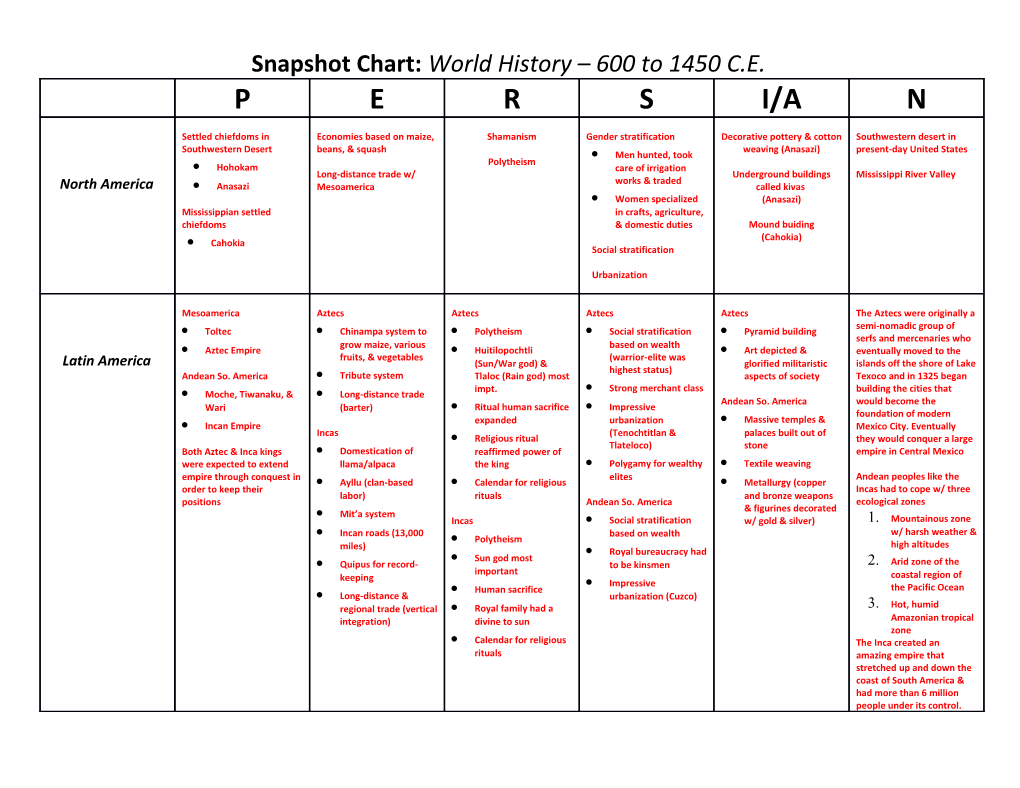
Snapshot Chart: World History – 600 to 1450 C.E. P E R S I/A N
Settled chiefdoms in Economies based on maize, Shamanism Gender stratification Decorative pottery & cotton Southwestern desert in Southwestern Desert beans, & squash weaving (Anasazi) present-day United States Men hunted, took Polytheism Hohokam care of irrigation Long-distance trade w/ Underground buildings Mississippi River Valley works & traded North America Anasazi Mesoamerica called kivas Women specialized (Anasazi) Mississippian settled in crafts, agriculture, chiefdoms & domestic duties Mound buiding (Cahokia) Cahokia Social stratification
Urbanization
Mesoamerica Aztecs Aztecs Aztecs Aztecs The Aztecs were originally a semi-nomadic group of Toltec Chinampa system to Polytheism Social stratification Pyramid building serfs and mercenaries who grow maize, various based on wealth Aztec Empire Huitilopochtli Art depicted & eventually moved to the fruits, & vegetables (warrior-elite was Latin America (Sun/War god) & glorified militaristic islands off the shore of Lake highest status) Andean So. America Tribute system Tlaloc (Rain god) most aspects of society Texoco and in 1325 began impt. Strong merchant class building the cities that Moche, Tiwanaku, & Long-distance trade Andean So. America would become the Wari (barter) Ritual human sacrifice Impressive foundation of modern expanded urbanization Massive temples & Incan Empire Mexico City. Eventually Incas (Tenochtitlan & palaces built out of Religious ritual they would conquer a large Tlateloco) stone Both Aztec & Inca kings Domestication of reaffirmed power of empire in Central Mexico were expected to extend llama/alpaca the king Polygamy for wealthy Textile weaving empire through conquest in elites Andean peoples like the Ayllu (clan-based Calendar for religious Metallurgy (copper order to keep their Incas had to cope w/ three labor) rituals and bronze weapons positions Andean So. America ecological zones & figurines decorated Mit’a system Incas Social stratification w/ gold & silver) 1. Mountainous zone Incan roads (13,000 based on wealth w/ harsh weather & Polytheism miles) high altitudes Royal bureaucracy had Sun god most Quipus for record- to be kinsmen 2. Arid zone of the important keeping coastal region of Impressive Human sacrifice the Pacific Ocean Long-distance & urbanization (Cuzco) regional trade (vertical Royal family had a 3. Hot, humid integration) divine to sun Amazonian tropical zone Calendar for religious The Inca created an rituals amazing empire that stretched up and down the coast of South America & had more than 6 million people under its control. Spread of Islam Trans-Saharan trade (gold, Islam Social stratification Mosques and Christian African societies emerged in salt, slaves) emerged with increase in churches blended Middle a variety of geographic Sub-Saharan Muslim regional kingdoms Christianity (Ethiopia) wealth from trade Eastern designs w/ diverse zones – grasslands of E. in W. Africa Iron working building styles of local Africa, dense tropical rain Africa Slavery emerged for labor African regions forests of W. & C. Africa, Ghana Indian Ocean trade network in mines but most slaves and deserts like the Sahara Mali (ivory, ebony, gold, animal specialized in service to Mosques were centers for in the North & Kalahari in skins) wealthy elites. They had education the south. Africa is almost Songhay opportunities at (madrasas) entirely in the tropical