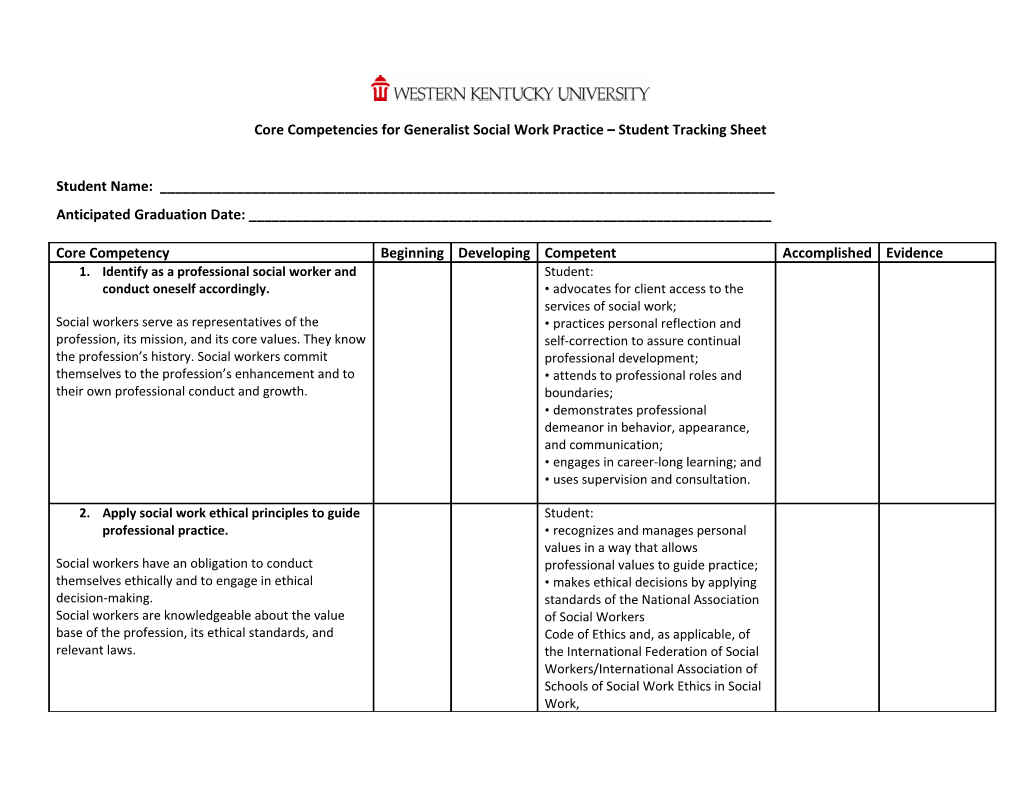
Core Competencies for Generalist Social Work Practice – Student Tracking Sheet
Student Name: ______Anticipated Graduation Date: ______
Core Competency Beginning Developing Competent Accomplished Evidence 1. Identify as a professional social worker and Student: conduct oneself accordingly. • advocates for client access to the services of social work; Social workers serve as representatives of the • practices personal reflection and profession, its mission, and its core values. They know self-correction to assure continual the profession’s history. Social workers commit professional development; themselves to the profession’s enhancement and to • attends to professional roles and their own professional conduct and growth. boundaries; • demonstrates professional demeanor in behavior, appearance, and communication; • engages in career-long learning; and • uses supervision and consultation.
2. Apply social work ethical principles to guide Student: professional practice. • recognizes and manages personal values in a way that allows Social workers have an obligation to conduct professional values to guide practice; themselves ethically and to engage in ethical • makes ethical decisions by applying decision-making. standards of the National Association Social workers are knowledgeable about the value of Social Workers base of the profession, its ethical standards, and Code of Ethics and, as applicable, of relevant laws. the International Federation of Social Workers/International Association of Schools of Social Work Ethics in Social Work, Core Competency Beginning Developing Competent Accomplished Evidence Statement of Principles; • tolerates ambiguity in resolving ethical conflicts; and • applies strategies of ethical reasoning to arrive at principled decisions.
3. Apply critical thinking to inform and Student: communicate professional judgments. • distinguishes, appraises, and integrates multiple sources of Social workers are knowledgeable about the knowledge, including research-based principles of logic, scientific inquiry, and reasoned knowledge, and practice wisdom; discernment. They use critical thinking augmented by • analyzes models of assessment, creativity and curiosity. Critical thinking also requires prevention, intervention, and the synthesis and communication of relevant evaluation; and information. • demonstrates effective oral and written communication in working with individuals, families, groups, organizations, communities, and colleagues.
