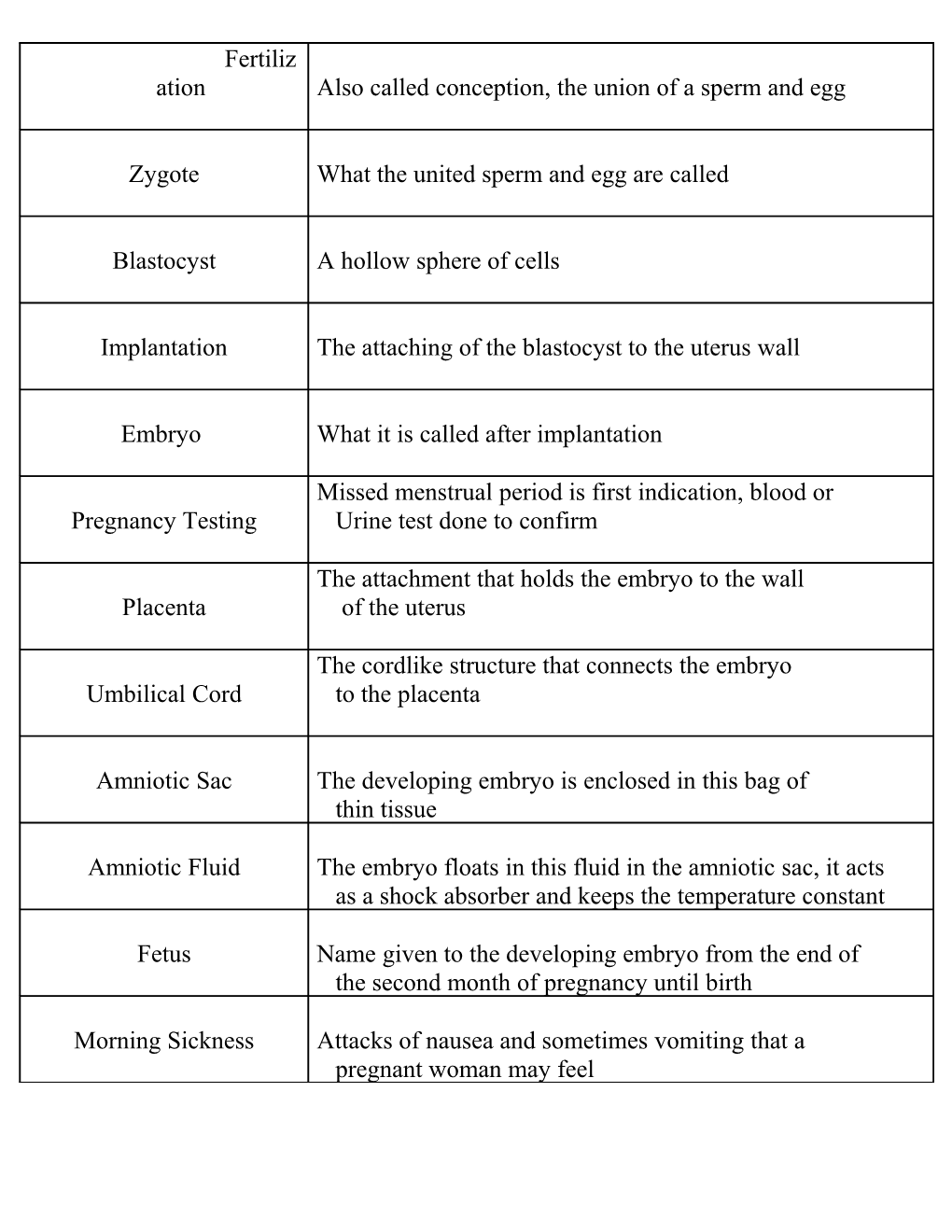
Fertiliz ation Also called conception, the union of a sperm and egg
Zygote What the united sperm and egg are called
Blastocyst A hollow sphere of cells
Implantation The attaching of the blastocyst to the uterus wall
Embryo What it is called after implantation
Missed menstrual period is first indication, blood or Pregnancy Testing Urine test done to confirm
The attachment that holds the embryo to the wall Placenta of the uterus
The cordlike structure that connects the embryo Umbilical Cord to the placenta
Amniotic Sac The developing embryo is enclosed in this bag of thin tissue
Amniotic Fluid The embryo floats in this fluid in the amniotic sac, it acts as a shock absorber and keeps the temperature constant
Fetus Name given to the developing embryo from the end of the second month of pregnancy until birth
Morning Sickness Attacks of nausea and sometimes vomiting that a pregnant woman may feel Fetal Alcohol Is mental retardation caused by alcohol use, which Syndrome damages the fetus’s brain cells
Prenatal Care Medical care during pregnancy
Obstetrician A doctor specialized in pregnancy and childbirth
Trimesters A pregnancy is divided into three periods
Involves the removal or a small amount of amniotic Amniocentesis fluid from around the fetus
Chorionic villus sampling Doctor removes a small piece of the placenta
Ultrasound High frequency sound waves that are used to make a picture of the developing fetus Labo r The work of pushing the fetus out
Delivery The actual birth of the baby, during which the baby is pushed out through the cervix and vagina
Afterbirth The third stage of labor when the placenta is delivered
Gestational Diabetes Diabetes that develops in pregnant women, marked by high blood sugar levels
Preeclampsia Also called toxemia, characterized by high blood pressure, swelling of wrists and ankles, and high protein in urine When the blastocyst forms and implants in the Ectopic Pregnancy fallopian tube or elsewhere in the abdomen, it results in the death of the embryo and surgery is required Miscarriage Expulsion of a dead zygote, blastocyst, embryo, or Fetus from the uterus – usual cause is a genetic defect
Stillbirth The birth of a dead, full-term fetus
Cesarean Section Is a surgical method of birth
Premature Birth Delivery of a live fetus before it is ready to be born
Lowbirth weight A newborn that weighs less than 5.5 pounds
Identical Twins Develop from the same fertilized egg or zygote, have identical inherited traits and are the same sex
Fraternal Twins Develop when two eggs are released from the ovary and are fertilized by two sperm
Postpartum Begins with delivery and lasts about six weeks. It is a Depression period of adjustment for the parents and their newborn