Section 1.2 MEASUREMENT
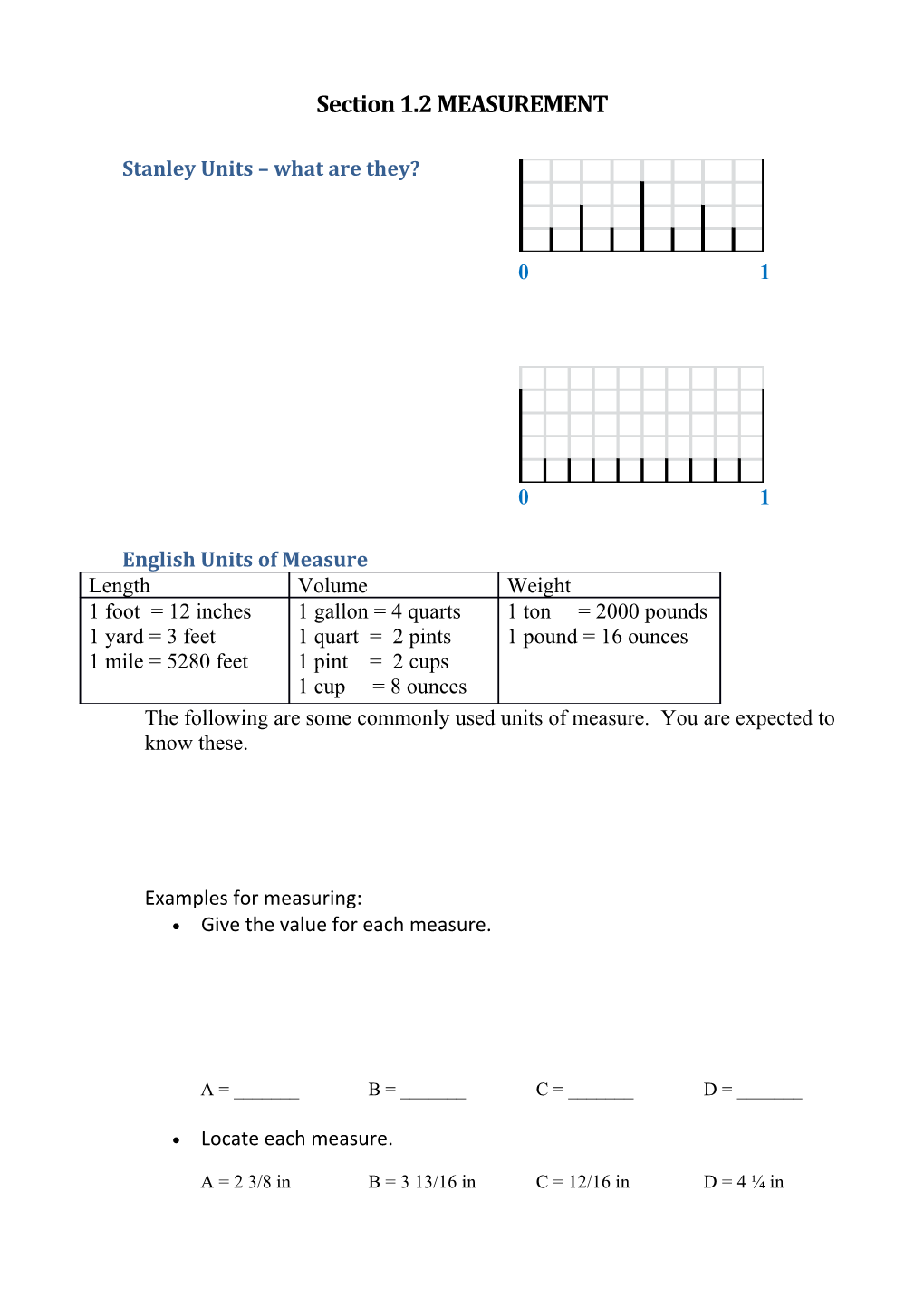
Stanley Units – what are they?