4. Engage diversity and difference in practice. Student: • recognizes the extent to which a Social workers understand how diversity culture’s structures and values may characterizes and shapes the human experience and oppress, marginalize, alienate, or is critical to the formation of identity. The dimensions create or enhance privilege and of diversity are understood as the intersectionality of power; multiple factors including age, class, color, culture, • gains sufficient self-awareness to disability, ethnicity, gender, gender identity and eliminate the influence of personal expression, immigration status, political ideology, biases and values in working with race, religion, sex, and sexual orientation. Social diverse groups; workers appreciate that, as a consequence of • recognizes and communicates their difference, a person’s life experiences may include understanding of the importance of oppression, poverty, marginalization, and alienation difference in shaping life experiences; as well as privilege, power, and acclaim. and Core Competency Beginning Developing Competent Accomplished Evidence • views her/himself as learner and engages those with whom s/he work as informants.
5. Advance human rights and social and Student: economic justice. • understands the forms and mechanisms of oppression and Each person, regardless of position in society, has discrimination; basic human rights, such as freedom, safety, privacy, • advocates for human rights and an adequate standard of living, health care, and social and economic justice; and education. Social workers recognize the global • engages in practices that advance interconnections of oppression and are social and economic justice. knowledgeable about theories of justice and strategies to promote human and civil rights. Social work incorporates social justice practices in organizations, institutions, and society to ensure that these basic human rights are distributed equitably and without prejudice. 6. Engage in research-informed practice and Student: practice-informed research. • uses practice experience to inform scientific inquiry and Social workers use practice experience to inform • uses research evidence to inform research, employ evidence-based interventions, practice. evaluate their own practice, and use research findings to improve practice, policy, and social service delivery. Social workers comprehend quantitative and qualitative research and understand scientific and ethical approaches to building knowledge. 7. Apply knowledge of human behavior and Student: the social environment. • utilizes conceptual frameworks to guide the processes of assessment, Social workers are knowledgeable about human intervention, and evaluation; and behavior across the life course; the range of social • critiques and applies knowledge to systems in which people live; and the ways social understand person and environment. Core Competency Beginning Developing Competent Accomplished Evidence systems promote or deter people in maintaining or achieving health and well-being. Social workers apply theories and knowledge from the liberal arts to understand biological, social, cultural, psychological, and spiritual development. 8. Engage in policy practice to advance social Student: and economic well-being and to deliver • analyzes, formulates, and advocates effective social work services. for policies that advance social well- being; and Social work practitioners understand that policy • collaborates with colleagues and affects service delivery, and they actively engage in clients for effective policy action. policy practice. Social workers know the history and current structures of social policies and services; the role of policy in service delivery; and the role of practice in policy development. 9. Respond to contexts that shape practice. Student: • continuously discovers, appraises, Social workers are informed, resourceful, and and attends to changing locales, proactive in responding to evolving organizational, populations, scientific and community, and societal contexts at all levels of technological developments, and practice. Social workers recognize that the context of emerging societal trends to provide practice is dynamic, and use knowledge and skill to relevant services; and respond proactively. • provides leadership in promoting sustainable changes in service delivery and practices to improve the quality of social services.
10. Engage, assess, intervene, and evaluate with Engagement individuals, families, groups, organizations, Student: and communities. • substantively and affectively prepares for action with individuals, Professional practice involves the dynamic and families, groups, organizations, and interactive processes of engagement, assessment, communities; intervention, and evaluation at multiple levels. Social • uses empathy and other workers have the knowledge and skills to practice interpersonal skills; and Core Competency Beginning Developing Competent Accomplished Evidence with individuals, families, groups, organizations, and • develops a mutually agreed-on focus communities. Practice knowledge includes of work and desired outcomes. identifying, analyzing, and implementing evidence- based interventions designed to achieve client goals; Assessment: using research and technological advances; Student” evaluating program outcomes and practice • collects, organizes, and interprets effectiveness; developing, analyzing, advocating, and client data; providing leadership for policies and services; and • assesses client strengths and promoting social and economic justice. limitations; • develops mutually agreed-on intervention goals and objectives; and • selects appropriate intervention strategies.
Intervention: Student: • initiates actions to achieve organizational goals; • implements prevention interventions that enhance client capacities; • helps clients resolve problems; • negotiates, mediates, and advocates for clients; and • facilitates transitions and endings.
Evaluation: Social workers critically analyze, monitor, and evaluate interventions.
E. Arnold 8/27/12