RAJIV GANDHI UNIVERSITY OF HEALTH SCIENCES, BANGALORE, KARNATAKA
ANNEXURE II PROFORMA FOR REGISTRATION OF SUBJECT FOR DISSERTATION
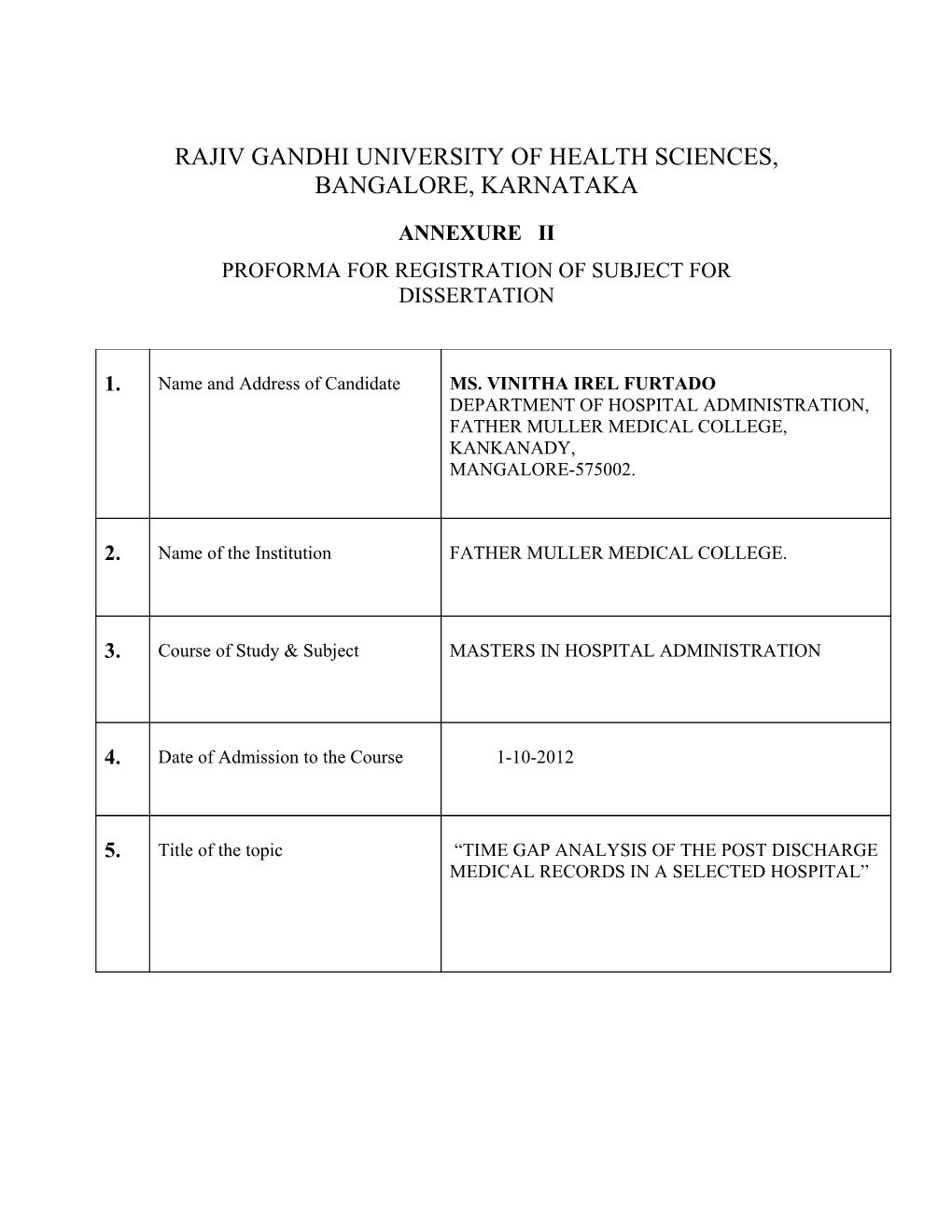
1. Name and Address of Candidate MS. VINITHA IREL FURTADO DEPARTMENT OF HOSPITAL ADMINISTRATION, FATHER MULLER MEDICAL COLLEGE, KANKANADY, MANGALORE-575002.
2. Name of the Institution FATHER MULLER MEDICAL COLLEGE.
3. Course of Study & Subject MASTERS IN HOSPITAL ADMINISTRATION
4. Date of Admission to the Course 1-10-2012
5. Title of the topic “TIME GAP ANALYSIS OF THE POST DISCHARGE MEDICAL RECORDS IN A SELECTED HOSPITAL” 6 Brief Resume Of The Intended Work: 6.1: Need for the study: The medical record is a powerful tool that allows the treating physician to track the patient’s medical history and identify problems or patterns that may help determine the course of health care. The primary purpose of the medical record is to enable physicians to provide quality health care to their patients. It is a living document that tells the story of the patient and facilitates each encounter they have with health professionals involved in their care.
In addition, complete and accurate medical records will meet all legal, regulatory and auditing requirements. Most importantly, however, they will contribute to comprehensive and high quality care for patients by optimizing the use of resources, improving efficiency and coordination in team-based and inter professional settings, and facilitating research.
The need for appropriate, written documentation of facts related to patients’ treatment in the hospitals cannot be brushed aside, because failure to maintain records means failure of duty towards the patients. Medical records through which hospital statistics are generated serve as eyes and ears to the hospital administrator. Medical records are of importance to the hospital for evaluation of its services for better patient care. They also serve as a resource for education & training of physicians and others, also being the basis for clinical research.
