Exam Review: Diagrams
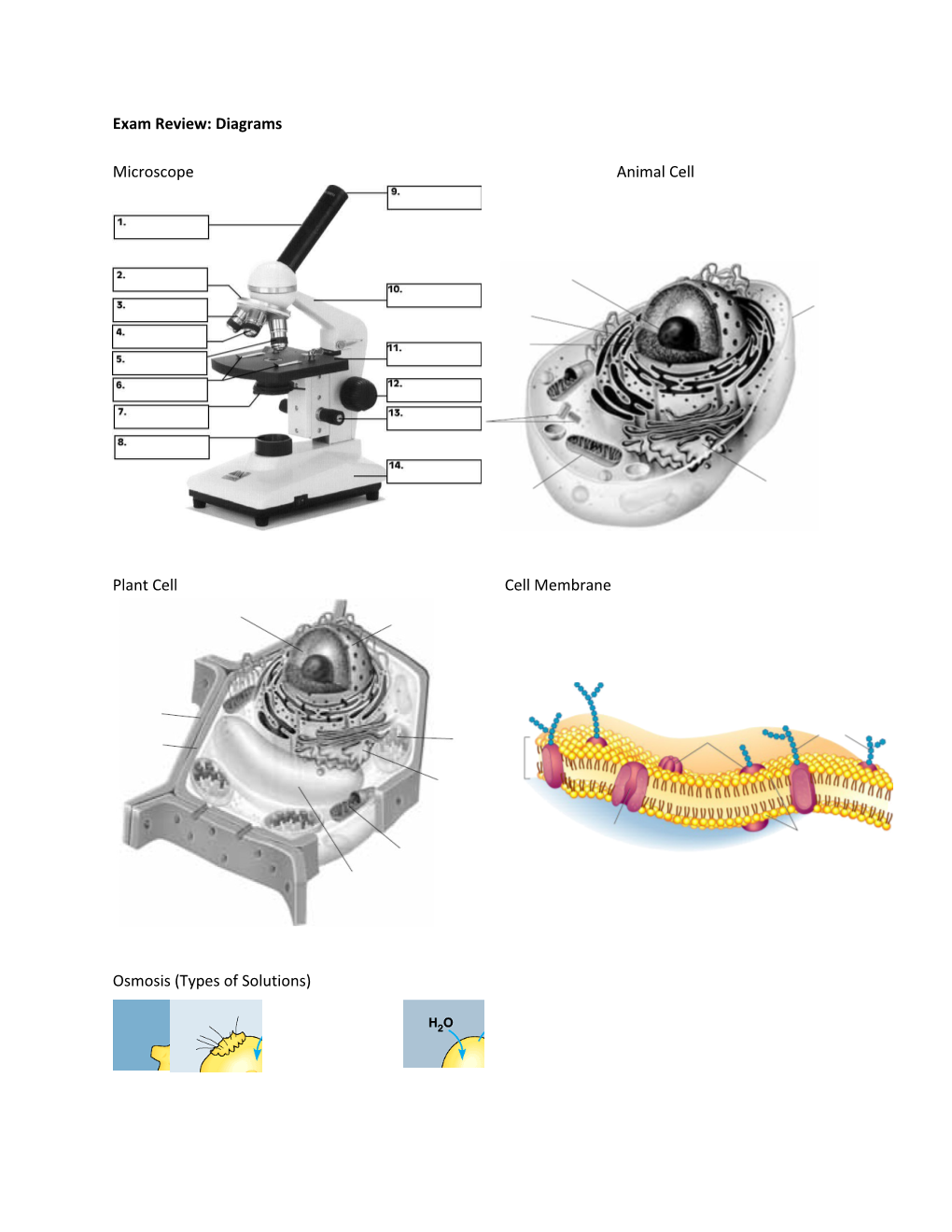
Microscope Animal Cell
Plant Cell Cell Membrane
Osmosis (Types of Solutions) Photosynthesis Chloroplast
Cellular Respiration Mitochondria
Digestive System Circulatory System (Heart) Respiratory System Excretory System
Bacteria Virus Fungi Seed
Biology Exam Review
Topics Covered:
1. Intro to Biology
a. Microscope Technologies
b. Early Scientists and their Contributions
c. The Cell Theory
2. Cell Structures and Functions
a. Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
b. Animal Cell
c. Plant Cell 3. Cell Membrane and Transport
a. Membrane Structure
b. Passive and Active Transport (Diffusion, Osmosis, Ion Pumps/Co-transport, Endocytosis, Exocytosis, etc)
4. Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
a. Mitochondria Structure
b. Chloroplast Structure
c. The stages of each Process
d. Fermentation
5. Body Systems
a. Homeostasis
b. Digestive and Excretory System
c. Circulatory System
d. Respiratory System
e. Immune System
6. Classification
a. Taxonomy (phylogenic tree, binomial nomenclature, dichotomous key)
b. The 8 Levels of Classification
c. The 6 Kingdoms and Characteristics of each
c.i. Archaebacteria
c.ii. Eubacteria
c.iii. Protista
c.iv. Fungi
c.v. Plantae
c.vi. Animalia Biology 112 Exam Review Questions:
Part I:
1. What is abiogenesis?
2. List the scientists from Aristotle to Pasteur and describe their experiments and what impact they had.
3. List the parts of the cell theory.
4. Explain the following types of microscopes: Single Lens Optical Microscope, Compound Microscope, Scanning Probe Microscope and Scanning Electron Microscope.
Part II:
1. Define the following:
a. Nucleus
b. Nucleolus
c. Nuclear Envelope
d. Cell Membrane
e. Cell Wall
f. Golgi Apparatus
g. Ribosome
h. Mitochondria
i. Lysosome
j. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
k. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
l. Chloroplast
m. Vacuole
n. Microtubule o. Microfilament
p. Eukaryote
q. Prokaryote
Part III:
1. Compare and contrast photosynthesis and cellular respiration (where do they take place, what is their chemical equation, what is their purpose, what cells do them, etc.). You may use a chart or a Venn diagram if you would like.
