2001.- 895 с. Supplementary 1. Лосев Ю.И., Бердников А.Г. Основы теории передачи информации (Foundations of Data Transfer Theory). - Х.: ХВУ. 1993. 2. Будилов В. Интернет-программирование на Java (Java-based Internet Programming). С- П.: БХВ-Петербург, 2002. 3. Хабибуллин И. Разработка Web-служб средствами Java (Java-based Web-Services Development) . С-П.: БХВ-Петербург, 2003. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION OPERATING SYSTEMS AND SYSTEM PROGRAMMING Lecturer : Duravkin Yevhen Volodymyrovych, PhD (Engineering), Associate Professor of Theoretical and Applied System Engineering Department Aim : To teach students to apply computer-oriented languages and to know their programming considerations. To teach students to develop programmes adjusted to multiprocession systems. To develop creativity, need for self-education, to instruct in developing software products maximally using modern operating systems performance potential. Targets : 1. mastering Assembly programming language for Intelx processors ; 2. mastering development and setting process of programmes designed on the basis of computer-oriented languages ; 3. stydying methods of interaction between multithreaded and multiprocession software systems ; 4. forming methodical recept about concepts, models and principles of organization taken as a basis for modern operating systems.
Following the completion of the course a student must KNOW : 1. EOM system software components ; 2. Programme structure and Assembly and Win API directives for programming definite objectives . 3. Compiler stages, programme optimization principles. 4. Assembler and high-level programming languages macro facilities . 5. Principles and methods of operating system development. 6. Operating system tools (interrupt processing, drivers, physical input-output). 7. Methods of external device control (timer, speaker, keyboard, etc.) 8. The ways of improving operating systems and software.
BE ABLE TO : 1. Develop Windows system applications. 2. Write Assembler- and C++-based programmes. 3. Develop translator from Assembler and C++ programming languages. 4. Put into effect lexical, syntactical and semantic analysis algorithms. 5. Develop macroprocessor. 6. Apply interrupt processing programmes. 7. Develop drivers. 8. Work with a disk on physical layer. 9. Control storage allocation, file processes and flows. 10. Protect information from unauthorized access. Subject description: Basics of operational systems construction. Classification of operational systems. Evolution of operational systems. Peculiarities of methods of operational systems construction. Processes. Model of a process. Creation and completion of a process. Hierarchy of processes. Realization of processes. Realization of processes in modern operational systems. Threads. Model of a thread. Use of threads. Ways of realization. Realization of threads in modern operational systems. Interprocess interaction. Mode of competition. Mutual stopping with active waiting. Primitives of interprocess interaction. Planning. Introduction to planning. Planning in systems of batch processing. Planning in interactive systems. Planning in real-time systems. Mutual process blocking. The notion of resource. Conditions of mutual blocking. Research ways of mutual blocking. Revealing and removing of mutual blocking. Memory organization and management. Memory protection. Memory allocation in modern operational systems. Virtual memory. Algorithms of paging. Management of outer resource access. Management of inputting/ outputting. Basic notions and conceptions of management of inputting / outputting in operational system. Principles of input/ output software. Control mode of input/ output. File systems. Files (naming, structure, types, access, operations, realization). Catalogues (one-level, two-level, hierarchic systems; operations, realization). Examples of file systems. Peculiarities of system software development. Interfaces of application programming. Principles of construction of operational systems interface. The notion of interface of application programming. Platform-independent interface POSIX. WinAPI. Multiprocessor system. Multiprocessor. Multicomputer systems. Safety. The notion of safety. Inner system attacks. Types of viruses. Types of antiviruses. Basics of system software construction. The notion of a compiler. The notion of an assembler. Differences between incoming and outgoing results. Data structure of Assembler. Peculiarities of their construction. Loaders (notion, task). Characteristics and peculiarities of an absolute loader. Variants of uniting loaders. Process of file loading to memory. Macroprocessor. Basic notions, modes of connection to Assembler. Potential of macrolanguage (title, ending, variables, branches). Characteristics of work of macroprocessor. The notion and structure of residential memory program. Basics of drivers construction. The notion of a driver, place of a driver in software, ways of driver inclusion into software. Format of DOS driver. Characteristics of application layer interfaces of platform NT5. Drivers classification of Windows NT5.
