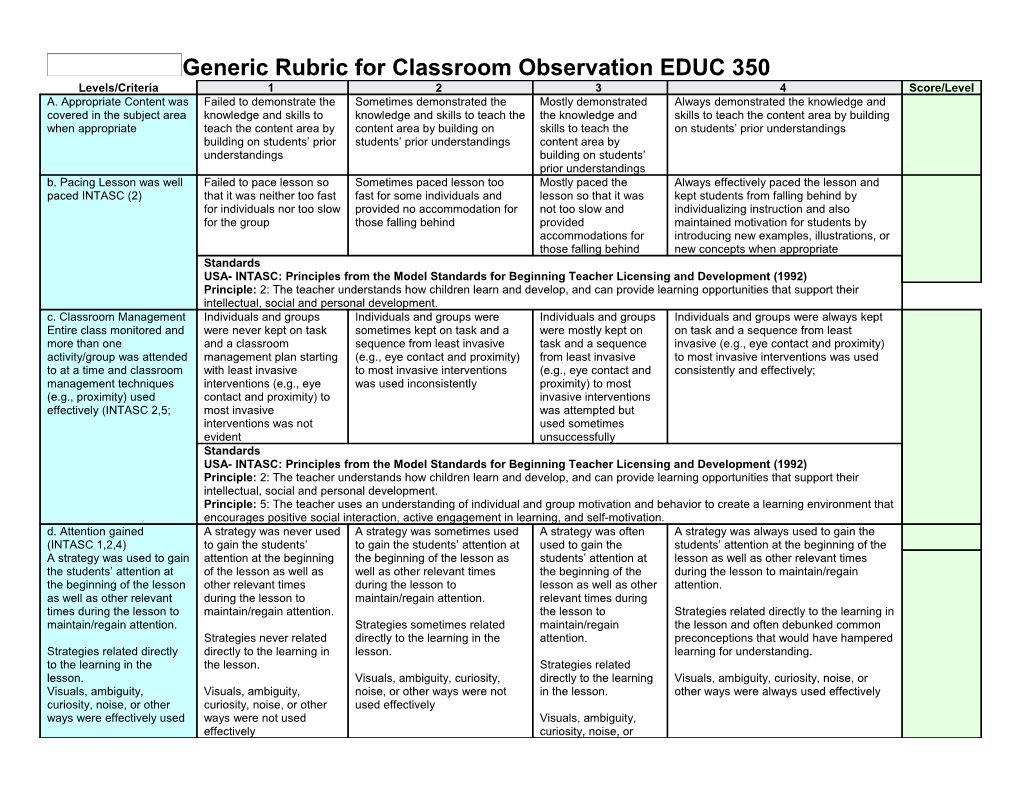
Generic Rubric for Classroom Observation EDUC 350 Levels/Criteria 1 2 3 4 Score/Level A. Appropriate Content was Failed to demonstrate the Sometimes demonstrated the Mostly demonstrated Always demonstrated the knowledge and covered in the subject area knowledge and skills to knowledge and skills to teach the the knowledge and skills to teach the content area by building when appropriate teach the content area by content area by building on skills to teach the on students’ prior understandings building on students’ prior students’ prior understandings content area by understandings building on students’ prior understandings b. Pacing Lesson was well Failed to pace lesson so Sometimes paced lesson too Mostly paced the Always effectively paced the lesson and paced INTASC (2) that it was neither too fast fast for some individuals and lesson so that it was kept students from falling behind by for individuals nor too slow provided no accommodation for not too slow and individualizing instruction and also for the group those falling behind provided maintained motivation for students by accommodations for introducing new examples, illustrations, or those falling behind new concepts when appropriate Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. c. Classroom Management Individuals and groups Individuals and groups were Individuals and groups Individuals and groups were always kept Entire class monitored and were never kept on task sometimes kept on task and a were mostly kept on on task and a sequence from least more than one and a classroom sequence from least invasive task and a sequence invasive (e.g., eye contact and proximity) activity/group was attended management plan starting (e.g., eye contact and proximity) from least invasive to most invasive interventions was used to at a time and classroom with least invasive to most invasive interventions (e.g., eye contact and consistently and effectively; management techniques interventions (e.g., eye was used inconsistently proximity) to most (e.g., proximity) used contact and proximity) to invasive interventions effectively (INTASC 2,5; most invasive was attempted but interventions was not used sometimes evident unsuccessfully Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 5: The teacher uses an understanding of individual and group motivation and behavior to create a learning environment that encourages positive social interaction, active engagement in learning, and self-motivation. d. Attention gained A strategy was never used A strategy was sometimes used A strategy was often A strategy was always used to gain the (INTASC 1,2,4) to gain the students’ to gain the students’ attention at used to gain the students’ attention at the beginning of the A strategy was used to gain attention at the beginning the beginning of the lesson as students’ attention at lesson as well as other relevant times the students’ attention at of the lesson as well as well as other relevant times the beginning of the during the lesson to maintain/regain the beginning of the lesson other relevant times during the lesson to lesson as well as other attention. as well as other relevant during the lesson to maintain/regain attention. relevant times during times during the lesson to maintain/regain attention. the lesson to Strategies related directly to the learning in maintain/regain attention. Strategies sometimes related maintain/regain the lesson and often debunked common Strategies never related directly to the learning in the attention. preconceptions that would have hampered Strategies related directly directly to the learning in lesson. learning for understanding. to the learning in the the lesson. Strategies related lesson. Visuals, ambiguity, curiosity, directly to the learning Visuals, ambiguity, curiosity, noise, or Visuals, ambiguity, Visuals, ambiguity, noise, or other ways were not in the lesson. other ways were always used effectively curiosity, noise, or other curiosity, noise, or other used effectively ways were effectively used ways were not used Visuals, ambiguity, effectively curiosity, noise, or Levels/Criteria 1 2 3 4 Score/Level other ways were used effectively Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 1: The teacher understands the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and structures of the discipline(s) he or she teaches and can create learning experiences that make these aspects of subject matter meaningful for students. Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. e. Previous knowledge Strategies were not used Strategies were sometimes Strategies related Strategies related directly to the learning in recalled (INTASC 2,4). to build on prior related directly to the learning in directly to the learning the lesson and addressed common knowledge nor did they the lesson and addressed in the lesson and often preconceptions that would have hampered relate directly to the common preconceptions that addressed common learning for understanding. learning in the lesson and would have hampered learning preconceptions that often debunked common for understanding would have hampered preconceptions that would learning for have hampered learning understanding for understanding Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. f. Purpose/Objective of the It was not clear what It could be somewhat inferred It could clearly be Objectives were clearly posted for all to lesson made clear students were to be what students were to be inferred what students see and there was a clear discussion of (INTASC 1,4) learning and why they learning but no discussion of were to be learning why they were learning it. were learning it. why they were learning it and it could be inferred as to why they were learning it. Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 1: The teacher understands the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and structures of the discipline(s) he or she teaches and can create learning experiences that make these aspects of subject matter meaningful for students. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. g. Teacher Input Provided Skills or concepts of the Skills or concepts of the lesson Skills or concepts of Skills or concepts of the lesson were (INTASC 2, 4, 6) lesson were never were sometimes introduced and the lesson were always always introduced and explained (2,4) by introduced and explained explained (2,4) by using introduced and using clear examples and language that (2,4) by using clear somewhat clear examples and explained (2,4) by debunked student preconceptions (2,4,6) examples and language language (2,4,6) and the using clear examples and the sequence and organization of (2,4,6) and the sequence sequence and organization of and language (2,4,6) instruction introduced new principles of and organization of instruction was not appropriate but the sequence and increasing complexity (2,4) instruction was not (2,4) organization of appropriate (2,4) instruction was not appropriate (2,4) Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their Levels/Criteria 1 2 3 4 Score/Level intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. Principle: 6: The teacher uses knowledge of effective verbal, nonverbal, and media communication techniques to foster active inquiry, collaboration, and supportive interaction in the classroom. h. Teacher guided practice The teacher and students The teacher and students The teacher and The teacher and students always worked was adequate and never worked through sometimes worked through students always through examples together as needed, the appropriate (INTASC 2, 4) examples together as examples together as needed worked through teacher provided scaffolding that needed and students were but students were not expected examples together as addressed individual student needs and not expected to do similar to do similar problems on their needed but students students were expected to do similar problems on their own own were not always problems on their own. expected to do similar problems on their own Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. i. Repetition of key No repetition took place Some repetition took place but Repetition took place Repetition occurred, mnemonic devices concepts occurred no use of mnemonics or and mnemonic devices used, chunking and the organization of the throughout the lesson organization of the material into used to help students material into meaningful patterns used to (INTASC 2,4) meaningful patterns was used to learn and remember help students learn and remember help students learn and (when appropriate) essential facts and concepts remember (when appropriate) Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. j. A variety of instructional No instructional materials Instructional materials were used A variety of A variety of instructional materials were materials were used to were used but their use was not aligned instructional materials used and they were aligned with the actively engage the with the lesson objectives were used and they lesson objectives and they helped to students. (INTASC 2,3,4,6) were aligned with the create a “hands-on-minds-on” experiences lesson objectives that motivated students to apply the lesson concepts to an authentic problem Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. Principle: 6: The teacher uses knowledge of effective verbal, nonverbal, and media communication techniques to foster active inquiry, collaboration, and supportive interaction in the classroom. k. All of the students were All students were off task Most students were off task All students appeared All students appeared to be engaged in actively engaged in the to be engaged in the the lesson activities and their learning throughout the lesson activities