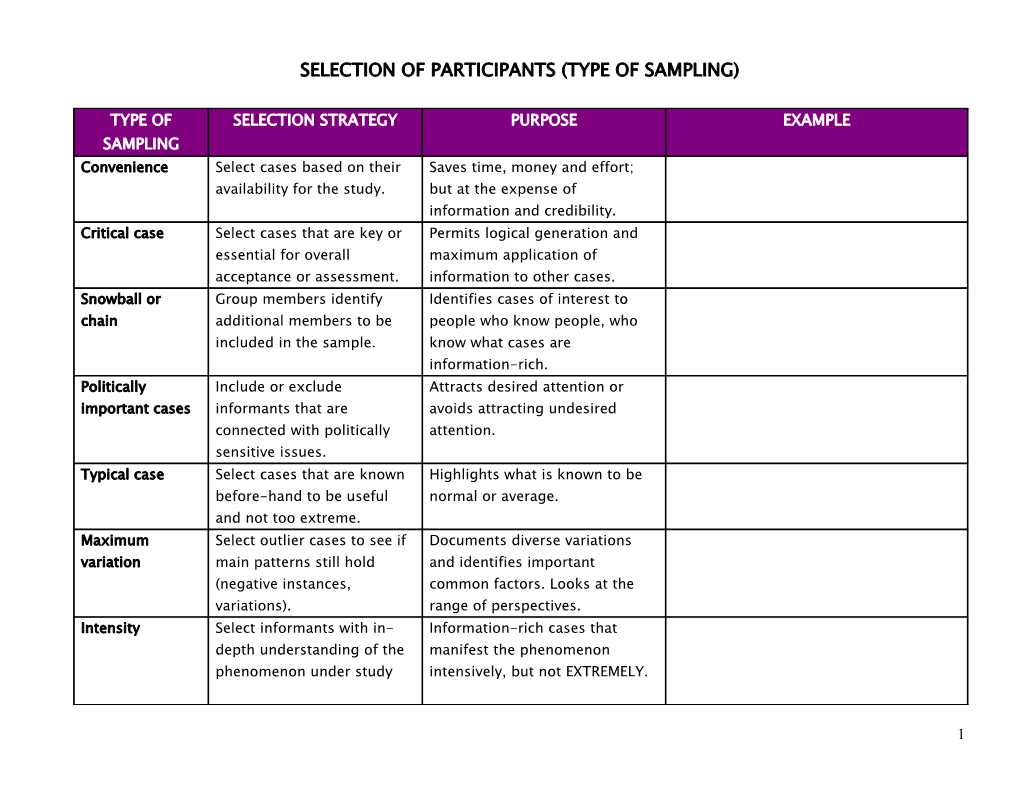
SELECTION OF PARTICIPANTS (TYPE OF SAMPLING)
TYPE OF SELECTION STRATEGY PURPOSE EXAMPLE SAMPLING Convenience Select cases based on their Saves time, money and effort; availability for the study. but at the expense of information and credibility. Critical case Select cases that are key or Permits logical generation and essential for overall maximum application of acceptance or assessment. information to other cases. Snowball or Group members identify Identifies cases of interest to chain additional members to be people who know people, who included in the sample. know what cases are information-rich. Politically Include or exclude Attracts desired attention or important cases informants that are avoids attracting undesired connected with politically attention. sensitive issues. Typical case Select cases that are known Highlights what is known to be before-hand to be useful normal or average. and not too extreme. Maximum Select outlier cases to see if Documents diverse variations variation main patterns still hold and identifies important (negative instances, common factors. Looks at the variations). range of perspectives. Intensity Select informants with in- Information-rich cases that depth understanding of the manifest the phenomenon phenomenon under study intensively, but not EXTREMELY.
1 Quota sampling Select a sample that yields Taking an arbitrary number of the same proportions as the cases from each subgroup; population proportions on increases analytic confidence easily identified variables. and representativeness. Theoretical Finds as many relevant cases Reach saturation point; when no saturation as possible. new information emerges. (sequential) Most Select cases that are judged Elaborating initial analysis, similar/dissimilar to represent similar seeking exceptions, looking for cases conditions or, alternatively, variation. very different conditions. Comparable case Select individuals, sites, and Be able to compare across cases, selection groups on the same relevant or over time (replication). characteristics over time. Criterion All cases that meet some Useful for quality assurance. criteria.
2