2. What are the stages of cellular respiration? Where does each of the stages occur? How much ATP is gained from each?
3. What happens if there is no oxygen present for cellular respiration to take place?
4. What are the stages of photosynthesis? Where does each stage take place?
Part IV: 1. Define the following:
a. Phospholipid f. Hypotonic b. Glycoprotein c. Glycolipid g. Active Transport
d. Isotonic h. Passive Transport
e. Hypertonic i. Pinocytosis j. Phagocytosis
2. Explain the following, using words and a diagram:
a. Diffusion d. Ion Pump/Co-Transport
b. Osmosis e. Endocytosis
c. Facilitated Diffusion f. Exocytosis
g. Part V: 1. What is meant by the term “Homeostasis”? 2. Explain how the body regulates internal temperature. 3. How are blood sugar levels controlled in the body? 4. Why does someone with diabetes need insulin injections? 5. Explain the filtration and reabsorption process that occurs in the kidneys. 6. What four organs are used for excretion? 7. Define: a. Ureter e. Nephron b. Urinary bladder f. Glomerulus c. Renal medulla g. Loop of Henle d. Renal cortex 8. What is the difference between mechanical and chemical digestion? 9. What enzyme is produced in the mouth? Why is it important that it is produced first? 10. Define the following: a. Bolus c. Epiglottis b. Chyme 11. In which digestive organ does the majority of absorption take place? What special features does this organ have which make absorption more efficient? 12. What role does the liver play in digestion? 13. What role does the large intestine have in digestion? 14. Complete the chart of digestive enzymes: 15. Enzyme 16. Site of Action 17. Site of 18. Nutrient Production Digested 19. Amylase 20. 21. 22. 23. Pepsin 24. 25. 26. 27. Lipase 28. 29. 30. 31. Trypsin 32. 33. 34. 35. Lactose 36. 37. 38. 39. Maltose 40. 41. 42. 43. Sucrose 44. 45. 46. 47. Peptidase 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. What are the four main components of blood and their functions? 53. What are the three main parts of the Circulatory System? 54. Define: a. Myocardium i. Atherosclerosis b. Pericardium j. Hemoglobin c. Atrium k. Erthrocyte d. Ventricle l. Leucocyte e. Septum m. Phagocyte f. Pulmonary circulation n. Lymphocyte g. Systemic circulation o. Valve h. Pacemaker 55. Describe the differences between a vein, artery and capillary. 56. List (in order) the path blood travels through the heart. 57. What function is performed by the respiratory system? 58. List (in order) the passage of air from the environment to the lungs. 59. Explain the processes of inhaling and exhaling. 60. Why is smoking dangerous? 61. List three diseases that can be caused by smoking. 62. Define: a. Cilia e. Alveoli b. Pharynx f. Larynx c. Trachea g. Diaphragm d. Bronchi 63. What is the primary first defense of the Immune System? 64. How do tears, mucus, sweat and saliva work as defense systems? 65. Draw the structure of an antibody. Explain the two ways an antibody works. 66. Explain the two types of white blood cells. 67. How does humoral immunity work? 68. How does cell-mediated immunity work? 69. Why do you get a fever when you are sick? 70. Why does an infected wound swell? 71. When would a doctor not prescribe antibiotics? 72. How does your body fight against viruses? 73. What is the body’s response to cancerous cells?
74. Why do organ transplants sometimes fail?
75. How do we become immune to different diseases?
76. How does a vaccine work? 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. Part VI: 1. Define: a. Taxonomy g. Convergent definition b. Classification h. Niches c. Binomial Nomenclature i. Adaptations d. Phylogeny j. Analogous Structures e. Systematics k. Dichotomous key f. Phylogenic tree l. Taxon 2. What four types of evidence are phylogenic trees based on? 3. Which 7 levels of classification is Linnaeus responsible for? Which was included later on? 4. Which of the two species below are more closely related? What proof can you use from the chart to support your claim? 5. 6. Explain the features of species living in the Kingdom Archaebacteria. 7. What are some characteristics of bacterial cells? 8. What are the criteria for classifying and identifying bacteria? 9. List and explain the three basic shapes of bacteria. 10. What are viruses? 11. Why are viruses impossible to classify using the current system? 12. What are characteristics of viruses? How does a virus work? 13. How are fungi and plants similar? How are they different? 14. Define: a. Mycelium g. Saprobes b. Hyphae h. Parasites c. Fruiting bodies i. Fragmentation d. Stolons j. Budding e. Rhizoids k. Spores f. Sporangium l. Zygospore 15. Why do you rarely see the mycelium? 16. What are the four phyla under fungi? Briefly explain each. 17. What is a lichen? 18. What are characteristics of a plant? 19. Fill in the Following: 20.
21. What do plants need to survive? 22. What does it mean to be vascular and non-vascular? 23. What is the difference between a xylem and a phloem. 24. What does it mean to be a diploid? A haploid? 25. What are the three main parts of a seed? 26. How can you distinguish between a monocot and a dicot? 27. Define: a. Vertebrate f. Pseudocoelomate b. Invertebrate g. Acoelomate c. Notochord h. Medusa d. Coelom i. Polyp e. Peritoneum 28. Explain the different body symmetries that can occur in animals? 29. Draw the Life Cycle of Animals from Gametes to Fetus. 30. What do the ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm become, respectively? 31. List the phyla under the Animal Kingdom and briefly explain each one. 32. List the seven classes of chordates and give an example of an animal belonging to each. 33. 34. 35. 36.