zone West African coastal trade advancement. of the Earth and its cycles Muslim city-states in with Portugal Increase in literacy as are rainy and dry seasons Central Sudan Spread of Islam had a Arabic was adopted & rather than hot and cold. Hausa Introduction of bananas & varied impact on women Arabic alphabet was used to Rivers were important to yams from Malay sailors with most having many write local languages the development of Kanem-Bornu from SE Asia roles in African societies & irrigation and agriculture reflected influence of local Swahili griots continued to with the three most crucial Christian kingdom of Export of Ethiopian coffee traditions & customs. transmit African history being the Nile (central Ethiopia to the Middle East orally Africa to north), Niger (W. Travels of ibn Battuta Africa), & Zambezi (south to Swahili city-states Copper wire & decorative central Africa). Africans Bubonic Plague Epidemic objects (SE Africa) found ways to produce food Great Zimbabwe in (14th c.) in all these varied regions. Southern Africa Copper & bronze statues (W. Africa)
Cities like Baghdad & The Rise of Islam (Saudi Long-distance trade along Islam Cordoba were essential to The Qur’an & language of th The Muslim World (dar-al- Arabia, 7 c.) Silk Roads (coins, textiles, Muslim Empire, both as Arabic united the many Islam) stretched from crafts) Shia/Sunni split after ways of spreading the faith diverse cultures within the places in the Middle East, Islamic Caliphates Muhammad’s death & as governing centers Islamic Empire at this time such as Syria, Palestine, Middle Position at the western end Abu Bakr’s (632-661) Shias believed present day Iran & Iraq, to of the Silk Roads made it Ulama (religious scholar Islamic scholars looked to East/North Africa succession should be North Africa, the southern Ummayad (661-750) major conduit of luxury class) preserved central many different sources for traced through part of Spain, and across goods from the East (silk, teachings & tenets of Islam knowledge including the Abbasid (750-1258) Muhammad’s Central Asia to the eastern porcelain, etc.) as the empire became more Greek classics, as well as bloodline; cousin Ali ends of the Silk Roads. diverse works from Persia and India Some provinces of the should’been 1st caliph Mongol tax farming (giving that had been translated caliphates broke away & & only his out private contracts to Women in Islam had into Arabic established their own descendents could be merchants to collect taxes greater legal freedom than caliphates by 9th c. imams by whatever means served Jewish or Christian women Muslim scholars built on Fatimid caliphate them best) Sunnis believed at this time. Although not earlier advancements in (Egypt) caliph should be considered the equally of science, mathematics, & chosen by men, they were influential technology including Samanid caliphate community; 1st three in family life, could own or algebra, trigonometry, (Iran) caliphs properly inherit property, divorce, astronomical observations, selected remarry, and testify in & medicinal studies. Turkish Sultanates (11th court. Practices such as -14th c.) Sufiism (mystical religious seclusion & veiling actually Mosques were central Seljuk Turks sect within Islam) came from the Byzantine & architectural landmarks Sassanid Empires & were Mamluks (Egypt) adopted by Islam later. Art & literature had Persian Timurid Empire influences Bubonic plague epidemic The Crusades (1095-1291) (14th c.)
