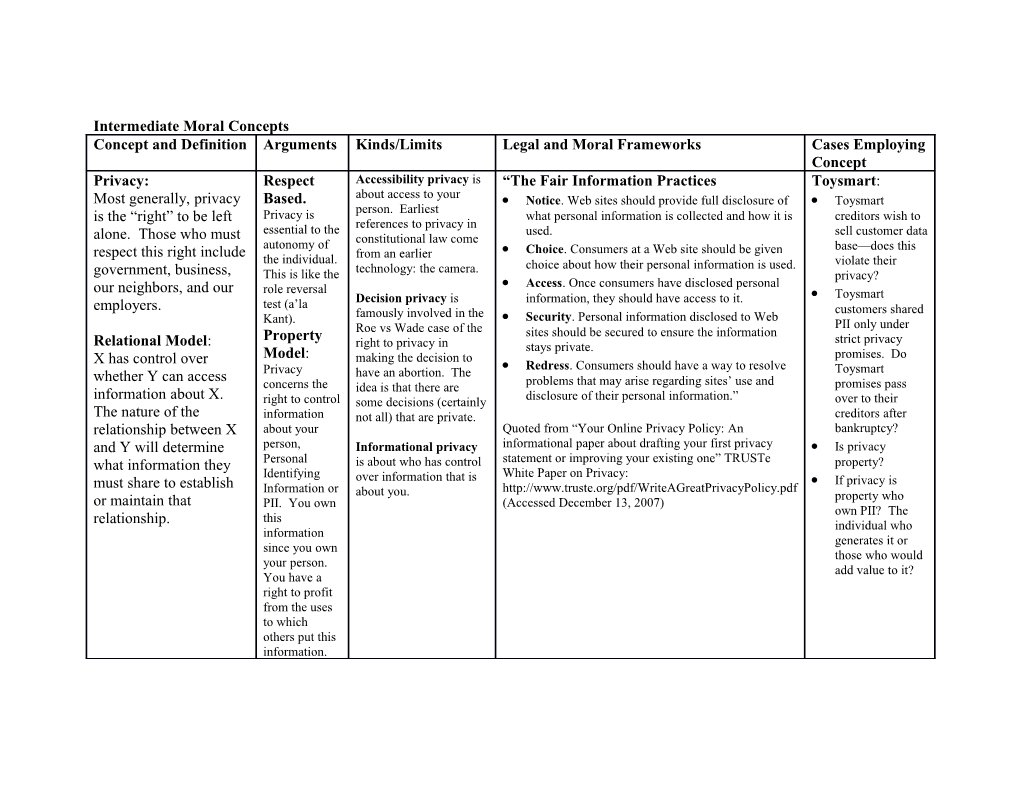
Intermediate Moral Concepts Concept and Definition Arguments Kinds/Limits Legal and Moral Frameworks Cases Employing Concept Privacy: Respect Accessibility privacy is “The Fair Information Practices Toysmart: Most generally, privacy Based. about access to your Notice. Web sites should provide full disclosure of Toysmart person. Earliest Privacy is what personal information is collected and how it is creditors wish to is the “right” to be left references to privacy in essential to the used. sell customer data alone. Those who must constitutional law come autonomy of base—does this respect this right include from an earlier Choice. Consumers at a Web site should be given the individual. violate their technology: the camera. choice about how their personal information is used. government, business, This is like the privacy? our neighbors, and our role reversal Access. Once consumers have disclosed personal Decision privacy is information, they should have access to it. Toysmart employers. test (a’la customers shared famously involved in the Security. Personal information disclosed to Web Kant). PII only under Roe vs Wade case of the sites should be secured to ensure the information Property strict privacy Relational Model: right to privacy in stays private. Model: making the decision to promises. Do X has control over Redress. Consumers should have a way to resolve Privacy have an abortion. The Toysmart whether Y can access problems that may arise regarding sites’ use and concerns the idea is that there are promises pass information about X. disclosure of their personal information.” right to control some decisions (certainly over to their The nature of the information not all) that are private. creditors after relationship between X about your Quoted from “Your Online Privacy Policy: An bankruptcy? and Y will determine person, Informational privacy informational paper about drafting your first privacy Is privacy what information they Personal is about who has control statement or improving your existing one” TRUSTe property? Identifying White Paper on Privacy: over information that is If privacy is must share to establish Information or http://www.truste.org/pdf/WriteAGreatPrivacyPolicy.pdf about you. property who or maintain that PII. You own (Accessed December 13, 2007) own PII? The this relationship. individual who information generates it or since you own those who would your person. add value to it? You have a right to profit from the uses to which others put this information. Concept and Definition Arguments Kinds/Limits Legal and Moral Frameworks Cases Employing Concept Public Good: Privacy is not a right but a public good. Society as a whole benefits if its members are allowed certain zones of privacy and intimacy. Free Speech Essential to Defamation is, OSP and ISP legal responsibility for defamatory Biomatrix: The right to express Autonomy: essentially, harm done content: three analogies Is the truth of one’s thoughts without The to another (usually Publisher—If OSP acts as publisher and speech governmental autonomous reputation, honor, etc.) exercises editorial content, then OSP is irrelevant in reprisals. individual by speech: responsible for the content of the speech cyberspace? FS is a conditional requires free Libel = printed Distributer—If OSP acts as a distributor, then In what sense, if right that can be speech to defamation it is not responsible for the content of what it any, is an OSP trumped by other develop and Slander = spoken distributes. It is only responsible for timely like Yahoo rights such as privacy. share defamation. removal of objectionable content upon responsible for thoughts. FS does not protect inflammatory speech is notification the defamatory Public one from social different from libelous Common Carrier—The common carrier is speech Good: Free reprisals nor does it speech (requires responsible neither for the content nor its displayed speech is impose on others the falsity) timely removal. It is only responsible for within its necessary to duty to listen. installing filters that prevent the entry of portals? acquire new objectionable content. Concern of and true Amicus Curiae: ideas. John Doe If true. lawsuits To (designed to suppress force OSPs to Concept and Definition Arguments Kinds/Limits Legal and Moral Frameworks Cases Employing Concept it would give out deprive identities of society users) could be of truth. used to identify If and retaliate partially against true. To legitimate suppress whistle blowers it would deprive society of the part that is true. If complete ly false. To suppress it would deprive the truth of the vitality purchase d by defendin g itself against the false. Concept and Definition Arguments Kinds/Limits Legal and Moral Frameworks Cases Employing Concept Property Labor theory Consequentialist theory copyright The shrinking of property. of property. Enshrined in legal right (usually of the author or composer or intellectual Attributes