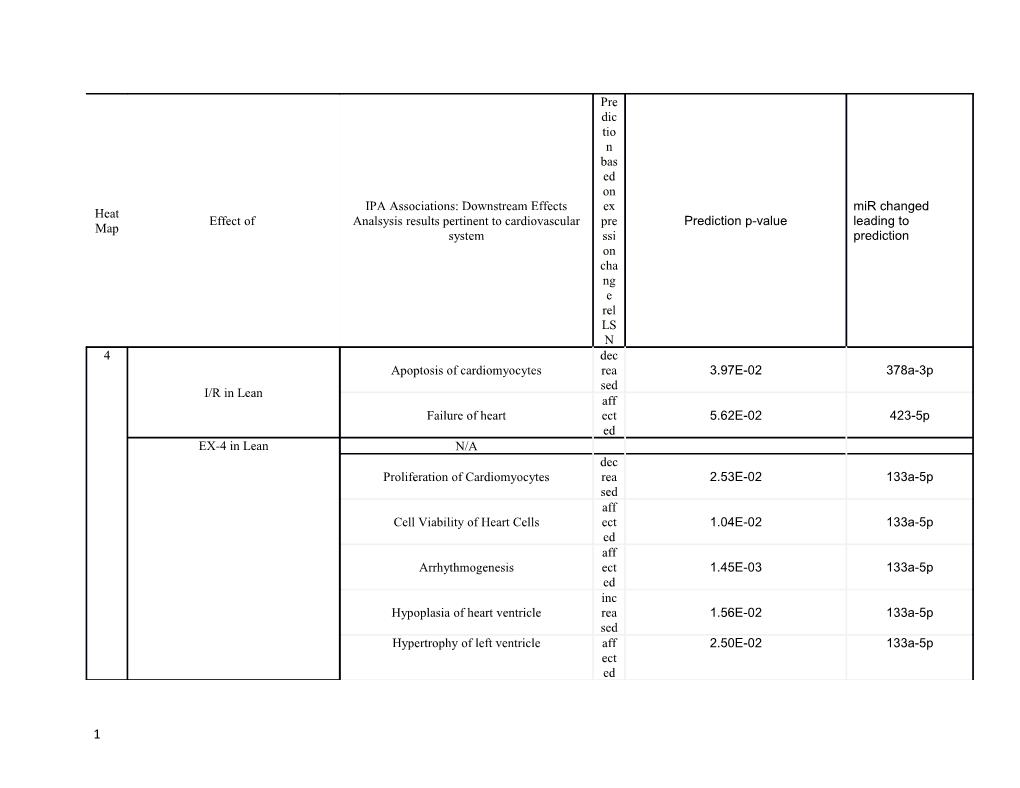
Pre dic tio n bas ed on IPA Associations: Downstream Effects ex miR changed Heat Effect of Analsysis results pertinent to cardiovascular pre Prediction p-value leading to Map system ssi prediction on cha ng e rel LS N 4 dec Apoptosis of cardiomyocytes rea 3.97E-02 378a-3p sed I/R in Lean aff Failure of heart ect 5.62E-02 423-5p ed EX-4 in Lean N/A dec Proliferation of Cardiomyocytes rea 2.53E-02 133a-5p sed aff Cell Viability of Heart Cells ect 1.04E-02 133a-5p ed aff Arrhythmogenesis ect 1.45E-03 133a-5p ed inc Hypoplasia of heart ventricle rea 1.56E-02 133a-5p sed Hypertrophy of left ventricle aff 2.50E-02 133a-5p ect ed
1 aff Acute myocardial infarction ect 2.93E-02 133a-5p ed aff EX-4 and I/R in Lean Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus ect 4.77E-02 129a ed 5 Obesity aff ect apoptosis of heart cells ed 4.06E-02 497 De cre ase d, inc rea Decreased 497; cell viability sed 4.06E-02 increased 30c aff ect diabetes mellitus ed 2.86E-02 497, 30c Inc rea sed ; aff ect Increased 497; dilated cardiomyopathy ed 6.93E-04 affected 30c inc rea dilation of heart sed 5.17E-03 497 inc rea disarray of muscle cells sed 1.15E-03 497 Inc rea disorganization of cardiomyocytes sed 3.84E-04 497 dec rea DNA damage sed 4.42E-02 497 failure of heart inc 5.67E-02 497 rea
2 sed aff ect fibrosis of heart ed 5.76E-04 497, 30c aff ect hypertrophic cardiomyopathy ed 2.08E-02 497 aff ect hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes ed 2.81E-02 497 inc rea proliferation of cardiomyocytes sed 1.68E-02 497 aff ect size of cardiomyocytes ed 1.15E-02 497 aff ect stenosis of aorta ed 1.17E-02 30c dec transmembrane potential of mitochondria rea 4.81E-02 497 sed aff diabetes mellitus ect 3.42E-03 129a, 130b, 378a ed aff 30b-3p, 130b, 30e- inflammation of organ ect 5.30E-03 3p ed aff non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus ect 5.58E-03 129a, 130b ed aff polymyositis ect 8.85E-03 30e-3p ed inc formation of autophagosomes rea 1.31E-02 130b sed size of infarct dec 4.66E-02 130b rea
3 sed dec apoptosis of cardiomyocytes rea 4.92E-02 378a sed I/R and Obesity inc Differentiation of muscle cell lines rea 8.73E-03 100 sed aff ect Affected 26a, 140*, ed, Fibrosis 1.41E-04 17-3p; Decreased dec 199a rea sed dec rea sed Decreased 26a, Hypertrophy , 1.82E-03 199a; Affected 214 aff ect ed aff 24, 143-3p, 152, Diabetes mellitus ect 2.34E-03 17-3p ed aff Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus ect 1.87E-02 24, 152 ed dec Vasoconstriction of aorta rea 3.05E-03 199a sed dec Enlargement of heart rea 3.49E-03 199a sed aff Nonischemic cardiomyopathy ect 5.58E-03 140*, 214 ed dec Interstitial fibrosis of heart rea 1.17E-02 199a sed Cytokinesis of ventricular myocytes dec 1.22E-02 152
