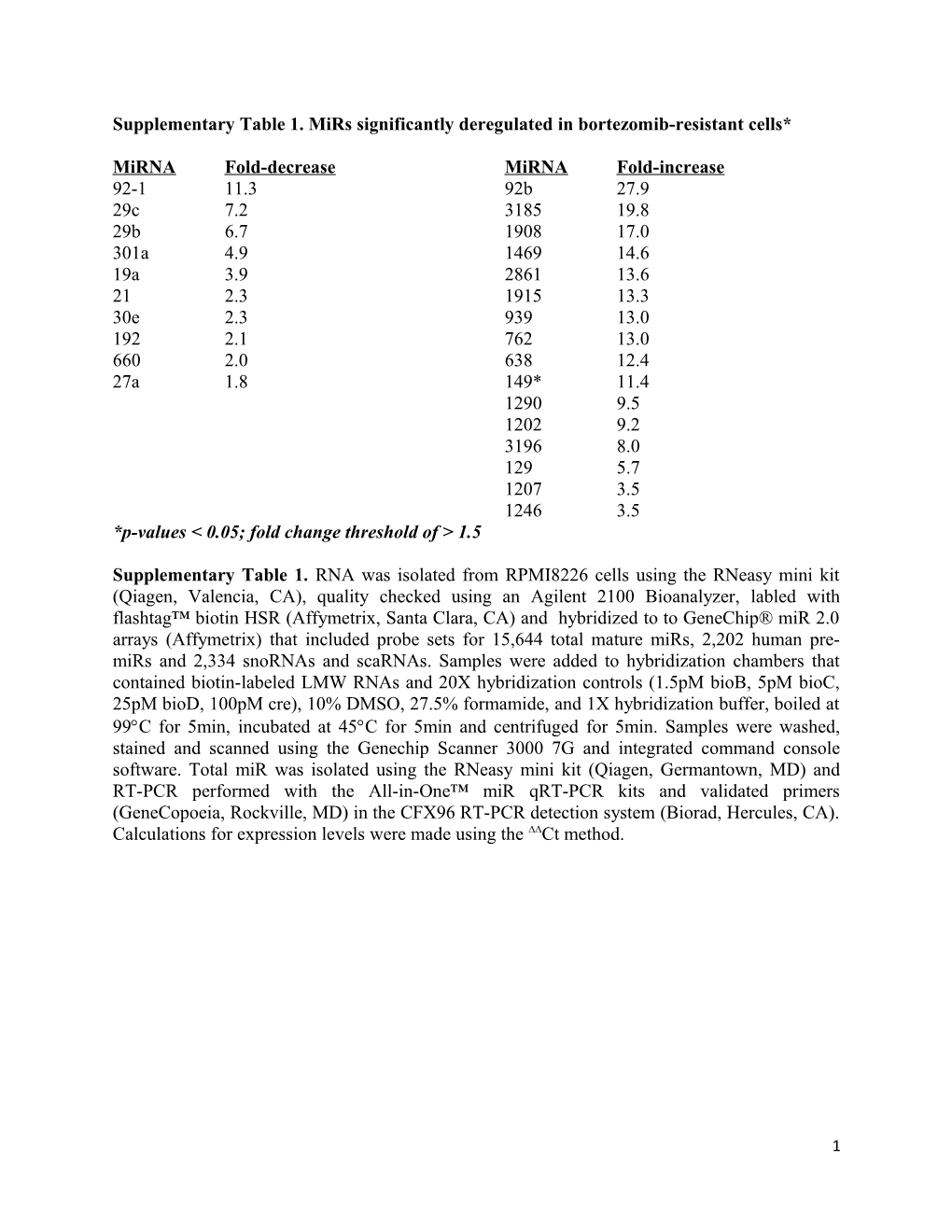
Supplementary Table 1. MiRs significantly deregulated in bortezomib-resistant cells*
MiRNA Fold-decrease MiRNA Fold-increase 92-1 11.3 92b 27.9 29c 7.2 3185 19.8 29b 6.7 1908 17.0 301a 4.9 1469 14.6 19a 3.9 2861 13.6 21 2.3 1915 13.3 30e 2.3 939 13.0 192 2.1 762 13.0 660 2.0 638 12.4 27a 1.8 149* 11.4 1290 9.5 1202 9.2 3196 8.0 129 5.7 1207 3.5 1246 3.5 *p-values < 0.05; fold change threshold of > 1.5
Supplementary Table 1. RNA was isolated from RPMI8226 cells using the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA), quality checked using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer, labled with flashtag™ biotin HSR (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA) and hybridized to to GeneChip® miR 2.0 arrays (Affymetrix) that included probe sets for 15,644 total mature miRs, 2,202 human pre- miRs and 2,334 snoRNAs and scaRNAs. Samples were added to hybridization chambers that contained biotin-labeled LMW RNAs and 20X hybridization controls (1.5pM bioB, 5pM bioC, 25pM bioD, 100pM cre), 10% DMSO, 27.5% formamide, and 1X hybridization buffer, boiled at 99C for 5min, incubated at 45C for 5min and centrifuged for 5min. Samples were washed, stained and scanned using the Genechip Scanner 3000 7G and integrated command console software. Total miR was isolated using the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD) and RT-PCR performed with the All-in-One™ miR qRT-PCR kits and validated primers (GeneCopoeia, Rockville, MD) in the CFX96 RT-PCR detection system (Biorad, Hercules, CA). Calculations for expression levels were made using the ∆∆Ct method.
