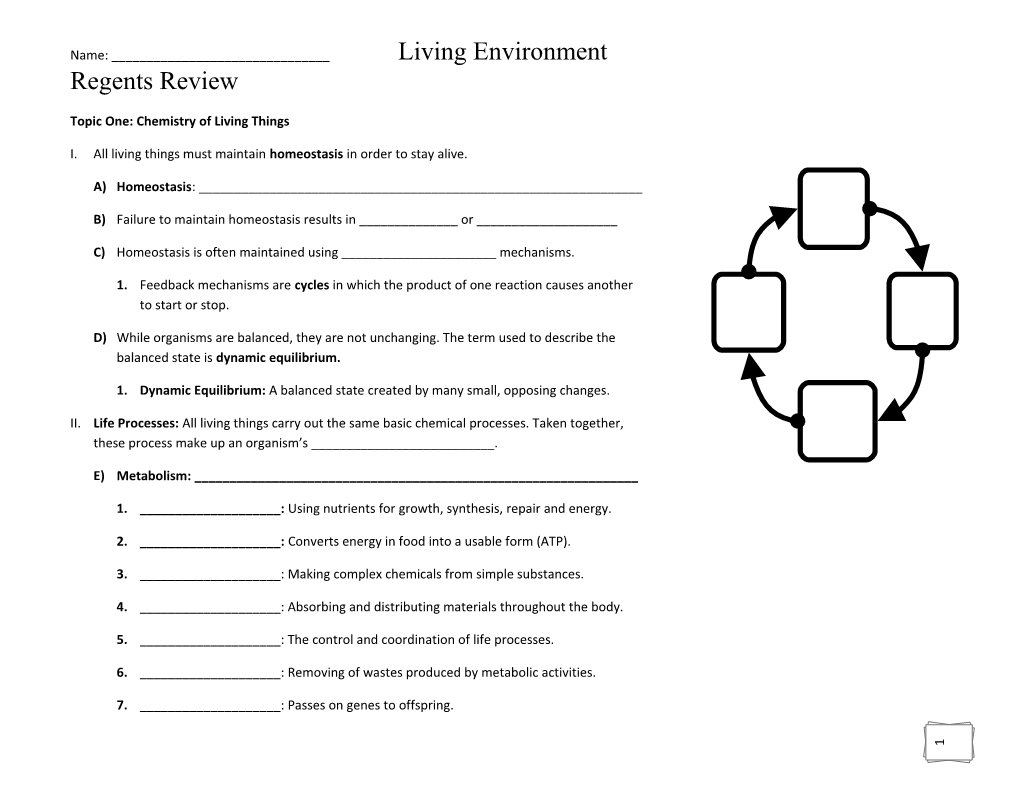
Regents Review ______Name: II. I. One:Chemistry ofLiving Topic Things C) B) A) All livingthings maintainmust E) makethese up process an organism’s ______. Processes: Life D) 1. Homeostasis is often maintained ______using mechanisms. to Failure maintain homeostasis results in ______or ______Homeostasis 7. 6. 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. Metabolism: 1. balanced state is areWhile organisms balanced,they are unchanging. not The usedterm describe to the to start start stop.to or Feedback mechanisms are ______: Passes on genes offspring. to ______: Removing wastes of metabolicproduced by activities. ______: The control and coordination processes. life of ______: Absorbing and distributing materials throughout the body. ______: Making complexchemicals simple from substances. ______: ______: Dynamic Equilibrium: All living carrythings the out same basic processes. chemical Taken together,
: ______: ______dynamic equilibrium.dynamic A balanced state by created many small, changes. opposing homeostasis Converts energy in into food usablea (ATP). form Using nutrientsUsing growth, for repair synthesis, and energy. cycles in which the productone of reaction another causes in order stay to alive.
Living Environment
1 38 III. F) ChemicalsInorganic I) H) G) Water Nitrogen Dioxide Carbon Oxygen ( _____) : common Most substance in all living (aboutthings 60% of mass)body (______): Neededby the body.the otherDissolves molecules into Needed forchemical reactions (won’t happenin “dry” conditions) and eatenand then animals. by into Converted makeNeeded to protein. Waste product of yeast). Theseorganisms need not todo breathe in oxygen. oxygen. so Gives less energy, used only someby simpleorganisms (some bacteria, Anaerobic respiration: that extracts Process energy glucose from usingwithout (sugar). Usedmost by organisms. Aerobic respiration: byReleased and plants algae as waste a product of (_____): common Most gas in air (70%) (______): With used water, by to plants make glucose ( : Simple compounds ______aerobic respirationaerobic Process that uses extract oxygento most (not all) for organisms solution, solution, by soil by bacteria. are Nitrates absorbed plantsby . allowing them be to cellular cellular respiration ______energy transported transported photosynthesis) from glucose . through through . . IV. (C)and hydrogen (H). simplerSynthesized from substances (building blocks). CompoundsOrganic J) M) L) K) Acids Bases:Acids and Used fordifferent in functions body (such digestion).as Proteins: Proteins: 1. ______Lipids: 2. 1. ______Carbohydrates: Functions: Functions: blocks Building acid, oracid, HCl). fastest in acidic environments, which is why we make acid stomach (hydrochloric pH can affect rates chemicalof for reactions; example, digestive and Very high very pHslow usually are lethal. Measured theby pH scale asExcreted wastein ______or ______. ______(starch) ______Complex compounds that out carry all the body’sactivities. : Larger,: morecomplex chemicals. Always contain the elements carbon : ______enzymes enzymes work lock andlock keymodel Thissimple the (C,D). also sugars aof is good example two is(B)A (A) enzyme starch into down by broken an .