Assessment Forms: laboratory works, module tasks, final assessment, examination. List of Recommended Literature: Basic 1. Современные операционные системы (Modern Operational Systems). 2-е изд./ Э. Таненбаум – СПб. Питер. 2004. –1040 с.: ил. 2. Гордеев Молчанов Системное программное обеспечение (Systems Software). 3. Столингс В. Операционные системы (Operational Systems). – М.: «Вильямс», 2002. Supplementary 1 Сетевые операционные системы (Network Operational Systems) /Олифер В.Г., Олифер Н.А. – Спб.: Питер, 2002. – 544 с DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION PARALLEL SYSTEMS AND CALCULATION Lecturer: Tolstoluzka Olena Gennadiyivna, PhD (Engineering), senior researcher, Associate Professor of the Department of Theoretical and Applied Systems Engineering. Aim: to make students acquainted with main methods of parallel concurrent data processing and their influence on technical indexes of parallel computer systems; basic principles of construction and functioning of modern parallel computer mono- and multisystems; character of number specification and visualization of parallel time model, modern programming technologies. Tasks: Following the completion of the course a student must: Know: methods of parallel concurrent data processing, parallel algorithms, parallel processes, indexes of effectiveness of parallel realization of algorithms and programs, principles of construction and functioning of modern parallel computer mono- and multisystems. Be able to: Studying the course allows to from approaches to conscious use of methods of computer-aided programming of parallel computer systems software. Mastering the course is important for teaching the practical ways of synthesis of number specification of parallel programs, their indexes evaluation and visualization of parallel static and dynamic objects. Discipline description: Introduction. General information about parallel computational processes and systems. Static and time parallel algorithms and processes. Time parallel algorithms. Indexes of efficiency of parallel algorithms organization and their connection with demands of practical work. Method of registering of independent operations. Method of formal synthesis of algorithm parallel time models. Design of trusted parallel software tools for management systems of critical technologies and objects. Parallel program classification. Peculiarities of parallel computing programming. Main directions of solving the problem of parallel programming. Introduction to parallel programming using MPI (Message Passing Interface). Data communication in MPI. Collective Message data communication in MPI. Introduction to parallel programming using PVM (Parallel Virtual Machine). Programming using PVM. Parallel processors classification. Architecture and functioning of superscalar processors. Parallel architectures. Parallel systems classification according to Flynn. Architecture and functioning of parallel processes of dataflow management. Multiprocessor computers with shared memory. Multimachine systems. Assessment Forms: the assessment of students’ work is held at workshops and laboratory works through testing. The final assessment is held through examination test.
Supportive materials 1. Multimedia equipment and electronic version of visual aids 2. Guideline to laboratory works.
List of Recommended Literature: Basic 1. Воеводин В.В., Воеводин Вл. В. Параллельные вычисления (Parallel Computing). – СПб.: БХВ-Петербург, 2002. – 608 с. 2. Немнюгин С.А., Стесик О.Л. Параллельное программирование для многопроцессорных вычислительных систем (Parallel Programming for Multiprocessor Computer Systems). – СПб.: БХВ-Петербург, 2002. – 400 с. 3. Корнеев В.В. Архитектура вычислительных систем с программируемой структурой (Architecture of Computer Systems with Programmable Structure). – Новосибирск: Наука, 1985. – 168 с. Supplementary 4. Транспьютеры. Архитектура и программное обеспечение (Transputers. Architecture and Software): Пер.с англ./Под ред. Г.Харпа. – М.: Радио и связь, 1993. – 304 с. 5. Корнеев В.В, Киселев А.В. Современные микропроцессоры (Modern Microprocessors). – М.: НОЛИДЖ, 2000. – 326 с. 6. Поляков Г.А. Проблемы создания систем совместного автоматического проектирования аппаратно-программных средств для мультипараллельной цифровой обработки данных (Problems of Creation of Systems of Combined Automatical Designing of Hardware and Software Means for Multiparallel Digital Data Processing) // Сб. науч. тр. / 1-й Международный радиоэлектронный Форум «Прикладная радиоэлектроника. Состояние и перспективы развития» МРФ-2002. – Х.: АНПРЭ, ХНУРЭ, Ч.2, 2002. – С.241-244 DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING Lecturer: Tolstoluzka Olena Gennadiivna, PhD (Engineering), senior researcher, Associate Professor of the Department of Theoretical and Applied Systems Engineering. Aim and tasks of the course: The aim of the course is to master theoretical grounds of object-oriented programming and obtain practical skills of its realization on the basis of language C++. Tasks: to form systematized image of conceptions, models and principles of organization which form basis of object-oriented programming technologies; to obtain practical experience in the sphere of choice and use of programming technology for the tasks of information processing and management automatization; to work out appraisal of modern state and perspective directions of these programming technologies development; Following the completion of the course a student must: know: spheres of use of object oriented programming technologies; basic notions and definitions used in object oriented programming technologies; peculiarities of realization of object oriented programming principles in language C++; modern tools of software creation.
