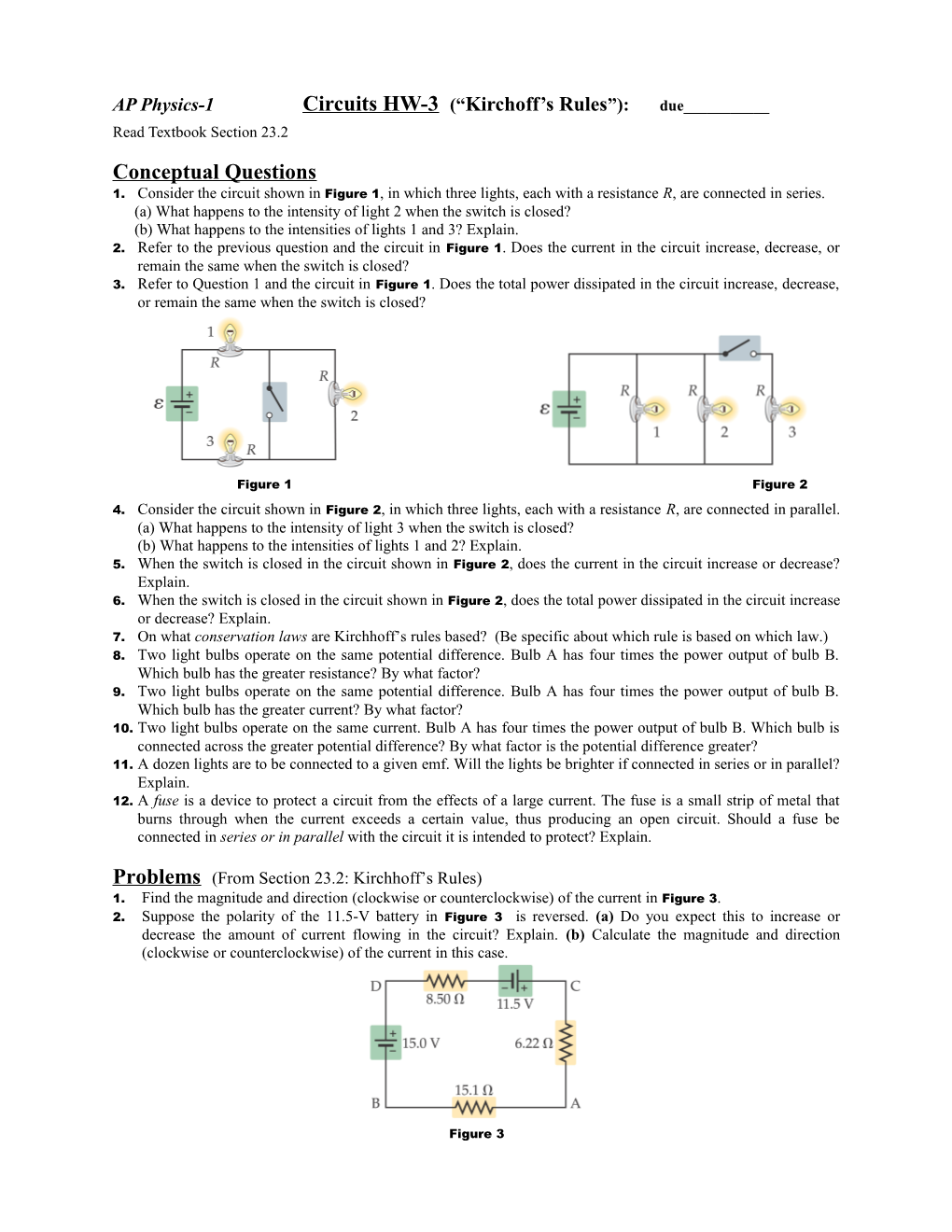
AP Physics-1 Circuits HW-3 (“Kirchoff’s Rules”): due______Read Textbook Section 23.2 Conceptual Questions 1. Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1, in which three lights, each with a resistance R, are connected in series. (a) What happens to the intensity of light 2 when the switch is closed? (b) What happens to the intensities of lights 1 and 3? Explain. 2. Refer to the previous question and the circuit in Figure 1. Does the current in the circuit increase, decrease, or remain the same when the switch is closed? 3. Refer to Question 1 and the circuit in Figure 1. Does the total power dissipated in the circuit increase, decrease, or remain the same when the switch is closed?