0 1
0 1
English Units of Measure Length Volume Weight 1 foot = 12 inches 1 gallon = 4 quarts 1 ton = 2000 pounds 1 yard = 3 feet 1 quart = 2 pints 1 pound = 16 ounces 1 mile = 5280 feet 1 pint = 2 cups 1 cup = 8 ounces The following are some commonly used units of measure. You are expected to know these.
Examples for measuring: Give the value for each measure.
A = ______B = ______C = ______D = ______
Locate each measure.
A = 2 3/8 in B = 3 13/16 in C = 12/16 in D = 4 ¼ in Metric Units of Measure The metric system is based on powers of ten. It is far more easily understood than our English system. One reason we may disagree is because we “grew up” with the English system. There was a time when there was a concentrated movement towards using metric, but because it met with such resistance, that effort has gone away. Kilo 1000 Hecto 100 Deka or Deca 10 Unit (meter, liter, gram) Deci 0.1 (one tenth) Centi 0.01 (one hundredth) Milli 0.001 (one thousandth) Some common conversions you should know: 1 km = ______m 1 m = ______km 1 m = ______cm 1 cm = ______m 1 m = ______mm 1 mm = ______m 1 cm = ______mm 1 mm = ______cm
The following are some metric units of measure. Those in bold are most commonly used metric measures. kilo hect deka UNIT deci centi milli 103 102 101 100 10-1 10-2 10-3 1,000 100 10 1 0.1 0.01 0.001 l kilometer hectometer dekameters meter decimeters centimeters millimeter e km hm dam m dm cm mm n 3-story g about 6 length of floor to a width of width of thickness tall door knob t city football palm little finger of a dime building h blocks field nail c kiloliter hectoliter dekaliter liter deciliter centiliter milliliter a kL hL daL L dL cL mL p between a 3 very full 15-minute ½ of a 5- 1 liter about 2 20 eye bathtubs 1/3 & 1/2 of c low flow gallon bottle of teaspoons dropper a cup i shower bucket Pepsi™ drops t y kilogram hectogram dekagram gram decigram centigram milligram m kg hg dag g dg cg mg a 1 liter about 3.5 about 1/3 a caffeine in a small 25 grains s bottle of ounces ounce papercli a cup of raindrop of sugar s water p or real coffee aspirin
Once you know and understand some basic relationships in the Metric system, finding others (converting from one unit of measure to another) can be easy; especially, if you have a TRICK.
So let’s say you have some conversions to do, but you don’t have a table handy and you’re not really sure about which one is which. Remember the following. King Henry King Henry Drinks Unsweetened Dark Chocolate Milk
_____|______|______|______|______|______| ______|_____ Kilo hecto deka unit deci centi milli meter liter gram Examples:
1) 5m = ______cm Move the decimal point the number of spaces and direction needed to go from “m” to “cm.”
2) 0.08kg = ______g Move the decimal point the number of spaces and direction needed to go from “kg” to “g.”
3) 435ml = ______l Move the decimal point the number of spaces and direction needed to go from “ml” to “l.”
4) 180064cm = ______km
5) 36.814kg = ______mg Examples for measuring:
Give the value for each measure.
In mm A = ______B = ______C = ______D = ______
In cm A = ______B = ______C = ______D = ______
Locate each measure.
A = 13 mm B = 100 mm C = 48 mm D = 125 mm
E = 2.6 cm F = 4 cm G = 9.3 cm H = 0.3 cm Examples: In each example below we are going to start with the number 14.3498. The whole portion of this number (14) is not going to change, so we only need to address the decimal portion.