be able to: ground the necessity of use of object oriented technology to solve a concrete task; use basic syntactical constructions of C++; use STL to solve applications; use tools of object oriented programs creation. Recommended Literature: Basic 1. Б.Страуструп. Язык программирования C++ (Programming Language C++), 3-е изд./Пер. с англ. – СПб.; М.: «Невский диалект» – «Издательство БИНОМ», 1999 г. – 991 с., ил. 2. А. Пол. Объектно-ориентированное программирование на C++ (Object Oriented Programming in C++), 2-е изд./Пер. с англ. – СПб.; М.: «Невский диалект» – «Издательство БИНОМ», 1999 г. – 462 с., ил. 3. Элджер Дж. C++: библиотека программиста (C++: Programmer’s Library). – СПб: ЗАО «Издательство «Питер», 1999. – 320 с.: ил. Supplementary 4. Г. Буч. Объектно-ориентированный анализ и проектирование с примерами приложений на C++ (Object Oriented Analisys and Design with Application Examples in C++ ), 2-е изд./Пер. с англ. – М.: «Издательство «Бином», СПб: «Невский диалект», 1998 г. – 560 с., ил. 5. Гамма Э., Хелм Р., Джонсон Р., Влиссидес Дж. Приемы объектно-ориентированного проектирования. Паттерны проектирования. (Methods of Object Oriented Programming. Programming Patterns) – СПб: Питер, 2001. – 368 с.: ил. (Серия «Библиотека программиста») 6. Керниган Б., Ритчи Д. Язык программирования Си (Programming Language C): Пер. с англ. / Под ред. и с предисл. Вс.С.Штаркмана. – 2-е изд., перераб. и доп. – М.: Финансы и статистика, 1992. – 272 с.: ил. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION BASICS OF COMPUTERS Lecturer: Dobrynin S.V., Professor, PhD (Engineering) Aim of the course is to master theoretical basics of computer means construction and cultivate practical skills of digital circuit and automatons synthesis. Tasks: To study main methods of number representation and conversion which can be used in main calculus systems; To familiarize with basics of presentation of information of different origin and nature in computer system; To familiarize with peculiarities of data presentation in the form which is the most suitable and convenient for processing in computer systems; To consider main logical operations and elements used in computer system construction; To give methods of minimization both completely defined and non-strict logical functions; To master basic notions and definitions connected to theory of digital automaton and methods of their synthesis; To consider principles of structural synthesis of such functional assemblies of combinatorial type as different adders, scramblers, decoders, multiplexers, demultiplexers, comparators, code converters; To consider principles of structural synthesis of such functional assemblies of sequential type as triggers, registers, counters. Following the completion of the course a student must: know: Historical, scientific and technical conditions of computer creation and computer science development; Main numeral systems, choice of numeral system for presentation in computer means and systems; Methods of numbers conversion from one positional numeral system to another; Algorithms of basic arithmetic operations in main positional numeral systems: binary, octal and hexadecimal; Essence and peculiarities of information encoding in computer engineering and main types of encoding; Forms of numeral presentation with fixed and movable point; Algorithms of arithmetical operations in direct, regressive and additional codes; Basics of logical algebra used in analysis and synthesis of digital circuits; Basic methods and algorithms used in the simplification of logical functions in the digital circuits synthesis; Methods of structural synthesis of combinative typed numerical units; Methods of structural synthesis of accumulative (sequential) typed numerical units; Main principles of the most common units construction in the combinatory and sequential typed digital computers. to be able to: Solve the task of reducing integers and non-integrals from one positional numeral system into another; Do main arithmetic operations using direct, regressive and additional codes of binary numbers; Do transformation of Boolean functions using different element bases; Do minimization of Boolean functions with the help of analytical methods and Karnaugh maps (Veitch diagrams); Do synthesis of numeral logical schemes of combinatory type according to the given analytical description; Solve tasks of synthesis of digital automatons on the stages of creation of structural tables and encoding of their inner states; Use program applied package of numeral electronic schemes modeling for analysis and synthesis of digital devices. Subject description. Subject and tasks of the discipline. Origin and development of computers and their peculiarities. Number representation in computer systems and operation with them. Information encoding and main forms of number representation in computer systems. Number encoding in computer systems. Logical operations and logical elements used in creation of circuits. Logical functions and their analytical description. Minimization of logical functions expressions. General characteristics of schemes of combinatory type. Structural synthesis of typical units of combinatory type. General characteristics of schemes of sequential type. Structural synthesis of typical units of sequential type.
Assessment Forms: The assessment of mastering is done via: Current assessment at workshops; Assessment of reports on laboratory works; Tests on basic framework of the course program; Final written assessment. Supportive materials 1. Добринін С. В. Комп'ютерні основи (Basics of Computer): Навчальний посібник. – Х.: “ХНУ", 2008. – 235 с. 2. Добринін С. В. Аналіз можливостей пакету моделювання електронних схем Electronics Workbench: (Electronic Circuits Electronics Workbench Package Design Capacity Analysis) Методичні рекомендації та завдання до лабораторних робіт . – Х.: "ХНУ", 2008. – 32 с. 3. Добринін С. В. Аналіз цифрових логічних елементів (Analysis of numeral logical elements): Методичні рекомендації та завдання до лабораторних робіт. – Х.: "ХНУ", 2008. – 20 с. 4. Добринін С. В. Структурний синтез і аналіз цифрових логічних схем комбінаційного типу (Structural synthesis and analysis of numeral logical schemes of combinatory type): Методичні рекомендації та завдання до лабораторних робіт. – Х.: "ХНУ", 2008. – 16 с. 5. Добринін С. В. Структурний синтез і аналіз цифрових логічних схем послідовнісного типу (Structural synthesis and analysis of numeral logical schemes of sequential type): Методичні рекомендації та завдання до лабораторних робіт. – Х.: "ХНУ", 2008. – 16 с.
