Chemistry 421/821 – Second Exam Spring 2010 page 1 Name Answer Key
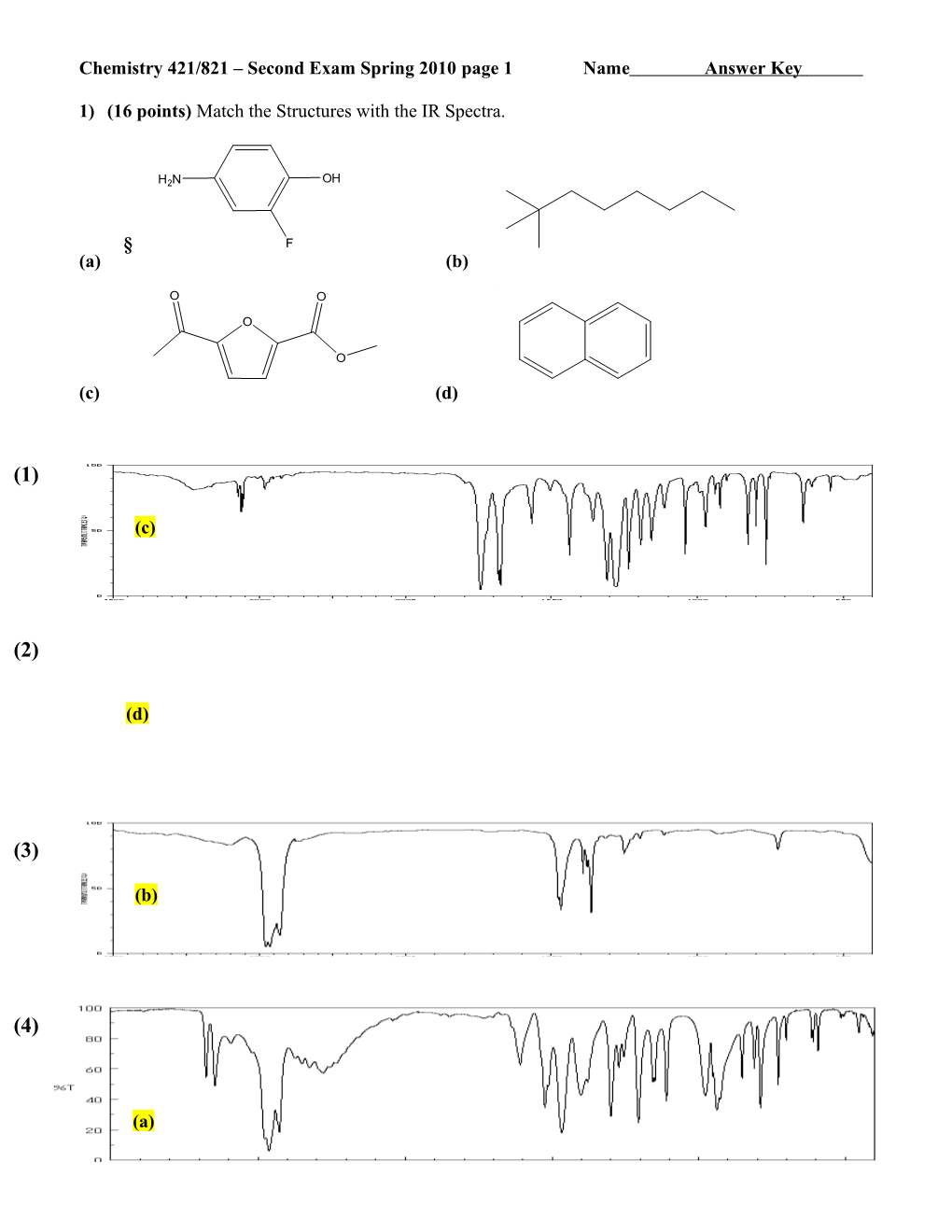
1) (16 points) Match the Structures with the IR Spectra.
H2N OH
§ F (a) (b)
O O
O
O
(c) (d)
(1)
(c)
(2)
(d)
(3)
(b)
(4)
(a) Chemistry 421/821 – Second Exam Spring 2010 page 2 Name Answer Key 4000 3000 2000 1500 1000 500 wavenumber (cm-1)
2) (16 points) Please explain why:
a. (8 points) Infrared spectrometer uses different detectors than Raman spectrometer.
While both techniques measure absorptions due to molecular vibrations, Raman spectroscopy measures the process indirectly through a frequency shift induced by a collision and scattering of the light source. Therefore, Raman requires an intense light source (Laser), but it doesn’t have to match the energy gap (infrared) between the ground and excited vibrational state like Infrared spectroscopy. Thus, Raman spectroscopy uses detectors that respond to visible laser light (induce current, photoelectric effect) and IR spectrometers use detectors that respond to IR (temperature changers)
b. (8 points) Atomic Absorption spectrometer uses a different light source than Atomic Emission spectrometer.
AES does not require a light source. In AES, the flame (temperature source) also generates the excited atoms/electron by simply following the Boltzmann’s equation – higher temperature generates a larger population of excited atoms/electrons. AES monitors the emission of light from these excited atoms/electrons. Conversely, AAS requires a separate hollow cathode lamp for each element detected, the emission spectrum of an element is used to detect an element. This supplies the extremely narrow bandwidth of light required to be able to detect an absorbance. Chemistry 421/821 – Second Exam Spring 2010 page 3 Name Answer Key
O
3) (13 points) For the molecule isobutyric acid (C4H8O2):
OH
a. (3 points) How many vibrational modes are expected?