37 38 II. I. The Two: Topic Cell Cell Theory Cell Definition: N) 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. 1. 1. Acids andNucleic RNA) (DNA Important types of proteins: and KeyLock Model: manyHave different as functions determined by their ______. After proteins water, theare plentiful most substances in the body. blocks: Building Unicellular –Unicellular celled single (amoeba, organisms paramecium) ______blocks Building ______has three parts: Antibodies Antibodies attack– foreign Cell receptors in – cell membrane; andreceive hormones neurotransmitters. Hormones will it the ofacanwith itsfunction.Changing protein interact shape what change Enzymes functioning. functioning. isThis whyfevers high dangerous.are High temperatures will enzymes cause denature to their and(lose shape) stop - act as and : Nucleotides; bases (ATCGU) molecular ______neurotransmitters catalysts Proteins must havethe right shape “fit” to other with molecules. : Make : up genes and chromosomes. , controllingall chemical reactions in the body. pathogens – carry – messagesthrough the body. Cell Organelles: Organelles: Cell III. Organization B) 3. 2. 2. 1. 2. 1. Cell to the Exceptions Theory the ideathe that livingthings regularly emerged from things. nonliving seemsThis obvious now, but oneat people time believed in ______and feeling. Whenget you sick, it is because yourcells not are correctly.working Everything you is do the the result of work yourcells talking, walking, – even thinking ______(humans).cells all structures Almost in multicelled organisms made are of orcells. by Multicellular havemore – than cell; may 1 be few a only or(vorticella), many ______ ______could obviously not comeanother from cell. somanyprocesses, considerbiologists not do them living true things. ______not are cells. made of However, they alsodo carry not all out life Fluid/liquid in the Fluid/liquid cell mostly – water Contains hereditary (chromosomes, material DNA)genes, Controls the cell These are the cell tiny thatparts make a up cell. spontaneous generation trillions , of
37 38 5. 4. 3. 8. 7. 6. ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Food vacuolesFood may digest molecules.large food, Stores waste water and proteinsMakes amino from acids. energyGives cell (Powerhouse of cell).the Carries cellular out respiration. Helps transport material ______. Controls what enters and cellleaves the using cellSeparates from interior environment found inNEVER animal cells. structureGives shape, and protection. andPlant algae cells only Carries out Waste may vacuoles excrete waste out cellthe membrane photosynthesis ______I. Reminder: Photosynthesisand Respiration Three: Topic Nutrition, Nutrition C) B) A) 3. 2. 1. 2. 1. ______) and convert them into organic nutrients (______). Nutrition: Autotrophic 1. Digestion Ingestion: 4. All life processes are ______ ______is most commonof form autotrophic nutrition Auto ______= ; troph= ______soAutotroph = ______ ______intothe bloodand of cells organisms. mustNutrients broken be down intosmaller parts so that they can be ______: Taking : (food)in nutrients for activitiesvarious including: the cellthe being from attacked by immune the system. Has ______which proteins are that identify the cell; prevent cells.other Has ______thatup pick from signals Proteins are digestedProteins are into ______. Starches digestedare into______. : ______: ______Organisms take ______(______,materials chemical activitieschemical which make your up metabolism .
37 38 II. D) E) D) C) B) A) Photosynthesis: 3. 2. 1. organisms. Nutrition: Heterotrophic 3. 1. adaptations:Plant 3. 2. 1. Benefits: ______and ______waste are products. ______Makes (______) as food. ______,Requires ______.and Includes: All ______and ______heterotrophs. are Hetero ______, = so Heterotroph ______. = Ex: Chloroplast ______Removes atmosphere. from ______Provides breathe.to foodProvides forall plants, andanimals organisms. other ______Herbivores:______Carnivores: ______Decomposers:______Ominivores:______Process in which sun’s energy is trapped in the chemical ______sugar. of : Cell: that organelle does photosynthesis Organisms mustOrganisms ______made nutrients by other III. of Respiration: Cellular ______. 3. 2. Transport: Gas exchange: Xylem and Phloem: Xylem cells: Guard : Stomates
Two different views of the different views of Two Process that takesProcess ______a under gases let inleaf; outand open and stomates close preventto ______“tubes” transport andfood water throughout the plant. energy energy stomates from from moleculessugar and places it in molecules and their and guard cells guard cells (X) .
37 38 E) D) C) B) A) G) F) molecule of sugar.molecule of Anerobic respiration carry organisms Most out ______and ______waste are products. ______,Requires ______.and ______is the Common mistakes: Common in cyclingoxygen, carbon, hydrogen and thewater through environment are and reactions! Respiration Cellular opposite Photosynthesis When When exercise human causes muscles to of run out oxygen, theircells do will into ATP. canNo organism energy fromget or sunlight sugar without first putting the energy Inhaling exhaling and does notgive you ATP. is Breathing “ All “ that will you respirationanaerobic Respiration isRespiration breathing.” usePlants photosynthesis, animals respiration.” use organisms, including plants, userespiration to gettheirenergy. molecule not does require not givesoxygen, but lessATP (energy) for each stop all uses life for respiration. Breathing exchangesthe for gases needed respiration. . . aerobic respiration respiration aerobic . . The waste product, energy . (uses oxygen) in their lactic acid , causes, muscles “burn” to so They alsoimportantare mitochondria . I. Body The Four: Topic Human A) Organization: D) C) B) 1. All humans most (and organisms) other begin life a as ______cell. As theAs body develop, continuesto tissues together work will ______form to . 2. 1. cellsAs divide, they begin develop to intospecialized 2. 1. Humans grow a as ______(cellresult of division). 2. This single single This iscell called ______. a byCells specialize turning genesorspecific on off. shape and function. Specialization allSince newcome from cells single the same cell, they allthe share same ______. organism. The this nucleus of has cell ______the genesto needed a become complete This increases quickly number the of in thecells body manyuntil there cells.trillions of Anaerobic organisms do not need oxygen, doand not tohave breathe. “ oxygen,Without you have no respiration, andno ATP, no energy. This is backwards. Breathing tois used get oxygen which is used respiration. for “ remain turnedremain nerves. It has still those butgenes, the only genesto needed a be white bloodcell A blood Ex: white hascell turned All living things All livingthings to need oxygen/need breathe.” isOxygen used breathe.” to The human body is madeof up ______. or Differentiation: Differentiation: on . Process in Process cell which a tochanges special havea off all genes needed make to skin, bone,or tissues .
