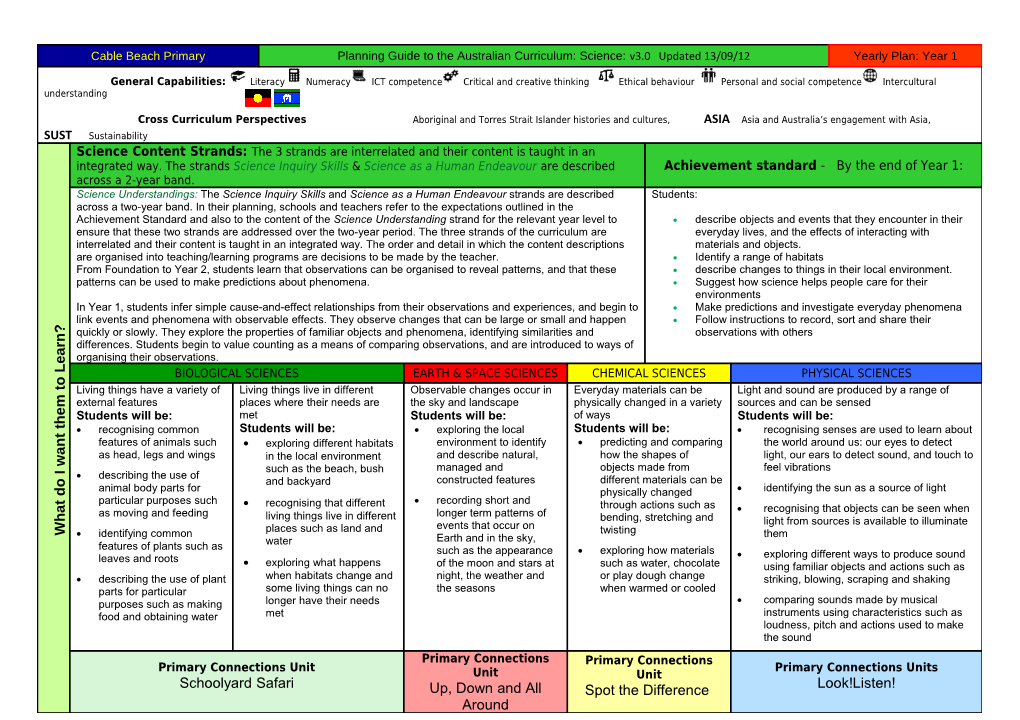
Cable Beach Primary Planning Guide to the Australian Curriculum: Science: v3.0 Updated 13/09/12 Yearly Plan: Year 1
General Capabilities: Literacy Numeracy ICT competence Critical and creative thinking Ethical behaviour Personal and social competence Intercultural understanding
Cross Curriculum Perspectives Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures, ASIA Asia and Australia’s engagement with Asia, SUST Sustainability Science Content Strands: The 3 strands are interrelated and their content is taught in an integrated way. The strands Science Inquiry Skills & Science as a Human Endeavour are described Achievement standard - By the end of Year 1: across a 2-year band. Science Understandings: The Science Inquiry Skills and Science as a Human Endeavour strands are described Students: across a two-year band. In their planning, schools and teachers refer to the expectations outlined in the Achievement Standard and also to the content of the Science Understanding strand for the relevant year level to describe objects and events that they encounter in their ensure that these two strands are addressed over the two-year period. The three strands of the curriculum are everyday lives, and the effects of interacting with interrelated and their content is taught in an integrated way. The order and detail in which the content descriptions materials and objects. are organised into teaching/learning programs are decisions to be made by the teacher. Identify a range of habitats From Foundation to Year 2, students learn that observations can be organised to reveal patterns, and that these describe changes to things in their local environment. patterns can be used to make predictions about phenomena. Suggest how science helps people care for their environments In Year 1, students infer simple cause-and-effect relationships from their observations and experiences, and begin to Make predictions and investigate everyday phenomena
link events and phenomena with observable effects. They observe changes that can be large or small and happen Follow instructions to record, sort and share their
? quickly or slowly. They explore the properties of familiar objects and phenomena, identifying similarities and observations with others n
r differences. Students begin to value counting as a means of comparing observations, and are introduced to ways of a organising their observations. e L
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES EARTH & SPACE SCIENCES CHEMICAL SCIENCES PHYSICAL SCIENCES o t
Living things have a variety of Living things live in different Observable changes occur in Everyday materials can be Light and sound are produced by a range of
m external features places where their needs are the sky and landscape physically changed in a variety sources and can be sensed
e Students will be: met Students will be: of ways Students will be: h t
recognising common Students will be: exploring the local Students will be: recognising senses are used to learn about t
n features of animals such exploring different habitats environment to identify predicting and comparing the world around us: our eyes to detect a as head, legs and wings in the local environment and describe natural, how the shapes of light, our ears to detect sound, and touch to w
managed and objects made from feel vibrations
I such as the beach, bush
describing the use of and backyard constructed features different materials can be o animal body parts for identifying the sun as a source of light
d physically changed
t particular purposes such recognising that different recording short and through actions such as
a recognising that objects can be seen when as moving and feeding living things live in different longer term patterns of h bending, stretching and light from sources is available to illuminate places such as land and events that occur on W identifying common twisting them water Earth and in the sky, features of plants such as such as the appearance exploring how materials leaves and roots exploring different ways to produce sound exploring what happens of the moon and stars at such as water, chocolate using familiar objects and actions such as describing the use of plant when habitats change and night, the weather and or play dough change striking, blowing, scraping and shaking parts for particular some living things can no the seasons when warmed or cooled purposes such as making longer have their needs comparing sounds made by musical food and obtaining water met instruments using characteristics such as loudness, pitch and actions used to make the sound Primary Connections Primary Connections Primary Connections Unit Primary Connections Units Unit Unit Schoolyard Safari Up, Down and All Spot the Difference Look!Listen! Around What do I want them to learn? (Science Understanding) (Review for balance and coverage of content descriptors)
YEAR 1 SCIENCE SCIENCE UNDERSTANDING