performances (answers to questions, Levels/Criteria 1 2 3 4 Score/Level lesson. (INTASC 2,4) results of projects/papers, etc.) demonstrated their engagement Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. l. Students were Open-ended questions Open-ended questions were Open-ended questions Open-ended questions were always used encouraged to understand, were never used, and sometimes used, and diverse were always used when appropriate, and diverse question, and interpret diverse perspectives were perspectives were never when appropriate, and perspectives were always explored and ideas from diverse never explored explored diverse perspectives students were encouraged to ask their perspectives. (INTASC 4) were sometimes own questions explored Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. m. Higher order thinking Higher levels of Bloom’s Higher levels of Bloom’s Higher levels of Higher levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy such skills were used. (INTASC Taxonomy such as Taxonomy such as analysis, Bloom’s Taxonomy as analysis, application, creating, and 4) i.e., critical thinking and analysis, application, application, creating, and such as analysis, evaluation were always reached when problem solving creating, and evaluation evaluation were sometimes application, were appropriate were never reached reached reached but creating, and evaluation were not reached when appropriate Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. n. Evaluation of student Students were never Students were sometimes asked Students were always Students were always asked questions or comprehension occurred asked questions or asked questions or asked to perform a asked questions or asked to perform a task that would throughout the lesson and to perform a task that task that would demonstrate asked to perform a demonstrate student understanding during appropriate feedback would demonstrate student understanding during the task that would the lesson when appropriate and the provided. (INTASC 8) student understanding lesson demonstrate student appropriate feedback was always given during the lesson understanding during and accommodations were made when the lesson when necessary appropriate but the appropriate feedback was not always given Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 8: The teacher understands and uses formal and informal assessment strategies to evaluate and ensure the continuous intellectual, social and physical development of the learner. o. The lesson ended with No summary took place The teacher candidate The students were The students were asked to summarize closure/review that focused summarized the lesson asked to summarize the learning and it focused on the main on the main objectives of the learning objectives of the lessons and included a the lesson. (INTASC 3,4) key takeaway (essential principle) or application of the objectives to students’ lives or the “real world” when possible. Levels/Criteria 1 2 3 4 Score/Level Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. p. Variety of teaching Failed to any of the Failed to use an appropriate An appropriate amount An appropriate amount of the following methods/instructional following strategies: direct combination of the following of the following strategies were used so that all of the strategies were used to instruction, discovery strategies so that the need of the strategies were used diverse students’ needs for learning were reach different types of learning, cooperative diverse students could be met: so that most of the met: direct instruction, discovery learning, learners. (INTASC 2,4,8) learning, role playing, direct instruction, discovery diverse students’ cooperative learning, role playing, discussions, technology learning, cooperative learning, needs for learning discussions, technology simulations, simulations, “hands- role playing, discussions, were met direct “hands-on/minds-on” materials, paired on/minds-on” materials, technology simulations, “hands- instruction, discovery students, etc. paired students, etc. on/minds-on” materials, paired learning, cooperative students, etc. learning, role playing, discussions, technology simulations, “hands-on/minds-on” materials, paired students, etc Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 4: The teacher understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage students’ development of critical thinking, problem solving, and performance skills. Principle: 8: The teacher understands and uses formal and informal assessment strategies to evaluate and ensure the continuous intellectual, social and physical development of the learner. q. Relevant subject areas & No reference to the A brief reference was made It was clear how the Students were engaged in real world “real world” problems were application of the content concerning the application of the subject could be problem solving by applying lesson integrated into the lesson. was made content applied to “real world” content to the solution of real world (INTASC 1,2,3,7) problems problems Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 1: The teacher understands the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and structures of the discipline(s) he or she teaches and can create learning experiences that make these aspects of subject matter meaningful for students. Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Principle: 7: The teacher plans instruction based upon knowledge of subject matter, students, the community, and curriculum goals. r. Inclusion of special No IEP’s were referenced, IEP’s were referenced, but no IEP’s were referenced, IEP’s were referenced, accommodations needs student occurred. no accommodations were accommodations were made, and some were made, many pathways to learning (INTASC 2,3) made, and many and many pathways to learning accommodations were were provided and students with special pathways to learning were were not provided made, but not enough needs were incorporated into the not provided pathways to learning classroom so that their strengths could be were provided showcased Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Levels/Criteria 1 2 3 4 Score/Level Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. s. Individual differences Individual differences Some instruction built on Instruction clearly built Instruction clearly built on students’ prior were addressed. (INTASC were not addressed students’ prior knowledge and on students’ prior knowledge and experiences, and 2,3,5) and adaptations experiences and some knowledge and differentiated instruction and made for diverse students differentiated instruction took experiences; however, accommodations took place so that the place more differentiated particular needs of the students in the instruction geared to class were clearly met. Multiple pathways the particular needs of were provided that met the needs of the the students was students’ learning styles. Student’s needed. More individualized learning opportunities were pathways to learning supported by providing meaningful need to be geared to experiences that engage their interests, students’ differing abilities, and culture learning styles, interests, abilities, and culture Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Principle: 5: The teacher uses an understanding of individual and group motivation and behavior to create a learning environment that encourages positive social interaction, active engagement in learning, and self-motivation. t. Classroom instruction No standards-based Some standards-based practices Standards-based Standards-based practices and strategies and assignments provided practices and strategies and strategies related to practices and related to planning, implementing, and for Limited English related to planning, planning, implementing, and strategies related to managing ESL and content instruction, Proficiency (LEP) students. implementing, and managing ESL and content planning, including classroom organization, were (INTASC 2,3) (TESOL managing ESL and instruction, and no integration of implementing, and clearly used and the integration of Standard 3) content instruction, language skills, and adapted managing ESL and language skills, and adapted classroom including classroom classroom resources were used content instruction, resources were used effectively organization, were used, including classroom and no integration of organization, were language skills, and mostly used and some adapted classroom integration of language resources were used skills, and adapted classroom resources were used Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. u. Diversity issues were Students were not at the Students were sometimes at the Students were mostly Students were always at the center of their addressed in an center of their learning center of their learning and at the center of their learning and had appropriate choices for appropriate manner. and did not have sometimes had appropriate learning and mostly applying course content to issues Levels/Criteria 1 2 3 4 Score/Level (INTASC 2,3,6,10) and appropriate choices for choices for applying course had appropriate important to them and examples and adaptations made for applying course content to content to issues important to choices for applying illustrations that were inclusive of diverse students issues important to them them and examples and course content to individuality, awareness of oneself and and examples and illustrations that were inclusive of issues important to one’s own preferences, and of multi- illustrations that were not individuality, awareness of them and examples cultures were used inclusive of individuality, oneself and one’s own and illustrations that awareness of oneself and preferences, of multi-cultures were inclusive of one’s own