Figure 1 Figure 2
4. Consider the circuit shown in Figure 2, in which three lights, each with a resistance R, are connected in parallel. (a) What happens to the intensity of light 3 when the switch is closed? (b) What happens to the intensities of lights 1 and 2? Explain. 5. When the switch is closed in the circuit shown in Figure 2, does the current in the circuit increase or decrease? Explain. 6. When the switch is closed in the circuit shown in Figure 2, does the total power dissipated in the circuit increase or decrease? Explain. 7. On what conservation laws are Kirchhoff’s rules based? (Be specific about which rule is based on which law.) 8. Two light bulbs operate on the same potential difference. Bulb A has four times the power output of bulb B. Which bulb has the greater resistance? By what factor? 9. Two light bulbs operate on the same potential difference. Bulb A has four times the power output of bulb B. Which bulb has the greater current? By what factor? 10. Two light bulbs operate on the same current. Bulb A has four times the power output of bulb B. Which bulb is connected across the greater potential difference? By what factor is the potential difference greater? 11. A dozen lights are to be connected to a given emf. Will the lights be brighter if connected in series or in parallel? Explain. 12. A fuse is a device to protect a circuit from the effects of a large current. The fuse is a small strip of metal that burns through when the current exceeds a certain value, thus producing an open circuit. Should a fuse be connected in series or in parallel with the circuit it is intended to protect? Explain.
Problems (From Section 23.2: Kirchhoff’s Rules) 1. Find the magnitude and direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) of the current in Figure 3. 2. Suppose the polarity of the 11.5-V battery in Figure 3 is reversed. (a) Do you expect this to increase or decrease the amount of current flowing in the circuit? Explain. (b) Calculate the magnitude and direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) of the current in this case.
Figure 3 3. Consider the circuit shown in Figure 4. Find the current through each resistor using (a) the rules for series and parallel resistors, and (b) Kirchhoff’s rules.
Figure 4
4. Suppose point A is grounded (V = 0) in Figure 4. Find the potential at points B and C.
5. (a) Find the current in each resistor in Figure 5. (b) Is the potential at point A greater than, less than, or equal to the potential at point B? Explain. (c) Determine the potential difference between the points A and B.
Figure 5 Figure 6
6. Two batteries and three resistors are connected as shown in Figure 6. How much current flows through each battery when the switch is (a) closed and (b) open?
7. A three-way light bulb has two filaments with resistances R1 and R2 connected in series. The resistors are connected to three terminals, as indicated in Figure 7, and the light switch determines which two of the three terminals are connected to a potential difference of 120 V at any given time. When terminals A and B are connected to 120 V the bulb uses 75.0 W of power. When terminals A and C are connected to 120 V the bulb
uses 50.0 W of power. (a) What is the resistance R1 ? (b) What is the resistance R2 ? (c) How much power does the bulb use when 120 V is connected to terminals B and C?
Figure 7
Answers 1. I = 0.889 A The current flows clockwise . 2. (a) Current will decrease …explain. (b) I = 0.12 A The current flows clockwise . 3. (a) I11 = 0.92 A, I6.2 = 0.27 A, I12 = 0.27 A, I7.5 = 0.65 A (b) Set up 3 equations/matrix to get same I’s.
4. VC = 10 V VB = 4.9 V
5. (a) I3.9 = 0.722 A, I9.8 = 0.722 A, I1.2 = 1.752 A, I6.7 = 1.03 A (b) VA VB … explain (c) VAB = 2.10 V 6. (a) About 0.9 A flows through the 9.0 V battery and about 0.2 A flows through the 6.0 V battery. (b) 0.50 A flows through both batteries. 7. (a) R1 = 190 (b) R2 = 96 (c) P = 150 W