Meiosis – V3
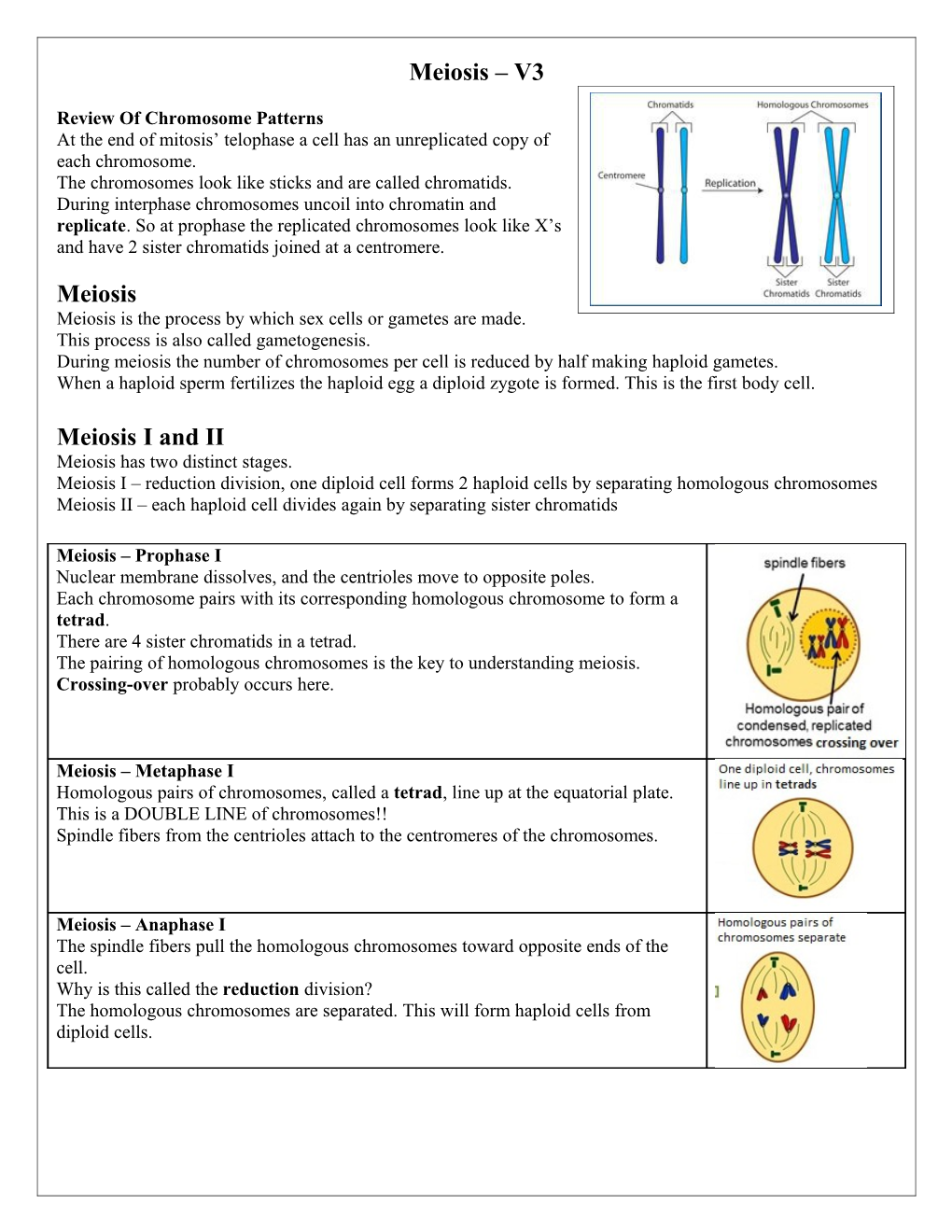
Review Of Chromosome Patterns At the end of mitosis’ telophase a cell has an unreplicated copy of each chromosome. The chromosomes look like sticks and are called chromatids. During interphase chromosomes uncoil into chromatin and replicate. So at prophase the replicated chromosomes look like X’s and have 2 sister chromatids joined at a centromere.
Meiosis Meiosis is the process by which sex cells or gametes are made. This process is also called gametogenesis. During meiosis the number of chromosomes per cell is reduced by half making haploid gametes. When a haploid sperm fertilizes the haploid egg a diploid zygote is formed. This is the first body cell.
Meiosis I and II Meiosis has two distinct stages. Meiosis I – reduction division, one diploid cell forms 2 haploid cells by separating homologous chromosomes Meiosis II – each haploid cell divides again by separating sister chromatids
Meiosis – Prophase I Nuclear membrane dissolves, and the centrioles move to opposite poles. Each chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosome to form a tetrad. There are 4 sister chromatids in a tetrad. The pairing of homologous chromosomes is the key to understanding meiosis. Crossing-over probably occurs here.
