Intermolecular Forces – Supplement on Crystalline and Amorphous solids
Pre-class Assignment: Read the following definitions and answer the questions below.
Crystalline solid: A solid in which particles are arranged in lattices, regular arrangements of row and columns (not always rectangular), like a stack of billiard balls. Crystalline solids have definite and specific melting points. Examples of crystalline solids include: snowflakes, dry ice, table salt, sugar, and quartz.
Amorphous solid: A solid in which particles are arranged in randomly, like a pile of spaghetti (not a lattice structure). Amorphous solids soften then liquefy over a wide temperature range. Examples of amorphous solids include: butter, road tar, and glass.
1 - How would you classify candle wax? Why? ______
______
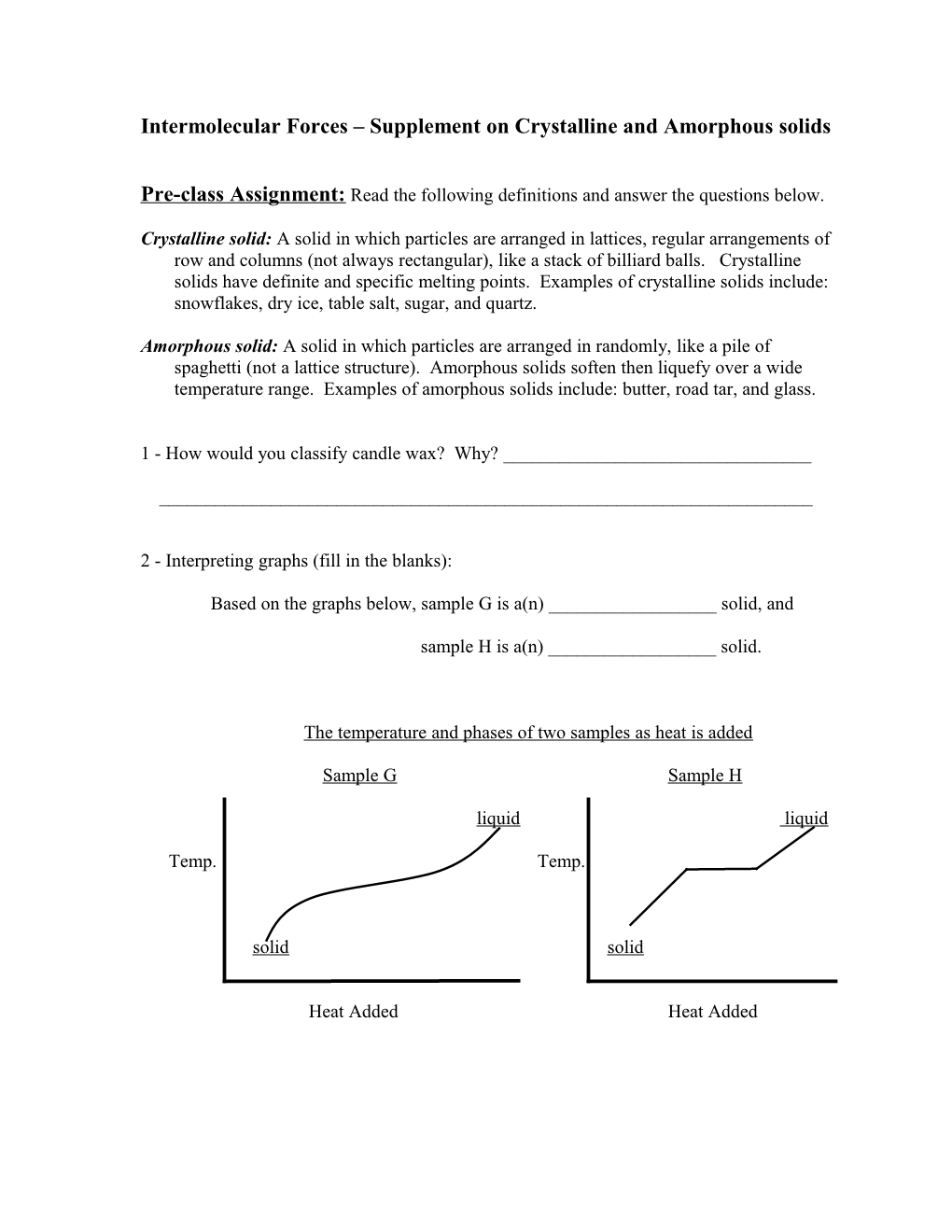
2 - Interpreting graphs (fill in the blanks):
Based on the graphs below, sample G is a(n) ______solid, and
sample H is a(n) ______solid.
The temperature and phases of two samples as heat is added
Sample G Sample H
liquid liquid
Temp. Temp.
solid solid
Heat Added Heat Added