of Intellectual Originated US constitution. Two publisher of a work) to exclusive publication commons. There is Property: with Locke. pronged argument production, sale, or distribution of some work for a social value in having Non-rivalrous: my An argument (negative) that not specified period. What is protected by the copyright a common “space” having an idea does not for property as protecting property is the "expression," not the idea. Notice that taking where information is prevent you from having a natural right. results in undesirable another?s idea without attribution may be shared (see arguments the same idea (Lighting We mix our consequences and plagiarism, so copyrights are not the equivalent of for intellectual candles from the same labor with (positive) that protecting legal prohibition of plagiarism. property). match.) something and it results in desirable patent Unrestricted exercise it becomes consequences. of property rights Non-excludable: like the (special, alienable, prima facie) legal right granted ours. caused damage to the air, it is difficult to by the government to use, or at least (in cases where Problematic in Social Role theory of environment. contain the spread of other patents that such use would infringe) to bar many ways. If (intellectual) property. Unrestricted exercise ideas. Ideas by their very others from using a device, design, or type of plant we assume Information wants to be of intellectual nature disseminate that one has created. In the United States restrictions property it shared. It is in the nature property rights may themselves. last for 17 years for useful devices, and 14 years for helps of information that it is cause damage to the designs. Specific provisions of U.S. patent law may understand our shared. Control over intellectual commons. soon change to bring it into conformity with the intuition about sharing is essential as is provisions of other technologically developed it. But it fails provision for sharing. Educational Laptop countries. To patent a device one must prove that it to establish a Case: Does is useful, original, and not obvious. Patents are natural right as digitalizing print subject to challenge in court and may be upheld or necessary. textbooks violate laws overturned. in intellectual trade secret property? device, method, or formula that gives one an advantage over the competition, and which must Toysmart: therefore be kept secret if it is to be of special value. Who owns the PII and It is legal to use reverse engineering to learn a TGI that I generate? competitor’s trade secret. "Know how" concerning research procedures may function as something like a trade secret. "Glossary" Online Ethics Center for Engineering 1/31/2006 6:57:46 PM National Academy of Engineering Accessed: Thursday, December 13, 2007 Concept and Definition Arguments Kinds/Limits Legal and Moral Frameworks Cases Employing Concept
Safety “A thing is Risk Assessment: The Advice from Leveson on System Safety Hughes safe is, were scientific and exact (Selections taken and quoted from Safeware: Harmful impacts its risks fully process of determining System Safety and Computers, pp. 510-511) if computer chips known, those the degree of risk. fail under Our most effective tool in making things safe is risks would be Risk Management: The stressful judged political process of simplicity and building systems that are environmental acceptable in determining if a certain intellectually manageable conditions light of settled degree of risk is socially Safety and reliability are different and must not be Therac-25 value acceptable. Requires the confused Leveson’s principles.” consent of the risk taker Placing too much reliance on probabilistic risk comments are MS 108 Risk Perception: How assessment is unwise relevant here people perceive risk “A risk is the diverges from how risk is Building safety into a system will be much more How does one go potential that assessed. Dread and effective than adding protection devices onto a about designing a something unknown factors increase completed design; The earlier safety is considered system like the unwanted and perceived risk without in the development process, the better will be the Therac-25 to harmful may increasing degree of risk results ensure, not only its reliability, but Concept and Definition Arguments Kinds/Limits Legal and Moral Frameworks Cases Employing Concept occur.” MS Risk Communication: To make progress, we must stop oversimplifying its safety? 