Recommended Literature: Basic 1. Добринін С. В. Комп'ютерні основи (Basics of Computer): Навчальний посібник. – Х.: “ХНУ", 2008. – 235 с. 2. Кравчук С. О., Шонін В. О. Основи комп’ютерної техніки (Basics of Computers): К.: "Політехніка", 2005. – 344 с. 3. Бабич М. П., Жуков І. А. Комп’ютерна схемотехніка (Computer Circuit Technique) : Навчальний посібник. – К.: "МК-Прес", 2004. – 412 с. 4. Бойко В. И. и др. Схемотехника электронных систем. Цифровые устройства (Circuit Technique of Electronic Systems. Digital Devices). – СПб.: "БХВ-Петербург", 2004. – 512 с. 5. Самофалов Г. К. и др. Прикладная теория цифровых автоматов (Applied Theory of Digital Automatons): Учебник. – К.: "Вища школа", 1987. – 375 с. Supplementary 1.Жмакин А. П. Архитектура ЭВМ (Computer Architecture). – СПб.: "БХВ-Петербург", 2006. – 320 с. 2.Леонтьев В. П. Новейшая энциклопедия персонального компьютера (The Newest Encyclopedia of Personal Computer) . – М.: "ОЛМА-ПРЕСС", 2004. – 734 с. 3.Брукшир Дж. Гленн. Введение в компьютерные науки. Общий обзор (Introduction to Computer Sciences. General Survey), 6-е издание: Пер. с англ. – М.: Издательский дом "Вильямс", 2001. – 688 с. 4.Малиновский Б. Н. История вычислительной техники в лицах (Histroy of Computer in Persons).– К.: "КИТ", 1995. – 384 с. 5.Самофалов Г.К. и др. Цифровые ЭВМ: Теория и проектирование. (Digital Computers. Theory and Design). – К.: "Вища школа", 1989. – 424 с. 6. Савельев А.Я. Прикладная теория цифровых автоматов (Applied Theory of Digital Automatons): Учебник. – М.: "Высшая школа", 1987. – 272 с. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION ALGORITHMIC LANGUAGES AND PROGRAMMING Lecturer: Tolstoluzka Olena Gennadiivna, PhD (Engineering), senior researcher, Associate Professor of the Department of Theoretical and Applied Systems Engineering. Prior requirements. Study of the discipline is based on the theoretical and practical knowledge obtained by students from the courses “Informational Science”, “Discrete Mathematics”, “Higher Mathematics”. Aim: to give students the information about algorithms, logics of programming and basics notions of structural programming in language C++ (words, grammar and punctuation of programming language, destination and proper use of each function). Tasks: Following the completion of the course a student must: know: Stages of problem solving with the help of computer. Essence of each stage. Basiс structures of algorithm. Main principle of structural design. Methods of algorithm creation. Program structure and stages of its processing. The notions of a compiler, an interpreter. Title files. Program specification. Rules of “fine style” in programming. Memory model. Number presentation in different numeral systems. Binary, hexadecimal systems. Additional code. Conception of a type. Constants, variables, data types. Types’ classification. Machine presentation of integer types. Enumeration. Types’ transformation. Operations, priorities, rules and examples of accomplishment. Main operators: assignment, branching, multiple selection, cycle. Types of cycles and principles of their use. Functions. Description, definition, activation. Formal and factual parameters. Structure of memory given to use (code, data, stack, array). Methods of transmission of parameters. Parameters – meanings. Dynamic arrays. Different ways of organization of multidimensional dynamic arrays. Structures, unions. Use of enumerations, structures and unions for storage of data with variable part. Recursive algorithms and functions. Files. Work with files. Text and binary files. Abstract data types. Stacks. Queues. Trees. Graphs. Means of representation of graphs. Standard algorithms on graphs. Tasks of sort and search. Simple algorithms of sort. Perfected algorithms of sort. Notion of external sort. Algorithms of external sort. Algorithms of search. Linear and binary search. To be able to: Create simple algorithms and programs using keyboard for entering incoming data and basic operators of language C++. To work with encoding table, particularly with different groups of symbols, including directive ones. Create programs where processed data series must be kept in static array. Specify and project functions from the point of view of repeated usage, distinguish incoming parameters, outgoing parameters and local changes of functions. Create programs using dynamic memory management: placement in data array, memory disposal for further usage, address arithmetic and data access with the help of drift from basic address. Use structures to keep information of different types. Use mechanisms of work of recursive functions. Work with lists and trees. Use simple and perfected sorting algorithms. Create programs with sorting algorithms. Subject description. Introduction. From the history of calculations. Stages of problem solving with the help of computer. Essence of each stage. Examples. Basic structures of algorithm. Main principle of structural design. Methods of algorithm creation. Single-step detalization, top-down and down-top projecting. Program structure and stages of its processing. The notions of a