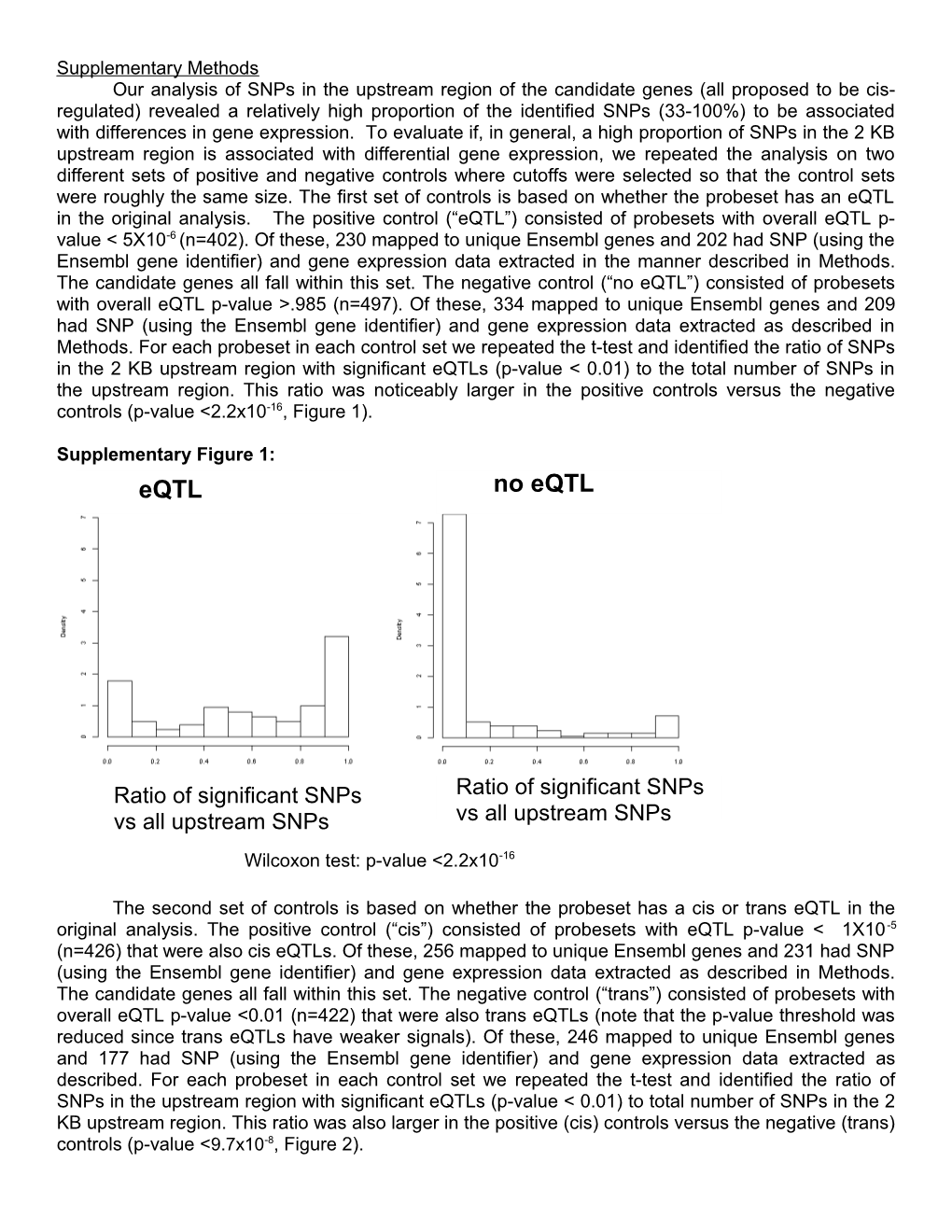
Supplementary Methods Our analysis of SNPs in the upstream region of the candidate genes (all proposed to be cis- regulated) revealed a relatively high proportion of the identified SNPs (33-100%) to be associated with differences in gene expression. To evaluate if, in general, a high proportion of SNPs in the 2 KB upstream region is associated with differential gene expression, we repeated the analysis on two different sets of positive and negative controls where cutoffs were selected so that the control sets were roughly the same size. The first set of controls is based on whether the probeset has an eQTL in the original analysis. The positive control (“eQTL”) consisted of probesets with overall eQTL p- value < 5X10-6 (n=402). Of these, 230 mapped to unique Ensembl genes and 202 had SNP (using the Ensembl gene identifier) and gene expression data extracted in the manner described in Methods. The candidate genes all fall within this set. The negative control (“no eQTL”) consisted of probesets with overall eQTL p-value >.985 (n=497). Of these, 334 mapped to unique Ensembl genes and 209 had SNP (using the Ensembl gene identifier) and gene expression data extracted as described in Methods. For each probeset in each control set we repeated the t-test and identified the ratio of SNPs in the 2 KB upstream region with significant eQTLs (p-value < 0.01) to the total number of SNPs in the upstream region. This ratio was noticeably larger in the positive controls versus the negative controls (p-value <2.2x10-16, Figure 1).
Supplementary Figure 1: eQTL no eQTL
Ratio of significant SNPs Ratio of significant SNPs vs all upstream SNPs vs all upstream SNPs Wilcoxon test: p-value <2.2x10-16