The Mongols Sacked Baghdad 1258 Il-khan Empire The main form of economic After the fall of the Roman production in medieval Christianity had both a Early medieval Western The Crusades brought Post-classical Europe Empire in the 5th c. CE, the Western Europe from 600- political and a religious Europe (600-1000) had a Muslim scholarship & derived from the fall of western part of the Empire 1000 could be found on the impact as the power of the very rigid system of social knowledge to Europe in the Rome in the 5th c. CE. The became a decentralized manor. The manor was a church grew in both stratification due to form of the ancient Greek western part of the old Europe feudal system while the single fortified dwelling Western & Eastern Europe, feudalism’s emphasis on classics (preserved by empire, that included the eastern part of the Empire which sustained a and the concept of the vassal relationship & Muslims) & the many present-day countries of continued under imperial community of people & Christendom took on a serfdom. Noblewomen scientific & technological France, Germany, Italy, & rule as the Byzantine included a mill, church, territorial context played an important role in achievements made by the Great Britain among others, Empire. workshops, and a village this system since they were Muslims themselves. replaced the imperial rule, where serfs lived. The In 1054, a schism (formal carefully & strategically culture, and laws of Rome Medieval Western Europe manor was self-sufficient & split) occurred between the married to create political Late medieval cities became with those of the Germanic (600-1000) rarely interacted with the Christian church in Western alliance & gain more lands. centers of learning as traditions and practices of outside world due to the & Eastern Europe over a Women could own land & universities specializing in tribes in the area. Feudalism lack of communication, series of doctrinal issues manage estates when fields such as education, Carolingian Empire trade, and strong such as the humanity & husbands were away on law, & theology sprang up The eastern half of the (founded by centralized gov’t at this divinity of Jesus, the place military service. The Church across Europe. Universities Roman Empire continued as Charlemagne) time Several important of icons, the role of Mary, provided the social allowed for new questions the Byzantine Empire, with economic changes occurred and the role & power of the framework for this entire about the relationship b/t Constantinople as its great Pope demanded in late medieval Western pope. From then one, the system. reason & faith known as capital located ideally b/t honor & respect from Europe (1000-1450). New church was split into the scholasticism. the Black Sea & the secular leaders agricultural technologies Roman Catholic (Latin) The tragic demographic Mediterranean. The such as a new plow, the Church in the west & the changes brought on by the Most Western European art Byzantine Empire Medieval Western Europe horse collar, & the use of Eastern Orthodox Church in Black Death epidemic & architecture at this time encompassed the Balkan (1000-1450) horses instead of oxen led the east. (1347-51) led to a revival of centered around the Area of southeastern Holy Roman Empire to an increase in the food trade & the emergence of church. Architecture Europe as well as Anatolia supply & thus a larger Monasticism developed in independent cities that flourished in the form of until it came to an end in Investiture conflict population. This surplus medieval Western Europe. offered more opportunities the Gothic cathedral. 1453 w/ the Ottoman Politically freed people to focus on for social mobility & Byzantine Empire enjoyed conquest. industries in artistry & independent cities individual opportunity. many cultural & artistic construction & thus trade in Italy & Flanders Western Europe’s Jews achievements all reflecting resumed. Production rose lived in cities and the Greek Orthodox again after the Black Death The Crusades (1095- experienced periods of interpretations of as serfdom ended & free 1291) great tolerance (Muslim Christianity. The Hagia laborers bought land for Spain) & also periods of Sophia is the greatest themselves & demanded Viking invasions horrific persecution (during example of Byzantine higer wages. Finally, Black Death). architecture. The Byzantine politically independent Byzantine Empire practice of painting icons cities in Italy, the Hanseatic The Byzantine Empire had a great influence on Constantinople League, & the Flanders moved from an urban way pre-Renaissance painting in (capital city) revived seaborne trade. The of life to a more rural one Western Europe. Reign of Justinian Crusades also renewed due to an epidemic of the economic contact w/ the th (527-565) bubonic plague in the 7 c. Muslim World. CE. Women also moved Justian’s Code from a freer existence to a preserved Roman The Byzantine Empire more secluded existence in Law continued Roman economic the home, marked by Collapsed in 1453 traditions including the wearing the veil in public. regulation of prices, the when the Ottomans trading of luxury goods, & Social interactions w/ men captured grain shipments. were limited to family Constantinople Constantinople’s ideal members. location made it a center of trade & travel.
