Biology notes-Chapter 2-The Chemistry of Life…. Name______
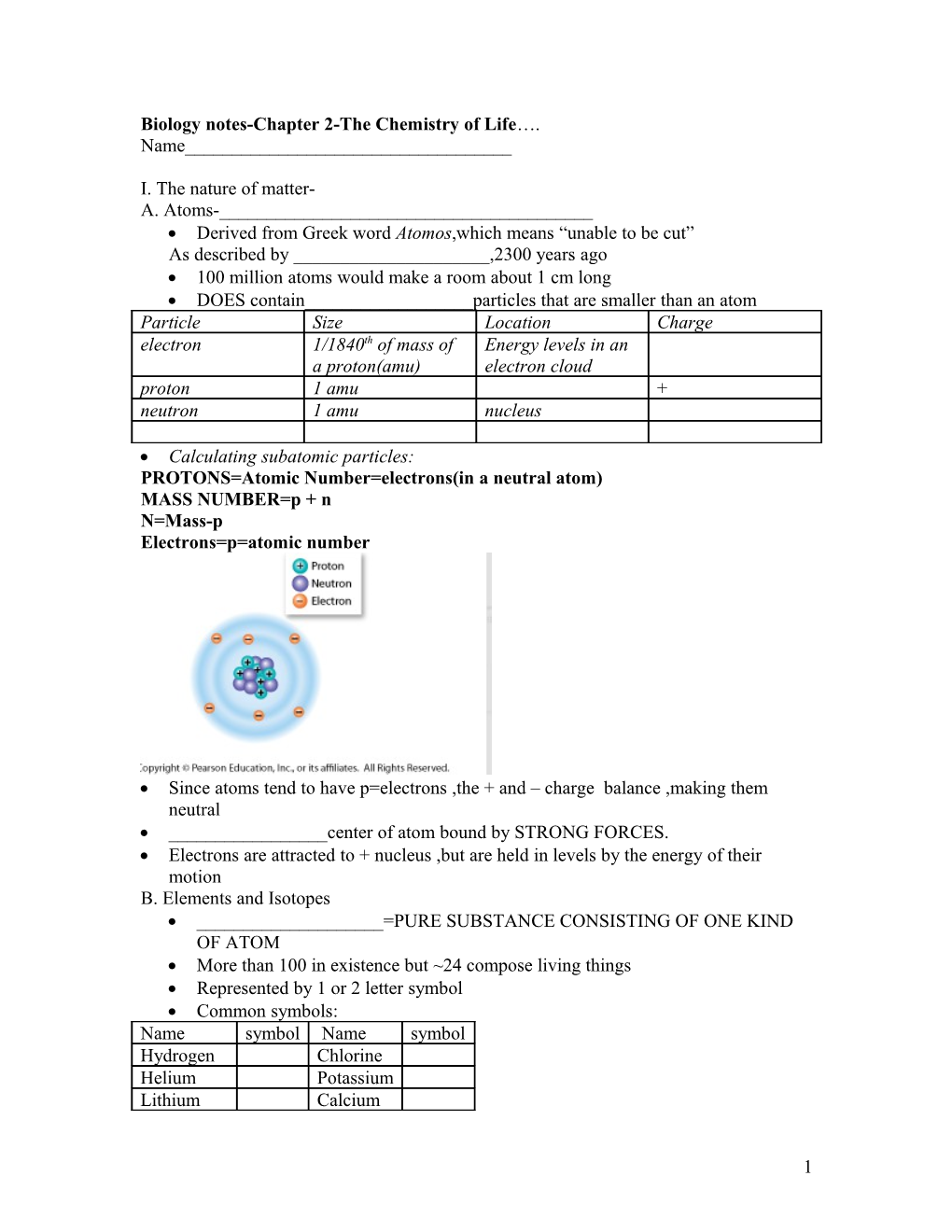
I. The nature of matter- A. Atoms-______ Derived from Greek word Atomos,which means “unable to be cut” As described by ______,2300 years ago 100 million atoms would make a room about 1 cm long DOES contain______particles that are smaller than an atom Particle Size Location Charge electron 1/1840th of mass of Energy levels in an a proton(amu) electron cloud proton 1 amu + neutron 1 amu nucleus
Calculating subatomic particles: PROTONS=Atomic Number=electrons(in a neutral atom) MASS NUMBER=p + n N=Mass-p Electrons=p=atomic number
Since atoms tend to have p=electrons ,the + and – charge balance ,making them neutral ______center of atom bound by STRONG FORCES. Electrons are attracted to + nucleus ,but are held in levels by the energy of their motion B. Elements and Isotopes ______=PURE SUBSTANCE CONSISTING OF ONE KIND OF ATOM More than 100 in existence but ~24 compose living things Represented by 1 or 2 letter symbol Common symbols: Name symbol Name symbol Hydrogen Chlorine Helium Potassium Lithium Calcium
1 Boron Arsenic Carbon Bromine Nitrogen Radon Oxygen Silver Fluorine Gold Neon Mercury sodium Tin Iodine Magnesium Aluminum Barium Silicon Radium Uranium Phosphorus Isotopes-atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons---- example:C-12,C-13,C-14----all averaged together for the atomic mass Isotopes are identified by ______. Radioactive Isotopes have unstable nuclei and break down at a constant rate over time… Radioactive Isotopes uses:______- All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties because they have the same # of ______-. ‘WEIGHTED MASS”-ie .Atomic weight=average mass of all isotopes for an element
C. Chemical Compounds=______ Shown by a chemical formula Physical and chemical properties for an element differ a lot when they are bound in a compound What is the ratio of H:O on H2O?______
2 Physical properties:______ Chemical properties:______D. Chemical Bonds hold together atoms in a compound 1. Ionic Bonds-electrons are transferred from one to another creating an electrical ,ionic charge that binds the atoms
Tends to happen between metals and nonmetals Looking @ p.37 ,draw what happens in a NaCl bond
2. Covalent Bonds-______ The moving electrons of both atoms travel in the orbits of both atoms Double or triple bonds occur when 4 or 6 electrons are shared ______-smallest unit of a compound See drawing 2-4 on p.37 and draw the bond of H2O
E. Van der Waals Forces_intermolecular forces that result from unequal sharing that results in tiny + or – charges in covalent bonds Help hold a molecule together a little more….see example of gecko on p.38 Rapid movement of electrons can create regions of tiny (+) and (-) charges/As some molecules are close together,slight attraction between oppositely charged regions of nearby molecule-esp. when molecule is large