Meiosis – Metaphase I Homologous pairs of chromosomes, called a tetrad, line up at the equatorial plate. This is a DOUBLE LINE of chromosomes!! Spindle fibers from the centrioles attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
Meiosis – Anaphase I The spindle fibers pull the homologous chromosomes toward opposite ends of the cell. Why is this called the reduction division? The homologous chromosomes are separated. This will form haploid cells from diploid cells. Meiosis – Telophase I Nuclear membranes might reform. Cytoplasm divides after telophase, resulting in TWO haploid daughter cells.
Meiosis – Prophase II The second part of meiosis resembles mitosis except the cells are haploid. The centrioles are replicated. Centrioles in the 2 new cells move to opposite poles. New spindle fibres form and attach to centromeres.
Meiosis – Metaphase II The chromosomes are in a single line on the equatorial plate. This is similar to metaphase in mitosis.
Meiosis – Anaphase II Spindle fibres separate sister chromatids which move to opposite ends of the cell.
Meiosis – Telophase II Cytoplasm separates, resulting in 4 haploid cells. Meiosis NOT a cycle like mitosis but forms haploid egg and sperm cells.
Meiosis forms gametes In males, meiosis or spermatogenesis results in 4 sperm cells. In females, meiosis or oogenesis results in 1 egg cell for reproduction and three polar bodies, which are not used in reproduction. The one egg cell has all the cytoplasm, while the polar bodies only have a haploid copy of the chromosomes. Haploid sperm will fertilize a haploid egg to form the zygote, the first diploid body cell. Self-Test - Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
MITOSIS MEIOSIS Starting # cells? 1 diploid 1 diploid Where does this occur? Somatic or body cells ovary or testes cells Are ending cells genetically Genetically identical Genetically DIFFERENT!! identical? Ending # cells? 2 4 Are end cells 2n or n? 2n n Ending cells haploid or diploid? diploid haploid Is it a cycle? YES NO Meiosis – V3 Review Of Chromosome Patterns At the end of mitosis’ telophase a cell has an ______copy of each chromosome. The chromosomes look like ______and are called ______. During interphase chromosomes uncoil into chromatin and ______. So at prophase the replicated chromosomes look like ______and have 2 sister ______joined at a ______.
Meiosis Meiosis is the process by which ______or ______are made. This process is also called ______. During meiosis the number of ______per cell is ______making ______When a haploid sperm fertilizes the haploid egg a ______is formed. This is the first body cell. Meiosis I and II: Meiosis has two distinct stages. Meiosis I – ______, one ______cell forms ______cells by separating homologous chromosomes Meiosis II – each haploid cell divides again by ______Meiosis – Prophase I Nuclear membrane dissolves, and the centrioles move to opposite poles. Each chromosome ______to form a ______. There are 4 sister chromatids in a tetrad. The pairing of homologous chromosomes is the key to understanding meiosis. ______probably occurs here. Meiosis – Metaphase I Homologous pairs of chromosomes, called a tetrad, line up at the equatorial plate. This is a ______of chromosomes!! ______from the centrioles attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
Meiosis – Anaphase I The spindle fibers ______the homologous chromosomes toward ______of the cell. Why is this called the reduction division? ______Meiosis – Telophase I Nuclear membranes might reform. Cytoplasm divides after telophase, resulting in ______.
Meiosis – Prophase II The second part of meiosis resembles mitosis except the cells are haploid. The ______are ______. Centrioles in the 2 new cells move to ______. New spindle fibres form and attach to centromeres.
Meiosis – Metaphase II The chromosomes are in a ______on the equatorial plate. This is similar to metaphase in mitosis.
Meiosis – Anaphase II Spindle fibres ______which move to opposite ends of the cell.
Meiosis – Telophase II Cytoplasm separates, resulting in ______Meiosis ______but forms haploid egg and sperm cells.
Meiosis forms gametes In males, meiosis or ______results in 4 sperm cells. In females, meiosis or ______results in ______cell for reproduction and ______, which are not used in reproduction. The one egg cell has all the ______, while the polar bodies only have a ______of the chromosomes. Haploid sperm will fertilize a haploid egg to form the ______, the ______. Self-Test - Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
MITOSIS MEIOSIS Starting # cells? Where does this occur? Are ending cells genetically identical? Ending # cells? Are end cells 2n or n? Ending cells haploid or diploid? Is it a cycle?
MEMORIZE THIS FOR TESTS