preferences, of were not consistently used individuality, multi-cultures were awareness of oneself consistently used and one’s own preferences, of multi- cultures were sometimes used Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 2: The teacher understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle: 3: The teacher understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Principle: 6: The teacher uses knowledge of effective verbal, nonverbal, and media communication techniques to foster active inquiry, collaboration, and supportive interaction in the classroom. Principle: 10: The teacher fosters relationships with school colleagues, parents, and agencies in the larger community to support students’ learning and well-being. v. Displayed Enthusiasm. Voice inflection, smiling, Voice inflection, smiling, Voice inflection, Voice inflection, smiling, gestures were (INTASC 1,6) gestures were never used gestures were sometimes used smiling, gestures were always used when appropriate and when appropriate when appropriate mostly used when students responded with their own appropriate enthusiasm Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 1: The teacher understands the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and structures of the discipline(s) he or she teaches and can create learning experiences that make these aspects of subject matter meaningful for students. Principle: 6: The teacher uses knowledge of effective verbal, nonverbal, and media communication techniques to foster active inquiry, collaboration, and supportive interaction in the classroom. w. Exhibited Confidence. Never projected voice, or Sometimes projected voice, but Always projected voice Always projected voice when appropriate, (INTASC 1) led the class by example did not lead the class by when appropriate, and and always led the class by example example mostly led the class by example Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 1: The teacher understands the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and structures of the discipline(s) he or she teaches and can create learning experiences that make these aspects of subject matter meaningful for students. x. Displayed empathy. Never listened to students Sometimes listened to students Always listened to Always listened to students when (INTASC 5,9,10) and never served as and attempted to serve as students when appropriate and always served as students’ advocate student advocate appropriate and students’ advocate when appropriate (e.g., sometimes served as when determining that factors in the students’ advocate students’ environment outside of school when determining, for may be influencing the students’ life and example, that factors in learning) the students’ environment outside of Levels/Criteria 1 2 3 4 Score/Level school may be influencing the students’ life and learning Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 5: The teacher uses an understanding of individual and group motivation and behavior to create a learning environment that encourages positive social interaction, active engagement in learning, and self-motivation. Principle: 9: The teacher is a reflective practitioner who continually evaluates the effects of his/her choices and actions on others (students, parents, and other professionals in the learning community) and who actively seeks out opportunities to grow professionally. Principle: 10: The teacher fosters relationships with school colleagues, parents, and agencies in the larger community to support students’ learning and well-being. y. Acted and appeared in a Failed to start and/or end Started and ended on time and wore professional manner. on time and failed to wear professional attire. (INTASC 9) professional attire. Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 9: The teacher is a reflective practitioner who continually evaluates the effects of his/her choices and actions on others (students, parents, and other professionals in the learning community) and who actively seeks out opportunities to grow professionally. z. Family and community No collaboration with Minimal collaboration with Some evidence of Significant collaboration with colleagues, connections (INTASC 10) colleagues, family, and colleagues, family, and collaboration with family and community that is appropriate community despite being community despite being colleagues, family, and for lesson. appropriate for lesson. appropriate for lesson. community that is appropriate for lesson. Standards USA- INTASC: Principles from the Model Standards for Beginning Teacher Licensing and Development (1992) Principle: 10: The teacher fosters relationships with school colleagues, parents, and agencies in the larger community to support students’ learning and well-being.
Generic Rubric for Classroom Observation EDUC 350
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Recommended publications