Progressivism – Liberal Reform or Conservative Reaction?
In the last 40 years of the 19th century, the Republican party, with financial backing from conservative businesspersons, dominated the government. Legislation contrary to business interests rarely received a hearing in Congress. Despite their initial suspicion of the Republican Roosevelt, business interests took his cooperation for granted when he became president. The power financial capitalist, JP Morgan, expected to do business as usual when, in 1902, Roosevelt threatened to take action against Northern Securities Company. However, rising discontent with business practices demanded new approaches. Edward Bellamy’s Looking Backward and Upton Sinclair’s The Jungle pointed to socialist solutions. The Socialist Party, organized in 1901, attracted increasingly large numbers of supporters. In 1912 Eugene V. Debs garnered six percent of the vote. The government could not afford to ignore this trend. Some historians view Progressivism as the fulfillment of the Populist agenda and the forerunner of New Deal reforms. Others question its impact.
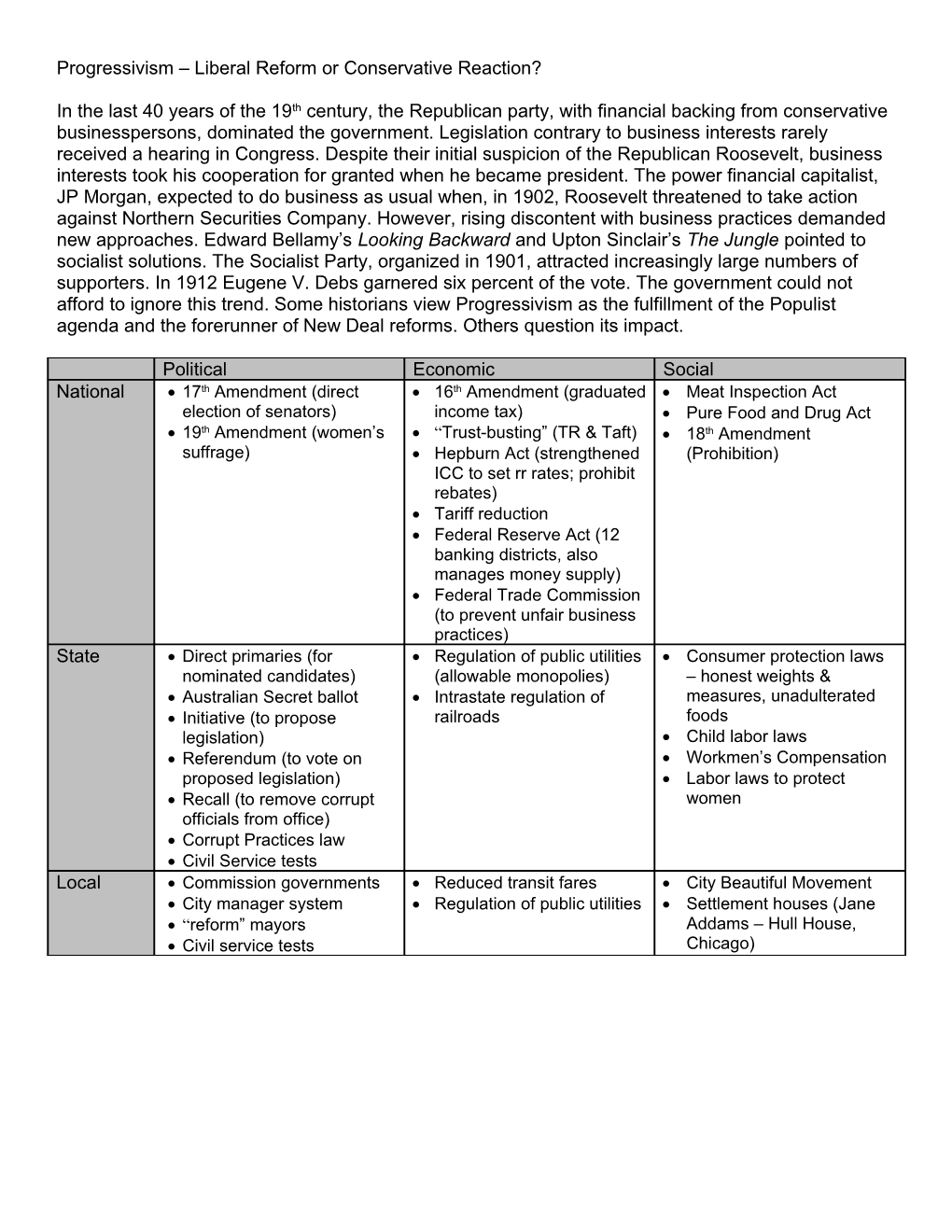
Political Economic Social National 17th Amendment (direct 16th Amendment (graduated Meat Inspection Act election of senators) income tax) Pure Food and Drug Act 19th Amendment (women’s “Trust-busting” (TR & Taft) 18th Amendment suffrage) Hepburn Act (strengthened (Prohibition) ICC to set rr rates; prohibit rebates) Tariff reduction Federal Reserve Act (12 banking districts, also manages money supply) Federal Trade Commission (to prevent unfair business practices) State Direct primaries (for Regulation of public utilities Consumer protection laws nominated candidates) (allowable monopolies) – honest weights & Australian Secret ballot Intrastate regulation of measures, unadulterated Initiative (to propose railroads foods legislation) Child labor laws Referendum (to vote on Workmen’s Compensation proposed legislation) Labor laws to protect Recall (to remove corrupt women officials from office) Corrupt Practices law Civil Service tests Local Commission governments Reduced transit fares City Beautiful Movement City manager system Regulation of public utilities Settlement houses (Jane “reform” mayors Addams – Hull House, Civil service tests Chicago)