Content Description Elaborations T1 T2 T3 T4 Biological sciences recognising common features of animals such as head, legs and wings describing the use of animal body parts for particular purposes such as moving and feeding Living things have a variety of external features identifying common features of plants such as leaves and roots describing the use of plant parts for particular purposes such as making food and obtaining water exploring different habitats in the local environment such as the beach, bush and backyard Living things live in different places where their recognising that different living things live in different places such as land and water needs are met exploring what happens when habitats change and some living things can no longer have their needs met Chemical sciences predicting and comparing how the shapes of objects made from different materials can be physically Everyday materials can be physically changed in a changed through actions such as bending, stretching and twisting variety of ways exploring how materials such as water, chocolate or play dough change when warmed or cooled Earth and space sciences exploring the local environment to identify and describe natural, managed and constructed features Observable changes occur in the sky and landscape recording short and longer term patterns of events that occur on Earth and in the sky, such as the appearance of the moon and stars at night, the weather and the seasons Physical sciences recognising senses are used to learn about the world around us: our eyes to detect light, our ears to detect sound, and touch to feel vibrations identifying the sun as a source of light Light and sound are produced by a range of recognising that objects can be seen when light from sources is available to illuminate them sources and can be sensed exploring different ways to produce sound using familiar objects and actions such as striking, blowing, scraping and shaking comparing sounds made by musical instruments using characteristics such as loudness, pitch and actions used to make the sound What do I want them to learn? (Science as a Human Endeavour) (Review for balance and coverage of content descriptors)
YEAR 1 SCIENCE SCIENCE AS A HUMAN ENDEAVOUR
Earth/ Biology Chemistry Physics Content Description Elaborations Space
Nature and development of science
posing questions about events and features of the local environment that are of interest and affect students’ lives Science involves asking questions about, and describing changes in, objects and events recognising that descriptions of what we observe are used by people to help identify change discussing why some plants only grow in certain areas
Use and influence of science
considering how science is used in activities such as cooking, fishing, transport, sport, medicine and caring for plants and animals considering that technologies used by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people require an People use science in their daily lives, including understanding of how materials can be used to make tools and weapons, musical instruments, when caring for their environment and living things clothing, cosmetics and artworks exploring how musical instruments can be used to produce different sounds comparing how different light sources are used in daily life identifying ways that science knowledge is used in the care of the local environment such as animal habitats, and suggesting changes to parks and gardens to better meet the needs of native animals What do I want them to learn? (Science Inquiry Skills) (Review for balance and coverage of content descriptors) YEAR 1 SCIENCE SCIENCE INQUIRY SKILLS
Earth/ Biology Chemistry Physics Content Description Elaborations Space Questioning and predicting using the senses to explore the local environment to pose interesting questions, make inferences Respond to and pose questions, and make and predictions predictions about familiar objects and events thinking about “What will happen if...?” type questions about everyday objects and events
Planning and conducting manipulating objects and materials and making observations of the results Participate in different types of guided investigations to explore and answer questions, researching with the use of simple information sources such as manipulating materials, testing ideas, and sorting objects and events based on easily observable characteristics accessing information sources
Use informal measurements in the collection and using units that are familiar to students from home and school, such as cups (cooking), hand spans recording of observations, with the assistance of (length) and walking paces (distance) digital technologies as appropriate Processing and analysing data and information using simple column graphs (bar graphs) with guidance from the teacher to record gathered information Use a range of methods to sort information, including drawings and provided tables using matching activities, including identifying similar things, odd-one-out and opposites
Through discussion, compare observations with comparing and discussing, with guidance, whether observations were expected predictions Evaluating Compare observations with those of others discussing observations with other students to see similarities and differences in results
Communicating Represent and communicate observations and ideas in a variety of ways such as oral and written discussing with others what was discovered from an investigation language, drawing and role play presenting ideas to other students, both one-to-one and in small groups