3N-6 = (3)(14)-6=36
b. (5 points) Why would you expect the Raman spectrum to show a strong absorbance at ~1400 cm-1 (weak or missing in IR spectrum), while the IR spectrum shows a strong absorbance at 1690 cm-1 (weak or missing in the Raman spectrum)?
Raman spectroscopy is sensitive to symmetrical stretches, change in polarization, that would occur for a C-C bond at ~1400 cm-1. Conversely, IR spectroscopy is sensitive to assymetrical stretches, changes in dipole moment, that would occur for a C=O stretch at 1690 cm-1.
c. (5 points) If the only information you had to interpret the IR spectrum for isobutyric acid was the harmonic oscillation model (i.e., no tables of frequencies for functional groups), why would you assign the absorbance at 1690 cm-1 to the C=O stretch and the absorbance at 1286 cm-1 to C-O stretch?
The harmonic oscillation model indicates that the frequency () is proportional to square-root of the force constant (k). In this model, force constant would be the bond strength, where a double bond is stronger (higher energy, frequency) relative to a single bond. Chemistry 421/821 – Second Exam Spring 2010 page 4 Name Answer Key
4) (10 points) Please explain how molecular vibrations deviate from the harmonic oscillation model.
At large stretch distances from the normal bond distance, the bond stretch energy is less than predicted by the harmonic oscillation model because the energy asymptotically approaches the energy required to dissociate the bond. Conversely, at short stretch distances from the normal bond distances, the the bond stretch energy is greater than predicted by the harmonic oscillation model because of va der waals repulsion, two atoms can’t occupy the same space.
5) (7 points) Calculate the ratios of the intensities of the anti-Stokes and Stokes lines for CCl4 at 459cm-1 and 20oC. Chemistry 421/821 – Second Exam Spring 2010 page 5 Name Answer Key
6) (9 points) The ionization potential of Cs is 3.893 eV. You want to maximize your signal for detecting Cs in AES, but you want less than 5% Cs ions. a. (7 points) What temperature would you choose to run the experiment at?
K
b. (2 points) Please identify one other type of interference (besides generating ions) that you may encounter in either AES or AAS.
Matrix or Chemical interference (salts, oxides, hydroxides, incomplete atomization) Light from the flame or heat source Chemistry 421/821 – Second Exam Spring 2010 page 6 Name Answer Key
7) (15 points) Given the following chromatogram, baseline peak width of ~ 10 seconds for component 1 and ~20 seconds for components 2 through 4, and a column length of 10 cm:
Void
Seconds 50 100 150 225240
Calculate:
(a) (3 points) separation factor () between components 1 and 2
capacity factor k’ = (tR –tM)/tM
k’(1) = (100-50)/50 = 1.00 k’(2) = (150-50)/50 = 2.00
= k’2/k’1 = 2.00/1.00 = 2.00
(b) (3 points) resolution (Rs) between components 3 and 4. Chemistry 421/821 – Second Exam Spring 2010 page 7 Name Answer Key
(c) (1 points) how would you classify the performance of the column based on the resolution between components 3 and 4?
Poor or unacceptable since the resolution (Rs) is less than 1
(d) (8 points) What column length is required for a resolution of 1.5 between components 3 and 4?
First, average number of plates:
Navg = 1600 + 900 = 2025 + 2304/4 = 1707.25
Then, calculate plate height:
H = L/N = 10 cm/1707.25 = 0.0059 cm
Then, number of plates for resolution of 1.5:
Then new column length:
L = HN = 0.0059 cm * 6829 = 40.29 cm Chemistry 421/821 – Second Exam Spring 2010 page 8 Name Answer Key
8) (14 points) Select the best/correct answer: a. (2 points) Oxide and hydroxide formation in AAS can be avoided by: i. placing the light source in the outer cone of the flame ii. increasing the oxidant/fuel ratio iii. increasing the temperature iv. changing the hollow cathode lamp
b. (2 points) The “fingerprint” region of an IR spectrum is routinely used to: i. identify the functional groups present in the structure ii. identify a compound through a database search iii. measure anharmonic vibrations iv. determine force constants
c. (2 points) The technique best suited for multielement analysis would be i. flame AAS ii. ICP AES iii. Raman iv. UV-VIS
d. (2 points) The intensity of Raman lines follows the following trend: i. Raleigh scattering >> Stokes >> anti-Stokes ii. Raleigh scattering >> anti-stokes >> Stokes iii. anti-Stokes >> Stokes >> Raleigh scattering iv. all the same intensity
e. (2 points) In chromatography, what factor contributes to peak broadening (band spread)? i. Doppler effect ii. Zeeman effect iii. nebulization iv. mobile phase mass transfer
f. (2 points) Which approach is important in atomic absorption spectroscopy to remove background interference: i. Protecting agent ii. Increase temperature iii. Two-line method iv. all of the above
g. (2 points) Which IR detector functions by a change in resistance caused by an increase in temperature: i. Pyroelectric detector Chemistry 421/821 – Second Exam Spring 2010 page 9 Name Answer Key ii. Thermocouple iii. Bolometer iv. All of the above