II. Properties of water Single most abundant compound in most living things A. The Water Molecule
3 ______-because of an uneven distribution of electrons between O and H atoms O side is more – pole because it has more electrons It is ,essentially ,neutral ,but has a more – and more + end Because of this polarity water molecules can attract one another Polar charges are written in ( ) to show they are weaker than ionic charges H bonds not strong ,but water can form______H bonds…..causing many of its properties/bonding with itself O,N, and F A single water molecule can be involved in as many as 4 H-bonds ______-attraction between molecules of the same substance…water is cohesive-example-surface tension allows spiders to walk on water ______-attraction between molecules of different substances-example-water creating meniscus as attaches to sides of graduated cylinder H20 bonding in H2O is Unique orientation that enables expanding as freezes HEAT CAPACITY---because of H-bonds ,takes a lot of heat to get water molecules moving faster, creating high heat capacity….helping organisms maintain body temp’s Look @ ppt and describe the effect of capillary action and how it is used in nature:______B.Solutions and Suspensions Water is often in a ______,where 2 or more elements or compounds are PHYSICALLY combined 2 types; 1) ______mixture where components evenly distributed Ions are surrounded by water molecules and evenly distributed ______-substance dissolved ______-substance that does dissolving 2) ______-mixtures of water and non dissolved materials—blood cells in a suspension of water in vessels
4 B. Acids,Bases and pH- Water molecule can react to form ions.Draw reaction as shown @ bottom of p.42:
______indicates concentration of H ions in solution
Acid BASE
5 Each step represents a power of 10-example-pH of 5 has 10 x as many H+ ions as same qty of ph 6 ______-higher concentrations of H+ ions and pH <7 ______-alkaline-lower H+ concentration and pH>7 ______weak acids or bases that react w/ strong ones to prevent sharp pH changes Buffers are dissolved in life’s fluids ,playing an important role in maintaining homeostasis in organisms
6 III. Carbon Compounds In the 1800’s,chemists thought compounds created by living things –organic compounds- were much different than others In 1838 a German chemist made the organic compound,urea ,from nonorganic ammonium cyanate…Thus principles of chemistry governing nonliving could be applied to living things
7 ______is actually the study of almost all C-compounds-many not having anything to do w/ living things. A. The Chemistry of Carbon Why is carbon special?---1) It has 4 valence electrons and can make 4 bonds 2)It can bond w/ many other elements. Includes H,O,P,S,N to make molecules of life 3)C can bond to other C’s in single,double or triple bonds 4)C can form chains and rings
methane acetylene
butadiene
benzene
isooctane Forms millions of different complex structures.