compiler, an interpreter. Title files. Program specification. Rules of “fine style” in programming. Memory model. Numeral system. Number presentation in different numeral systems. Binary, hexadecimal systems. Additional code. Conception of a type. Constants, variables, data types. Types’ classification. Machine presentation of integer types. Types’ transformation. Operations, priorities, rules and examples of performation. Work with bitmap flags. Main operators: assignment, branching, multiple selection, cycle. Types of cycles and principles of their use. The notion of an array. Work with static arrays. Functions. Description, definition, activation. Formal and factual parameters. Structure of memory given to use (code, data, stack, array). Methods of transmission of parameters. Parameters – meanings. Global and local variables, principle of localization. Classes of memory. Local static variables. The notion of an index. Address transmission of parameters. Dynamic arrays. Different ways of organization of multidimensional dynamic arrays. Lines. Functions of work with lines. Line index. Functional type. Function as a parameter. Function arrays. Structures, unions. Use of enumerations, structures and unions for storage of data with variable part. Recursive algorithms and functions. Files. Work with files. Text and binary files. List. Singly linked list. Double-linked list. Abstract data types. Review. Stack. Means of realization. Queue. Means of realization. Trees. Trees organization. Binary trees. Ways to bypass trees. Basic functions of work with binary trees. Graphs. Means of representation of graphs. Standard algorithms on graphs. Tasks of sort and search. Survey of standard algorithms. Simple algorithms of sort: sort by choice, sort by inserting, sort by bubbles. Perfected algorithms of sort: Shell sort, pyramid sort, quick sort. The notion of external sort. Algorithms of external sort. Algorithms of search. Linear and binary search. Assessment forms: the subject “Algorithmic languages and programming” is studied in 1st and 2nd semesters and includes lectures, laboratory works, workshops and independent work. Students pass a credit in the 1st semester and examination in the 2nd semester. Recommended Literature: Basic 1. .Павловская, Татьяна Александровна C/C ++. Программирование на языке высокого уровня (C/C++. Programming in the language of the high level): учебник для вузов : / Павловская, Татьяна Александровна . - СПб.: Лидер, 2010 . - 460 с. 2. Павловская Т. А., Щипак Ю.А. С\С++. Структурное программирование (C/C++. Structural programming): Практикум - СПб.: Питер, 2002 . - 240 с. 3. Прата, Стивен Язык программирования C ++. Лекции и упражнения. Platinum Edition (Programming Langugae C++. Lectures and exercises. Platinum Edition): Методическое пособие : перевод с : англ. / Прата, Стивен . - М.; СПб.; К. : ДиаСофтЮП, 2005 . - 1097 с. Supplementary 1. Глушаков, Сергей Владимирович. Язык программирования С++: Учебный курс (Programming Language C++: Educational Course): / Глушаков, Сергей Владимирович, Коваль, Александр Викторович, Смирнов, Сергей Викторович . - Х. : Фолио ; Ростов-н/Д : Феникс, 2001 . - 500 с. 2. Харви Дейтел, Пол Дейтел. Как программировать на С (How to Program in C): пер с англ. – М.: ЗАО «Издательство БИНОМ», 2000. – 1008с. Information resources 1. Computer Class Integrated environment Microsoft Visual Studio 2008. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION ECOLOGY Lecturer: Popov Gennadiy Fedorovych, Associate Professor of the Department of System and Technologies Modeling. Status: Mandatory Year, Semester: 4th year, 7th semester. Number of hours: 54 hours, including 24 hours of lectures, 8 hours of workshops, 4 hours of seminars, 18 hours of independent work. Module 1 – course of lectures, testing knowledge obtained at lectures. Independent work. Examination. Prior requirements. Knowledge of Physics, Biology, Higher Mathematics, Computer Science. Discipline description (content, aims, structure): Radiation ecology is one of the important divisions of general ecology. Radiation ecology studies nature and sources of radioactive emanation, influence of ionizing radiation on a human being and environment, migration of radioactive nuclides in environment, radiation sensitivity of living organisms, results of radioactive pollution of environment, radioactive problems of nuclear energy production, principles of radiation rating, principles of monitoring and dosimetry control, ways of protection from radiation, legislation in the sphere of radiation safety. Radiation is an important natural and man-caused factor in the life of biosphere and is the most critical for human. Fast development of nuclear energy production and wide use of sources of ionizing radiation in different branches of science created the threat of radiation hazard for human and pollution of environment with radiators. In last years the problem of environment pollution by radiators became very urgent. The accidents at nuclear stations and atomic-powered vessels, plants of nuclear reclamation influence local zones sharply but they also