37 38 III. II. A) SystemNervous F) E) A) Endocrine System D) C) B) 3. 2. 1. ______. systemThe nervous Org an work systems will atogether help to person will togetherOrgans work to ______form ______. 3. 2. 1. Uses The The organs main the of nervous system the are ______and ______nerve isA cell also called ______.a The the shape of receptor molecule determines which neurotransmitter it can receive. ______cellin the membrane of the cell.next nerve releasedNeurotransmitters by nerve 1 cell by received are ______The portion chemical of nerve a impules is called ______a Hormone Hormone are levels bycontrolled Hormones slowerthanare nerve impulses, but longer with effects. lasting hormoneA ischemical a ______by secreted endocrine spinal spinal cord ______controls reflexes and impulses relays thebetween brain and body. A feedback mechanism A ______to regulate regulate feedback mechanismsfeedback the
body. yourbody electrochemical with maintain homeostasis . . glands. the signal from one cellthe next.the fromto signal one where(3) a shows neuronsTwo carry an impulse to a muscle cell. a an to muscle impulse cell. carry neurotransmitter would carry wouldcarry I. D) C) B) F) E) made in the made in the for gonads (testes males, for ovaries females). Testosterone Adrenal make glands The 4. Materials usually Materials usually andenter leave the bloodthrough 4. 3. 2. 1. Transported includes: material A. System Circulatory can receive. thatwhichhormone it itthe of is proteins, determines shape receptormolecule moleculesReceptor ______from theall to cells ______from toglands target cells ______from all to cellslungs the of body. ______and ______from ______pressure. (andInsulin glucagon) directly control blood mistake:Common Moves materialMoves through body the to organsthe and that cells need them. (male), adrenaline estrogen on surface the of cellthe membrane receivehormones. makes “Insulin lowersblood “Insulin pressure.” and when theis under body stress. ______progesterone excretory organs. excretory (female) the are sex hormones. Theseare and glucagon which controlblood sugar. sugar diffusion. intestines some endocrine glands.some system) brainandThe (nervous (or glucose) not levels, blood
to allof cells body. As with all example ofexample the good This shape. of a is the correct molecules only can membrane accept MoleculesReceptor Lock andLock Key Model. in the cell the cell in
37 38 IV. II. G) A) System: Digestive D. Platelets the clot blood. 3. C. B. 2. 1. 2. 1. is broken Food down so that it is small enough enter to the body tissues/cells. 1. blood. E. D. C. B. energy sugar from make to ______). A. System:Respiratory your body. Technically true, but theheart pumps blood (which carries the oxygen) everywhere in the of blood. transports It everything ProteinHemoglobin: in redbloodcells that carriesoxygen. ______: concentration. Diffusion Nutrients andNutrients water absorbed are into bodythe in the small and intestines. large is broken Food down mechanically and chemically. capillaries. No diffusematerials in or outof the it isblood when theheart.in This only occurs in 1. Common mistakes: ______oxygen carry carbon dioxideand The______is the pump that the drives circulatory system. lungsthe intothe blood, which has lessoxygen. Ex The surrounded are alveoli by The breathe You faster when CO The theExcretes waste______which is produced cellular from respiration. Breathing ______provides needed for 2. : There ishigh a concentration oxygen of in the lungs, sooxygenwill diffusefrom alveoli a alveoli diaphragm : Process: in which material moves a from concentration high to low a “ “ Oxygen diffusesOxygen into and of out the heart.” The heart pumpsThe heart oxygen the to brain.” re microscopic sacs where oxygen enters the blood and CO is the muscle that breathing allows to occur. 2 builds in theup blood(not when you need oxygen). Microscopic bloodvessels where diffusion occurs. capillaries except oxygen which pick which pick and oxygen up drop off CO . cellular respirationcellular ______is the fluid
(which (which uses 2 leaves the 2 . white blood cells (C) white blood platelets (A), (B)Red and cells V. E) D) C) B) C) B) A) SystemImmune C. B. 2. 1. III. 2. 1. Common mistakes: foodUndigested is eliminated as waste solid ( is moved throughFood the digestive system by muscular (peristalsis).contractions stomach The digestive system isone a way passagethrough the body that includes the 1. White CellsBlood 1. Pathogen: The the job of immune system is protect to the body against ______. 1. F. E. 1. urine. D. The digestiveThe system gives nutrients. Energy is gained cellular by respiration. “ digestiveThe system does notexcrete waster (see excretory system) “ Different w.b.c’sDifferent have differentroles, including: Types of includepathogens viruses, bacteria, and parasites. “eliminated” or “egested.” Feces never ofenters cells the body, so it technically is not excreted. The correct term is The digestive system gives energy.” you The digestive system excretes waste.” The Lungs These wastesinclude ______, ______, ______and ______. ofyourby cells the wasteproduced body Removes System:Excretory “ Common mistake: dead toxins cells fromblood. liver red The and filters blood the also Kidneys thecontrol ______amount of in yourbody. The and The body excretesThe body feces.” ______. kidneys skin intestines excrete ______and ______. excretes ______and ______as sweat. are the componentsmain the of immune system. excrete ______excrete and ______and substances other as . feces ). .