108 How to communicate accidents and recognize their complex, How does one risk to risk takers as a multifactorial nature. Fixing only symptoms while identify and trace part of the consent leaving root (level three) causes intact will not the cause(s) of process. (Concrete prevent the repetition of most accidents. system language and careful Human “error” is integrally related to human malfunctions? analogies.) flexibility and creativity. Can one prevent Safety is a system problem and can only be solved normal accidents by experts in different disciplines working together. given that their causes are often Just because the events leading to an accident are related to human not foreseen does not mean the accident is not flexibility and preventable. The hazard is usually known and often creativity? can be eliminated or reduced significantly. Complacency is perhaps the most important risk factor in a system, and a safety culture must be established that minimizes it We must learn from the past so that we do not repeat the same mistakes Public “those persons whose lack of information, technical knowledge, or time for deliberation renders them more or less vulnerable to the powers an engineer wields on behalf of his client or Concept and Definition Arguments Kinds/Limits Legal and Moral Frameworks Cases Employing Concept employer” Davis Whistle-blowing The duty the Morally Permissible: serious and considerable harm, There are different engineer has to made known to supervisor, exhausted internal channels ways of blowing the make risk whistle information Morally Obligatory: above conditions plus documented 1) Inside vs. Outside generally evidence and reasonable chance of avoidance of harm by 2) Anonymously vs. available to publicity Not anonymously the public 3) With documented (This duty evidence vs. without entitles 4) As a first resort vs. engineers the as a last resort right to the 5) To protect public means health vs. to promote necessary to selfish interests carry it out) 6) With protection vs. Without Protection Conflict of Interest (a) he is in a (b) he has an interest Actual: the outside interest is actually and currently Hydrolevel Case A person has a conflict of relationship tending to interfere with adversely affecting professional judgment. interest if… with another the proper exercise of Latent: all that is required for the outside interest to requiring him judgment in that actually and currently adversely affect professional to exercise relationship judgment is a change in circumstances. judgment in Potential: all that is required for the outside interest to that other’s become a latent conflict of interest is a change of service and… circumstances. Informed Consent Free and Belmont Report: Institutional Research Boards IRBs) now require Therac-25 Case Consent of risk taker to informed Conditions for Informed documentation of informed consent on research projects Patients receiving understand the nature consent is Consent carried out under that university’s auspices. This is in radiation therapy and breadth of the risk he essential to Information: research response to requirements by federal granting agencies should be made or she is being asked to autonomy procedure, their such as the NIH and the NSF. aware of the risks take. purposes, risks and of this treatment Belmont Report: The standard anticipated benefits, http://www.hhs.gov/ohrp/humansubjects/guidance/belmont.htm including the threat occurs alternative procedures (Accessed December 13, 2007) “subjects, to the degree possible when crucial (where therapy is that they are capable, be Consenting to the transfer of PII (personal malfunction of Concept and Definition Arguments Kinds/Limits Legal and Moral Frameworks Cases Employing Concept given the opportunity to risk involved), and a identifying information) online the machine or its choose what shall or information is statement offering the Opt-in: information transferred only with express software shall not happen to them. not uncovered subject the opportunity to consent. Default is not transferring information This opportunity is in risk ask questions and to Opt-out: information transfer is halted when person to provided when adequate assessment or withdraw at any time whom PII refers does something positive. Default is on standards for informed is covered up from the research. transferring information consent are satisfied.” by those who Comprehension: stand to lose manner and context in Liability Rules and Property Rules: due to its which information is Sagoff makes this distinction with reference to activities publication conveyed is as important that have an impact on the environment. An injunction as the information itself. referring to liability rules stops the activity to protect the Informed Voluntariness: an individual who proves impact. Property rules require Consent does agreement to participate only that the producer of the environmental impact suffer limits in in research constitutes a compensate the one who suffers the impact. terms of its valid consent only if feasibility. Do voluntarily given. This private element of informed indivuals have consent requires the right to conditions free of veto large coercion and undue scale influence. government projects? (This is not just a utilitarian vs. deontological issue: it could also be framed as a conflict within deontology between different, Concept and Definition Arguments Kinds/Limits Legal and Moral Frameworks Cases Employing Concept conflicting rights and duties)