8 B. Macromolecules
“Giant molecules found in organisms “ Formed by ______,in which large compounds are built by joining smaller ones. ______-small units –join to form ______-large molecules
The 4 groups of macromolecules are______C. Carbohydrates
Made up of C,H and O in ,uaually, a ratio 1:2:1. Used by organisms for energy-main source. Used for structure-by plants and some animals. Break down of sugars,like glucose(C6H12O6)provides immediate energy for cell activities
9 sucrose CARB Starches are complex carbohydrates-stores extra energyMONOMER Single sugars are called ______,like glucose,galactose and fructose. Sucrose=disaccharide-made of 2 sugars(notice structure in picture) ______are large molecules formed from monosaccharides -such as glycogen or animal starch—glycogen from the liver helps out when glucose levels run low.This is also stored in muscles for energy.
Plants have plant starch and cellulose ,which gives plants their structure----major component of wood and paper.
10 D. Lipids
Large ,varied group of macromolecules that are generally are ______in water Includes fats ,oils,waxes Made mostly of C,H and O Groups are ______. Can be used to store energy Some are parts of biological membranes or waterproof coverings Many are formed when glycerol is combined w/ fatty acids 1) If each C atom is joined to another C atom by a single bond it is called
11 ______.This is because it has the max # of H-atoms.These are______.
2) If there is at least 1 C-C double bond ,it is called ______.These are ______@ room temp.example-olive oil
If there is more than 1 C-C double bond,it is______examples:oils such as corn,sesame,canola and peanut Monomer basically glycerol and fatty acids….see analyzing data,p.48
E. ______=macromolecules containing C,H,O,N and P
12 Polymers assembled from monomers called______, which contain 3 parts: 1. 5-C sugar 2. phosphate group 3. nitrogenous base Nucleic Acids store and transmit ______or genetic info…2 types of nucleic acids
1. ______-,involved in protein synthesis and has the sugar______. 2. Single strand
RNA 3. ______-contains genetic code and has the sugar ______.
DNA Double helix Contains deoxyribose
13 For heredity F. ______=macromolecules containing C,H,O and N and composed of amino acids (monomer) ______are compounds w/ an amino group(-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group(-COOH) on the other end. Look @ Fig 2-17 on p. 48
basic amino acid formula More than 20 amino acids in nature All amino acids alike in region where they may be joined by covalent bond.Thus any amino acid can be joined to any amino acid-by bonding an amino group to a carboxyl group The portion of each amino acid that is different is the side chain called a ____group.Some of these R groups are acidic and some are basic…some polar and some nonploar.Some have C rings . The instructions for assembling amino acids into different proteins is stored in____.
Each protein has a specific role….various functions include: 1. control ______rates(enzymes). 2. regulate cell processes . 3. forming bones and muscles 4. transporting substances into and out of cells 5. fighting diseases
14 up to 4 levels of organization 1st –sequence of amino acids in a protein chain 2nd –amino acids within a chain can be twisted or folded 3rd –chain itself is folded—If there is more than one chain,each chain has a specific arrangement in space. 4th –Van der Waals forces and H-bonds help maintain a protein’s shape.
IV. Chemical Reactions and Enzymes A. Chemical reactions=______Some are fast and some are slow The elements entering into the reaction are ______and that which is produced are the ______. Co2 + H2OH2CO3 reaction that allows release of CO2 from the bloodstream The above reaction is reversed in reactants products the lungs.
15 Chemical reactions always involve the breaking of bonds in ______and the formation of new bonds in ______. B. Energy in Reactions Energy is released or absorbed in chemical reactions. 1. Energy Changes- Chemical Reactions that release energy are called ______and often occur spontaneously. Example: 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O….energy released as heat/sometimes as light and sound
Chemical reactions that require energy are called______and usually doesn’t occur by itself Example: 2 H2O 2H2 + O2 requires an electrical current---NEEDS AN ENERGY SOURCE
Organisms must have a source of energy to carry out necessary reactions.Plants get this from products of ______and animals get it from consuming plants or other animals….thus from metabolizing food 2. Activation energy- ______
16 B. Enzymes- ______A ______is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering activation energy. Enzymes speed up reactions that take place in a cell ______speeds up the release of CO2 from the bloodstream. Enzymes are specific to the reaction they speed up and usually named on the basis of the reaction. C. Enzyme Action-
Reactants must collide w/ sufficient energy to make ______. 1. ENZYME-SUBSTRATE COMPLEX-enzymes provide a site where reactants can be brought together to react,thus reducing energy needed for the reaction.-made of proetein Reactants of enzyme-catalyzed reactions are called ______. Enzymes themselves unchanged in a reaction Often end in –ase/sugars in -ose
17 Substrates bind to a site on the enzyme called the ______.These are complementary shapes..These are bound together by intermolecular forces making an______These are bound together until the reaction is done. 2. REGULATION OF ENZYME ACTIVITY Affected by many variables,such as temperature ,pH Cells can regulate enzymes in many ways—often w/ a protein that turns the key enzymes on and off.
18