. mouth
, excretory system.excretory Tract Kidneys and Urinary - part of the human part of - the
37 38 E) D) H) G) F) Antigens 1. Antibodies Common mistake:Common 2. 1. ______3. 2. 1. ______A an is injection orpathogen. of a weakened dead 2. 1. target (lock and model).key pathogen. with As all proteins, this is because shape ofthe the antibody must its fit Every antibody isin its specific action – it can attack and one only type ofone notAntibiotics will workagainst viruses. Can prevent only disease, cure not it. againstEffective both and viruses bacteria. theTriggers body maketo antibodies against that pathogen. blood ororgan an transplant. andattacked, destroyed. is mustThis why you match blood types before receiving Any of cell the virus with wrong antigen will seen be as byforeign yourimmune system, nether O). (type bloodtypeYour is determined by yourantigens (you can haveA or antigens,B or both Unlike antibiotics vaccines, can cure diseases. Make Make Destroy usingpathogen chemicals Destroy bypathogen eating it. “ pathogensIdentify are protein“tags” that identify a orcell virus. Tag” pathogens Tag” pathogens for destruction by wbc’s.other are ______made whiteby bloodcells attack to pathogens. antibodies are drugs are to used infections stop by bacteria . .
cells and antibodies attack a and virus. antibodiesattack cells immuneAn response – white blood –white blood VI. VII. A) between body systemsInteractions A) Disordersand Diseases 4. 3. 2. 1. The differentsystems of body together the work to maintain homeostasis. example: For 1. 2. 1. are: tohow prevent/treat/cure The it. most important disordersdiseases youand for know to Typically the exam asks name to you disease, a what it, causes its effectthe on and body, 5. disease. ______The system protects the______system from control thebody. ______The and ______systems work together to system. fromWastes the______system by removed are the______system. Nutrients the from ______system transported are cellsto the by “ Cancer AIDS Antibodies Antibodies that cells are attack pathogens.” Treatments includeTreatments surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy.and viruses. be May caused radiation,by chemicals as (such asbestos or smoke), cigarette and Cancer cells Caused when a reproduces cell (divides) at uncontrolled an rate, forming a transfusion. (using condoms),not needles, sharing or testing blood before it for using a beCan’t cured, spreadbut mayprevented be by sexual abstinence, “safe” sex (sharing needles),or bloodtransfusions. Spread through bodily fluids,sexual usually contact, intravenous (IV) use drug Weakens human immune system, vulnerableleaving body to diseases. other Caused by virus (a pathogen) HIV do not do not specialize and take and take fromresources healthy tissue. Antibodies proteins, are not cells. tumor .
37 38 V. IV. III. II. I. Five:ReproductionTopic Mitosis B) A) Sexual reproduction: B) A) reproduction: Asexual A) System Reproductive Male D) C) B) A) Meiosis D) C) B) A) Disadvantage: ______Advantage: ______Disadvantage: ______Advantages: ______4. 3. 3. 2. 1. ______produce and store sperm. daughtercellEach (gamete) gets one only half thatfrom parent. pairs Separates of 1. cell One divides 1. ______Makes used in sexual reproduction. 1. division One a of cell reproduce.to organisms Large mitosis ______and for use ______. organisms Simple it use parent cell. andThe number types of chromosomes in the daughter cells ______are in theas Used in all of forms asexual reproduction. Allergies Diabetes Sperm Sperm smallerare than the egg and mobile Sperm producedare in large throughout numbers malesa life cellsSperm haploid are made by ______Haploid: Cellwith ______ofset chromosomes ( normal) ½ Sexcells; eggGamete: and sperm Cell Diploid: awith ______of sets chromosomes. Asthma Asthma Occur when immune system reacts a to substance harmless (such pollen) as engineered bacteria. Some diabetics maytreated be injectionsusing of Affects body’sability controlblood to sugar. twice is a of form caused allergy aby reaction dust to in particles air. the
chromosomes sothat offspring get ______chromosome each of pair
two identical, cells.diploid (2n) four DIFFERENT (1n)haploid cells. of the the chromosomes of “parent” cell. insulin insulin made by genetically halved in meiosis. in halved stays the same mitosis,chromosomes and in is Mitosis vsMeiosis. Notice the number of the number Notice VII. VI. B) A) System Reproductive Female D) C) B) C) B) A) Development E) D) C) The menstrual The menstrual 28 lasts cycle days (on average) 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. ______produce eggs. 1. isSemen the that fluid carries sperm. transfersPenis into sperm female the reproductive system. Testosterone is the male hormone, andsex is made in the testes. 4. 2. 1. blood of fetus throughthe the process ______. of The______transfers nutrients and the from oxygen mother’s blood into the 4. 3. 2. 1. zygoteA develops in the order: following 2. 1. Fertilization ______.occurs in the The vaginais the birth canal where the leave baby will body.the The ______is the womb baby where the develop. will The ______carries the egg theto uterus. 3. 2. 