Name: ______What do Genes Look Like? - notes (part 1)
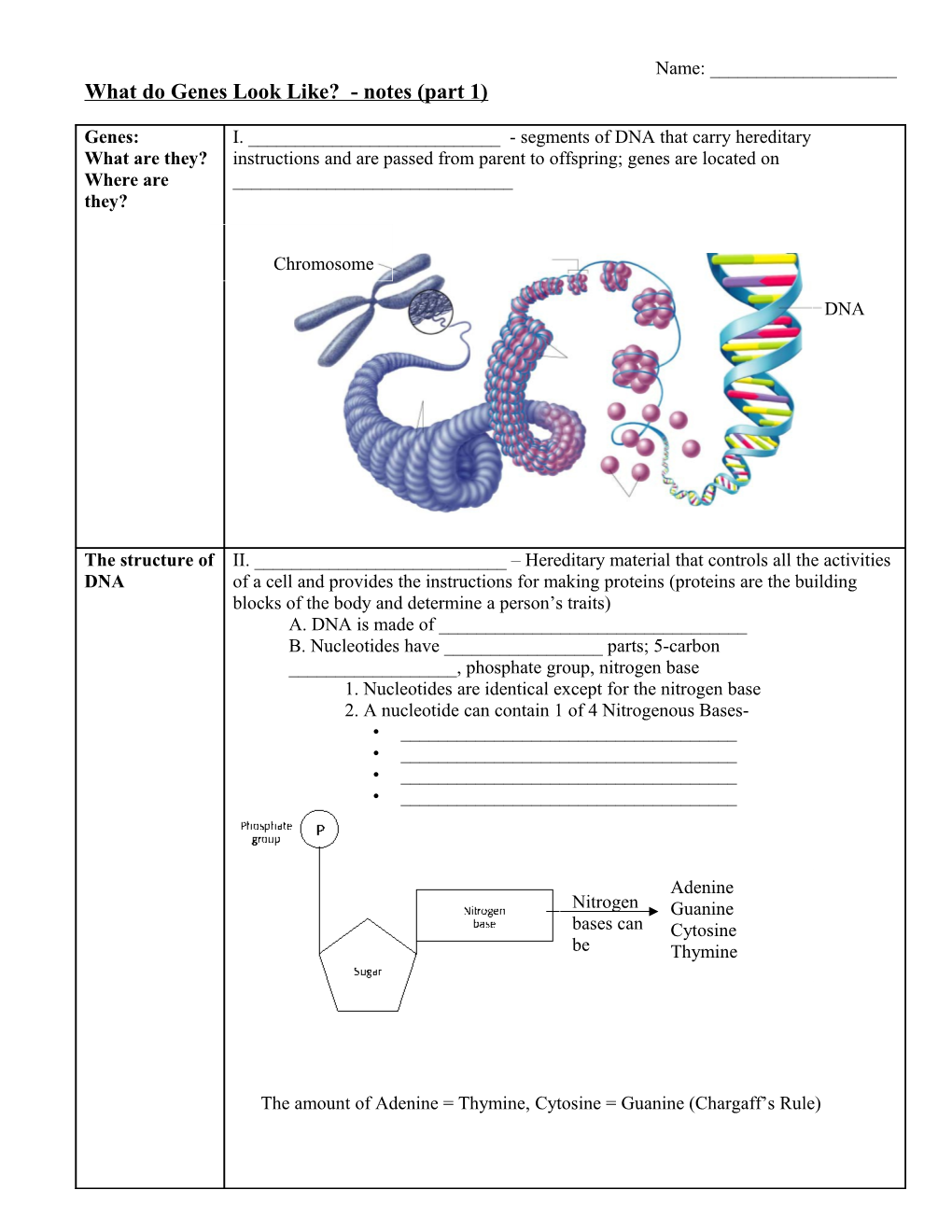
Genes: I. ______- segments of DNA that carry hereditary What are they? instructions and are passed from parent to offspring; genes are located on Where are ______they?