1 Supplementary Table 2. Northern Blot probe sequences
miRNA Probe Sequence (5’ – 3’) miR-29b AACACTGATTTCAAATGGTGCTA U6 snRNA CACGAATTTGCGTGTCATCCTT Lysine tRNA TACCGACTGAGCTATCCGGGC
Supplementary Table 2. Transfection efficiency was verified by probing the subcellular fractions by northern blot with tRNAlys (cytoplasmic fraction) or U6 snRNA (nuclear fraction). Total RNA (10ug) was harvested using PARIS™ Kit (Invitrogen) and was separated on formaldehyde-agarose gels and transferred to Hybond™ nucleic acid blotting membrane (GE Healthcare, Buckinghamshire, England). Oligonucleotide probes were 5' end-labeled with digoxigenin-3-0-methylcarbonyl-ε-aminocaproic acid-N-hydroxy-succinimide ester (DIG). Hybridizations and washes were performed at 52oC and 65oC respectively in a model 400 hybridization oven (Robbin’s Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA). Blots were incubated with anti- digoxigenin-AP, Fab fragments (Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN) followed by CSPD ready- to-use (Roche). Chemiluminescence was visualized on Hyblot CL® Autorad film (Denville Scientific, NJ) using a M35A X-OMAT X-Ray film processor (Eastman Kodak, Rochester, NY).
2 Supplementary Table 3. Proteasome genes upregulated in bortezomib-resistant cells Gene Fold change Log-fold PSMA1 proteasome subunit, alpha type, 1 7.3 2.9 PSME3 proteasome activator subunit 3 (PA28 gamma) 3.5 1.8 PSMD1 proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 1 3.2 1.8 PSMD2 proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 2 3.1 1.6 PSME3 proteasome activator subunit 3 (PA28 gamma 2.9 1.5 PSMD2 proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase 2.9 1.5 PSME3 proteasome activator subunit 3 (PA28 gamma) 2.8 1.5 PSMD1 proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase 1 2.7 1.4 PSME4 proteasome activator subunit 4 (PA200) 2.5 1.4 PSMF1 proteasome inhibitor subunit 1 2.3 1.2 PSMD2 proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 2 2.2 1.2 PSMA3 proteasome subunit, alpha type, 3 2.2 1.2 PSMC3IP PSMC3 interacting protein 2.2 1.1 PSMC3 proteasome 26S subunit, ATPase, 3 2.1 1.0 PSME2 proteasome activator subunit 3 (PA28 gamma) 2.0 1.0 PSMC2 proteasome 26S subunit, ATPase, 2 2.0 1.0 PSMB2 subunit, beta type, 2 2.0 1.0 PSMD12 proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase 12 2.0 1.0 PSMD9 proteasome 26S subunit non-ATPase 9 1.9 1.0 PSMC4 proteasome 26S subunit ATPase 4 1.8 0.9 PSMG1 proteasome assembly chaperone 1 1.8 0.8 PSMA4 proteasome subunit alpha type 4 1.8 0.8 PSMC5 proteasome 26S subunit ATPase 5 1.8 0.8 PSMA3 proteasome subunit alpha type 3 1.7 0.8 PSMB3 proteasome subunit beta type 3 1.7 0.8 PSMB6 proteasome subunit beta type 6 1.7 0.7 PSMD3 proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase 3 1.7 0.7 PSMA7 proteasome subunit alpha type 7 1.6 0.7 PSMD11 proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase 11 1.6 0.7 PSMD12 proteasome 26S subunit , non-ATPase 12 1.6 0.7 PSMC2 proteasome 26S subunit, ATPase 2 1.6 0.6
Autophagy Pathway genes upregulated in bortezomib-resistant cells Gene Fold change Log-fold ATG3 autophagy related 3 homolog 6.6 2.7 ATG5 autophagy related 5 homolog 1.8 0.8 ATG13 autophagy related 13 homolog 1.7 0.7 ATG4D autophagy related 4D homolog 1.6 0.7 ATG4 autophagy related 4 homolog 1.6 0.7
Autophagy Pathway genes downregulated in bortezomib-resistant cells Gene Fold change Log-fold ATG14 autophagy related 14 homolog 6.8 2.7
3 ATG9B autophagy related 9B homolog 1.9 0.7
