Name: ______1.4.6 Energy Flow Worksheet What is an ecosystem? An ecosystem is a ______with ______and their ______within ______, e.g. woodland, etc.
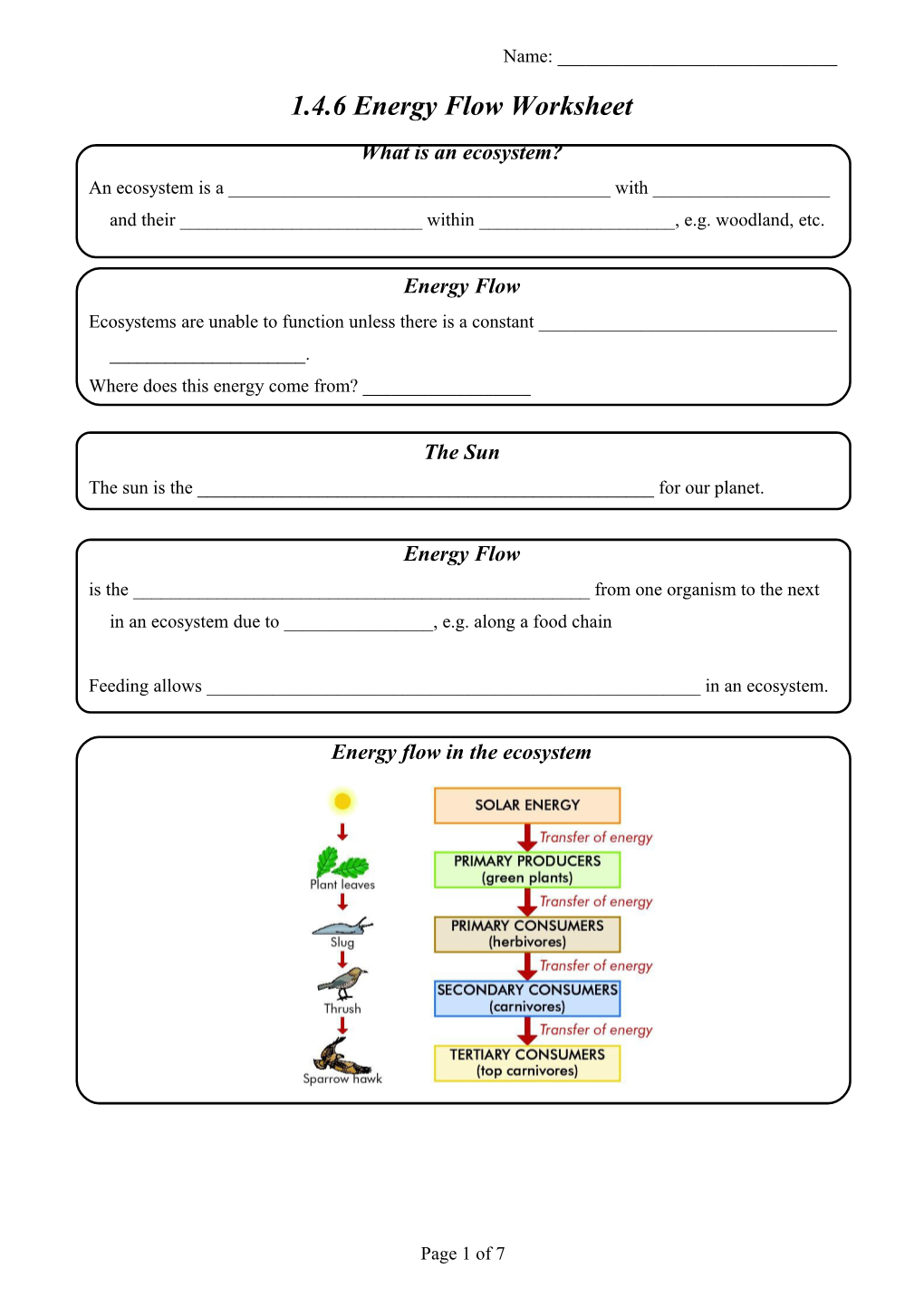
Energy Flow Ecosystems are unable to function unless there is a constant ______. Where does this energy come from? ______
The Sun The sun is the ______for our planet.
Energy Flow is the ______from one organism to the next in an ecosystem due to ______, e.g. along a food chain
Feeding allows ______in an ecosystem.
Energy flow in the ecosystem
Page 1 of 7 Name: ______
Food Chain Is a flow diagram that begins with a ______and shows how ______is passed through a series of ______. Each organism feeds on the one before it.
A food chain ends when there is ______.
An example of a food chain: ______ ______ ______
A Grazing food chain is one where the ______e.g.
______ grasshoppers frogs hawks
______ aphids ladybirds thrushes
______ winkles crabs herring gulls
______ zooplankton copepod herring
Grazing Food Chains
Page 2 of 7 Name: ______
A Detritus food chain is one where the chain begins with ______e.g.
______ edible crab seagull
______ earthworms blackbirds hawks
Detritus Food Chain
Food Web This is a chart showing all the ______.
Constructed by showing the links between all the interconnecting food chains in the habitat.
Food Web the interconnected food chains in an ecosystem e.g.
Page 3 of 7 Name: ______
A woodland food web
Construct two food chains (4 ‘links’) from the above food web
Another food web
What is the longest food chain you can construct from this food web?
Page 4 of 7 Name: ______
Producers Producers are organisms capable of making ______, e.g. green plants.
Primary producers are the ______
Consumers Consumers are organisms that ______. They cannot ______. There are three types:
• Primary consumers – feed on ______
• Secondary consumers – feed on ______
• Tertiary consumers – feed on ______
Page 5 of 7 Name: ______
Woodland food chain Honeysuckle aphids ladybirds thrushes
Primary Secondary Tertiary Producer consumer consumer consumer
Trophic Level This refers to the ______in a food chain. ______are at the 1st trophic level (T1) and ______occupy the 2nd trophic level (T2). ______that eat herbivores are at the 3rd trophic level (T3). The 4th trophic level (T4) is often occupied by the ______.
Trophic levels
Pyramid of Numbers A diagram that represents the ______at each ______in ______. Bottom layer is the ______and represents a very large number of ______The next layer ______and represents a smaller number of ______The next layer – the number of ______The uppermost layer where there may be only one ______
Page 6 of 7 Name: ______
Pyramid of Numbers
To construct a pyramid of numbers 1. Count the ______and place them at the ______2. Count each ______and include them according to their status (______or ______consumer) in the pyramid 3. The ______should include tertiary or top carnivores 4. Draw the pyramid so that the ______of each level ______to the ______
Need to know Name the sun as the primary source of energy. Name feeding as the pathway of energy flow. Present a grazing food chain. Present a food web. Construct a pyramid of numbers and explain its use.
END
Page 7 of 7