influence on global scape, increasing average level of radioactivity in biosphere. Biosphere pollution is also the result or former nuclear weapon tests. It is necessary to mention that many territories in the world having high level of natural radiation. Higher radioactivity background for some places on the Earth is a constant ecological factor, that influences differently on living organisms. The course “Radiation Ecology” is to help in understanding how radiation influences living organisms. Aim: Form students’ idea of influence of ionizing radiation as ecological factor on all structural elements of biosphere. Tasks: to study: Physical nature and laws of radioactive decay; Physical and chemical processes of radiation influence on living tissues; Evaluation of danger of radiation treatment and basics of radiation treatment rating; Ways and means of monitoring and radiation protection; Man-caused and natural sources of radiation. State of environment in places around nuclear stations and other enterprises of complete nuclear atomic cycle and on territories with radioactive pollution. Protection and preventive measures from radiation. Following the completion of the course a student must know: schemes of radioactive transformations and units of radiation measurement; natural and artificial sources of radiation and structure of emanation; basic patterns of radioactive nuclides’ actions in environment and ways they come into plants, animals and human body; radio-biological effects and ecological changes resulted from influence of radiation on environment; character of influence of nuclear objects on the environment while their normal functioning and in case of accidents; main ecological problems of nuclear energy cycle; ways of solving the problem of radioactive waste; norms of radiation safety. The program of the course includes 1 module which consists of 18 topics and the list of recommended literature Module 1. The phenomenon of radioactivity. Nuclear reactions. Ionizing radiation. Sources of ionizing radiation. Interaction of ionizing radiation and substances. Radioactivity of environment. Artificial sources of ionizing radiation. Affecting factors of nuclear weapon. Detectors and systems in radioactive environment monitoring. Nuclear reactor. Atomics. Nuclear power plants. Ecological problems of nuclear power cycle. Atomic-powered vessels. Floating nuclear power plants. Power reactor cycle. Problems of exhaust nuclear fuel. Stop of nuclear power plant exploitation and conservation of it. Radioactive catastrophes. Radiobiological effects. Norms of radiation safety. Dozes of irradiation. Forms of teaching: lectures and independent work Methods of teaching: lectures giving main systematized material of the course, the lectures are given in the form of Power Point presentations on multimedia equipment; students’ answers to the question to each paragraph of the topic, discussion of the most difficult problems of the lecture; watching films about the principle of work of nuclear reactor work, nuclear power plant, radioactive equipment, atomic weapons; individual tasks for independent work. The independent work of students includes work with educational and scientific literature, Internet and results in writing a report. Assessment Forms: current tests, final test examination. Assessment System: Students who completed the syllabus (attended lectures, have outlines, have lecture notes) are allowed to take final examination. Supportive Materials syllabus; Curriculum; Digital outline of lectures; Lectures in the form of Power Point presentations; Video films; List of tasks for independent work; List of literature and informational sources; List of examination questions. Language of Instruction: Russian (as groups include many foreign students who have Russian language as the language of teaching in the contract). Recommended Literature: Basic 1. Коваленко Г.Д. Радиоэкология Украины (Radioecology of Ukraine). Изд. ИНЖЭК. Харьков.2008. 2. Вальтер А.К., Залюбовский И.И. Ядерная физика (Nuclear Physics). Высшая школа. Харьков. 1974. 3. Ю. Одум. Основы экологии (Basics of Ecology). Издательство "Мир", Москва. 1975. 4. Белозерский, Г. Н. Радиационная экология (Radiation Ecology). - М. : Академия, 2008. - 384 с. 5. Безопасность жизнедеятельности. Защита населения и территорий в чрезвычайных ситуациях (Life Safety. Protection of Population and Territories in Case of Extreme Situations): учебное пособие для вузов. М. : Академия, 2008. - 297 c. 6. Прохоров, Б. Б. Социальная экология (Social Ecology): учебник для вузов. М. : Академия, 2007. - 412 с. 7 . Сапожников, Ю. А. Радиоактивность окружающей среды. Теория и практика (Radioactivity of Environment. Theory and Practice): учебное пособие / 2006. - 286 с. 8. Пивоваров, Ю. П. Радиационная экология (Radiation Ecology): учебное пособие для вузов / М. : Академия, 2004. - 240 с. 9. Ярмоненко С.П. “Радиобиология человека и животных” (Radiobiology of Human and Animals), ВШ, Москва. 1997г. 10. Лисовский Л.А. “Радиационная экология и радиационная безопасность” (Radiation Ecology and Radiation Safety), Мн. 1997г.