Supplementary Table 3. Gene Expression Microarray: Total mRNA was isolated from parental and resistant cells using the RNeasy kit (Qiagen, Inc., Germantown, MD). Samples were analyzed using the Genechip primeview assay for target synthesis and labeling. Samples were hybridized to the Genechip primeview human gene expression array and those demonstrating a cutoff greater or less than 1.5-fold difference from the parental cell line used for further analysis. The quality of the total RNA was confirmed using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer using the RNA 6000 Nano Assay. For each sample, the 3’ IVT Express Kit (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA) synthesizes biotin – label cRNA target from 100ng of total RNA. A hybridization cocktail which includes 10 g of cRNA target is created for each sample. The samples are hybridized to a standard Probe Array Cartidge (GeneChip Primeview Human Gene Expression Array–Affymetrix) in the GeneChip Hybridization Oven 640 (Affymetrix). Probe arrays are washed and stained using the Fluidics Station 450 (Affymetrix). Arrays were scanned with the Affymetrix GeneChip Scanner 3000 7G. Raw data files were created by Command Console, the Affymetrix operating software program. The Affymetrix Expression Console Program was used to examine the Affymetrix Gene Array quality control factors for all samples in a project. Two separate independent algorithms were used to normalize the data for all samples within a project. Data is normalized using the Robust Multi-Array Analysis (RMA) algorithm and the MAS5 algorithm. Specific quality control metrics examined include signal histogram, relative log expression signal, Pearson's correlation, pm mean (average signal intensity of probes), % genes called present, 3’5’ ratio of housekeeping genes, expression values of spiked-in poly-A RNA controls, and values of spiked-in hybridization controls.
Software Programs: The quality of total RNA was checked by the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer using the RNA 6000 Nano Assay. For each sample, the 3’ IVT Express Kit (Affymetrix) synthesizes biotin – label cRNA target from 100ng of total RNA. A hybridization cocktail which includes 10 micrograms of cRNA target is created for each sample. The samples are hybridized to a standard Probe Array Cartidge (GeneChip Primeview Human Gene Expression Array– Affymetrix) in the GeneChip Hybridization Oven 640 (Affymetrix). Probe arrays are washed and stained using the Fluidics Station 450 (Affymetrix). The arrays are scanned with the Affymetrix GeneChip Scanner 3000 7G. Raw data files are created by Command Console, the Affymetrix operating software program. The Affymetrix Expression Console Program is used to examine the Affymetrix Gene Array quality control factors for all samples in a project. Two separate independent algorithms are used to normalize the data for all samples within a project. Data is normalized using the Robust Multi-Array Analysis (RMA) algorithm and the MAS5 algorithm. Specific quality control metrics examined include signal histogram, relative log expression signal, Pearson's correlation, pm mean (average signal intensity of probes), % genes called present, 3’5’ ratio of housekeeping genes, expression values of spiked-in poly-A RNA controls, and values of spiked-in hybridization controls.
4 5 Supplementary Figure 1. Dose-dependent effect of PIs on parental cells and PI-resistant cells.
BTZ-Resistant CFZ-Resistant IXZ-Resistant
Bortezomib (nM) Carfilzomib (nM) Ixazomib (nM)
Supplementary Figure 1. Parental (drug-naïve) RPMI8226 cells or RPMI8226 cells that were generated separately with acquired resistance to the PIs bortezomib, carfilzomib or ixazomib (MLN9708) were treated with PIs at indicated concentrations. Cells were then cultured for 72h under standard conditions and viability determined using the XTT assay. Shown is the average of triplicate measurements.
6 Supplementary Figure 2. MiR replacement effect on MM, lymphoma, amyloidosis and Waldenströms cells.
Supplementary Figure 2. Myeloma cells KMS28BM, MM1.S, the lymphoma cell line KG-1, amyloidosis cell lines AMCL-1 and
7 AMCL-2 and the Waldenström’s cell line WMCL-1 were transfected with indicated miR replacements, cultured for 72h, treated with bortezomib and viability determined using the XTT assay. Shown are the average of triplicate measurements.
8