1. offspring will needoffspring to will and grow develop. chromosomesContain 23 all celland (mitochondria, parts ribosomes,etc) that the moveEggs not ondo their own. Eggs largest are in thecells body. born are Females all eggswith they will ever need. Eggs haploid are madecells by ______. contains sugarSemen give to energy. sperm offspringSperm provide only with 23 chromosomes everything – iselse in the egg. The fetus is attached the to placenta by ______.the The bloodof motherthe and fetusnot do mix. ______– majormost organs formed are (butnot completed) ______–Differentiation Cellsbegin form to andinto tissues organs Cleavage A – of form ______; divide cells do but differentiatenot thefrom egg 23 + the from = sperm 46). Fertilization restores the set complete chromosomes,of sothe is diploid zygote (23 fertilizedA egg is called a occurs,If pregnancy the menstrual willcycle temporarilystop. Menstruation shedding– of uterine the if wall fertilization occur doesn’t Ovulation release – an of egg (typically cycle) per 1 Females are born are Females millionswith eggs, of enough forseveral lifetimes. egg isAn not developed fully until ovulation Continues to grow Continues grow to cellthrough division (mitosis) ______. number of chromosomes.number of Fertilization retores the correct retores the
37 38 D) cleavage (B) cleavage – development Early developing. The is child vulnerable alcohol, to drugs, etc because andorgans systems still are 3. Waste produced by fetus alsothe is the removed by placenta. which will eventually create a layered ball ofform ball cells a will the that embryo. eventuallylayered which create will Since theSince not fetus does eat solid food,it does haveto not eliminate feces. Waste (CO Fertilization (A) forms a single celled aFertilization singlecelled forms (A) 2 , urea, , salts) diffuse Front and views side maleFront of and the femalesystems reproductive from placenta from intomother’s blood. zygote which then begins the process of process which then begins the umbilical cord, placenta and placenta sac. amniotic cord, umbilical Note bethe readyto born. nearly here is DevelopmentLate – The fetus pictured –The fetus I. Genetics Six: Topic II. C) B) A) Chromosomes: F) E) and GenesChromosomes D) 1. – chromosomes Sex 1. pairs Chromosome 1. Humans have______chromosomes, or ______homologous pairs 1. codes gene Each protein fora particular chromosomeEach has hundreds or thousands of genes. incorrectother number).” mistake Common These numbers often are confused. You must memorize themcorrectly. The Y chromosomeThe is Y much ______than the soit missingX, is many genes. theof homologous pair. have organisms Most genes for two trait each - from 1 parent, each each on 1 member Homologous: Common mistake: Common meansThis many genes on the X chromosome not do “partner”have a so: called called toable it with “hide” dominant a gene, so... If malea has recessivetrait on X chromosome,the the chromosome Y not will be This makes more tomales likely havesome color traits (like Theseareblindness). sex linked traits.sex : ______
“Humans have23 chromosomes (or pairs of 46 chromosomes, or some carry genes for carry same the traits. In humans,In femalesare ______malesand are ______. “Genes/DNA are“Genes/DNA made protein.” from . . .
37 38 2. While genes determine our traits, nucleic acids. carryGenes the instructions to make protein. genes The themselves made are from the environment affect environment expression ofgenes.can the III. IV. J) I) H) G) DNA K) Synthesis Protein 1. made DNA is 4 of bases: The DNA shape of allows ______it to (copy) almost itself perfectly. ladder. The a shape of DNA molecule is a______, which aresembles twisted 1. theDNA chemicalis that makes yourgenes up chromosomes.and
A codon Base Base ______pairs: and ______DNA be paperwould the it is printed on. your Analogy: If genes and chromosomes theare manual” “instruction for yourbody, The a shape of protein determines its ______. ______of protein. the The the order of amino (determinedacids by sequence) the DNA determines the The acids amino will make ______. a listed in the DNA codons. ______assemble amino acids in the same order that they are codonEach represents specific a in pairs RNA arethe ______and ______is a sequence of : This : is how genes yourbody:control ______bases amino acidamino in DNA . . . .
37 38 L) ______ Therefore: How your body functions depends on the order of the bases in your inyour basesgenes! orderof the the on depends yourbody functions Therefore: How determines the protein’s ______.and The order of DNA ______in your genes orderdetermines ofthe ______in your proteins, which carries geneticthe code to The proteinsbuild and run the body. ______all the of proteins body.in the Therefore: ofThe sequence bases in DNA will determine the ribosomes . V. VI. P) O) N) M) ______Mutations: R) Q) Genetic technology: chromosomes. mutationsChromosome 1. ______. will This havean effect on way thethe proteinworks worksat(if it still all). mutations Gene 1. Common Can be only passed they if on occur in reproductive (sperm cells or egg). 1. ______. Genetic engineering: Ex: ______breeding Selective 2. 1. Gene mutationsGene are when DNAcaused bases in are way changed.some agent:Mutagenic ______. ______are used cut to and paste the DNA segments. chromosome 21. only (Note– can chromosome 21 Downcause Syndrome). SyndromeDown’s Chromosome mutations affect many genes at are Most once. lethal mutagenic agentsmutagenic may may a cause in achange gene which can change the ______a of :______: Non: mutation, lethal caused inheritance by anof extra copy of are caused usually when a inheritsperson many too or too few include ______.