11. Бабаев Н.С. В.Ф. Демин, Л.А. В.А. Легасов, Ю.В. Сивинцев. Ядерная энергетика, человек и окружающая среда (Nuclear Energy and Environment). М: «Энергоатомиздат», 1984. Supplementary 1. Кудряшов Ю.Б. Радиационная биофизика (Radiation Biophysics). М.: Физматлит, 2004. 2. Н. Г. Гусев, Е. Е. Ковалев, В. П. Машкович, А. П.Суворов. Защита от ионизирующих излучений (Protection from Ionizing Radiation). М.: "Энергоатомиздат", 1990. 3. Жабо В.В. Охрана окружающей среды на ТЭС и АЭС (Environment Protection at Thermoelectric and Nuclear Power Stations). - М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1992. 4. Изотопы: свойства, получение, применение (Isotopes: Properties, Production, Usage). В 2-х томах. ФИЗМАТЛИТ. Москва. 2005. 5. Ковальський О.В. Лазар А.П., Людвинський Ю.С. та ін. Радіаційна медицина (Radiation Medicine). Київ. Здоров’я.-1993.. Information Sources 1. http://nuclearenergy.ru 2. http//ruatom.ru 3. http// nuclphys.sinp.msu.ru 4. http//atomas.ru 5. http//www.cpce.ru/tools/rtad_iocham_main.shtml
6. http://ru.wikipedia.org/ DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION DIRECTION “SAFETY OF INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS” Graduate Level
Patents and Intellectual Property Rights
Lecturer: Head of the Laboratory of System Engineering, Junior Member of the Department Artyukh О.А. Aim: To make students acquainted with basic notions of patent system, main objects and subjects of intellectual and industrial property, achieve skills of defining the technology level of on the basis of patent and technical information, achieve skills of patent work and certification. Tasks: Following the completion of the course a student must: know: classification of person’s rights which are part of industrial property, normative and legislative basis in the sphere of industrial property, main notion of objects and subjects of industrial property as parts of patent system, form of search of scientific and technical and patent information, stages of patent examining, order and methods of writing application for a patent, documents for objects of industrial property, system of international classification of objects of industrial property. Be able to: use normative and legislative basis in the sphere of industrial property and patent law, do patent search and write a report on patent research, write license agreements about the conveyance of industrial property and application for a title of protection. The Syllabus Module 1. Patents and intellectual property rights. Basic notions. Legislative basis of protection of copyright and patents owners’ rights. Topic 1. Introduction. Structure and content of the discipline “Patents and Intellectual property rights”. The role and place of invention in the development of society. Basic notions. Topic 2. Legal regulation of relations in the sphere of science and technique. Subjects and objects of patent legal relations. Basic principles of patent law. Legal safeguard of inventions, discoveries, utility models, industrial models, trade marks, software and data bases. The notion of priority. Patent and copyright law. International obligations of Ukraine. Topic 3. Invention as an object of legal safeguard. Objects of invention: method, construction. Features of invention. Substance, culture, use for a new destination. Reveling an invention enough to its reconstruction. Topic 4. The notion of industrial property. Characteristics of objects of industrial property. History of development of industrial property in Ukraine. The notion and criteria of objects of industrial property registrability: novelty, industrial appropriateness, level of invention, priority. Topic 5. Objects of patent legal relations (objects of protection): inventions, utility models, industrial models, trade marks and marks of service, firm names, names of product origin, protection from unfair competition, the notion of know-how. Topic 6. Objects of industrial property law - titles of protection: patent, author's certificate, industrial model patent, trade mark certificate. General regulations. Matter of patent rights. Obligations and rights of author and patent owner. Rights and obligations of third persons. Determination of patent. Topic 7. Contracts and license in the sphere of industrial property. Basic notions: license, licensor, licensee. Kinds of licenses and license contracts: patent and non-patent license, license to sell, personal license, enterprise license, license for production, patent selling. Exclusive and personal license, non-exclusive (simple) license and compulsory license. License value and types of payment for license. Module 2. The form of patent search and obtaining a title of protection. Topic 1. Procedure of issuing titles of protection. Application procedure to patent authority. Rules of writing application for invention, utility models, industrial models, trade marks and service marks, names of product origin, software and data bases. Topic 2. Patent information. Reference and search tools of patent information. Procedure of patent search and examining. Writing a report on patent examining. Methods of teaching The material is mostly given at lectures. The great attention at lectures is paid to all latest changes in legislation concerning protection of intellectual and industrial property. Multimedia equipment ensures the visuality of teaching. Practical skills promote extending of knowledge obtained at lectures and achieving practical skills. Assessment Forms Assessment is realized at workshops via tests. Final assessment is realized via final written test. Recommended Literature: Basic 1. Кузнєцов Ю.