The second set of controls is based on whether the probeset has a cis or trans eQTL in the original analysis. The positive control (“cis”) consisted of probesets with eQTL p-value < 1X10 -5 (n=426) that were also cis eQTLs. Of these, 256 mapped to unique Ensembl genes and 231 had SNP (using the Ensembl gene identifier) and gene expression data extracted as described in Methods. The candidate genes all fall within this set. The negative control (“trans”) consisted of probesets with overall eQTL p-value <0.01 (n=422) that were also trans eQTLs (note that the p-value threshold was reduced since trans eQTLs have weaker signals). Of these, 246 mapped to unique Ensembl genes and 177 had SNP (using the Ensembl gene identifier) and gene expression data extracted as described. For each probeset in each control set we repeated the t-test and identified the ratio of SNPs in the upstream region with significant eQTLs (p-value < 0.01) to total number of SNPs in the 2 KB upstream region. This ratio was also larger in the positive (cis) controls versus the negative (trans) controls (p-value <9.7x10-8, Figure 2). Supplementary Figure 2: cis trans
Ratio of significant SNPs Ratio of significant SNPs vs all upstream SNPs vs all upstream SNPs
Wilcoxon test: p-value <9.7x10-8 Supplementary Table 1. Total SNPs contained within 2 KB upstream region of candidate genes and SNPs associated with differences in expression ("Significant SNPs").
Percent Significant Significant Probe id Gene Symbol Gene Name Total SNPs SNPs SNPs 1417432_a_at 1110032A03Rik RIKEN cDNA 12 12 100 1110032A03 gene 1417432_a_at Gnb1 Guanine 3 3 100 nucleotide 1454696_at Gnb1 binding protein, 3 3 100 beta 1 1417063_at C1qb Complement 30 11 37 component 1, q subcomponent, beta polypeptide 1449401_at C1qc Complement 19 7 37 component 1, q subcomponent, C chain 1434008_at Scn4b Sodium channel, 3 1 33 type IV, beta 1438409_at Cep 63 Centrosomal 13 13 100 protein 63 1430317_at Ube2j2 Ubiquitin- 20 20 100 conjugating enzyme E2, J2 homolog (yeast) 1456111_at D930028F11 Rik RIKEN cDNA 16 15 94 D930028F11 gene
SNPs were extracted from the 2 kB upstream regions of the genes as described in Methods. Expression levels were analyzed to determine if they differed depending on the allele present. (p<0.01, t-test = "significant SNP").