37 38 T) S) 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. answer.cannot Genetic research posedhas many 2. 1. genetictreat though disease, cannot we them. yet cure technologiesNew ( The exampleof you gene splicing know: MUST ______are often becauseused they are simple and reproduce quickly. the as one theproduced by original organism. The new protein/enzyme/hormone will______be ______or coded thatfor by gene. thatOrganism receives new gene willthe begin make to the ______, Ethics: ______Ethics: sequence.DNA base finerprintingDNA Karyotype: to normalto human hormones. bothIn casesthe engineeredhormones safe are to because use they are identical been have to ______.make Bacteria engineered been have to ______make Bacteria engineered fo r diabetics. genetic relationships genetic twobetween people,or eventwo of groups organisms. ofFingerprints relatives similar are other, each to socan usedbe determine to fingerprintEach is unique, so it can be used identify to people. Can determine a if has person chromosome a disorder such as Down Syndrome. identifies this as a male. asidentifies a this karyotype A A photograph A anof organism’s chromosomes. karyotyping, fingerprintingDNA karyotyping, , or gel, electrophoresis,createsbanded patterns based a on person’s shows all 23 pairs of humanshows the pair 23pairs chromosomes. last all of Note ethical ethical problems right wrong)(ie and that alonescience ) making are it easier diagnose to and Topic Seven:Evolution Topic III. II. I. B) A) TheoryofEvolution: Modern Evolution Environment and and Evolution Environment contains the ideas: following The theory modern (which combines Darwin’s ideas genetics with and new other ideas) 2. 1. Darwin:Charles 6. 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. Darwin didn’t Darwin about genes,know so he know couldn’t about mutations. not Was the first think to but evolution, of he didfigure howout it works(mostly). ______. traitsNew arisespecies in a ______from and thatSpecies can not adapt become ______. common ancestor Descent: Common change. ______theAs environment changes, causesevolution speciesadapt to theirto environment. is oldEarth (4.55 billion years)and is constantly changing. : ______. Modern speciesfromModern evolved different earlier, species and a share : usually Species evolvewhen the environment changes. is the mechanism that species causes to
37 38 IV. B) A) A) Selection: Natural C) 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. can Changes include: needChanges to long be species – term evolvebecause not do of changes in the season. 1. dueother mutations to and sexual reproduction. ______: Members a of species different are each from 1. change not does forceitself a species change to itscharacteristics. inherited Environmental change 6. Introduction of Introduction of new food, predator)species (new new in foodChange availability in waterChange availability in tempChange Climate change No variation evolution no = or natural asselection, is nothing there “select.” to and extinction would a rarebe event.very theIf this were case, then all species would ablebe adapt to the to new environment, maySpecies be moveda to (accidentallynew location taken to island an for example) changes. withSpecies variation no usually are the whenfirst die the to environment The basic steps in natural selection are: DOES NOTDOES
CAUSE evolution evolution occur.Ato temperature or climate D) C) B) F) E) 3. 2. 1. ______: ______: Offspring must to struggle and survive reproduce. ______: Too many offspring produced. are of repetitiveof selection to theweed out unfit traits. ______: does Evolution not happen overnight. It takes many generations 3. 2. 1. ______: 4. environment mayunfit be in another. Noteenvironment. thatis no there absolute rule forfitness what – is fit in one Fitness: “unfit”Offspring with traits have will survivingmore difficulty and finding mates. predatorsfrom and mates. find Offspring who “fit” inherited traits are, average, on better able get to resources, escape common. thelooking at ENTIRE population that willyou see “fit”the traits become more inherit “unfit” traits (though beit will unlikelyto andsurvive reproduce). It is by only TraitsNOTE: still are randomly. inherited Individuals offspring of parents “fit” can still unfit ones. average, theOn next generation will havemore traits the from “fit” than theparents organismsMore fit reproduce and on pass their genes than unfit organisms. doesn’t.who It result is the theof conditions the of organism’s environment. Note: This “selection” is a not conscious actno – is “choosing” one who survives and A measurehow of a well trait helps organisman survive to and reproduce in its
37 38 V. VII. VI. D) C) B) A) Speciation: Evidence: Evidence: C) B) A) Classification 1. interbreed, even when brought together. Isolation: Reproductive time:Add This ways. results in physical and differences genetic between thepopulations. two and variation adaptation:New IsolationGeographic Branching tree Branching tree (cladograms)diagrams often are to evolutionaryused relationships. show 1. A Kingdoms species species. are canbreed new no they twolonger considered Once populations together, Species) many,are many examplesin which the lines between species are (see blurry Ring anddogs wolves. Because evolution isconstantly a ongoing gradualand process, there thatNote this not perfectis a definition Lions – and tigerscan breed together, can as Evidence Evidence ofin support comes evolution manyfrom fields: The process of amaking new speciesan from existing one. is able to is able successfully reproduce amongst its members. - are Organisms classified based theirevolutionary on relationship. are large are of groups organisms related (fungi, bacteria, protists, animals, plants). The longertwo populations apart,theare greater theirdifferences will become. : A: population is separatedinto2 or moredifferenthabitats. Eventually the changepopulations somuch that they unableare to Each population adapts its to new environment in different
VIII. D) C) B) A) C) B) A) 2. 1. Examples include: observationDirect and species confirmgenes of expected relationships. ofComparisons the (physical anatomy structures), embryology (development), chemistry Dating Radiometric organisms.of Fossil “ organismsIndividual do notevolve. Only populations can evolve. “ or stupid, fast, than strong or It smart. all depends on theenvironment you in. are always There better. manyare examples of species for it is whom better to weak, be slow, to asurvive in particular environment can who and passon their Strongergenes. is not Evolutionary fitness is not physical is fitness. Fitness determined who by is better adapted “ Mistakes Common 4. 3. The could organism adapt not and it went extinct.” The to evolved organism in live its environment.” Stronger are organisms morefit than weak ones.” Insects Bacteria Observed examplesof speciation naturalModeling selective selection with breeding a alter to species’ traits.