М. Патентознавство та авторське право (Patents and Copyright). – Кондор, 2004, - 428с. 2. Дахно І.І. Право інтелектуальної власності (Intellectual Property Right). – Центр навчальної літератури, 2006, - 278с. 3. Патентные исследованя: Часть 1. Работа с патентной информацией (Patent Research. Part 1. Work with Patent Information) (методическое пособие)/ Под ред. Шаншурова Г.А. – Новосибирск: НГТУ, 2003. 4. Шаншуров Г.А. Патентные исследованя: Часть 2. Правила проведения патентных исследований (Patent Research. Part 2. Rules of Patent Research) (методическое пособие). - Новосибирск: НГТУ, 2003. DISCIPLINE ANNOTATION METHODOLOGY AND ORGANIZATION OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH Lecturer: Lazuryk Valentin Tymofiyovych, the Head of the Department of System and Technology Modeling, Full Professor, Doctor of Science (Physics and Mathematics) Status: Mandatory Year, semester: 5th year, 9th semester Number of hours: 54 academic hours including 10 hour of lectures, 6 hours of workshops, 2 hours of seminars, 36 hours of independent work. Final control – credit. Prior requirements: knowledge of Mathematics, Programming in the amount of the first 4 courses of the University “Discrete Mathematics”, “Programming and Algorithmic Languages”, “Object-Oriented Programming” Discipline description (contents, aims, structure): At the present level the classification of scientific research and classification of experimental research are discussed. It is defined how systems are explored. The notion of “model”, requirement for models, model construction are accepted. The attention is paid to random factors, check of agreement between theoretical and empirical distribution on criteria. Structure of imitation models, construction of imitation model, creation of flow block and check of its adequacy are examined. The choice of approximate mathematical model and its grounding are discussed. It is explained how regressive analysis is used in modeling, how to check adequacy of regressive model. Also the attention is paid to planning of optimization experiments. Aim: to provide students with knowledge adequate to modern requirements concerning independent solving of theoretical and practical tasks of information and technological processes, form students’ knowledge and skills concerning conducting scientific research, scientific analysis of the results of experiments and observations, scientific generalization of informational and technical processes. The curriculum consists of 8 topics, plan of workshops and seminars and list of recommended literature. Forms of Teaching: lectures, workshops, independent work. Methods of Teaching: elements of problematic lectures, individual tasks for independent work, modeling of problem situations while doing practical and independent work, consulting the lecture. Assessment Forms: final assessment during the credit. Assessment System: Students who completed the syllabus (attended lectures, did practical tasks and work independently) are allowed to take final assessment. Supportive Materials Syllabus Schedule of the subject Textbooks Manuals of the department Electronic outline of lectures Sets of individual tasks for independent work List of questions and tasks for the credit. Language of Instruction: Russian (as groups include many foreign students who has Russian language of instruction defined by the contract). Recommended Literature: Basic 1. А.Я. Баскаков, Н.В. Туленков. Методология научного исследования (Methodology of Scientific Research). – К.: Телесик, 2004. – 215 с. 2. Крушельницька О.В. Методологія та організація наукових досліджень (Methodology and Organisation od Scietific Research). – К.: Кондор, 2003. – 192 с. 3. П’ятницька-Позднякова І.С. Основи наукових досліджень у вищий школі (Basics of Scientific Research in Higher School). – К.: Вища школа, 2003. – 116 с. Supplementary 1. Основы научных исследований (Basics of Scientific Research) / Под ред. В.И. Крутова, В.В, Попова. – Москва: Высшая школа, 1989. – 224 с. 2. Р. Шеннон. Имитационное моделирование систем – искусство и наука (Imitational Sys- tem Modelling – Art and Science). – Москва: мир, 1978. – 418 с. 3. Афифи А., Эйзен С. Статистический анализ: подход с использованием ЭВМ (Statistical Analysis: Computer Approach). - Москва: Мир, 1982. - 488 с. 4. Вознесенский В.А. Статистические методы планирования эксперимента в технико- экономических исследованиях (Statistical Methods of Planning Experiment in Technical and Economical Research). - Москва: Финансы и статистика, 1981. - 263 с. 5. Клир Дж. Системология. Автоматизация решения системных задач (System Studies. Automatization of System Tasks Solving). - Москва: Радио и связь, 1990. - 544 с. 6. Митропольский А.К. Техника статистических вычислений (Technique of Statistic Calcu- lation). - Москва: Наука, 1971. - 576 с. 7. Гальчук В.Я., Соловьев А.П. Техника научного эксперимента (Technique of Sientific Experiment). – Ленинград: Судостроение, 1982. 8. Джонсон Н., Лион Ф. Статистика и планирование эксперимента в технике и науке: Методы планирования эксперимента (Statistics and Planning of Experiment in Technolo- gy and Science. Methods of Experiment Planning) . – Москва: Мир, 1981.