Online Appendix
Jackson GL, Oddone EZ, Olsen MK, Powers BK, Grubber JM, McCant F, Bosworth HB. Racial Differences in the Effect of a Telephone-Delivered Hypertension Disease Management Program
This supplementary material has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work.
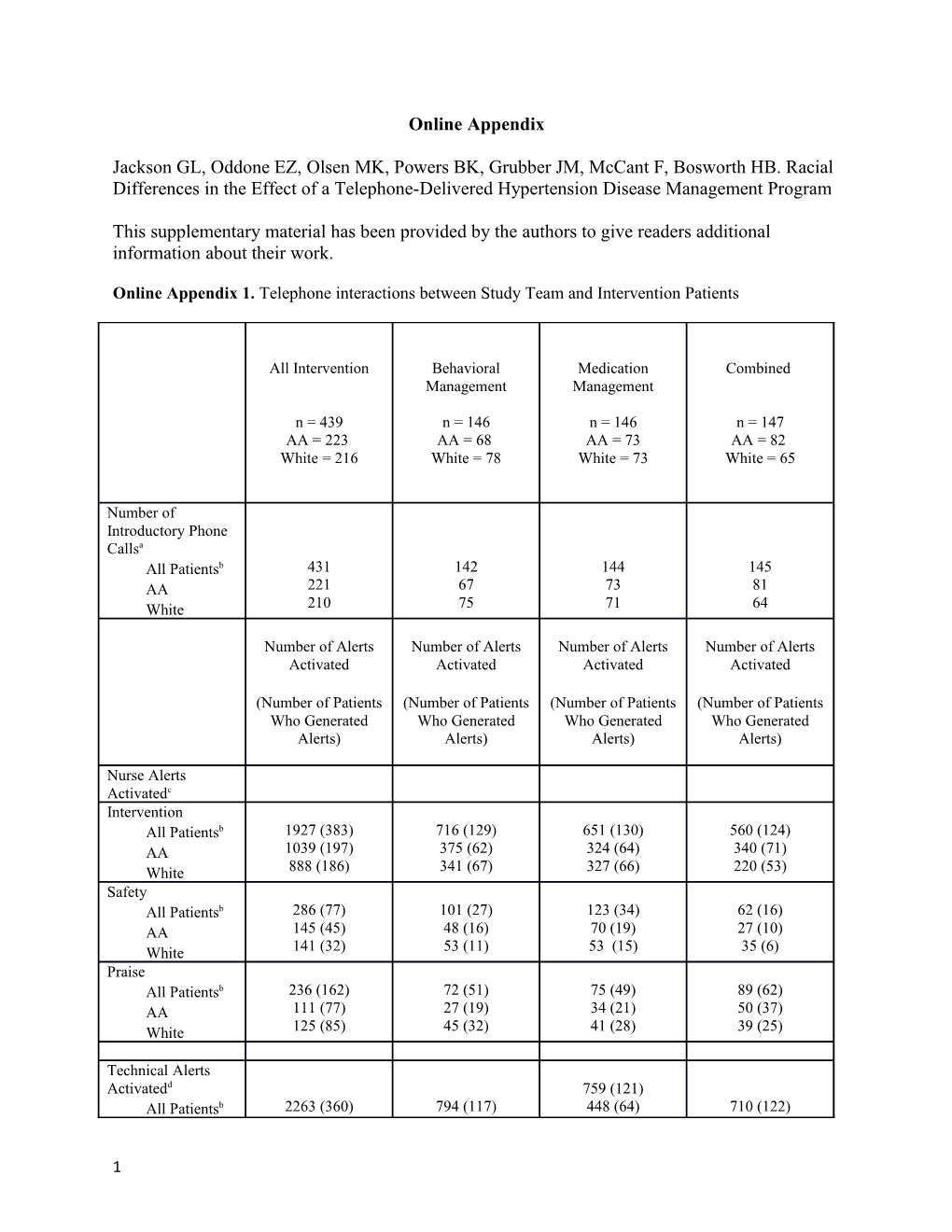
Online Appendix 1. Telephone interactions between Study Team and Intervention Patients
All Intervention Behavioral Medication Combined Management Management
n = 439 n = 146 n = 146 n = 147 AA = 223 AA = 68 AA = 73 AA = 82 White = 216 White = 78 White = 73 White = 65
Number of Introductory Phone Callsa All Patientsb 431 142 144 145 AA 221 67 73 81 White 210 75 71 64
Number of Alerts Number of Alerts Number of Alerts Number of Alerts Activated Activated Activated Activated
(Number of Patients (Number of Patients (Number of Patients (Number of Patients Who Generated Who Generated Who Generated Who Generated Alerts) Alerts) Alerts) Alerts)
Nurse Alerts Activatedc Intervention All Patientsb 1927 (383) 716 (129) 651 (130) 560 (124) AA 1039 (197) 375 (62) 324 (64) 340 (71) White 888 (186) 341 (67) 327 (66) 220 (53) Safety All Patientsb 286 (77) 101 (27) 123 (34) 62 (16) AA 145 (45) 48 (16) 70 (19) 27 (10) White 141 (32) 53 (11) 53 (15) 35 (6) Praise All Patientsb 236 (162) 72 (51) 75 (49) 89 (62) AA 111 (77) 27 (19) 34 (21) 50 (37) White 125 (85) 45 (32) 41 (28) 39 (25)
Technical Alerts Activatedd 759 (121) All Patientsb 2263 (360) 794 (117) 448 (64) 710 (122)
1 AA 1290 (192) 429 (59) 311 (57) 413 (69) White 973 (168) 365 (58) 297 (53) aThe introductory phone call introduced the patient to the nurse interventionist and allowed the nurse to obtain an initial listing of prescribed hypertension medications from the patient. It was not activated by patients, but rather delivered to all patients in all intervention arms that the nurse interventionist was able to contact. bThe category “all patients” refers to the total number of enrolled patients who reported being African American or non-Hispanic white. This represents 573 of 591 total patients enrolled in the trial. cThree types of alerts could potentially be activated by patients with a subsequent attempt by a study nurse to deliver the appropriate interaction: intervention, which was triggered by out of control blood pressure; safety which was triggered by 2 consecutive BP readings > 175/105 or pulse < 40 or > 110; or praise, which triggered if patients had gone 6 months without triggering an intervention or safety alert, meaning BP was in control, and < 3 technical alerts. dTechnical alerts were activated by the patients when < 3 BP readings had been received by the system for their specified two week period or patient notified team they were having problems with equipment. These alerts were addressed by study research assistants rather than nurses.
2