Change to 4ths Change to 8ths Change to 16ths
14-1/4in 14-3/8 in 14-3/8 in
Change to 32nds Change to 64ths
14-11/32 in 14-22/64 in Now is a good time to check out the appendix in your text. Mark this page with a post-it or sticker as it will prove to be very helpful in working your problems. Common Abbreviations & Symbols:
Metric:
mm = millimeter cm = centimeter m = meter km = kilometer
mL = milliliter dm = decimeter L = liter dL = deciliter
mg = milligram cg = centigram g = gram kg = kilogram
Standard:
“ = in = inch ‘ = ft = foot yd = yard mi = mile
gal = gallon oz = ounce lb = pound
Common Conversions:
Length: Standard Length Metric Length Standard to Metric 1 ft = 12 in 1 m = 100 cm 1 in = 2.54 cm 1 yd = 3 ft 1 m = 10 dm 1mi = 1.61 km 1 mi = 5280 ft 1 m = 1000 mm 3.281 ft = 1 m 1 km = 1000 m
Area: Standard Area Metric Area Standard to Metric 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 ft = 144 in 1 m = 10,000 cm 1 in = 6.452 cm 2 2 2 2 1 yd = 9 ft 1 cm = 100 mm 2 1 acre = 43,560 ft 2 1 mi = 640 acre
Volume: Standard Volume Metric Volume Standard to Metric 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 ft = 1728 in 1 m = 1,000,000 cm 1 in = 16.387 cm 3 3 3 3 3 1 yd = 27 ft 1 cm = 1000 mm 1 oz = 29.574 cm 3 3 3 1 yd = 46,656 in 1 L = 1000 cm 1 gal = 3.785 L 3 1 gal = 231 in 1 L = 1000 mL 3 1 ft = 7.48 gal 1 L = 10 dL 3 1 gal water = 8.345 lb 1 mL = 1 cm
Weight: Standard Weight Metric Weight Standard to Metric 1 ton = 2000 lbs 1 g = 1000 mg 1 ton = 907.2 kg 1 lb = 16 oz 1 kg = 1000 g 1 oz = 28.35 g 1 lb = 453.6 g Example 1: Calculate the space between each fence slat if the spaces are all equal. Give your answer to the nearest 8th of an inch.
Example 2: Calculate dimensions X & Y so that all 8 gaps between the circles are the same size. Give your answer to the nearest 16th of an inch.
Homework: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 (16 problems). Work needs to be labeled, neat, and organized. 18 6 Section 1.2 17 7 1. A = 1 , B = 2 , C = 3 , D = 4 , E = 5 16 7 2. A = 1 , B = 2 , C = 3 , D = 4 , E = 5
3. A = 1.8 cm, B = 4.1 cm, C = 7.6 cm, D = 11.9 cm
4. A = 25 mm, B = 52 mm, C = 76 mm, D = 108 mm, E = 139 mm
5. A = 35, B = 25, C = 32, D = 13, E = 36, F = 16, G = 20, H = 53, I = 19, J = 19, K = 20, L X-Coordinate Y - Coordinate = 26, M = 51, N = 21, P = 19, Q = 33, R = 26, S = 12 *Note: copy machines will P2 0.000 1.875 have an effect on the measurements (all in millimeters). P4 1.250 3.750 P6 3.750 0.000 6. A = 1 , B = 1 , C = 1 , D = , E = 1 , F = , G = , H = 2 , I = , J = , K = , L = 1 , M = 2 , P9 1.375 3.000 N = , P = , Q = 1 , R = 1 , S = *Note: H3 0.625 2.500 copy machines will have an effect on the measurements. H6 2.500 2.750
7. H8 1.875 2.250
8. 26 boards, spacing = H9 3.000 0.750
9. a) .025” ≈ 15.
b) .041” ≈
c) .065” ≈
10. Loose pilot holes: , , ,
Tight pilot holes: , , ,
11. Width = Height = 1
12. 7 X-Coordinate Y - Coordinate
13. 15 Rises, Rise height = 7 P1
14. Number of rises Rise height P3 -1 2
20 6 P5 2 3
19 6 P7 1 1 P8 1 2
P10 1
H1 0 0
H2 1
H4 2
H5 2
H7 1 1
16. 17. 4
18. 4
19.
Working Tooth Clearance Depth Thickness
.253 in .020 in .199 in
1.687 cm .133 cm 1.325 cm
.358 in .028 in .281 in
.300 in .024 in .236 in