4 rea sed aff ect ed, Affected 214; Hypertrophy of heart 1.31E-02 dec Decreased 199a rea sed aff Stenosis of aorta ect 2.59E-02 140* ed aff Ischemic cardiomyopathy ect 2.76E-02 140* ed Decreased 26a, 24, dec 143-3p; Affected Cell death rea 3.42E-02 214, Increased 17- sed 3p aff Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy ect 3.86E-02 214 ed
inc Ex-4 and Obesity Disruption of focal adhesions rea 5.82E-04 491 sed
EX-4, I/R and Obesity inc Quantity of ventricular myocytes rea 2.91E-04 206 sed aff Arrhythmogenesis ect 4.85E-04 206 ed aff Ischemia of heart ect 4.46E-03 206 ed Stenosis of aorta aff 5.81E-03 206 ect
5 ed dec Proliferation of muscle cell lines rea 6.29E-03 192 sed aff Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy ect 8.71E-03 206 ed aff Acute myocardial infarction ect 9.87E-03 206 ed aff Hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes ect 1.39E-02 206 ed aff Dilated Cardiomyopathy ect 2.02E-02 206 ed dec Arrhythmia rea 2.17E-02 206 sed aff Coronary artery disease ect 3.20E-02 206 ed aff Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus ect 4.77E-02 206 ed N/A 106a, 126, 51-3p, aff 425-5p, 365-3p, Inflammation of organ ect 1.01E-08 221, 181d-5p, 140, ed 15a let-7i, 324-5p inc G1/S phase transition of fibroblast cell lines rea 2.27E-06 106a, 15a, let-7i sed aff Affected 106a, Dilated cardiomyopathy ect 2.20E-05 199a-3p, let-7i; ed Decreased 15a Fibrosis aff 1.89E-04 106a, 126, 140, ect 15a, let-7i
6 ed aff 126, 221, 15a, let- Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus ect 6.22E-04 7i ed inc DNA damage rea 7.88E-04 106a, 15a, let-7i sed aff 365-3p, 28-3p, Dystrophy of muscle ect 1.10E-03 199a-3p ed aff Ischemic cardiomyopathy ect 1.25E-03 199a-3p, let-7i ed dec Disorganization of cardiomyocytes rea 1.65E-03 15a sed dec Proliferation of cardiomyocytes rea 2.35E-03 199a-3p, 15a sed dec Repression of mRNA rea 4.11E-03 let-7i sed aff Arrest in cell cycle progression ect 4.37E-03 106a, 199a-3p, 15a Disarray of muscle cells ed dec re-entry into cell cycle progression of rea 6.58E-03 199a-3p ventricular myocytes sed dec Regeneration of heart rea 8.21E-03 199a-3p sed dec Dilation of heart rea 2.20E-02 15a sed aff Coronary artery disease ect 3.01E-02 126, 221 ed Hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes aff 1.12E-01 15a ect
7 ed aff Fibrosis of heart ect 1.56E-01 15a ed aff Apoptosis of heart cells ect 1.63E-01 15a ed dec Failure of heart rea 2.18E-01 15a sed aff Polymyositis ect 5.23E-03 30e-3p ed aff Inflammation of Organ ect 1.97E-02 30b-3p, 30e-3p ed Supplemental Table 4. IPA predictions of molecular and cellular functions associated with miR changes. The P-values are generated by IPA and are representative of the likelihood that the association between a set of genes in the group and a related function is due to random association. The smaller the p-value, the less likely that the association is random. The p-value of overlap is calculated by the Fisher’s Exact Test.
8