Electronic Supplementary Material (ESM)
Highly sensitive fluorescent chemo-sensor for copper (II) based on amplified fluorescence quenching of a new near-infrared water-soluble conjugated polymer PPEASO3
Lilin Sun · Dan Hao ·Weili Shen· Zhangsheng Qian ·Changqing Zhu* Anhui Key Laboratory of Chemo-Biosensing, College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Anhui Normal University, Wuhu 241000, People’s Republic of China
*Corresponding author, E-mail: [email protected], Tel: 86-553-3937136, Fax: 86-553-3869303
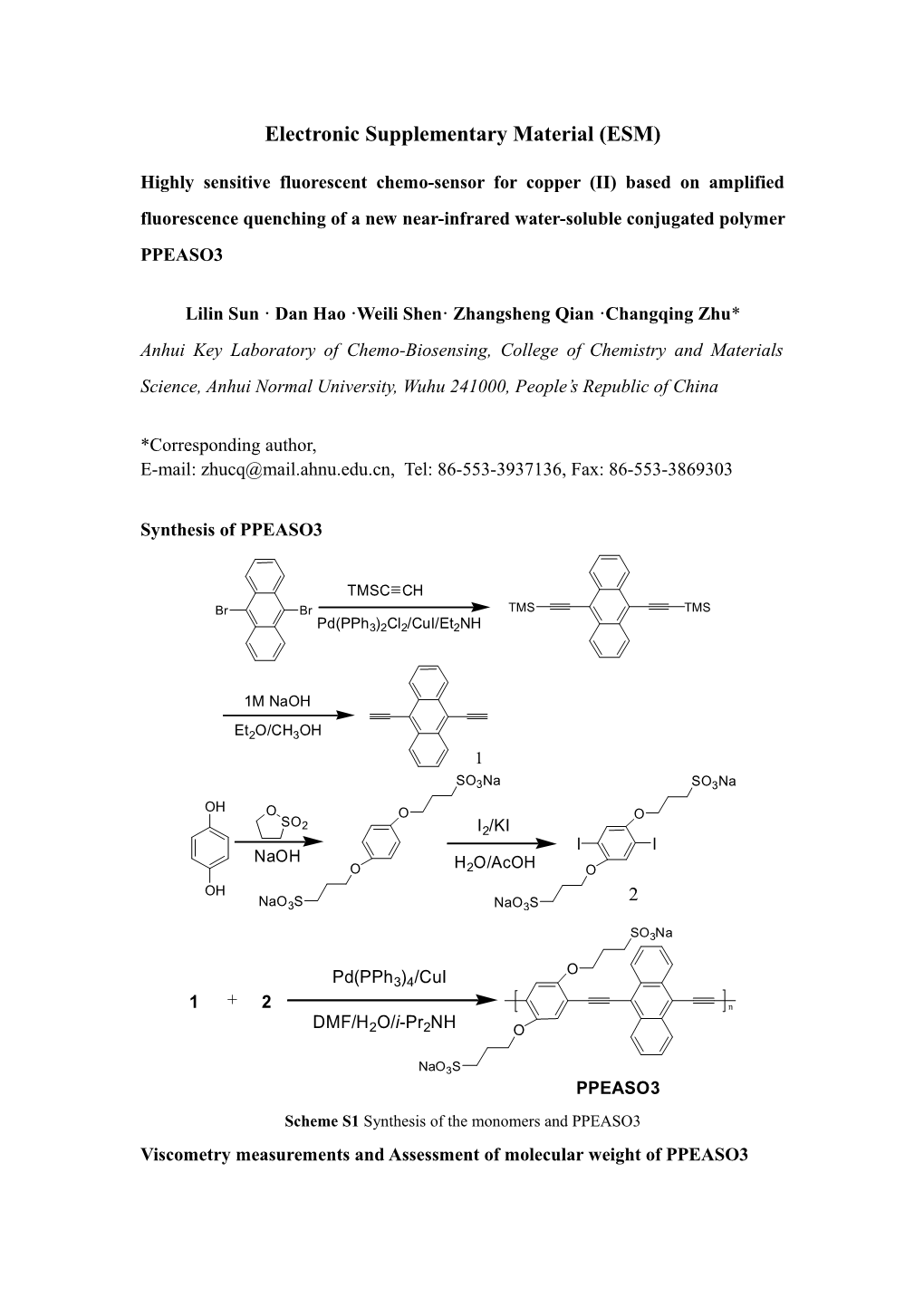
Synthesis of PPEASO3
TMSC CH Br Br TMS TMS Pd(PPh3)2Cl2/CuI/Et2NH
1M NaOH
Et2O/CH3OH 1
SO3Na SO3Na OH O O O SO 2 I2/KI I I NaOH O H2O/AcOH O OH 2 NaO3S NaO3S
SO3Na
O Pd(PPh3)4/CuI
1 + 2 n DMF/H2O/i-Pr2NH O
NaO3S PPEASO3 Scheme S1 Synthesis of the monomers and PPEASO3 Viscometry measurements and Assessment of molecular weight of PPEASO3 The solvent and polymer solutions were first filtered through 2# sand core funnel before use. Relative viscosities were measured in an Ubbelohde viscometer, with an external temperature controlled water thermostat (20 ± 0.1℃).