Research to be effective requires scientifically recorded observations as reflected in the medical record. And, the importance of accurate records for legal purpose is well established. Father Muller Medical College Hospital is 1250 bedded hospital with a well set Medical Records Department. The Investigator would like to study the average time needed for the recieval of post discharge patient’s medical record and to study the cause for the delay.
6.2: Review of literature
According to McGibony(1) medical record is a clinical, scientific, administrative and legal document relating to patient care in which are recorded sufficient data written in the sequence of events to justify diagnosis and warrant treatment and end results.
According to B M Sakharkar Medical records is defined simply as a systematic documentation of a patient’s personal and social data, history of his or her ailment, clinical findings, investigation, diagnoses, treatment given, and an account of follow- up and final outcome.(2)
Gap Analysis is a technique that businesses use to determine what steps need to be taken in order to move from its current state to its desired, future state. Also called need-gap analysis, needs analysis, and needs assessment.(3)
According to Mac Eachern(4), as in the large hospital medical record should be written promptly accurately and completely. There should be absolutely no difference in the amount and quality of information provided. Every member of the medical staff of the hospital must be keenly anxious to accept individual responsibility for his medical records, regardless of the method adopted for securing them. It should be understood by every physician on becoming a member of the medical staff or accepting hospital privileges that he must consciously discharge his obligations as for medical records are concerned. This he should do not only for the sake of hospital but more particularly for the patient and for himself. Through this work, he can treat his patients more scientifically and add to personal knowledge for diagnosis and therapy.
According to Christopher Kim, MD(5) Discharge is a three- step process. First, physicians had to write discharge orders. Next, clerks had to prepare them. Finally, nurses had to give patients their discharge instructions. It was a formula for lots of waiting time —“waste” in lean terminology. The lean team “found that everything was happening in a serial basis,” Dr. Kim recalls. “Clerks would only write orders when the physicians finished and the nurses would not do anything until clerks finished.”Physicians often would tell their patients they were to be discharged but fail to inform the nurses. “Nurses would find out from the patients,” Dr. Kim says. It was sometimes hours before the physicians got around to writing up the orders. No orders meant no paperwork. No paperwork meant no nurse-patient instructions. One bottleneck would delay the entire process. The lean team instituted a parallel procedure. Now, Dr. Kim says, “Discharge order slips are available at the patient’s bedside.” Those forms go directly to the clerks, who notify the nurses, who then begin their discharge instructions. In theory, no one is waiting for anyone else to finish one job before starting another. In practice, discharge time has decreased from 7 about 195 minutes to 89, a 54% reduction. Knowing early how many beds will become available each day has “also eased the backlog of patients in the ER trying to get into beds and offloads workloads at those places,” Dr. Kim says. That there still is room for improvement. “It’s still a work in progress,” Dr. Kim admits. “We’re still working on our doctors to write their orders even sooner. That’s our next goal.”
6.3: Objectives of the study
* To assess the average time taken for the receival of medical records in MRD after patient discharge in a selected hospital.
* To find the causes for the delay in receival of medical records from the wards.
Materials and Methods: 7.1: Source of data: Observation of inpatients medical records in the surgical ward, medical ward, paediatric ward, gynaecology ward and orthopaedic ward.
7.2: Method collection of data: 7.2.1 Study Type The research approach adopted in this study is Descriptive study.
7.2.2 Sample and sampling techniques. A sample size of 25 records in each of the selected wards will be chosen randomly for the study. Observation method will be adopted to find the time interval between the after discharge of the patient to the time required by the MRD personnel for further process.
7.2.3 Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria Death and MLC cases are excluded. Case sheet of patient admitted for minimum of three days will be considered.
7.2.4 Plan for data analysis: Collected data will be analyzed by frequency, percentage, mean, standard deviation and coefficient of variation.
.7.3: Does the study require any investigations or interventions to be Conducted on patients or other humans or animals? No 7.4: Has ethical clearance been obtained? Yes 8. LIST OF REFERENCE
1. McGibony JR: Principles of Hospital Administration GP Putnam’s Sons’. New York, 1969.
2. BM Sakharkar: Principles of Hospital Administration & Planning. Second edition 2009,page no 236. 3. What is gap analysis? definition and meaning - BusinessDictionary ... http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/gap- analysis.html
4. Mac Eachern MT..The medical record department, Hospital organization and management, Chicago : Physicians record company; 1957, 719-834pp. 5. Christopher, M.B., Fernandes, M.D., Worster, A., Hill, S.,McCallum, C., & Eva, K. (2004, March). Root cause analysis for laboratory turnaround times for patients in the emergency department. [Electronic version]. Journal of the Canadian Association of Emergency Physicians, 6(2), 116-122
9 Signature of the candidate :
10. Remarks of the guide :
11. Name &Designation
11.1: Guide : MRS SONIA D’SOUZA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR FATHER MULLER MEDICAL COLLEGE, MANGALORE
11.2: Signature :
11.3: Co-Guide(if any) :
11.4: Signature :
11.5: Head Of The Department : DR. JAYAPRAKASH ALVA DEAN FATHER MULLER MEDICAL COLLEGE, MANGALORE
11.6: Signature : 12. 12.1:Remarks Of The Chairman &Principal :
12.2: Signature :