record evolving resistancepesticides. to evolving resistanceantibiotics. to preserves extinct as well speices as transitional forms between different types : Humans: haveseen evolution in occur both and nature in the lab. of consistently rocks the ageconfirm of the andEarth fossils
37 38 E) D) more fitmore traits.Better answers are (orgiraffes slow antelope) is thatthey were outcompeted by members of theirspecies with givenare speed confrontedwhen a by predator. The there reason noare short necked Shortcould! necked weregiraffes never given long anynecks than more slower antelopes Species do notevolve traits because they need them- would Life be much better weif “ squirrel playswho traffic in will notevolve resistance.automobile exposed to them, Chihuahua whoa is left outin thecold will notgrow long, warmfur a and adaptation). Bacteria who notdid already a have toresistance antibiotics would die when To evolve, variations must exist a in species the BEFORE environment changes (pre- “ organismsIndividual they die; cannot go extinct. Only species can become extinct. Giraffes gotGiraffes necks long because they The bacteria became resistant antibioticsto when they were exposed them” to functions. perform differentmodified to bethe can same body parts Homologous Structures between living and extinctspecies. between Evolutionary trees long necklong giraffes lived and reproduced.” “ toadapted than get shortfood neck giraffes.” “ Giraffes evolved evolved Giraffes neckslong because moreshort necked giraffes died, and more Giraffes necks evolved long because the ones necks longer with betterwere can show thecan relationship reveal thatreveal needed them to eat theleaves at tops trees.”of small, ancestor. many-toed horse aof the modern from the evolutiondiagram shows the fossilin This record. be can foundmany species Transitional forms than those above them. than those older aretypically fossils Deeper for I. Eight: Ecology Topic II. C) B) A) Ecology: A) Organization 1. with each interact organisms other:How 1. Niche: Habitat: Abiotic ______Abiotic Factors: 3. 2. Competition: ______Competition: night). toresources reduce competition (ex: birds eat insects duringthe day, eat thembats at occupying nichea at anytime. one Organisms similar with needs will often divide create trying species towill theTwo fill inan ecosystem sameniche closeSymbiosis: A relationship between two in organisms which least benefits.at one organismFeeding: One feedson another. ______
______organism harmingorganism another (parasite-host). Can include organisms 2 togetherworking formutual benefit(bee and flower)or 1 decomposer. Consumer A – heterotroph; mayan be herbivore, carnivore, oromnivore substances. – Producer An organisms autotroph; that makes nutrientsits own simple from A Ex: andsquirrel chipmunk a for compete food. ______, which usually results inone only species
37 38 C) B) Levels ofLevels organization: Factors:Biotic ______III. IV. C) B) A) Populations E) D) C) B) A) in EcosystemEnergy an number ofnumber organisms off untildying a new balance reached.is Overpopulation: aWhen population carrying exceeds the capacity. results Usually largein a AnythingLimiting factors: which limitssize the of population, a including: capacity:Carrying ______2. 1. Energy pyramid: Showsthat energy gets lost with stepeach food in a chain web –Food Shows many energy pathways. chain Food way Shows1 – that throughenergy can “flow” an ecosystem. ______. energySun’s is stored chemicalin the ______food of through theof process ______allprovides energy life for Earth. on prey. isThis why populations predators of typically are populationsless than the of their aboutprocesses. Only 10% of energy is passed one from step the to next. Energy is organismlost because every uses of energysome for the own it’s life : given A area can only enough resourcessupply a for limited number organisms. of
37 38 V. VI. B) A) Biodiversity C) B) A) ______Succession Ecological 3. 2. 1. be to because:bad habitats areAs lost and extinct, species become biodiversity isThis reduced. is considered diverse.not ecosystems Diverse again. disruptionAny temporary aof will community beginprocess the of all succession over 1. CommunityClimax to organisms in replacemove them.and The in organisms each succession stage of change the and environment, allow new biodiversity webiodiversity losing are potentially valuable resources. Humans use for organisms suchmany asthings food medicine; and by reducing withEcosystems diversity low take recover longerto from environmental changes withEcosystems diversity low lessstable are than ecosystems with more diversity, The climax is community determined by the climate. local area back area forest, into a it much but throughfirst pass all the stages. necessary IfEx: forest a firekills trees all the in an area, succession eventuallywill return the withstops and grasses shrubs. KansasEx: has fertile very but soil, enough not rain to trees,support sosuccession refers the to varietylife of earth. on : ______: : ______: (those (those many typeswith of species) morestableare than ones that are VII. C) B) A) environment. ImpactHuman D) Human actions that generally havea negative impact the on environment include: Choosing“right” weighing actionsbenefits risks. the requires consequences. the with the areEverysolution negative solutionscan tohave noany problem. easy There ecological andwater space. is as greatersuch food, population demand whichplaces onhuman resources growing, a impact humansenvironment the because ais reason on negative the primary have The 4. 3. 2. 1. to repair reduce to include: being byhumans the Actions damage taken or environment 6. 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. Protection habitats of endangeredand species cleaner Using (ex: solarresources over fossil fuels) Conserving available resources Recycling wastes Introduction of species foreign cutting/deforestationClear Overhunting,/overgrazing Farming Pollution Development/industrialization : Humanactions can haveboth negativea impact or onpositive the
37 38 9. 8. 7. 6. 5. Passing Passing control to laws pollution, management,land hunting, fishing, etc. orRotating crops planting cover crops reduceto soil loss. Planting replace to trees cut down.those Farming native plants (ex: in cocoa the rainforest) Use biological of insteadcontrols of pesticides and herbicides VIII. B) A) C) Depletion ozone layer of 3. 2. 1. Acid rain Problems: Specific Environmental 3. 2. 1. Industrialization 3. 2. 1. What done: can be effect: Negative Cause: What done: can be effect: Negative Cause: What done: can be effect: Negative Cause:
37 38 E) D) G) F) 2. 1. diversityLoss of 3. 2. 1. habitatLoss (ex:of deforestation) 1. species Introduced 3. 2. 1. warmingGlobal 3. Negative effect: Negative Cause: What done: can be effect: Negative Cause: Cause: What done: can be effect: Negative Cause: What done: can be II. I. Labs Nine:Experiments and Topic B) A) Terms: C) B) A) experimental groups a with “normal” group. Experiments: Controlled D) C) Inference: Inference: Observation: 3. 2. needed whenneeded using human subjects. Placebo: except group: Control group: Experimental 2. 1. Theory: 2. 1. and effect. Hypothesis: What done: can be effect: Negative not Mistake: Common tieTheories together many facts, scientific hypotheses and laws. patients thispill,then The easiest away write to correct hypothesis isan as experiment correctA hypothesis can be This is an incorrect useof the “theory”word in scientific a context. scientific A theory is one a simple a guess or conjecture, and An A pill sugar or “fake” other treatment given the to group. control Usually only : it does receive thenot new treatment. A conclusion based observation on or evidence. explanation A What measured. is seen or prediction “Normal” group. Should be identical experimentalto group in every way . Compares the an results of experiment between one or more Group being tested or receiving treatment. “Theories things are that are or are opinions, proven.”not of natural of events supportedthat byis evidence. strong based on available evidence. A hypothesis statesgood both cause they will get not sick.) tested tested and and is strongly supportedby evidence. falsified falsified
(proven incorrect) incorrect) (proven anusing “if-then” statement. (ex:
If
I I give before and after the experiment. You test should people’smemories both Data Collected way. group alsobeshould tested in the same mixes sexes, of ages, ethnicities.and Each health with memory, similar similarwith People ingroup each be should of similar Should be same the for groups: both Constants treatment) control nevergroup receivesthe new Doesn’t gum chew – (remember the Control Group Group that gum. chews Group Experimental experiment see to itif was improved. memory checked both and afterbefore the Memory all– should groups havetheir Dependent variable gum, willsome not. Chewing –gum people some will chew Independent variable: memory. If people gum chew it will their improve Hypothesis: Example ofa ControlledExperiment:
37 38 III. A) and DataTablesGraphs E) D) D) C) B) 4. 3. 2. 1. Data tables 2. 1. Variable: Dependent 2. 1. Variable: Independent a bar bar a insteadgraph of line graph a will be credit this denied for ofpart test. the date,To all graphs drawn the on have LE Regents been 4. 3. 2. 1. The and x axis y must numbered. be 2. 1. title.the same usedones in the data table. Onceagain units measurement of must written be with the Both x yand of axis the graph be must titled. labeled or Theselabels typically are the order. Data in the table be must arranged in ascending or descending columnEach be should titled, and include of units measurement. column isSecond First column in the is for table the The dependent is alwaysvariable plotted on Ythe axis. The “then” ofpart “If-then” an hypothesis. The independent is alwaysvariable plotted on X axis.the The “If” of part “If-then”an hypothesis. You need with 0 numberingyour axis You do to not start them. The bottom makescorner the impossible graph and read to no willcredit be given. up numericalscales shouldtake oftheYour most axes 5’s,2’s, 10’s, etc). by increase uniform must increment a These numbers The The numbers must line up must numbers line grid lineswith the dependent variable dependent variable independent are used are organize to data which will plottedbe in a graph. another for the
Variable that is measured the at end of experiment;an the results. Variable that tested is being drug, new(ex: fertilizer).new is always plotted on the is always plotted on the dependent variable. independent variable of the of graph, with not betweenspaces y-axis x-axis line graphs line .
. . . Squeezing it all intothe (that is(that you must 1’s,count by . . . Any. student who draws IV. I. Labs Ten:State The Topic (Part D) F) E) D) C) B) A) ofa good experiment: Characteristics E) C) B) A) (aka Lab) Connections Clothespin The Making H) G) Must and itwrong theshowwhether is or right hypothesis Must test reviewed – Are peer thebe same. independent variable. only one Test over periods longer oftime.Are performed subjects. samplesize/manytest large Have the be samewaythe repeated and Can results.get same triangle, on depending directions).the All plotted points your on must graph be Part B 2. 1. Part A2 2. 1. Part A The established experiment follows mixed.not – Is objective What you learned: minute What you did: What you learned: What you did: muscles were fatigued.muscles were squeezedIf you lessthe secondround, it may havebeen because your finger “warmedmuscles up” were increased from circulation. squeezedIf you morethe secondround, it may have your been because finger the the experiment and conclusionfair are and measured exercise affectedhow pulse rate. Squeezed Squeezed clothespina 1 for then minute, squeezed it again for another examined other by scientists determine to its accuracy. exercise increases pulse rate ethical ethical All characteristics other of tested the should groups surrounded bya circle surrounded and legal legal standards. unbiased (or sometimes (or a square or . . . andFact opinion are
37 38 II. B) A) ( and Biodiversity Relationships 3. 2. 1. What you learned: (chemical and genetic) traits. What you did: 2. 1. Related similar willorganisms show banding patterns because theirDNA have similar base sequences. organism.every of DNA carried are fromfarther the thanwell larger pieces). An – Gel Electrophoresis Restriction enzymesRestriction Endangered Endangered species be should becauseprotected they may offer humans. benefitsto toused determine relationships between organisms. techniquesDifferent (such as that Species are sharerelated similar traits. What you learned: clothespin. What you did: electric currentelectric Compared 4 species of plants, based structural on (physical) and molecular Designed experiment an test to exercise how affects squeezing a carries DNA fragments the through gel, separatingthe them size to according (smaller pieces How to andesign experiment (see pages 3-5). cut DNA intofragments, which are placed intoa in well a plate.gel A used technique to howshow species related are one to another. Botana curus Botana gel electrophoresis lab) and paper paper chromatography This creates a creates ofbands pattern whichis for This unique ) can be III. B) A) ofFinchesBeaks finch, allowing finch, some survive reproduce,to and but others.not What you learned: What you did: Played different finch species competing for food. Different environmental conditions (food) favoreddifferent species of
37 38 IV. A) A Diffusion Through Membrane B) 2. 1. Part A 3. 2. 1. Part B 3. What you saw: What you did: What you learned: What you saw: What you did: What you learned through thethrough membrane. Used glucose indicator blue (Benedict’s solution) see to that glucose diddiffuse thethrough membrane. Because of outside the was black,cell not know you the starch didnot diffuse of turnedInside cell black because iodinediffused starchPut indicator (iodine) celloutside glucose andPut starch inside your “cell.” Made model a using cell In willdiffuse water,water aIn cell.pure into to water water diffuse out ofa cell.Salt causes Distilled water the cause to cells backnormal.swell to causedSalt water the to onioncells shrivel. Added distilled (pure) water the to onion cells. waterAdded salt to onion the cells. atLooked redonioncells theunder microscope. can You indicatorsuse identify to the of presence specific substances. moleculeLarge (starch) cannot diffusethrough a membrane theirown. on molecules (glucose, Small iodine) can
dialysis tubing diffuse . through through membrane ona their own. into the the cell