Chromosome
DNA
The structure of II. ______– Hereditary material that controls all the activities DNA of a cell and provides the instructions for making proteins (proteins are the building blocks of the body and determine a person’s traits) A. DNA is made of ______B. Nucleotides have ______parts; 5-carbon ______, phosphate group, nitrogen base 1. Nucleotides are identical except for the nitrogen base 2. A nucleotide can contain 1 of 4 Nitrogenous Bases- • ______• ______• ______• ______
Adenine Nitrogen Guanine bases can Cytosine be Thymine
The amount of Adenine = Thymine, Cytosine = Guanine (Chargaff’s Rule) Name: ______Replication – III. The Double Helix- 1953, 2 American scientists, ______how DNA and Crick, discovered the structure of DNA using the X-rays made by makes a copy of itself Rosalind Franklin A. 2 ______wound around each other like a twisted ladder B. Strands are held together by ______between nitrogenous bases. C. Adenine bonds to ______and Cytosine bonds to ______
Structure of DNA
______bonds
Sugar Phosphate Backbone
Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine
IV. ______: Before a cell divides to produce new cells, DNA on every chromosome is copied so that each new cell has an identical set of chromosomes.
Simulate Replication: Make a complimentary strand of DNA ATT CGT ACG TTT ACT ______
Self Check – 1.The process of Making a copy of DNA during mitosis is called ______part 1 2. How do bases pair up during replication?
3. Replicate the following strand of DNA : ACA GGC TAT AAT ______4. Where is DNA stored in a eukaryotic cell? ______Name: ______What do Genes Look Like? - notes (part 2)
From DNA to I. How DNA works – DNA cannot leave the nucleus. A copy of the DNA code is made Protein in the nucleus into RNA. RNA travels out of the nucleus to the ribosome where the code is read and the protein is assembled. A. The nitrogen bases in every gene make a ______B. Every three bases makes one ______C. One codon is the code for one ______D. Long chains of amino acids make______. E. Proteins determine an organisms characteristics and traits Translation: II. Making a Protein: Translation Using RNA and The Genetic DNA in the Nucleus: ATA GCT CCG TTA Code to make Proteins Code is made into RNA: UAU CGA GGC AAU ***In RNA Thymine is replaced by ______******
Amino Acid Chain is made at the ribosome: Tyrosine: Arginine: Glycine: ______
Genetic III. ______- changes in the DNA sequence that affect Mutations genetic information; Can affect all types of cells (not all are harmful).
A. ______- affect sex cells – inherited by offspring (ex- Down Syndrome) B. ______– affect other cells- not inherited by offspring (many cancers caused by somatic mutations)
Two Types of IV. 2 types of mutations DNA mutations A. ______(#1) - changes in a single gene. 2 types of gene mutations- 1. ______- affect only one nucleotide *Can be caused by substitutions 2. ______- type of point mutation where nucleotide is inserted or deleted; affects every amino acid after that point. *Can be cause by insertions or deletions
B. ______(#2) - changes in whole chromosomes. 4 types of chromosomal mutations.
1. ______-- loss of all or part of chromosome
2. ______- segment of a chromosome is repeated
3. ______-chromosome becomes reversed
4. ______- part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to a different chromosome Name: ______Effects of DNA mutations V. What are the effects of______-?
A. ______are altered.
B. ______are unable to perform “normal” functions.
Sometimes ______are harmful, sometimes there is no affect, and sometimes mutations can be helpful. (Helpful when mutation produces a trait that aids in survival) Changing DNA on purpose VI. ______- when humans change the genes of an organism to achieve a desired result
A. ______- allowing only the individuals with desired traits to reproduce. 2 types
1. ______-crossbreeding dissimilar individuals: offspring will have the best of both Ex: donkey x horse = mule
2. ______-breeding individuals with similar characteristics: maintain certain characteristics in offspring Ex: German Shepard x German Shepard = German Shepard
VII. ______– Desired genes are removed from one organism and added or recombined into another organism. This forms a transgenic organism with recombinant DNA A. This is used to make proteins not normally made by the cell. Can be used to produce: Drugs like insulin, Vaccines, Plants resistant to Insects, Reduce pollution, Better crops/meat
DNA and VIII. Evolution –natural process through which species ______over Evolution time
A. The ______“selects” the best traits – only those best suited will survive and pass on their traits to offspring.
B. ______– occurs because of genetic differences caused by mutations in DNA