Kievan Russia stood as Economic prominence in Kievan Russia followed Kievan Russia had a Kievan Russian churches Kievan Russia emerged an independent state Kiew came from trade, the traditions of highly stratified society were built & icons north of the Byzantine from 980 until the arrival which provided the Orthodox Christianity in which the princes painted in the Byzantine Empire with large cities Russia/ of the Mongols in the money to pay soldiers. were the elite class, style. Byzantine such as Kiev & Novgorod 13th c. Princes & artisans lived Pastoral nomads artisans & soldiers were missionaries influenced which were located in Central Asia in cities & focused on believed in shamanism valued, & Slavs were the formation of the such present-day Steppe diplomacy of the trade while the Slavs used to work the land in Cyrillic alphabet, which Eastern European Central Asian worked the lands. By the Though the Mongols a form of serfdom became the written countries like the th pastoralists 12 c. CE, the Orthodox often adopted other language of Slavic & Ukraine. Church had taken faiths that spread along Pastoral societies like Russian Orthodox th In the 13th c. CE, the control of economic the Silk Roads, such as the Mongols tended to Christians. In the 13 c. CE, the Mongols established the roles such as tax Buddhism, Christianity, be more egalitarian, Mongols established the largest contiguous land collection. & Islam, they still especially in regards to Though the Mongols largest contiguous land empire in world history, maintained their the roles of women who were pastoral nomads, empire in world history, stretching from China to Pastoral nomads of the shamanistic traditions had a voice in tribal the best example of stretching from China to Baghdad in Persia & Central Asian steppes councils. These tribes their architecture were Baghdad in Persia & Western Russia. This were actively involved in did select a leader their yurts, they did Western Russia. was due mostly to trade along the Silk known as a khan. The foster the exchange of military tactics such as Roads due need to trade most powerful families goods, ideas, and After Chinggis (Genghis) their horsemanship and for goods from settled could voice their technological Khan’s death, the the use of the Central societies they could not opinions to the khan, achievements across the Mongol Empire was Asian bow. After the produce from settled and they grew more Eurasian continent. The separated into four death of the empire’s societies, and as carriers powerful through Mongols also adopted Khanates. They were… founder Chinggis Khan, of goods along the Silk intermarriage & warfare. many of the local Yuan Dynasty the Mongols divided Roads. cultural traditions (China) their empire into The Mongol conquests depending on the areas IL-Khanate (Persia) khanates. The khanates In securing and also unknowingly spread they conquered. in Central Asia were the controlling Eurasia, the disease, most notably Chagatai Khanate Chagatai Khanate ruled Mongols allowed the bubonic plague (Central Asia) most of Central Asia missionaries, merchants, pandemic. In addition, Golden Horde while the Khanate of the and diplomats to move the Mongols spread (Russia) Golden Horde ruled freely and exchange influenza, typhus, & Russia ideas and goods. The smallpox that spread peace they established death & destruction during their reign (the across Eurasia. Pax Mongolica) allowed trade along the Silk Roads to flourish.
The Mongols also enacted practices like tax farming & collected tribute from their conquered territories.