Fig. S1. Reduced viscosity (ηsp/C´) vs. relative concentration (C´) for PPEASO3 in -3 -1 H2O(0.1M NaNO3) at 20℃(the start concentration of PPEASO3: C0=2.0×10 g·mL )
Figure S1 shows the results of viscometry studied of dilute solutions of PPEASO3 20℃ in water with added salt (0.1M NaNO3). In the high ionic strength solution, intrachain electrostatic repulsions are suppressed, and the viscosity varies as expected for a “normal” polymer solution, i.e. ηsp/C´ increases with C´. Under these conditions the intercept A is obtained by extrapolating the plot of ηsp/C´ vs. C´ to C´=0, and by -1 using the relation of [η]=A/C0, [η]=176.8 mL·g was obtained for PPEASO3. The experimentally obtained value of [η] has been used to compute the polymer’s α Mη value by use of the Mark-Houwink relation [η]=K Mη .
Table S1 lists values of Mη computed for PPEASO3 using K and α values obtained from the literature for three different polyelectrolytes. As can be seen from this analysis, the viscometry data obtained for PPEASO3 in water with NaNO3 suggest that for this polymer Mη ≈ 150KD.
Table S1. Reference Polymers used to Compute Mη for PPEASO3 polymer conditions comments K/mL·g-1 α Computed Ref. a Mη/kD poly(sodium 0.1MNaCl Semi-flexible 1.46×10-2 0.80 127.0 [1] acrylate) polyelectrolyte Cellulose DMA, Worm-like 1.28×10-4 1.19 144.5 [2] 9%LiCl polymer poly(γ-benzyl- DMF Rigid-rod(helix) 1.60×10-5 1.34 180.4 [3] L-glutamate) a Computed molecular weight for PPEASO3 using experimentally determined value of [η]=176.8 mL·g-1 and the K and α values listed for the reference polymer.
References [1] T. Kato, T. Tokuya, T. Nozaki, A. Takahashi, Molecular characterization of sodium poly(acrylate) by an aqueous g.p.c./LS method Polymer 1984, 25, 218-224 [2] Charles L. McCormick, Peter A. Callais, Brewer H. Hutchinson Jr, Solution studies of cellulose in lithium chloride and N,N-dimethylacetamide, Macromolecules 1985, 18, 2394-2401 [3] Satoru Itou, Noboru Nishioka, Takashi Norisuye, Akio Teramoto, Rodlike nature of .alpha.-helical polypeptides in solution Macromolecules 1981, 14, 904-909
Effect of pH on the fluorescence intensity of the PPEASO3
F 300 0 F )
. F -F 0 u . a ( 200 y t i s n e t
n i
e
c 100 n e c s e r o u l 0 F
5 6 7 8 9 pH
Fig. S2 Effect of pH on the fluorescence intensity of the PPEASO3 in the absence (F0) and presence (F) of Cu2+. The concentration of Cu2+ is 5.0×10-6mol/L. Other conditions are the same as described in the procedure. Effect physiologically relevant metal ions on the fluorescence of PPEASO3
2.0
1.5 F
/ 1.0 0 F
0.5
0.0 blank Cu Ca K Na Zn Mg Co Mn Fe
Fig. S3 Effect physiologically relevant metal ions on the fluorescence of PPEASO3. The concentration of these ions: 5.0×10-6 mol/L. Other conditions are the same as described in the procedure.