Chinese dynasties, China rose as the most starting w/Tang Confucianism was Neo-Confucianism Mahayana Buddhism Chinese territory was influential state in East reestablished the reestablished as the promoted the expanded into central Asia in terms of tributary system in philosophy of the state application of Confucian Neo-Confucianism Asia to the eastern East Asia economic & political which independent & examination system respect for authority & border of Bactria dominance states gave gifts to the revived under Sui family to everyday life of Japanese bushido (present-day Chinese emperor for all levels of Chinese (samurai code) Afghanistan) including Imperial Dynastic Rule in trade privileges. Mahayana Buddhism society. It heightened portions of Tibet, China exerted significant the tendency of Chinese Chinese writers Manchuria, & South Sui (589-618) Chinese cities such as social, cultural, and elite classes to withdraw produced popular short Vietnam Chang’an, Kaifeng, & political influence in from contact w/ other stories & poetries Tang (618-907) Hangzhou were thriving China, Japan, Korea, & peoples. Chinese cultural, Song (960-1279) economic & cultural Vietnam. Tang dynasty Chinese artists political, & economic Yuan (Mongol centers attacked Buddhism as a China remained a highly expressed themselves influence extended into rule; 1271-1368) scapegoat for the patriarchal society. through landscape Korea, Japan, & China had much problems causing the Chinese women did NOT paintings Vietnam Ming (1368-1644) economic success as empire’s decline. have the right to own many of its goods, property, divorce, or Japan, Korea, & Vietnam especially silk & Neo Confucianism, a remarry, & rarely had accepted some aspects porcelain were traded blending of Buddhist & educational of Chinese culture & extensively across the Confucian ideas, opportunities. The rejected others, carving Silk Roads & Indian emerged during the practice of footbinding out their own unique Ocean. Song Empire became a status symbol cultural & political amongst Chinese identities Chinese technological women & made them advancements: In Japan, Shinto (the unable to work Japan became a Grand Canal (Sui) traditional Japanese decentralized feudal belief system that China experienced a state that recognized the Compass (Tang) revered spirits of nature significant decline in emperor & shogun but Junk (Tang) & ancestors) mixed w/ population during the did not unify politically Paper money both Confucianism & Yuan Empire for a until the threat of Buddhism. variety of reasons, Mongol invasion. Flying money including the bubonic (letters of credit) plague pandemic. Land redistribution Population would (Tang) increase during the Ming Gunpowder (Tang) Empire Tea & fast-growing rice imported from Vietnam (Tang) Printing w/ movable type (Song) Abacus (Song) Improvements in iron & steel production (Song) Zheng He Expedition (1405- 1433)
After decline of Gupta The Delhi sultanate profited The Dehli Sultanate The old Hindu caste system Islamic cultural, artistic, Delhi Sultanate (1206-1526) Empire, India was divided tremendously from the introduced Islam to the continued to be practiced philosophical, & was a Muslim Empire into separate feuding states Indian Ocean trade network Indian subcontinent though members of lower technological developments established by Turkish b/c it held control over creating ongoing tension Hindu castes & spread to India at this time invaders who ruled almost South Asia Delhi Sultanate (1206-1526) many of the key port cities between Hinduism & Islam untouchables found Islam all of the northern part of was a Muslim Empire & regions along this trade in South Asia that is still appealing b/c of its the subcontinent. The established by Turkish route evident today. accepting & egalitarian southern part of the invaders that did much to nature. subcontinent was centralize northern India Arab dhows (a boat fitted controlled by Hindu princes. under a strict government with a lateen sail) were the The Delhi Sultanate bureaucracy. typical ship of the Indian required Hindus to pay Ocean b/c they were able special tax in return for In 1398, Timur (Tamerlane) to master the monsoon protection sacked & conquered Delhi winds & effectively in 1398 which signaled the navigate the currents end of prominence of the Delhi sultans.
Vietnam was divided These kingdoms grew Strong Hindu & Buddhist Foreign ideas, especially Hinduism & Buddhism Many of these trade into two rival kingdoms wealthy & prominent by influences religious ones, affect continued to affect kingdoms emerged on – Annam & Champa. being active members in social structure & development of thought, the Malay peninsula & Southeast Asia Annam was culturally, the Indian Ocean trade Islam emerged later behavior art, and architecture the islands of what is politically, & network (esp. trade in today Indonesia, while economically tied to spices & gold). The emergence of Islam also emerging on the China. Champa was later would further peninsula that today heavily influenced by Malay sailors were affect cultural, artistic, & contains the countries of India & Malaya. Both active across the entire philosophical Vietnam, Laos, & were tribute states of Indian Ocean network development of this Cambodia. The port China. region. cities in this region were ideally located along the Indian Ocean Commerce Indian Ocean trade created several large network. kingdoms in SE Asia – Srivijaya (Malay peninsula), Saliendras (central Java) , & Khmer state of Angkor (Burma) After 600 CE, the Polynesian Tribal governments Established villages based Polytheism Polynesian (Austronesian) Paleolithic cave art people were involved in (Australia’s Aborigines) on agriculture & fishing migrations brought highly migration & expansion from Animism (Dreamtime) stratified societies to the Polynesian canoes island to island in the Regional kingdoms (ex. many tiny islands in the Pacific. From their base in Oceania Hawaii; the Maori of New Pacific Polynesian pictographs the islands of Fiji, Samoa, & Zealand) Tahiti, the Polynesians The Maori of New Zealand sailed northward & settled set up a stratified society the islands of Hawaii. About that included slaves 1200 CE, another group of Polynesians migrated to the island of New Zealand